Year 11 Human Biology ATAR
1/279
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
280 Terms
Metabolism
The sum of all the chemical reactions that occur within an organism
Catabolism
Metabolic pathways that break down molecules, releasing energy.
Anabolism
Metabolic pathways that construct molecules, requiring energy.
Cellular Respiration Equation
Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water + ATP energy
Enzyme
A protein that acts as a biological catalyst to speed up a chemical reaction
Enzyme-substrate complex
When an enzyme binds to its substrate
Active Site
A region on an enzyme that binds to a substrate during a reaction.
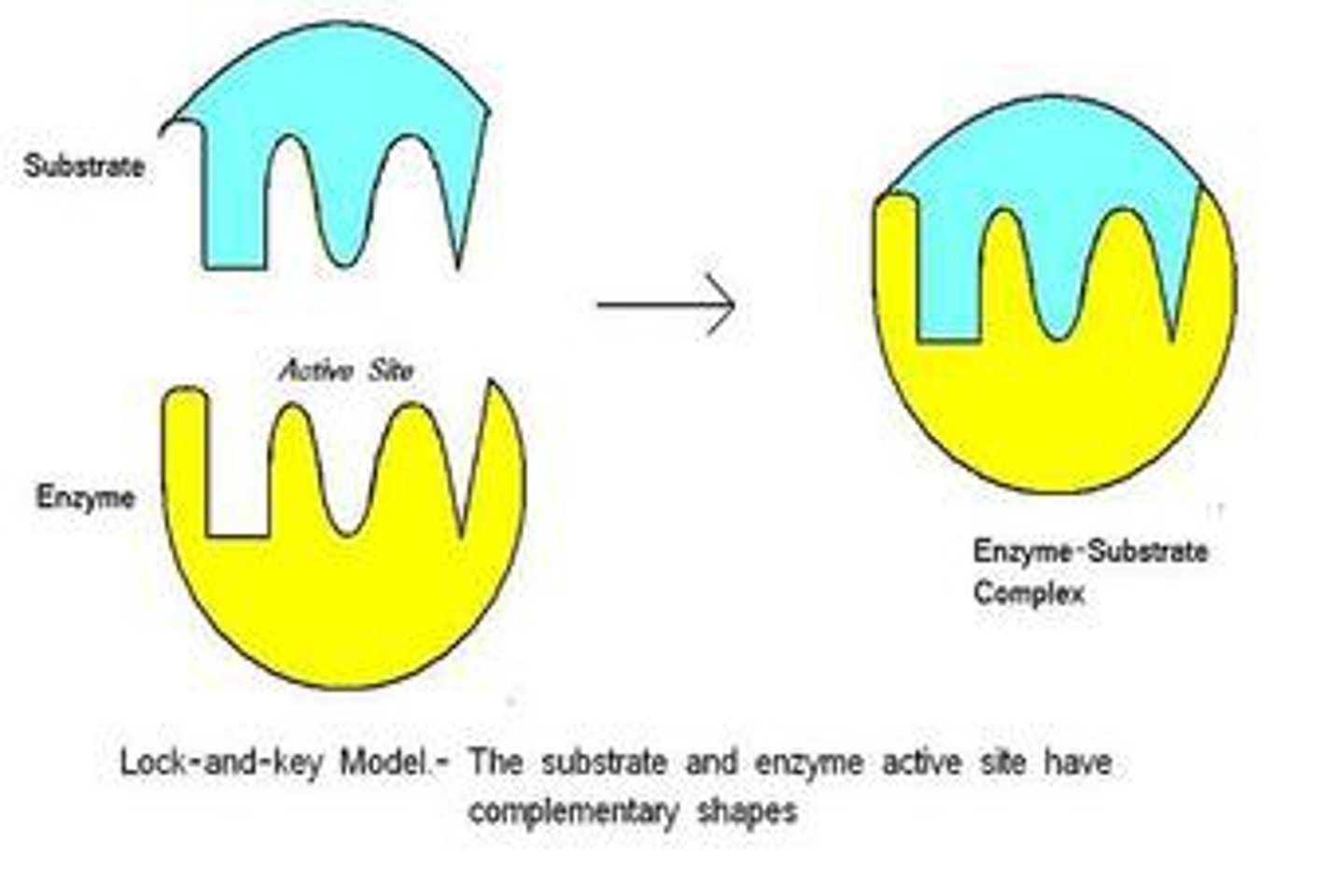
Lock and Key Theory
Enzyme's active site (lock) is already in appropriate conformation for the substrate (key) to bind
Substrate easily fits into active site
Glycolosis
Breaking glucose into two molecules of a compound called pyruvate; Creates a net total of 2 ATPs; anaerobic; occurs in cytosol
