Vaccines P1 (Fouty)
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Additional Material (Lecture)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Variola major
Smallpox
scraped lesions from infect and put in nose or skin of uninfected
Variolation
People inoculated through variolation could still spread
smallpox
but individual mortality was reduced to 1-2%
1774 use of cowpox to protect against small pox by _______ but in 1796 more formally done by inoculation by ________
Benjamin Jesty; Edward Jenner
Jenner’s experiment
Inoculated gardener’s son with cowpox
6 weeks later inoculated him with smallpox via variolation
Smallpox vaccine changed from cowpox to _____ virus
Vaccinia
both live viruses of same genus orthopoxvirus
1950 ____ begins intensive international effort to eradicate smallpox
WHO
______ smallpox was eradicated from the world
1978 only stock solutions still exist
Pasteur’s model of rabies vaccine
desiccated spinal cords from rabies infected rabbits
Pasteur gave a series of SQ injections containing minced desiccated rabies-infected rabbit spinal cords to Joseph Meister
Injected progressively less-desiccated (fresher_ rabbit spinal cord over time
Boy survived rabies
Strangling angel of children
Diphtheria
Pseudomembrane occlude upper airway
Clinical diphtheria is caused by a
toxigenic strain (phage contaminated diphtheria)
Diphtheria+ phage + low bacterial irons=________ which inhibits
diphtheria toxin
protein synthesis
Diphtheria toxin was the first described
exotoxin
______ inactivated diphtheria toxin injected into guinea pigs protected them from subsequent toxin injections
Heat
serum from an animal given heat-inactivated Diptheria toxin protected an unimmunized animal that was given virulent toxin
Anti-toxin
In 1891 Emil von Behring used animal immune serum to treat a child with diphtheria
Child survived
variolation: live attenuated virus
Vaccination: live cowpox/vaccinia virus
Smallpox
Inactivated (dead) virus
Rabies
Passive immunity (antibody therapy)
Diphtheria
The individual receives protective antibodies from other source
Passive immunity
Natural method of passive immunity
maternal antibodies
Maternal antibodies decline by
4-6 months baby is vulnurable
Before the antibiotic era _____ immunity with antibody (serum) administration was the only therapeutic option against many bacterial disease
