G2 - The Changing Economic World 2
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
What is the economical state of India?
NEE
Key facts about India
World’s largest democracy
Southern Asia
2nd largest population
What are the Types of Job Industries?
primary
secondary
tertiary
quaternary
What is the primary job industry?
Involves getting raw materials from the land, eg farming or forestry
What is the secondary job industry?
Making products out of raw materials, eg food processing and car manufacturing.
What is the quaternary job industry?
ICT and research, eg computer software designers and scientists.
What is a countries industrial structure?
The percentage of people working in each job type.
What can help the country develop (in terms of sectors)?
Changing the balance between these four sectors of industry.
Open until the 1980s what was India’s main type of industry?
Primary
Many people were subsistence farmers, which is not very profitable.
What happened in India in the 1980s?
The Indian government encourage foreign TNCs to help with the country.
Factories were built and secondary job in manufacturing were created. Factory workers earn more money, so can afford to pay for services such as entertainment and healthcare. Workers in the tertiary sector are paid more than in primary and secondary.
What is subsistence farming?
Farming which produces food only for the farmers dependents.
The additional wealth generated from changing the industrial structure of India has created a __________________.
Multiplier effect - As one thing improves, it allows other things to improve too.
India - Multiplier Effect diagram
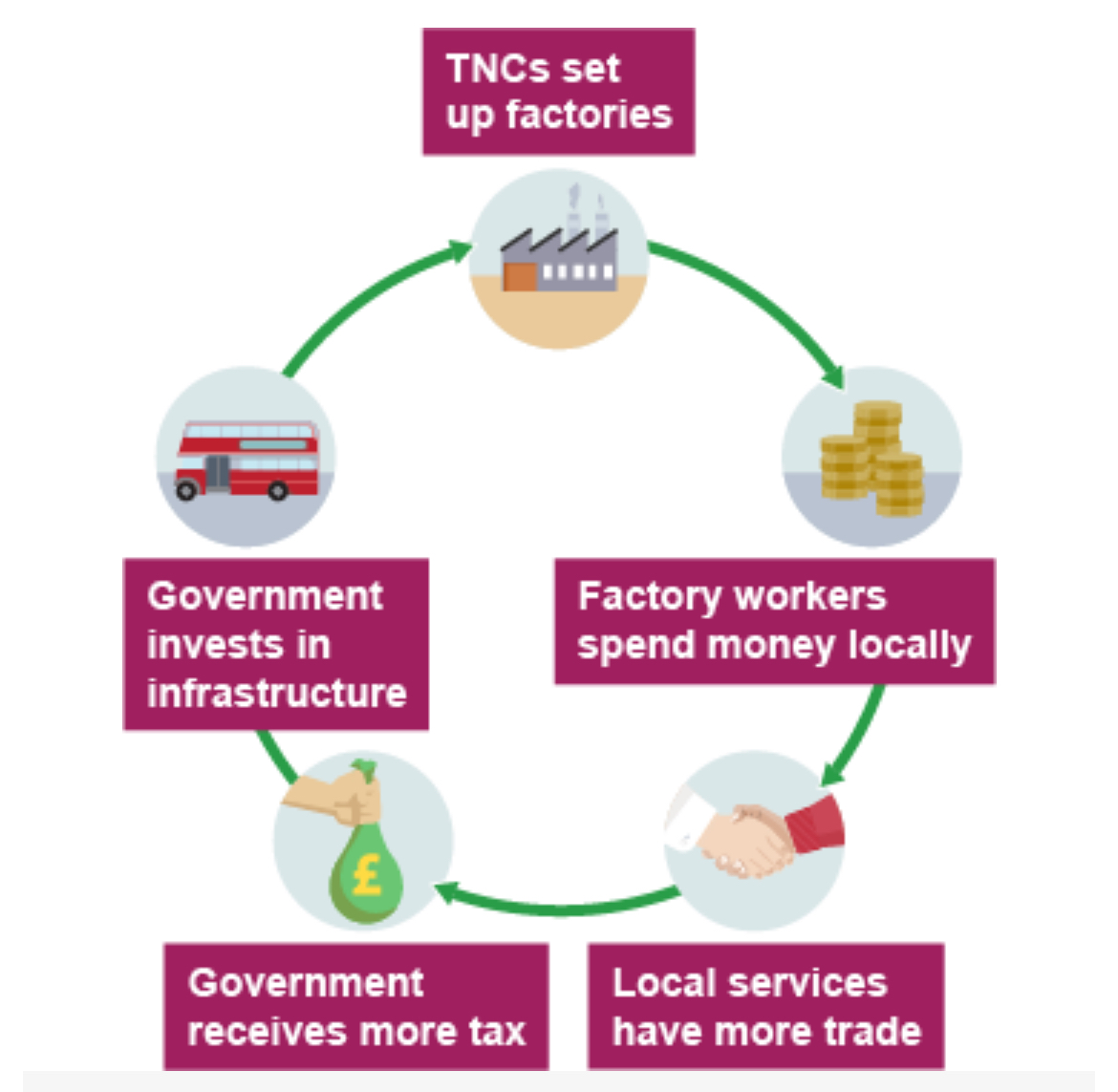
What do TNCs stand for?
Transnational corporations
Why is India attractive to TNCs.
Well educated population
Employees willing to work for lower wages
Which companies have set up in India?
Hyundai and Honda → manufacture cars
Microsoft, Ford and Virgin Media → set up call centre
What are advantages of TNCs in India? (5)
Created jobs and offered education and training to employees
Additional wealth → Multiplier effect
Some TNCs set up schemes to provide new facilities for local local communities
Infrastructure of country has been improved → New road and Internet cabling
TNCs pay tax to governments → Can be spent on development projects
What are disadvantages of TNCs in India? (5)
Some corporation leaders have taken advantage of the black environmental laws → Pollution
