Week 7 Quiz - 25-3: Angioplasty
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
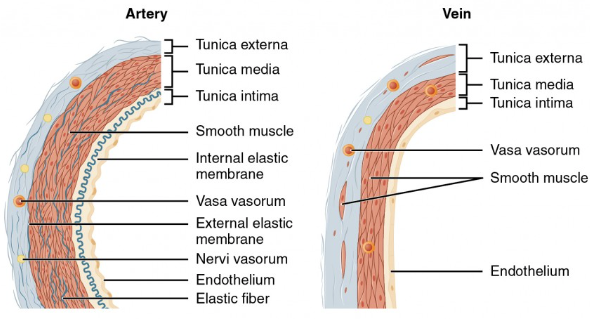
Which layer of the artery wall is the outermost and contains connective tissue and tiny vessels called vasa vasorum?
a) Tunica intima
b) Tunica media
c) Tunica adventitia
d) Endothelium
c) Tunica adventitia
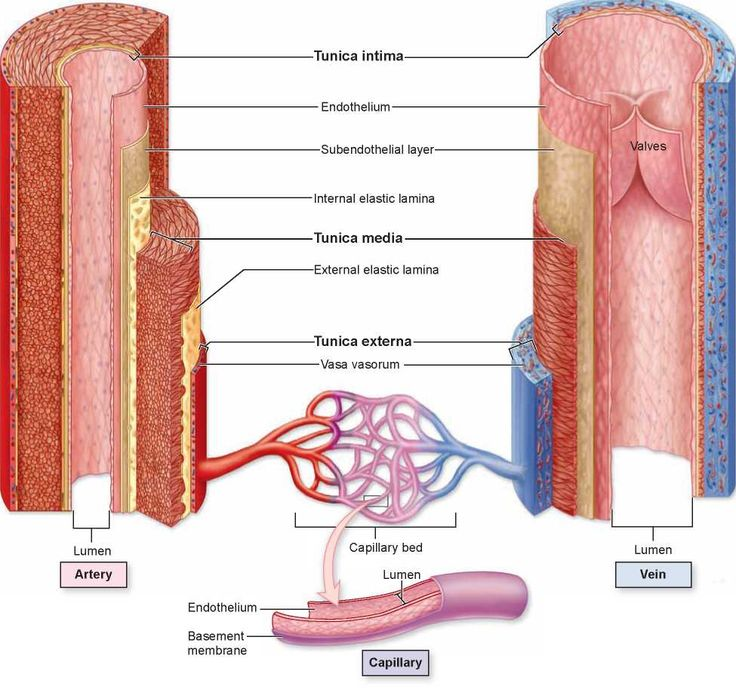
What is the thickest layer of the artery wall composed of elastic fibers and smooth muscle fibers?
a) Tunica adventitia
b) Tunica media
c) Tunica intima
d) Vasa vasorum
b) Tunica media
Which nervous system controls the smooth muscles in the tunica media that cause vasoconstriction?
a) Parasympathetic nervous system of ANS
b) Somatic nervous system
c) Sympathetic nervous system of ANS
d) Central nervous system
c) Sympathetic nervous system of ANS
a) Parasympathetic nervous system - “Rest and Digest”, Slows HR, Increases Digestion, Constricts Pupils
b) Somatic nervous system - Controls voluntary movement and transmits sensory information
c) Sympathetic nervous system - “Fight or Flight”, Releases adrenaline, Increases HR, Dilates Pupils
d) Central nervous system - Control Center, Processes and interprets Sensory Input, Motor Output
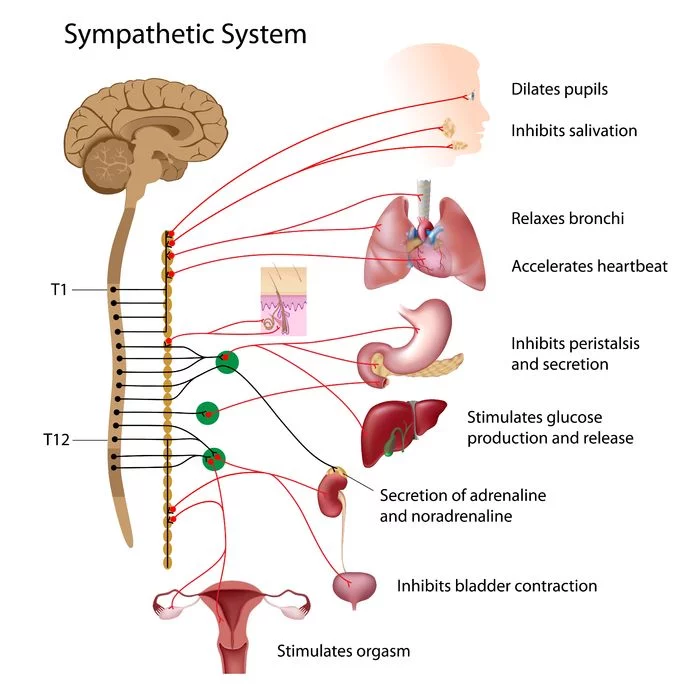
What is the term for the narrowing of the arterial lumen caused by contraction of smooth muscle fibers?