Krebs Cycle
second stage of cellular respiration; occurs in mitochondria; pyruvate molecules are turned into ATPs;Generates 2 ATPs; aerobic
Electron Transport Chain
Uses the high-energy electrons from the Krebs cycle to convert ADP into ATP; aerobic; Generates 34 ATPs
Epithilial tissue
Tissue composed of layers of closely spaced cells that cover organ surfaces; e.g. skin
Connective Tissue
A tissue that provides support for the body and connects its parts; e.g. blood, cartilage
Muscular Tissue
Long thin tissue that contracts to create movement; e.g. cardiac muscle, skeletal muscle
Nervous Tissue
Tissue that carries info between the brain and other parts of the body; e.g. neurones
Lungs
Two organs, located in the thoracic cavity responsible for breathing
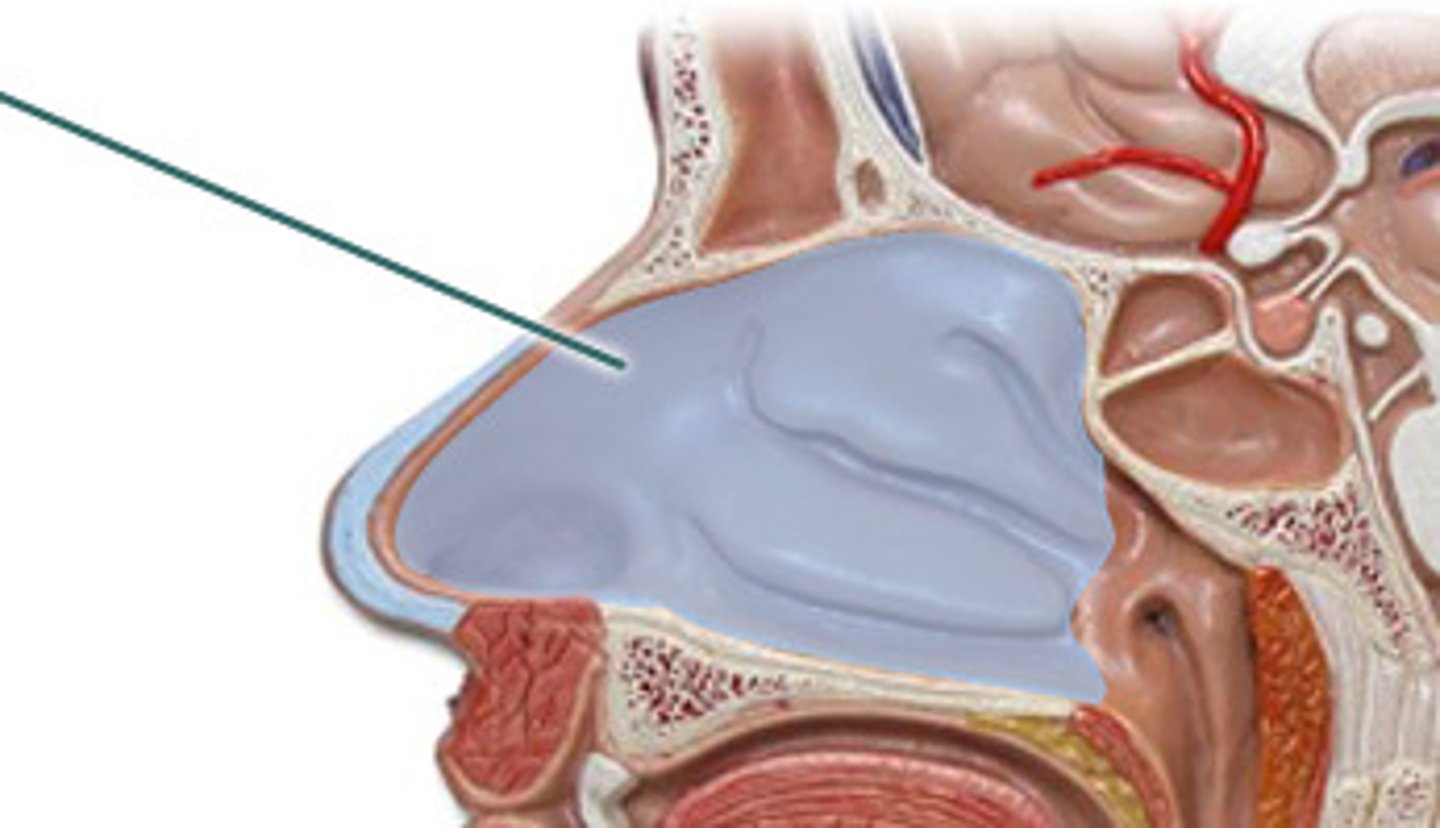
Nasal Cavity
hollow space behind the nose; filters and warms air
Pharynx