Harsh conditions for workers in factories
TNC is owned by foreign countries → Economic leakage, profit sent abroad
Best jobs are often given to foreign workers from the TNCs country of origin
TNCs use countries’ natural resources → soft drink bottling plant in Kerala, India, shut down due to impact on local supplies
The value of India’s exports is increasing/decreasing overtime.
increasing

India has a positive/negative balance of trade.
Explain.
negative
Spend more on imports than it receives for exports.
What is the general pattern of India’s imports?
Raw materials and products from many countries.
Which countries do India import from?
China
United Arab Emirates (UAE)
Saudi Arabia
The United States of America (USA)
What do India import?
Raw materials…
Oil
Precious and semi precious stones
Gold
Electrical machinery and equipment
What are oil and machinery used for in India?
running factories
What are gold silver and electronic goods used for in India?
Luxury items → country is becoming wealthier
Where do India export to?
Most high value exports go to…
USA
UAE
China
Bangladesh
UK - Seventh biggest importer of Indian products
What are India’s biggest export?
Petroleum products
Jewellery
Pharmaceutical products
Rice
What is helpful for a country? (in terms of imports and exports)
Import cheaper raw materials and export more expensive finished products.
What are the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)?
15 year target set by the United Nations (UN) in the year 2015.
Aim to achieve most sustainable future and all countries including India.
How many SDG’s was India set?
17
What were India’s SDG’s (top 5)?
No Poverty
Quality Education
Gender Equality
Clean Water and Sanitation
Climate Action
How has India made progress with its SDGs? (6)
Reduced NO.of people live below poverty line
Decrease gender disparities in schools – girl:boy ratio in classes more even
Reduce women’s childbirth deaths
Increase percentage of households with access to clean safe water
Reduced spread of diseases: HIV/AIDS, Malaria, etc. → healthier, more able to work
Reduced Carbon emissions
What more to be done for SDG in India? (5)
Households with adequate sanitation % still too low
Role of women within workplace still lower than men
Child and infant mortality rates → curable diseases, poor hygiene
Overall enrolling at school → attendance is low
Literacy rates → many adults cannot read/write
Aid is given from a ___ to a ___ to help with ______________.