a) Vasodilation
b) Vasoconstriction
c) Endothelial damage
d) Clotting
b) Vasoconstriction
What effect does inhibition of impulses from the autonomic nervous system have on the arterial lumen?
a) Vasoconstriction
b) Vasodilation
c) Clot formation
d) Increased blood pressure
b) Vasodilation
Which layer of the artery is the innermost and must remain smooth to prevent platelet damage and clot formation?
a) Tunica media
b) Tunica adventitia
c) Tunica intima
d) Vasa vasorum
c) Tunica intima
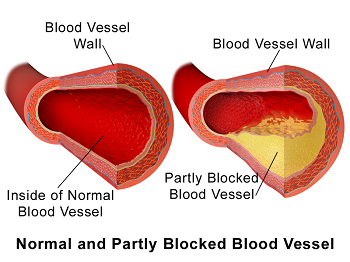
What is arteriosclerosis obliterans characterized by?
a) Thinning and increased elasticity of arterial walls
b) Thickening and loss of elasticity of arterial walls
c) Decreased cholesterol levels
d) Increased blood flow to organs
b) Thickening and loss of elasticity of arterial walls
Which of the following is a type of arteriosclerosis?
a) Vasculitis
b) Atherosclerosis
c) Thrombophlebitis
d) Embolism
b) Atherosclerosis
Which risk factor is NOT commonly associated with atherosclerosis?
a) Tobacco use
b) Hypertension
c) Diabetes mellitus
d) Low levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol
d) Low levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol
LDL stands for Low-Density Lipoprotein, often referred to as “bad cholesterol.”
What are the yellow-colored plaques called that form in atherosclerosis?
a) Atheromas
b) Thrombi
c) Emboli
d) Fibromas
a) Atheromas
Atheromas form on the the inner layers of the walls of medium-sized and large arteries. The formation of the atheroma is usually segmental.
Where are the two main areas of early peripheral involvement in atherosclerosis?
a) Carotid artery and renal artery
b) Aortic bifurcation and distal superficial femoral artery
c) Coronary artery and pulmonary artery
d) Subclavian artery and iliac artery
b) Aortic bifurcation and distal superficial femoral artery
Atherosclerosis often begins at areas of turbulent blood flow, such as:
The aortic bifurcation (where the aorta splits into the iliac arteries)
The distal superficial femoral artery, a common site of peripheral arterial disease (PAD).
What complications can the plaque from atherosclerosis place the patient at risk for?
a) Thrombosis, CHD, angina pectoris, and MI
b) Stroke and meningitis
c) Thrombosis and coronary heart disease
d) Pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis
a) Thrombosis, CHD, angina pectoris, and MI
Which physical exam finding is NOT typically seen in patients with severe peripheral arterial disease?
a) Severely thickened, deformed nails
b) Shiny skin
c) Increased hair growth
d) Significant pallor of the skin with exercise
c) Increased hair growth
Which of the following materials is NOT commonly used to make vascular stents?
a) Stainless-steel mesh
b) Titanium
c) Polypropylene
d) Silicone
d) Silicone
What is the primary physiological process of angioplasty?
a) Vasodilation of the vessel
b) Cracking of the plaque with healing and new intima growth
c) Removal of the plaque by suction
d) Injection of thrombolytic agents
b) Cracking of the plaque with healing and new intima growth
The primary goal of angioplasty (specifically percutaneous transluminal angioplasty, or PTA) is to:
Use a balloon catheter to compress and crack the atherosclerotic plaque against the arterial wall.
This reopens the narrowed vessel lumen and restores blood flow.
The vessel then heals over time with new intimal growth forming a smoother inner surface.
What is the risk of selecting a balloon that is too large for angioplasty?
a) Under dilation and early stenosis
b) Dissection of the vessel
c) Balloon rupture
d) Excessive vasodilation
b) Dissection of the vessel
Using a balloon that is too large during angioplasty can overstretch the vessel wall, leading to a tear in the intimal layer. This is known as a vessel dissection, which can:
Disrupt blood flow
Create a flap that obstructs the lumen
Lead to thrombosis or require emergency stenting or surgery
Other risks like balloon rupture (c) or excessive vasodilation (d) can occur, but vessel dissection is the most clinically significant and immediate complication of oversizing.
