Pysch 3
1/203
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
204 Terms
Sensation
is the detection of the external stimuli and the transmission of this information to the brain
Perception
is the process, organization, and interpretation of sensory signals
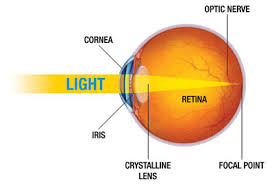
Lights Path:
cornea → pupil → iris → lens → retina
Rods:
are apart of the retina, they are what is sensitive to low levels of light and motion
Cones:
are apart of the retina, they require high levels of light and result in color perception and detail
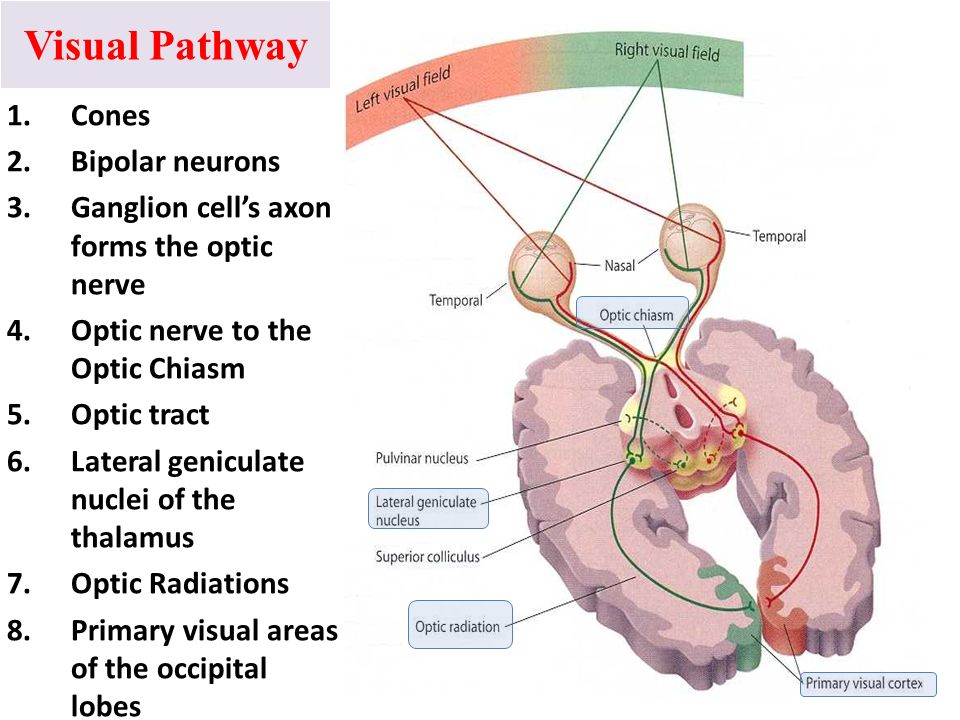
Explain how light is processed by the brain--specifically the path from the eye to the cortex, and what part of the cortex processes this information.
Cornea → pupil → retina (rods/cones) → ganglion cells → optic nerve →visual cortex
Trichromatic theory
is when color vision results from activity in three different types of cones that are sensitive to different wavelengths
Trichromatic theory wavelengths
The most sensitive and shortest wavelengths is blue-violet light
The most sensitive to medium wavelengths is yellow-green light
The most sensitive to long wavelengths is red-orange light
Opponent-Process Theory
is there are different types of ganglion cells working in opposing pairs, create the perception of R/G and B/Y are opposites
Gestalt principle
explains how our brains group the prescribed features of a visual scene into organized wholes “the whole is greater than the sum of its parts”
BInocular depth cues:
because the distance between the eyes, each eye receives a slightly different retinal image
When a person views a nearby object, the eye muscle turns the eyes inwards
Monocular depth cues:
Occlusion,Position relative to horizon, Relative size,Familiar size,Texture gradient:
Occlusion;
a nearby object blocks an object that is further away
Position relative to horizon:
below horizon; higher in the visual field → further away, above horizon; lower in the visual field → further away
Relative size:
far-off objects project a smaller retinal image than close objects do
Familiar size:
because we know how large familiar objects are we can tell how far away they are by the size of the retina images
Linear perspective:
seemingly parallel lines appear to converge in the distance
Texture gradient:
as a uniformly textured surface receded, its texture continuously becomes denser
Size perception:
the size of an object's retinal image depends on that object’s distance
Motion perception:
Neurons specialized for detecting movement fire when movement occurs
Object Constancies:
correctly perceiving objects as constant in their shape, size, lightness, and color, despite raw sensory data that could mislead perception
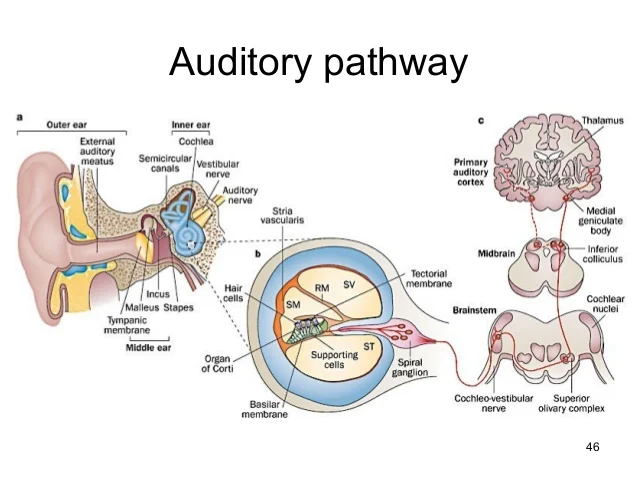
Describe how sound waves are transduced into neural activity in the ear.