HIC → LIC
for development
What are the different forms of aid? (7)
Short-term aid
Long-term aid
Tied aid
Charitable aid
Bilateral aid
Multilateral aid
What is short-term aid?
Help given to a country in times of need, e.g. after a natural disaster.
What is long-term aid?
Help given to a country to allow it to develop, e.g. building a hospital to improve healthcare.
What is Tied Aid?
Aid given with conditions attached.
What is Charitable Aid?
Aid raised by donations from charities.
What is Bilateral Aid?
The process of one country giving money to another. Only 2 countries are involved.
What is Multilateral Aid?
When more than one country gives a ton another country, e.g. through the World Bank.
What aid does India receive?
What is it spent on?
Who gives India this aid?
ODA (Official Development Assistance)
Spent on things like infrastructure projects and education.
Japan, Germany, France, and the UK are amongst the biggest contributors of ODA to India.
What is quality of life?
The well-being of individuals or groups of people. It refers to where people live and whether they are healthy and happy.
The quality of life with India has been increasing/decreasing over the last __ years.
increasing dramatically over the last 40 years
What social improvements have been made in India? (3)
Health and hygiene improvements → Life expectancy from 58 to 70 within the last thirty years
Increase in older people → Less youthful population
Nature of workforce changing → Growing middle-class
Why is a less youthful population good?
There are fewer dependents and more people of working age.
Why are environments improvement so important?
The quality of the environment has a direct impact on the health and well-being of residents.