passive
Passive immunity is _____ dependent
time (better to give before exposure of post exposure but no signs of disease yet)
Standard immunoglobulins indications
Primary humoral immunodeficiencies (example CVID): hep A, measles, varicella, rubella
babies after maternal antibodies have dissipated but before vaccination
Hyperimmunoglobulins indications
antibodies after a person has been vaccinated then given to someone who is not
Anthrax, infant botulism, hep B, CMV, rabies, tetanus, varicella
Animal derived IG (mostly equine) indications
Envenomation: black widow, scorpion, rattlesnake/cottonmouth
Diphtheria, botulism
Monoclonal antibodies indications
SARS-CoV-2, RSV, inhalation anthrax
The individual develops their own immune response against a pathogen due to either infection or vaccination
Active immunity
Adjuvants main goal is to
activate and attenuate innate immune response
recruiting in immune cells like dendritic cells to connect to adaptive immune response
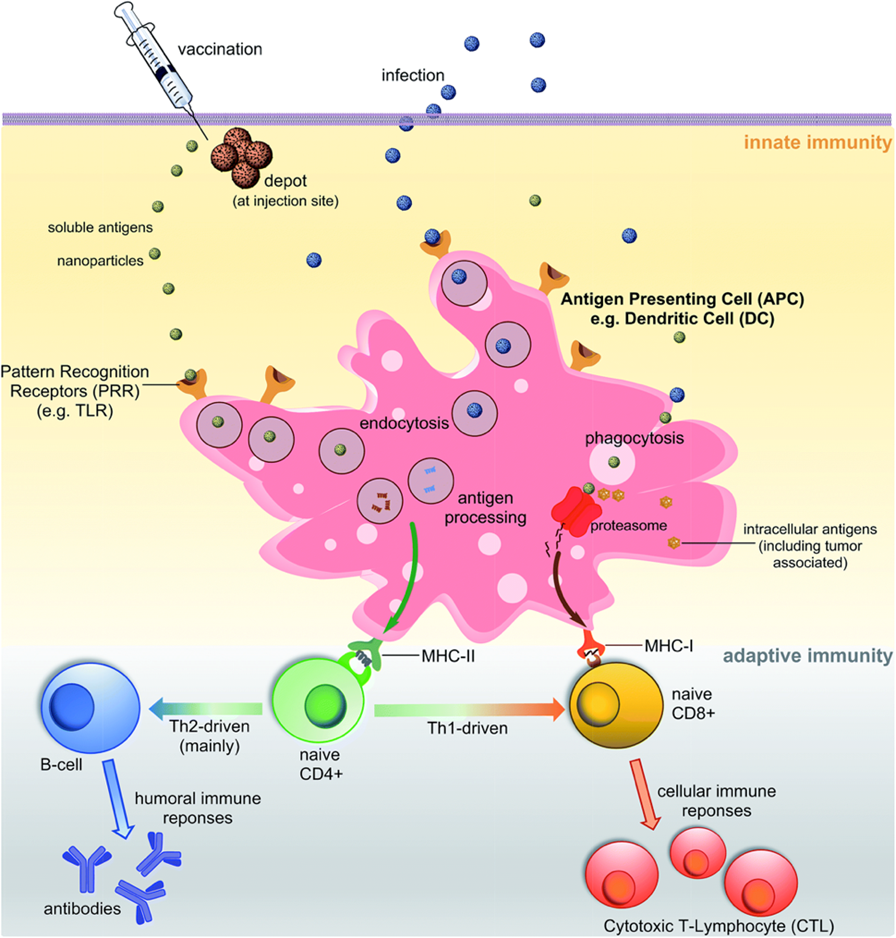
Initiation of vaccine response
Immune mechanisms triggered by vaccines
Antibodies
CD4 t cells
CD8 t cells
Following primary antigen exposure
antibodies are generated
Upon re-exposure to antigen ___ titer of antibodies and _____ presentation
higher; earlier
persist a lot longer
highly avid antibodies (well tailored suit)
Protection is due to induction of antigen specific
antibodies
_____ are critical to the induction of high affinity antibodies and immune memory
T cells
Antibodies prevent/reduce infection by
–Neutralizing viral replication by blocking cell adhesion and entry
–Binding to enzymatic active sites or preventing diffusion of toxins
–Promoting opsonization/phagocytosis of bacteria
–Activating complement
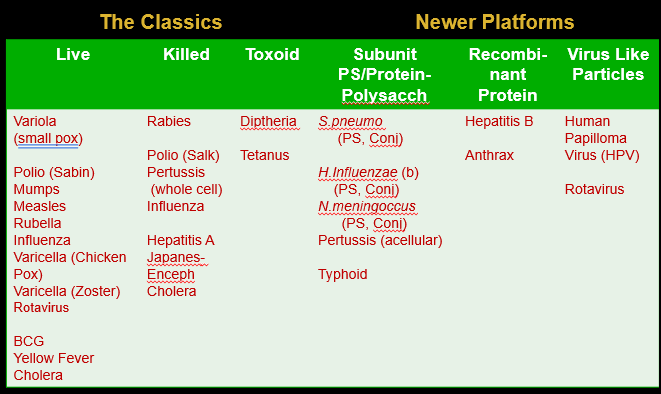
Classic methods of generating vaccines
Live
Killed
Toxoid
Live (attenuated) virus vaccine
Isolate virus, grow in cultured human cells
Infect non-human cells
Virus mutates to grow in non-human cells
Attenuated virus no longer grows well in human cells. given back to humans to recognize antigen but not cause disease
Attenuated strains held by CDC/CBER
expanded by vaccine manufacturers
tested for titer and infectivity
Provided alone or in combination with other attenuate viruses (MMR example)
Live attenuated vaccine