How far beyond the atherosclerotic lesion should the balloon extend during angioplasty?
a) 1-2 mm
b) 3-5 mm
c) 1-2 cm
d) 3-5 cm
c) 1-2 cm
What area is included in the skin prep for a peripheral artery angioplasty?
a) Hip to ankle
b) Inguinal groin to knee joint
c) Mid-thigh to ankle
d) Abdomen to groin
b) Inguinal groin to knee joint
Why is detailed angiographic mapping necessary before angioplasty?
a) To check for blood clots
b) To measure blood pressure
c) To locate and define the lesion
d) To confirm anesthesia placement
c) To locate and define the lesion
What is the name of the procedure involving balloon dilation of the peripheral artery?
a) Endarterectomy
b) Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty
c) Atherectomy
d) Vascular bypass
b) Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty
Where is the arterial introducer needle initially inserted during a percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty?
a) Ipsilateral femoral artery
b) Contralateral femoral artery
c) Radial artery
d) Brachial artery
a) Ipsilateral femoral artery
Ipsilateral - Same side
What is the purpose of the sheath introducer in coronary angioplasty?
a) To inject contrast dye
b) To keep the artery open and control bleeding
c) To place the stent
d) To measure vessel diameter
b) To keep the artery open and control bleeding
What is injected through the guiding catheter to visualize the lesion during coronary angioplasty?
a) Heparin
b) Nitroglycerine
c) Contrast dye
d) Saline solution
c) Contrast dye
What is the role of nitroglycerine during the angioplasty procedure?
a) To reverse vessel spasm
b) To expand the stent
c) To coagulate blood
d) To induce anesthesia
a) To reverse vessel spasm
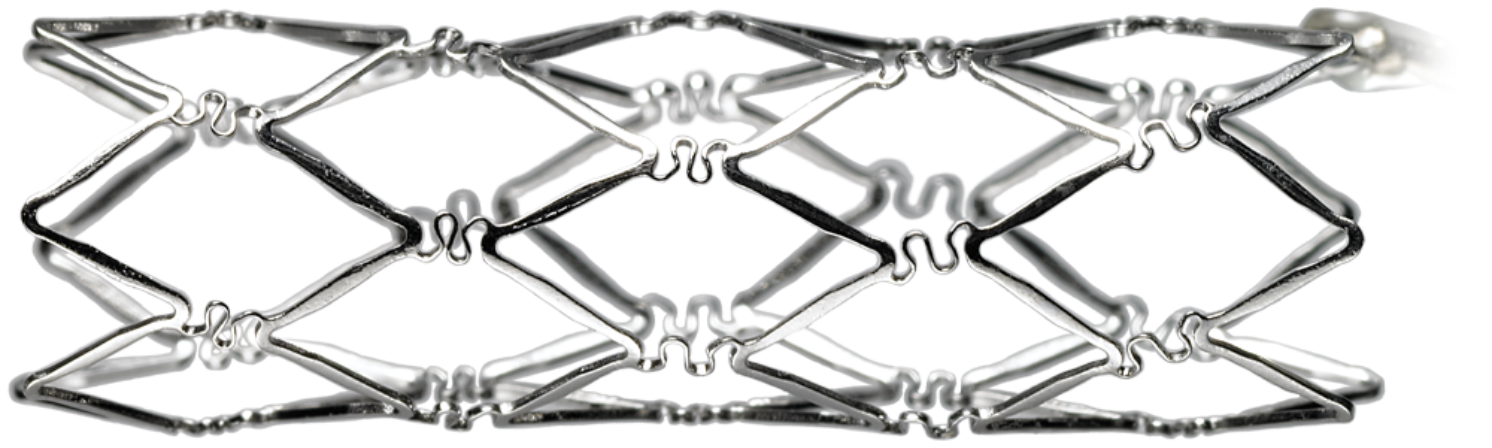
What is the function of the Palmaz stent in angioplasty?
a) To dissolve the plaque
b) To maintain patency of the vessel lumen
c) To remove the balloon catheter
d) To deliver heparin
b) To maintain patency of the vessel lumen
The PALMAZ Stent is a stainless-steel mesh tube that can be placed inside a narrowed pulmonary artery (blood vessel in the lung) and expanded to widen it.
Which of the following is NOT a complication of coronary angioplasty?
a) Myocardial infarction
b) Hematoma at the femoral artery insertion site
c) Allergic reaction to contrast dye
d) Pulmonary embolism
e) Stroke
d) Pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism is not typically a complication of coronary angioplasty since the procedure focuses on coronary arteries, not the venous system where emboli usually originate.
Which complication places a patient at increased risk for stroke if angioplasty is performed soon after it occurs?
a) Deep vein thrombosis
b) Myocardial infarction
c) Pulmonary embolism
d) Hypertension
b) Myocardial infarction
25-3. Angioplasty
Describe arteriosclerosis obliterans.
to the organs that the arteries supply. A type of arteriosclerosis is atherosclerosis.
Common disorder of the arteries characterized by thickening and loss of elasticity of the arterial walls.
This results in a decreased blood flow
25-3. Angioplasty
The sudden loss of circulation to an extremity is usually an indication of _______ ________.
arterial embolism