What’s environmental improvements have been made in India? (5)
The National Green tribunal set up in India in 2010
Cleaned in India’s cities → e-waste recycling
In Mumbai…
New Metro system
Ban on diesel cars
Regular checks on factory waste
What is e-waste?
Electronic rubbish from old computers and technology.

What is the National Green Tribunal?
An environmental court, which deals with issues of developmental protection and conservation.
Can make companies and individuals pay compensation under the ‘polluter pays’ principle.
What is the ‘polluter pays’ principle?
Assist with those causing pollution have to pay to clean it up.
What challenges has the National Green Tribunal experienced in recent years? (2)
Lack of human resources
Declining levels of support
The UK is experiencing a period of ________________.
economic change
Why is the UK experiencing economic change?
As a result of several factors, eg.
Globalisation
Government policies
Deindustrialisation
Globalisation
The way in which the world has become more interconnected.
What has globalisation led to?
An increase in…
World trade
Foreign investment
Communication between different countries
Sharing of ideas
What is development?
The process of a country becoming richer or having better healthcare and education.
The level of development of a country shows…
…how economically, socially, culturally or technologically advanced that country is.
The way in which countries are classified is ________.
changing
What is the Brandt line?
A line which seperates the rich north of the world from those in the poorer south.
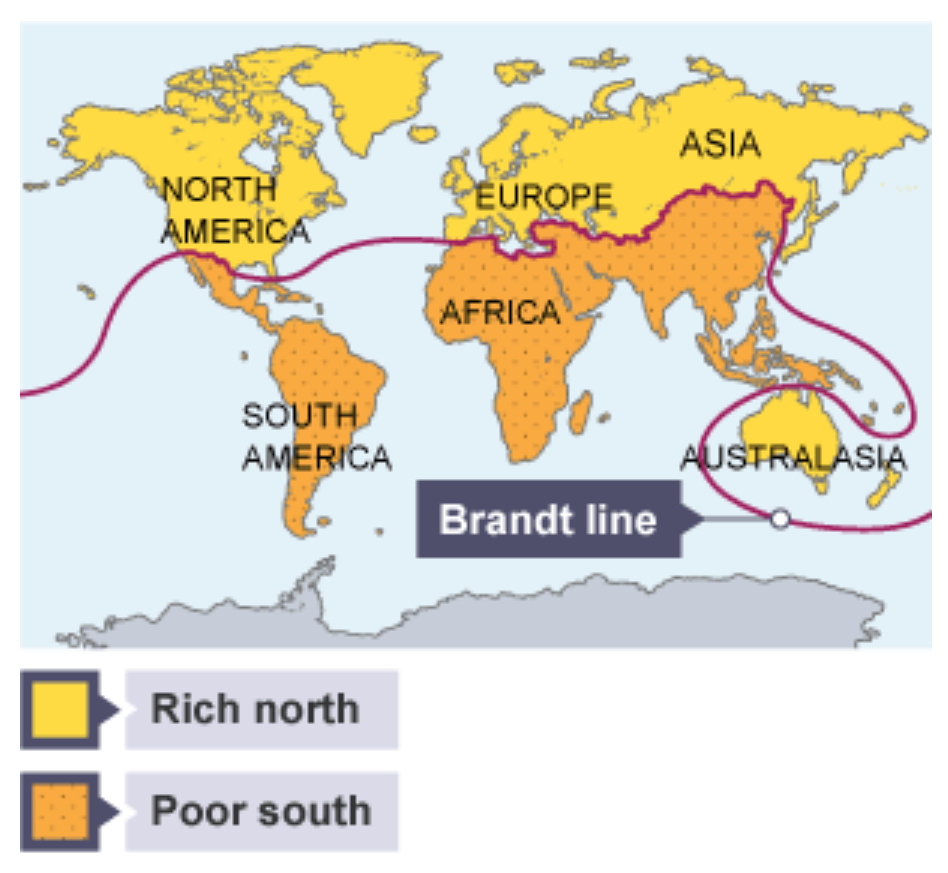
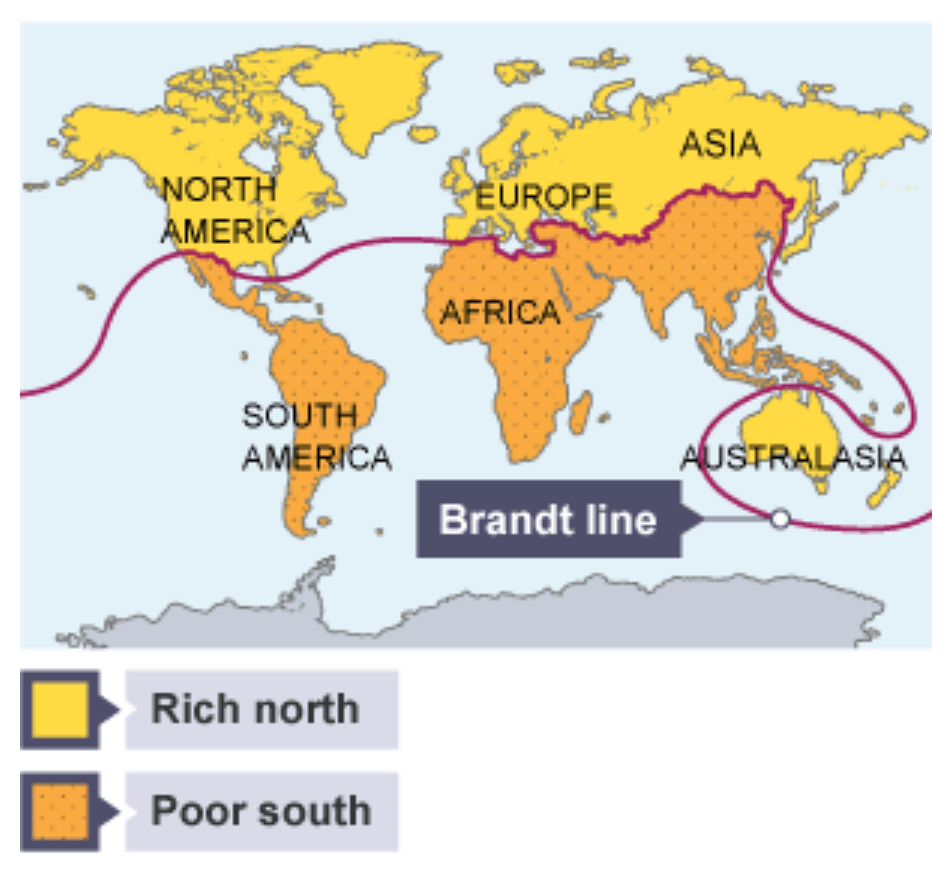
Is the Brandt line still used today?