throat; passageway for food to the esophagus and air to the larynx
Larynx
passageway for air moving from pharynx to trachea; contains vocal cords
Pleural Membrane
membrane that encloses the lungs within the rib cage
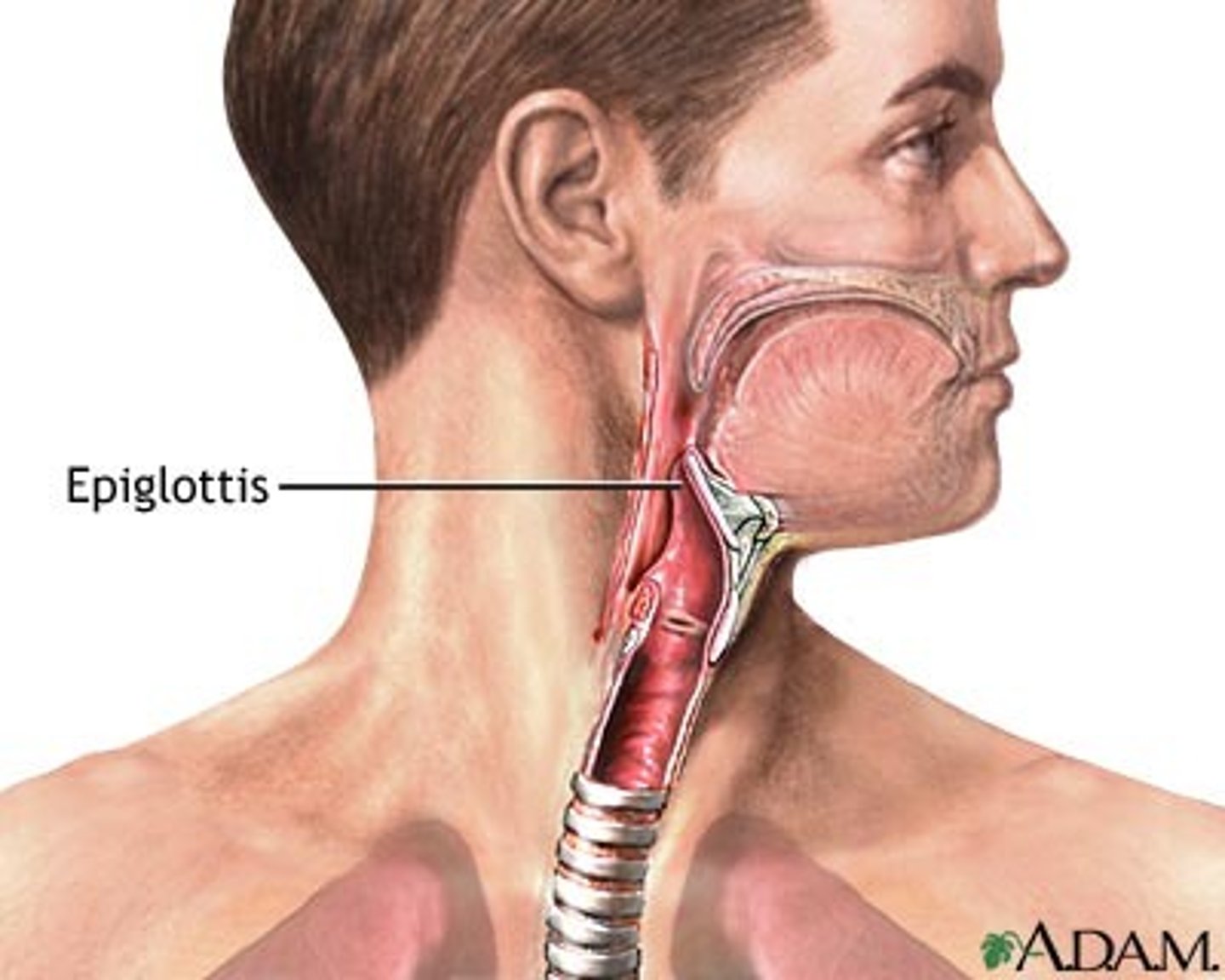
Epiglottis
A flap of tissue that seals off the windpipe and prevents food from entering.
Trachea
Allows air to pass to and from lungs
Ribs
The bones in the chest that protect the heart and lungs.
Bronchi
The passages that direct air into the lungs
Intercostal Muscles
Muscles which move the rib cage during breathing
Cell Membrane
A cell structure that controls which substances can enter or leave the cell.
Alveoli
small sacs within the lungs where gas exchange takes place with the bloodstream
Gas Exchange
The uptake of molecular oxygen from the environment and the discharge of carbon dioxide to the environment; occurs in alveoli
Alveoli Adaptations
→moist lining