Variola
Polio (sabin)
Mumps
Measles
Rubella
Influenza
Varicella (chicken pox)
Varicella (Zoster)
Rotavirus
BCG
Yellow fever
cholera
Inactivated (killed) viral vaccines
Prevailing live strains obtained from CDC/CBER
Monovalent strain incubated with 11 day old embryonated chick egg (or human diploid cell) (single strain)
Virus harvested (titer, infectivity, sterility, specificity assessed)
Virus inactivated by formaldehyde
All inactivated monovalent strains can be combined into single vaccine
Killed vaccines
Rabies
Polio (Salk)
Pertussis
Influenza (quadrivalent)
Hep A
Japanes
Eneceph
cholera
Toxoid vaccines
Toxogenic bacterial strains
Vat of toxin
Centrifuged and purified
toxin
inactivated with formalyn
toxoid given
Toxoid vaccines
Diphtheria
Tetanus
New platforms of vaccines not RNA/DNA
Subunit PS/protein-polysaccharide
Recombinant protein
Virus like particles
Polysaccharide-protein conjugate vaccine
polysaccharide itself does not activate T cells so no long term
Conjugate with toxoid very potent and immunogenic
Subunit PS Protein-polysaccharide vaccines
Strep pneumo (PS, conj. given to children)
H influenzae Hib (PS, conj)
N meningococcus (PS, conj)
Pertussis
Typhoid
need exposure to ____ to get memory
protein
Recombinant protein vaccines
Hep B
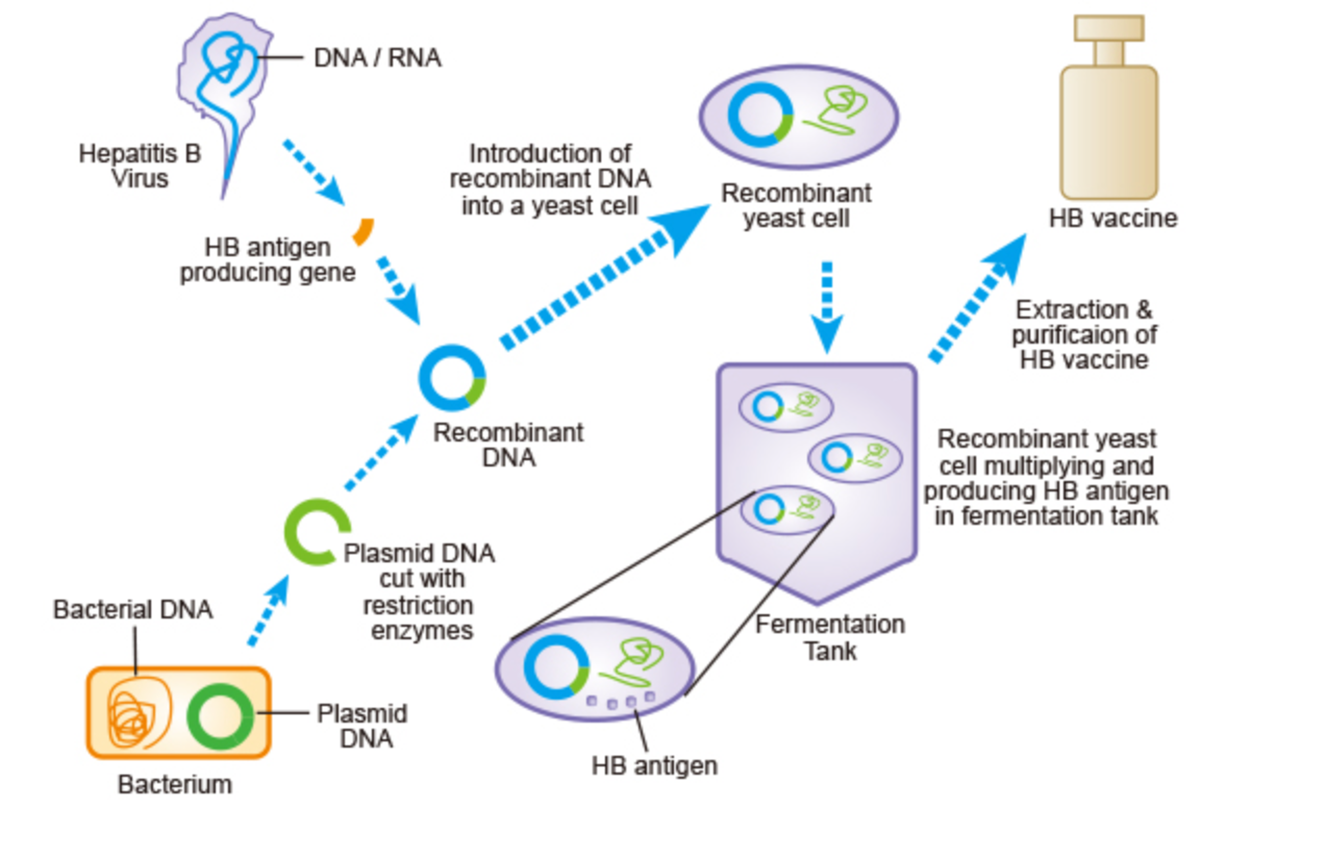
surface antigen into recombinant DNA
extract and purify
very potent
Recombinant protein vaccines
Hep B
Anthrax
Virus-like particle vaccines
Get rid of genetic material
Virus -like particles
HPV
Rotavirus
Vaccine summary slide
All Six Vaccine Platforms Are Used In The First __ Months Of Life
9
Vaccines contained weakened or killed disease antigens +
ingredients and byproducts
thimerosol
preservative
sugar and gelatin
stabilizer
aluminum salts
adjuvants
Egg/cell proteins
media
Cell culture products
formaldehyde
inactivating ingredients
neomycin
antibiotics
14 Infectious Diseases Mostly Controlled By Vaccines
•Smallpox
•Diptheria
•Tetanus
•Yellow fever
•Polio
•Measles
•Mumps
•Rubella
•Pertussis
•H.influenzae, type b
•Typhoid
•Rotavirus
•Hepatitis B
Important Diseases Caused by Intracellular Organisms are Difficult to Target with Vaccines (antibodies do not enter cells)
Malaria
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
HIV
Burkholderia pseudomallei
Orientia tsutsumagumshi (scrub typhus)