No - the world has changed a lot in the last 20 years, and the Brandt line is now too simplistic.
For example, China and India are no longer seen as poor countries.
What is now used to classify a country’s level of development?
The World Bank Classification
LICs
MICs
HICs
What are LICs?
Countries with a GNI per capita of $1,045 or less.
e.g. Chad and Ethiopia.
What are MICs?
Countries with a GNI per capita between $1,045 but less than $12,695.
e.g. Mexico and Iraq
What are HICs?
Countries with a GNI per capita of $12,696 or more.
e.g. Germany and the USA
What factors can be considered when deciding the development of a country?
Social measures
Economic measure
How is development measured?
Using the Human Development Index (HDI).
Who calculates the HDI?
The United Nations
What is the range of HDI?
0 - 1
Undeveloped: 0
Developed: 1
What is used to calculate HDI?
Average life expectancy
Level of education
Income
Why is HDI the best measure of development?
It takes into account both social and economic factors.
HDI across the world - Map
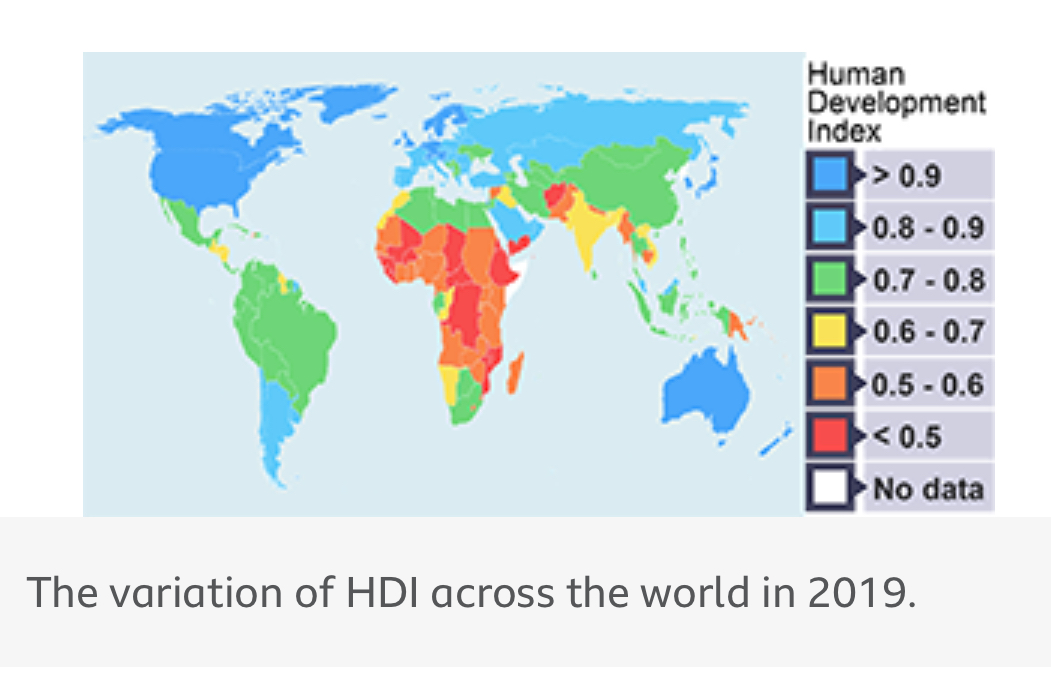
What else can be used to measure development? (8)
Access to safe water
Birth rate
GNI per capita
Infant mortality rate
Life expectancy
Literacy rate
People per doctor
What is the birth rate?
The number of live births per 1,000 people.
What does death rate?
The number of deaths per 1,000 people.
What is GNI per capita?