→good blood supply
→very thin walls
→enormous surface area
Blood
Connective tissue made of plasma, erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets.
Erythrocytes
red blood cells; carry oxygen; is biconcave and contains no nucleus to carry more oxygen
Leukocytes
white blood cells; fight infection
Thrombocytes
platelets; forms blood clots
Plasma
Liquid part of blood; carries nutrients, wastes and bicarbonate (which carries the bulk of Carbon Dioxide)
Pulmonary Circulation
Blood circulates through lungs → Gas exchange occurs → Blood becomes oxygenated
Cytoplasm
A watery materials inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended
Cytosol
Fluid portion of cytoplasm; 70-90% water
Nucleus
Control structure and function of the cell
Nucleolus
Found inside the nucleus and produces ribosomes; composed of RNA
Nuclear Membrane
A highly-porous membrane that separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm
Ribosomes
site of protein synthesis; can be attached to Endoplasmic Reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Provides a site for chemical reactions; stores and transports molecules
Golgi body
Modifies and packages proteins for secretion
Lysosomes
Filled with enzymes needed to break large molecules
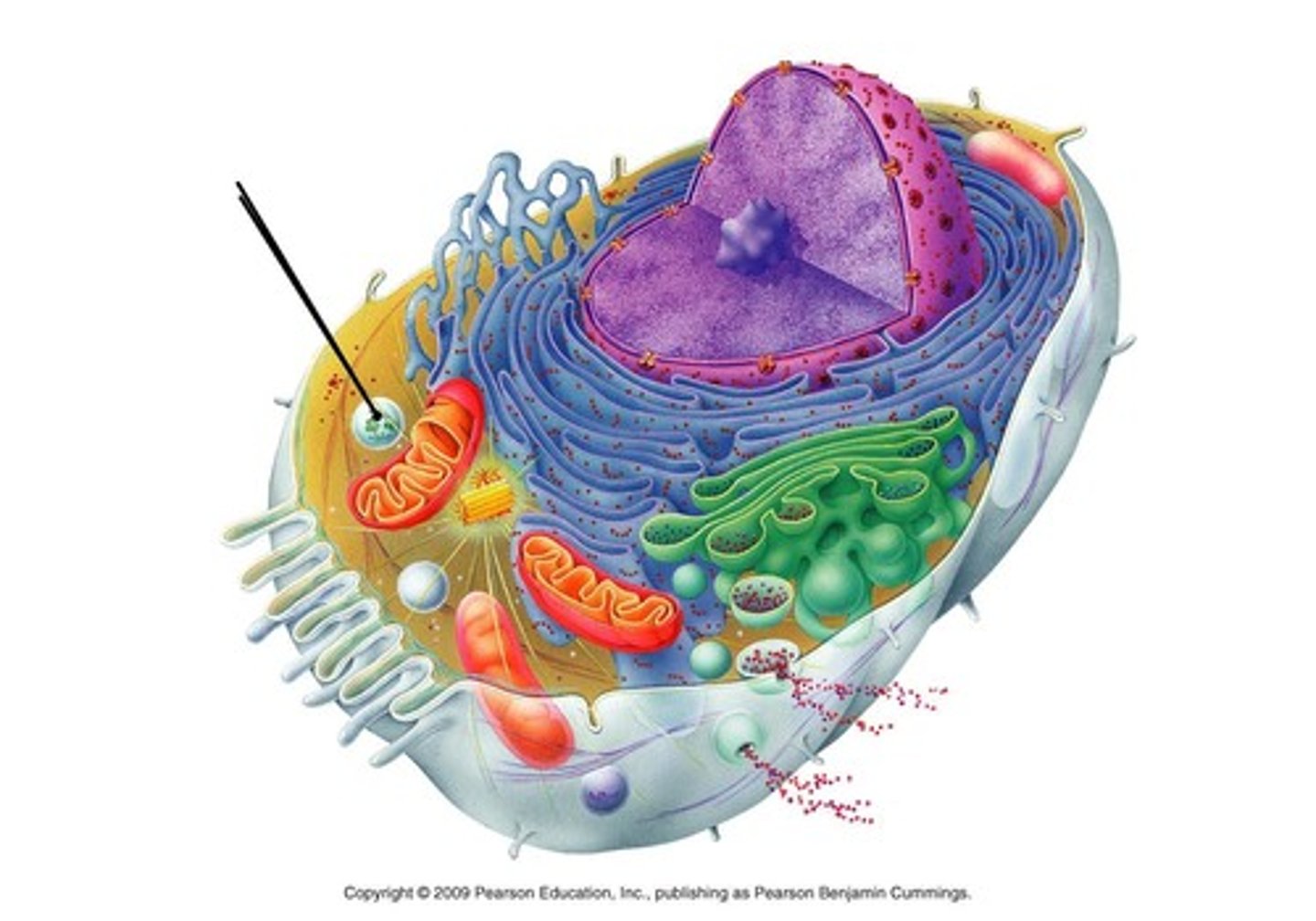
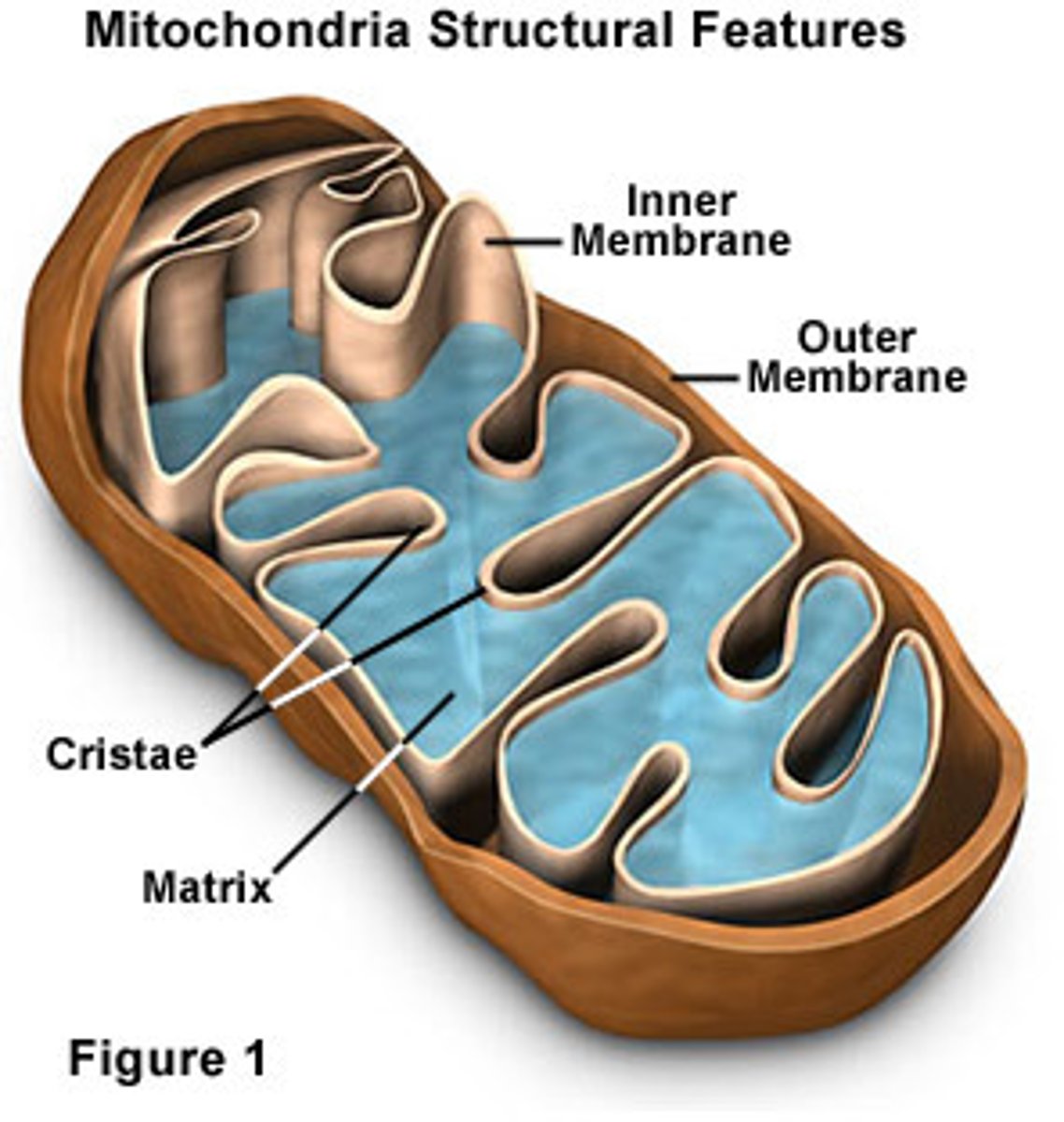
Mitochondria
organelle that is the site of ATP (energy) production
Cilia and Flagella
hairlike structures that extend from the surface of the cell, where they assist in movement
Cytoskeleton
A network of fibers that holds the cell together, helps the cell to keep its shape, and aids in movement
Inclusions
Substances that aren't part of the cell but found in the cytoplasm. E.g. Haemoglobin, melanin
Centrioles
Cell organelle that aids in cell division in animal cells only
Fluid Mosaic Model