Pinna gathers air pressure waves → Eardrum vibrates when waves of air hit it → Hammer, anvil & Stirrup transfer movements of eardrum to inner ear → Semicircular canals articulate a sense of balance → Cochlea hair cells and basilar membrane are the receptors → goes to the auditory nerve that sends signal to the brain → Primary auditory cortex processes the sound
Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of cochlear implants.
Helps those with severe hearing loss to be able to hear by stimulating the auditory nerve, but does not amplify sound and can cause some negative attitude towards people who are deaf or hard of hearing
Temporal coding:
a mechanism for encoding low-frequency auditory stimulus which the firing rates of cochlear hair cells match the frequency of the sound waves (up to 4,000 Hz)
Place coding:
a mechanism used for encoding high-frequency auditory stimuli in which the frequency of the sound waves is encoded by the location of the hair cells along the basilar membrane
Gate control theory
is when pain receptors are activated, a neural gate opens in the spinal cord and allows pain signals to be carried by nerve fibers, these fibers can fire and close the gate thus preventing pain reception
Discuss the five basic gustation (taste) sensations
Sweet, Sour, Salty, Bitter and Umami
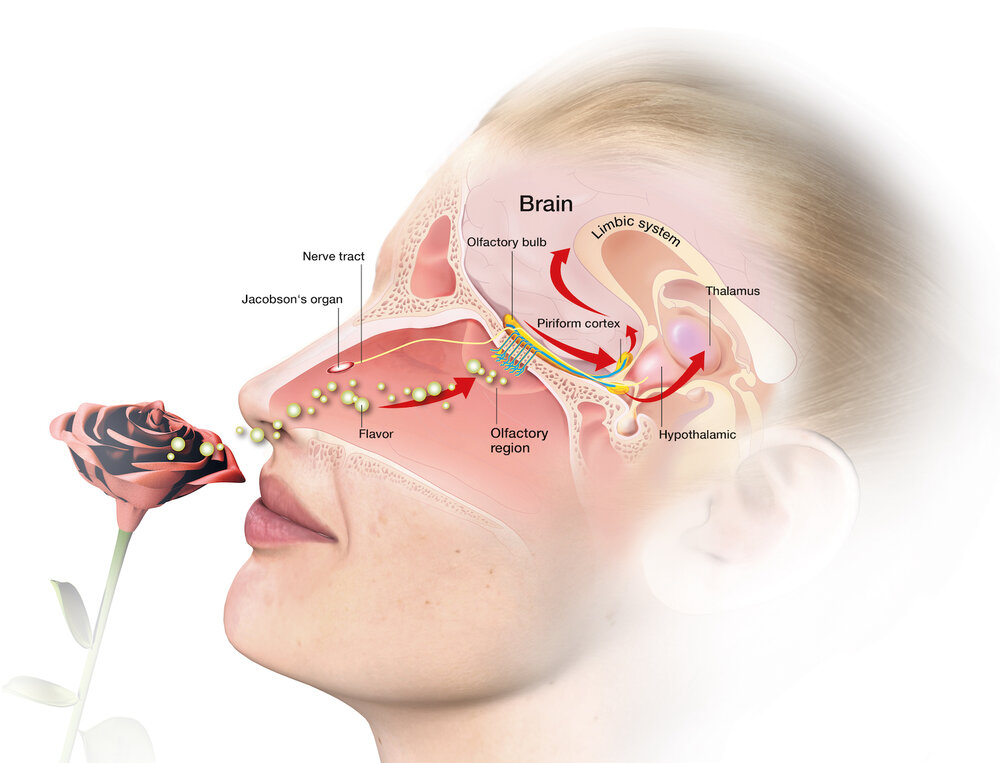
Describe the neural pathway for olfaction (smell).