The gross national income per person.
The value of a countries income divided by the number of people in that country.
What is infant mortality rate?
The number of babies who don’t survive to the age of 1 per 1,000 live births.
What is people per doctor?
A ratio to show the number of people per doctor.
The lower the ratio, the more developed a country is.
What graph can be used in this topic?
The Demographic Transition Model (DTM)
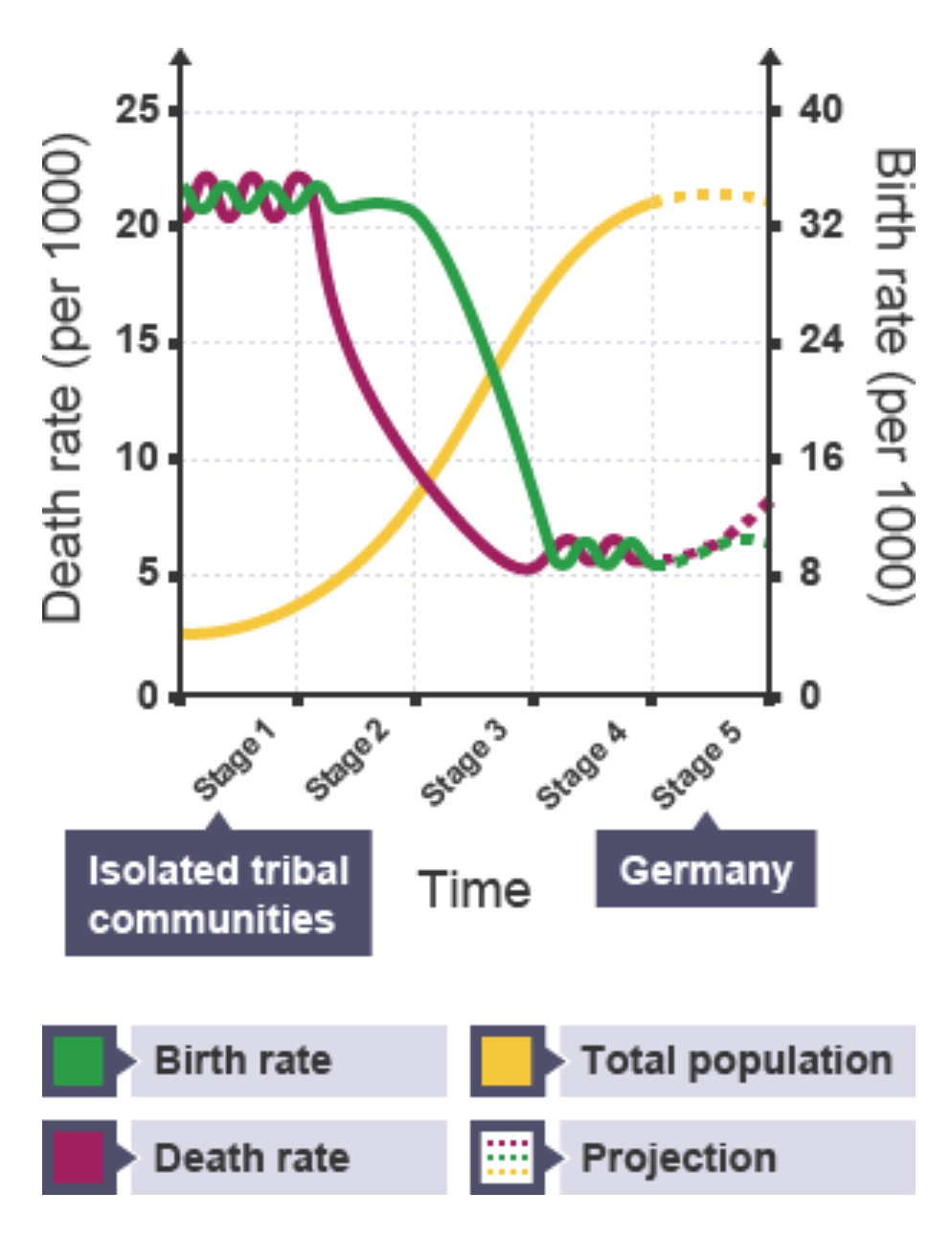
How many stages are there on the DTM?