The currently accepted model of cell membrane structure; where the cell membrane is a mosaic of protein molecules drifting in a fluid bilayer of phospholipids
Cell Membrane Features
→Physical Barrier
→Sensitive
→Supports the Cell
→Monitors what goes in and out
Passive Transport
The movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of energy by the cell
Active Transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration gradient
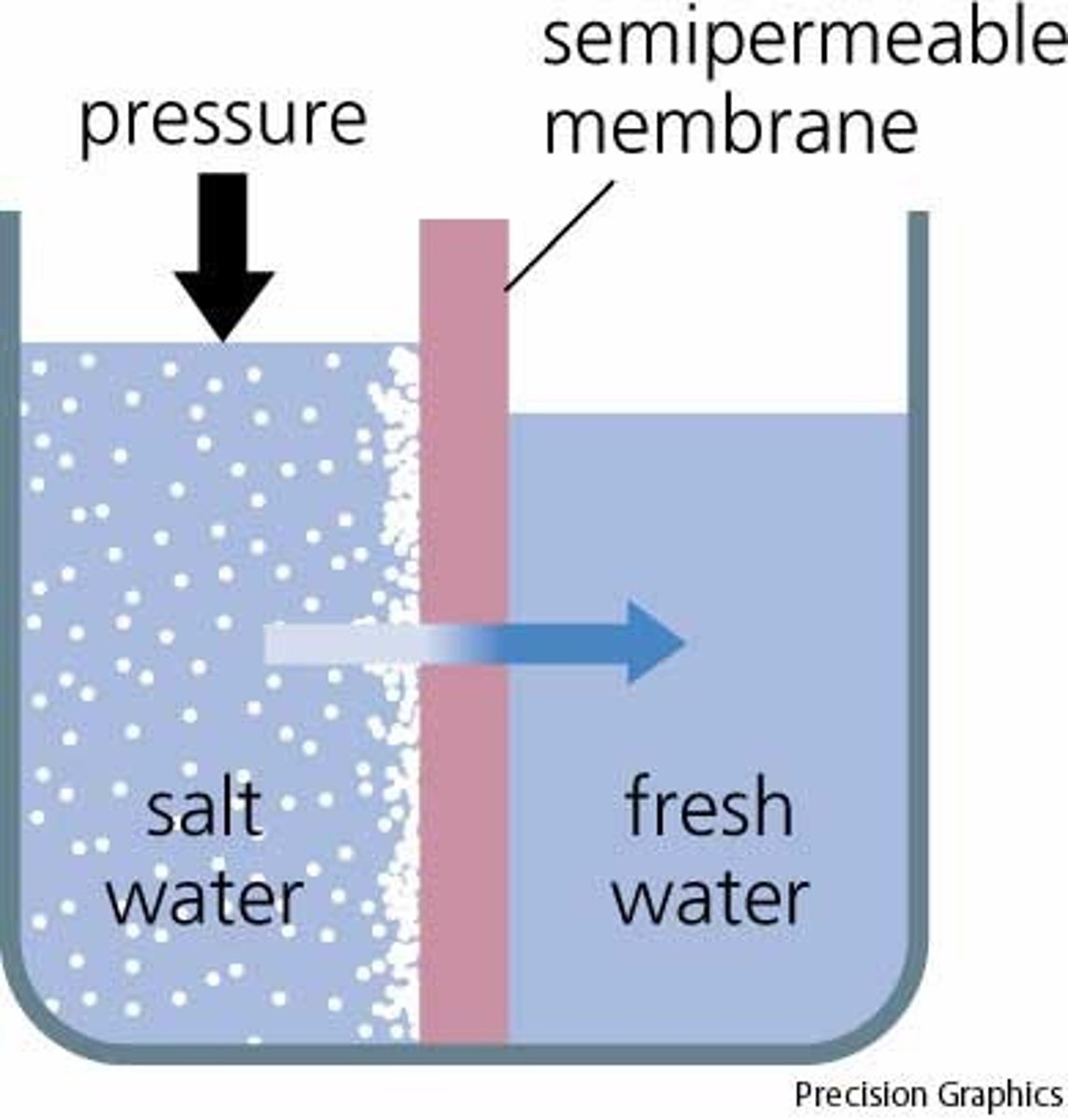
Osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
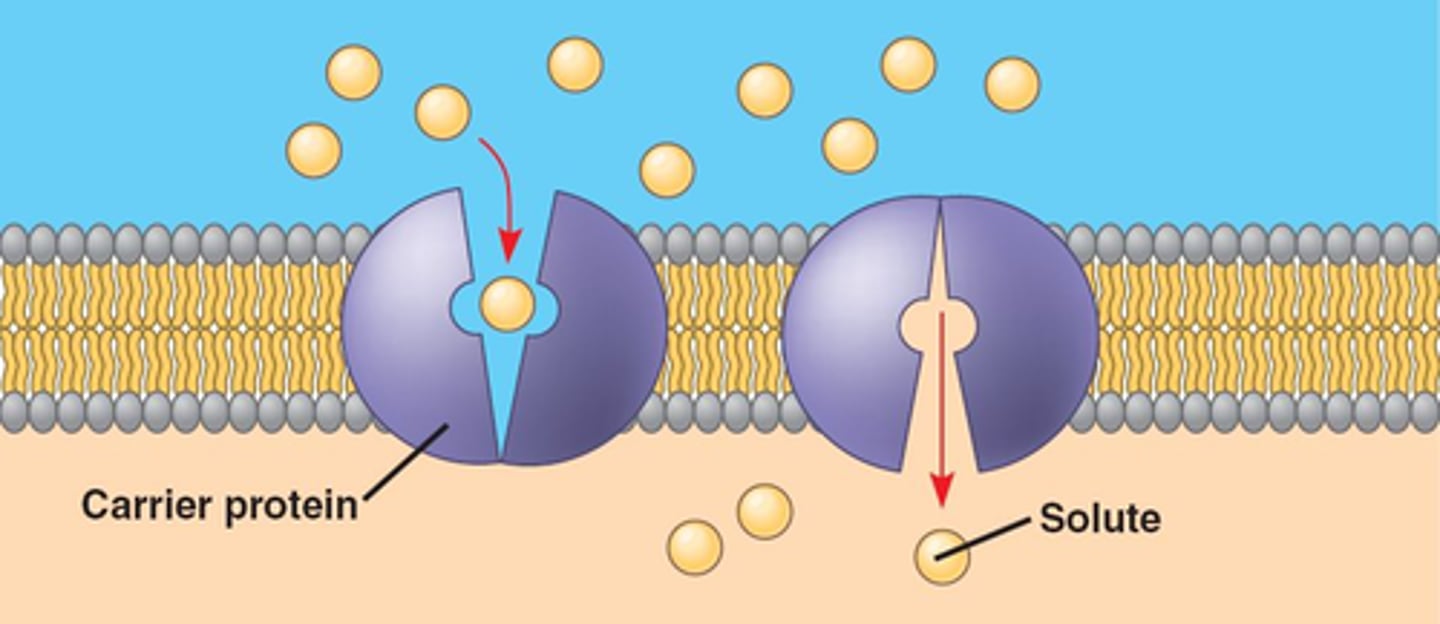
Facilitated Diffusion
The transport of substances through a cell membrane along a concentration gradient with the aid of carrier and channel proteins
Endocytosis
Process by which a cell takes material into the cell by infolding of the cell membrane
Exocytosis
A process by which the contents of a cell vacuole are released to the exterior through fusion of the vacuole membrane with the cell membrane.
