3B Enzyme Kinetics
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
How do enzymes accelerate the rate of chemical reaction?
By lowering the activation energy
What characteristic features define enzymes?
decrease the activation energy necessary for a chemical reaction to occur by stabilizing the transition state.
-Enzymes can accelerate reactions as much as 10^21 over uncatalyzed rates
-Urease is good example:
-uncatalyzed rate: 3x10^-10/sec (around 106 years)
-Catalytic power is 1x10^14 difference in ratio
What does decreasing the activation energy does?
It increases the reaction rate
The activation energy is related to the rate constant. What is the equation?
A: Arrhenius factor (constant)
High activation energy = low rate constant (k) = low rate (v)
v = k[S] >>>>>> High [S] = high rate (v)
Transition State
The overall free energy change for a reaction, free energy, is related to what?
The free energy of activation for a reaction, activation energy, is related to?
-Related to the equilibrium constant (K)
-Related to the rate constant (K)
What equations define the kinetics of Enzyme-Catalyzed reactions?
Michaelis-Menten Kinetics
-The quantitative theory of enzyme kinetics was proposed by two scientists Leonor Michaelis and Maud Leonora Menten in 1913
-Enzyme reactions in Michaelis-Menten kinetics theory occur in two stages: The substrate binds reversibly to the enzyme, forming the enzyme-substrate complex. This is sometimes called the Michaelis-Menten complex.
-The enzyme then catalyzes the chemical step in the reaction and releases the product
For the Kinetics of Enzyme-Catalyzed reaction, what happens at low concentrations of substrate?
the rate becomes proportional to [S] in a linear fashion, so as we add more substrate the reaction increases.
What happens to the reaction at higher concentration of substrate?
the enzyme reaches saturation. This behavior is called a Saturation Effect.
As [S] increases, what happens to v?
-v reaches Vmax
-Instead of a linear relationship that you will get with most chemical reactions that have a first order kinetics, you get a hyperbolic relationship
How do we explain the unique behavior of enzymes?
-We use Michaelis-Menten Kinetics, which is the most unique way of explaining enzymatic activity.
Who came up with the Michaelis-Menten Kinetics?
Leonor Michaelis and Maud Menten
What are the three assumptions of the Louis Michaelis and Maud Menten's theory?
Formation of an enzyme-substrate complex (ES)
ES complex is in rapid equilibrium with free enzyme. It is going back and forth evenly, this is reversible. ES complex can form and reform.
The breakdown of ES to form products is irreversible.
What is the derivation of the Michaelis-Menten Kinetics?
The Michaelis-Menten equation arises from the general equation for an enzymatic reaction: E + S ↔ ES ↔ E + P, where E is the enzyme, S is the substrate, ES is the enzyme-substrate complex, and P is the product.
What is Vmax?
the maximum rate of reaction -- when the enzyme is saturated with substrate.
What is the Michaelis-Menten equation?
The rate equation for a one-substrate enzyme-catalyzed reaction.
What is the Michaelis-Menten Equation?
What is Vmax?
What is V?
What is the Kcat?
What is Km?
v = Vmax / (Km/[S]) +1
rate at high [S] = Kcat x [E]total
rate at a given substrate.
turnover number
[S] that results in ½ the Vmax
What is the Michaelis-Menten Mechanism between the reactants [S], [E] and product?
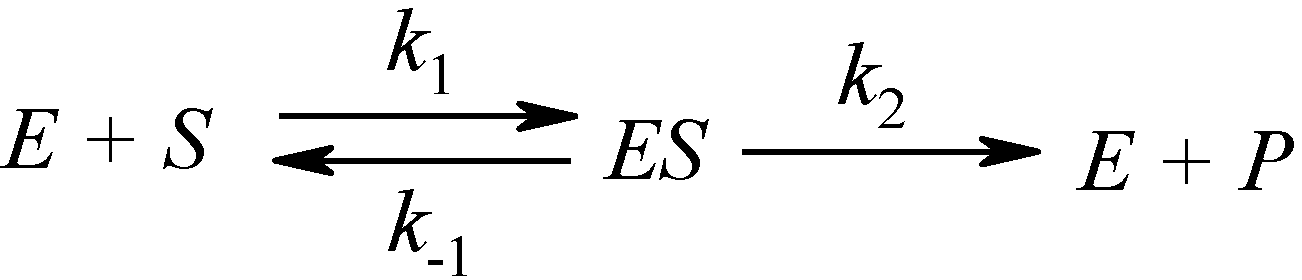
What is the equation for Km?
Km = (K-1 + K2) / K1