5
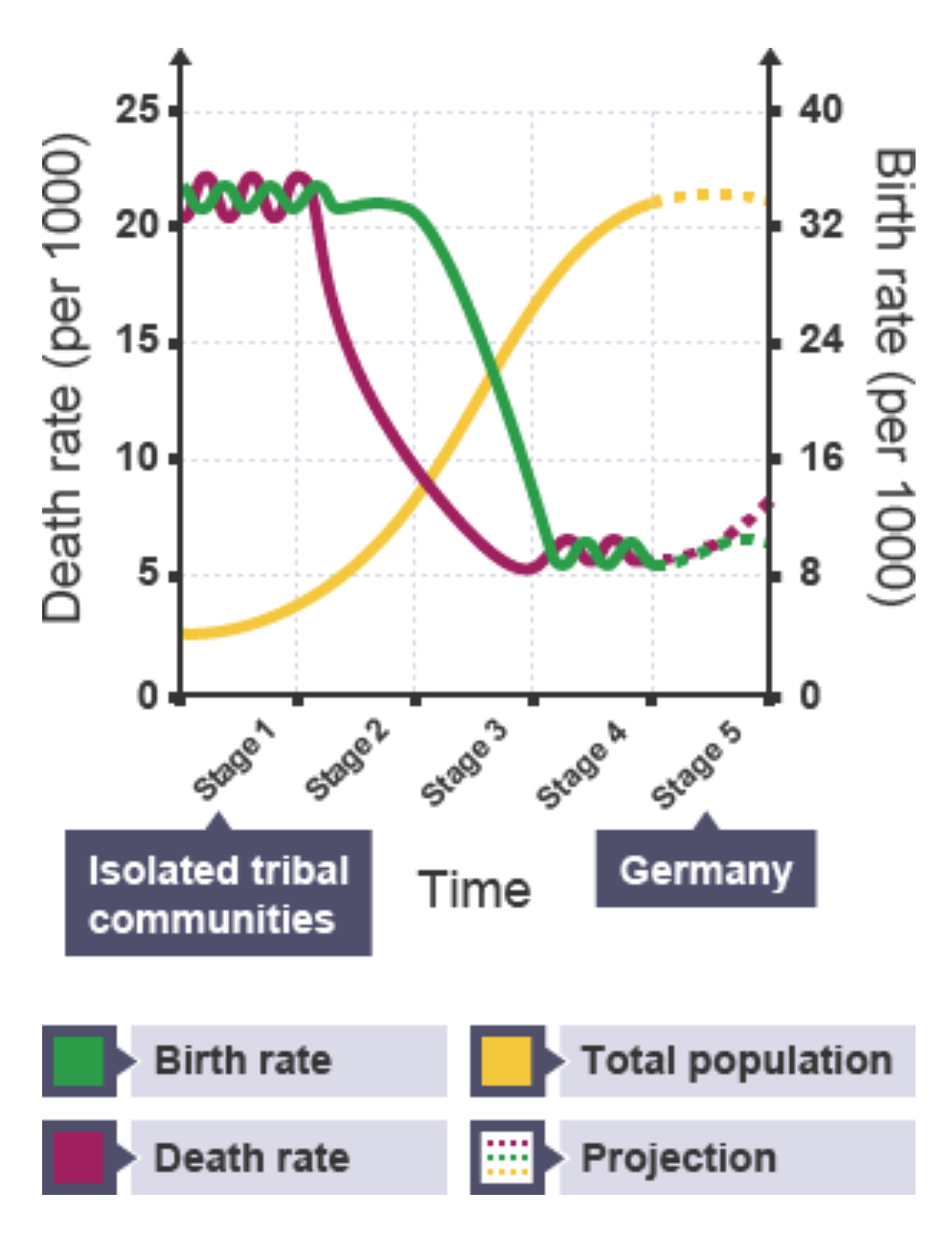
The five stages of the DTM can be linked to…
…levels of development.