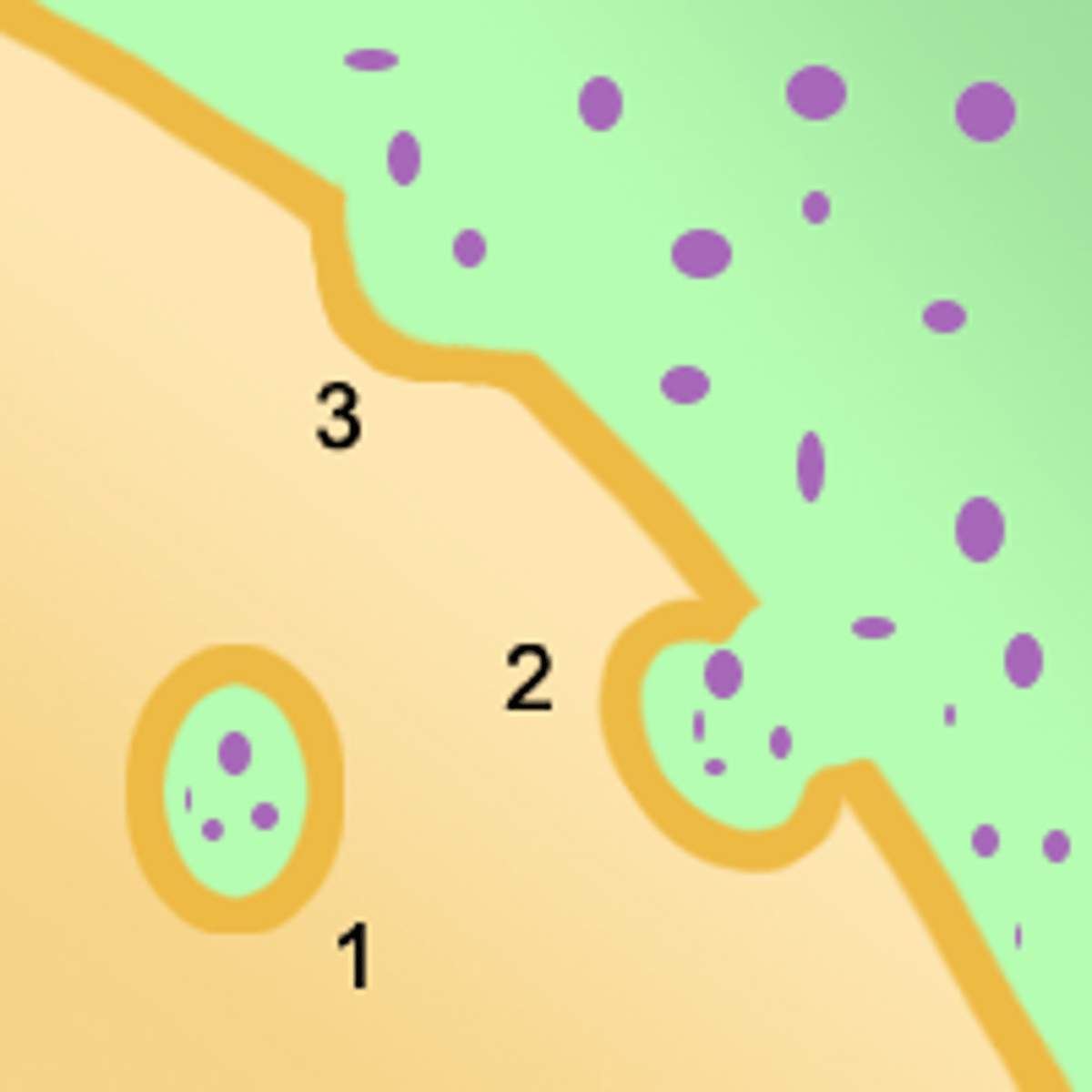
Pinocytosis
A type of endocytosis in which the cell ingests extracellular fluid and its dissolved solutes.
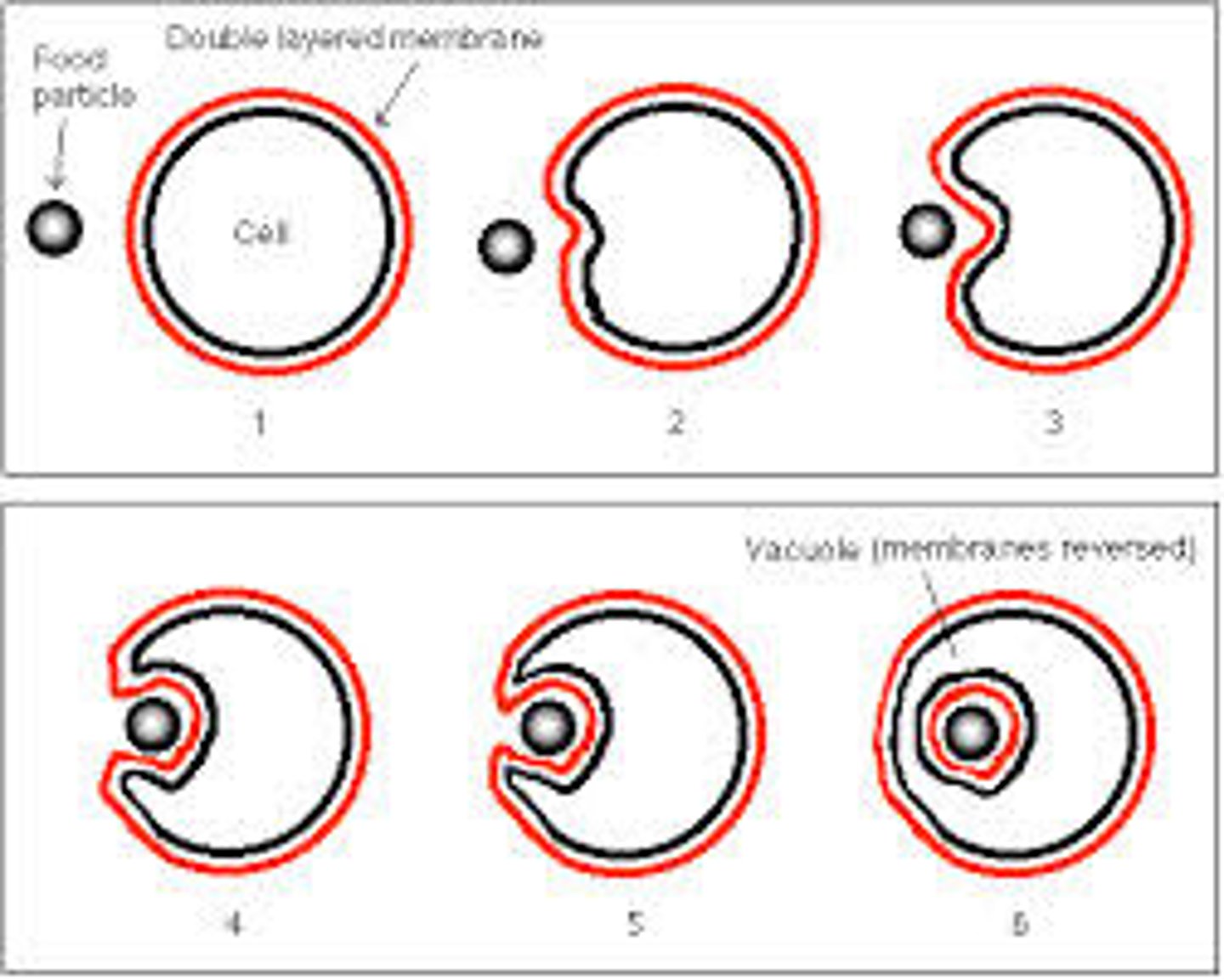
Phagocytosis
A type of endocytosis in which a cell engulfs large particles or whole cells
Breathing
movement of air into and out of the lungs (not to be confused with respiration)
Arteries
Blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood away from the heart; thick, elastic, small lumen, no valves, have a pulse
Veins
Blood vessels that carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart; has less smooth muscle, valves to prevent back flow; lower blood pressure
Hepatic Portal Vein
The vein that collects blood from the Gastro-Intestinal Tract and conducts it to the liver
Renal Vein
blood vessel that carries blood away from the kidney and toward the heart
Renal Artery
blood vessel that carries blood to the kidney
Capillaries
The smallest vessels where materials are exchanged between the blood and body cells.
Peritubular Capillaries
The network of tiny blood vessels that surrounds the proximal and distal tubules in the kidney
Tricuspid Valve
valve between the right atrium and the right ventricle
Bicuspid Valve
valve between the left atrium and the left ventricle.
pulmonary valve
valve positioned between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery
aortic valve
heart valve between the left ventricle and the aorta
Systemic Circulation
→Blood circulates through body
→ Nutrients and Oxygen given to cells & waste products are collected
→ Blood becomes deoxygenated
Systole
Contraction of the heart; pumping phase
Diastole
Relaxation of the heart; filling phase
Atrial Systole
Atria contract
→ Atrioventricular valves open
→ blood forced from atria to ventricles
→ Semilunar valves shut
Ventricular Systole
Ventricles contract
→ Semilunar valves open
→ Blood forced from ventricles to arteries
→ Atria are relaxed
→ Atrioventricular valves shut
→ Atria refills with blood