Odorant pass into the nose and nasal cavity → contact the olfactory epithelium (a thin layer of tissue within the nasal cavity that contains the receptors for smell) → olfactory bulb (the brain center for smell in the frontal cortex) → information for weather the smell is pleasant or unpleasant is process in the prefrontal cortex
Learning
a relatively enduring change in behavior resulting for experience
Nonassociative learning:
learning about a stimulus such as sight or sound, in the external world
Associative learning:
learning the relationship between two pieces of information
Observational:
learning by watching how others behave
Habitual:
a decrease in behavioral response after repeated exposure to a stimulus
Sensitization:
an increase in behavioral response after exposure to a stimulus
Classical Conditioning:
a neutral object comes to elicit a response when it is associated with a stimulus that already produces a response
UR:
a response that does not have to be learned such as a reflex
US:
a stimulus that elicits a response such as a reflex without any prior learning
CS:
a stimulus that elicits a response only after learning has taken place
CR:
a response to a conditioned stimulus: a response that has been learning
Acquisition:
the gradual formation of an association between CS and US
Extinction:
the process in which the CS is repeated without the US and CR is gradually weakened
Spontaneous Recovery:
a process in which a previously extinguished conditioned response reemerges after the presentation of the CS
Generalization:
stronger resemblance → more generalization
Discrimination:
making a distinction between the CS and a related object
Counterconditioning:
exposing a patient to small doses of a the CS while they engage in a relaxing task; gradually extinction takes place
Operant Conditioning:
modification of voluntary behaviors
Reinforcement: consequences
→ behavior more likely
Positive Reinforcement:
adding desirable stimulus
Negative Reinforcement:
removing undesirable stimulus
Punishment: consequences
→ behavior less likely
Positive Punishment:
adding undesirable stimulus
Negative Punishment:
removing desirable stimulus
Interval
= time
Fixed interval:
reinforced after designated amount of time passes
Variable interval:
reinforced after varying amount of time passes
Ratio
=effort
Fixed ratio:
reinforced after designated amount of work
Variable ratio:
reinforced after varying amounts of work done
Shaping:
teach complex behaviors by successive approximations ( gradually getting closer and closer to desired behavior)
Observational learning:
Ex: exposing children to violence encourages them to act aggressively
the acquisition or modification of a behavior after exposure to another individual performing that behavior (social learning)
Ex of observational learning
Ex: exposing children to violence encourages them to act aggressively
Modeling
the imitation of observed behaviors,
ex of modeling
:ex: children who associate smoking with admirable figures are more likely to start smoking
Vicarious Learning:
learning the consequences of an action by watching others being rewarded or punished for performing the same action,
ex of Vicarious Learning:
Analogical representations:
corresponding to some physical characteristic of objects, they are analogous to the objects (more time goes by, the more the arm turns on a clock)
Symbolic representations:
abstract, do not represent physical characteristics of objects (nothing about the way 9 looks tell you the is it more than 8)
Concept:
a category of release of related items; it consists of mental representation of those items
Prototype:
the best example for that category, the more similar an object is to the prototype the faster we can think of a concept (Concept: Fruit Prototype: Apple)
Exemplar:
a way of thinking about concepts; all members from the concept and determine categorical membership, can explain how we spontaneously form categories (organize photo albums into ‘fashion’ ‘food’ ‘animals’)
Schema:
a cognitive structure that helps us perceive, organize,and process information as we move around the world, enables us to make quick judgments with little effort
Script:
a schema that directs behaviors over time within a situation (going to the movie)
Huestricis:
are shortcuts used to reduce the amount of thinking that i needed to make decisions (helps to make fast almost unconscious decisions)
Anchoring:
the tendency to rely on the first piece of information encountered in making judgments
Framing:
the influence of the way a question is phrased on the decisions people make
Loss aversion:
losses feel more bad than gains feel good
Mental set:
problem solving strategies that have worked in the past
Functional fixedness:
having fixed ideas about the typical function of objects
Means-End Analysis
: we may have to move away from the solution to get the solutions
Insight:
realization of a solution to a problem
Somatic Markers:
bodily reactions that arise from an emotional evaluation of an actions consequences
Brocas’ area:
in the left frontal contrex, interrupts one's ability to speak and deficits of syntax
Wernicke;s area
in the left hemisphere where the temporal and parietal lobe meets, involved in speech and comprehension, trouble understanding the means of words - semantics
Explain how language develops
Children begin to use language in more sophisticated ways by 4, Overgeneralize
Overgeneralize:
apply rules even where they do not apply in the language they are learning
Phonemes:
the basic sounds of speech, the building blocks of language
Phonology:
the human vocal tract has the capacity to make many more sounds than any language uses
Morphology:
the smallest language units that have meaning
Syntax:
the system of rules that govern how words are combined into phrases and how phrases are combined to make sentences
Semantics:
the system of meaning that underlie words, phrases and sentence
Mental age:
an assessment of a child's intellectual standing compared with that of same-age peers
Intelligence Quotient (IQ):
Mental age/chronological age x100
What is the evidence that it is a reliable and valid measure of intelligence?
IQ scores tend to be correlated from test to retest and typically predict about 25% percentage of the variations in school and work performance
General intelligence (g)n:
the idea that one general factor underlies intelligence
Sternberg intelligence:
analytical intelligence: being good at problem solving and other academic challenges
Creative intelligence:
ability to gain insight and solve novel problems
Practical Intelligence:
dealing with everyday tasks
Gardner Intelligence:
people can be intelligent in ant number of ways, such as musically or athletically
Emotional Intelligence:
ability to manage, recognize, and understand emotions and use emotions to guide appropriate thought and actions
Fluid Intelligence:
the ability to process information, understand relationships and think logically particularly in novel or complex circumstances; (related to working memory and decreases as we get older)