Atrial and Ventricular Systole
Atria and Ventricles relax
→Semilunar valves shut
→Atrioventricular valves open
→Atria refilling with blood
→Ventricles receive blood from atria
Lymph
Excess tissue fluid carried by lymphatic vessels
Lymph Capillaries
microscopic vessels that draw lymph from tissues to the lymph vessels
Lymph Nodes
Bean-shaped filters that cluster along the lymphatic vessels of the body; also called l____ glands
Carbohydrates
The starches and sugars present in foods
Carbohydrate Digestion
Carbohydrate → Polysaccharides → Disaccharides → Monosaccharides
Protein
A compound made of small carbon compounds called amino acids; used for structural support, storage, transport;
Protein Digestion
Protein → Polypeptide → Peptide → Amino Acid
Lipid
Macromolecule made mostly from carbon and hydrogen atoms; includes fats and oils
Lipid Digestion
Lipid → Fatty acids & Glycerol
Mouth Cavity
Place where food enters ;mechanical digestion by teeth; chemical digestion of starch by saliva
Salivary Glands
Glands of the mouth that produce saliva
Saliva
Digestive juice produced by salivary glands; contains amylase and mucus
Oesophagus
Muscular tube connecting the mouth to the stomach; uses peristalsis to move bolus to the stomach
Stomach
Large muscular sac that continues the mechanical and chemical digestion of food
Gastric Juice
A digestive fluid secreted by the stomach; contains HCl and gastric protease
Pyloric Sphincter
Ring of muscle that guards the opening between the stomach and the duodenum
Duodenum
First part of the small intestine
Liver
Produces bile; performs deamination; detoxifies alcohol & drugs
Gall Bladder
Stores bile and releases it as needed into the small intestine
Bile
Emulsifies (increases surface area of) fats; neutralises HCl from the stomach
Pancreas
Produces pancreatic juice
Pancreatic Juice
Contains pancreatic protease, amylase, lipase and nuclease; used for digestion in the duodenum
Small Intestine
Secretes intestinal juice; absorbs simple sugars, amino acids and glycerol