Why is it better to use multiple measures of development?
Using just one maybe misleading.
Example of misleading economic development
Zimbabwe is an LIC, but 84% of people living there can read and write.
What is another example of misleading economic development?
China has a low birth rate, but is not listed in the World Bank’s list of HICs.
This is because of their one child policy.
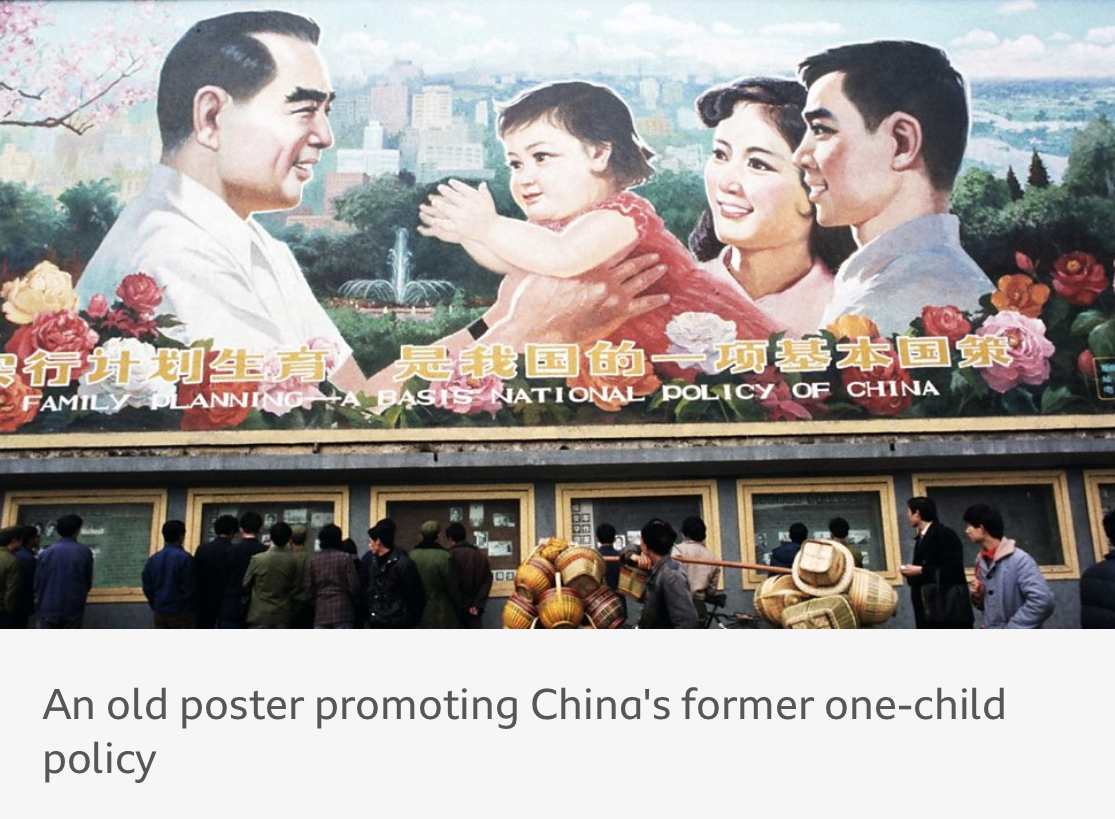


What negative effects has China’s one child policy had?
May lead to a demographic crisis because…
Gender imbalance
Population growing old → due to longer life expectancy and lower fertility rates (1.6)
UK estimates by 2050, 37% of China’s population will be over 60.
Working age population continues to decline → threatens economic growth
What has China done to improve this 1 child policy?
Government now allows couples to have 2 children if 1 parent is an only child.
Advantages and Disadvantages of using Birth Rate
Good indicator of social progress
Can be changed by government policies → misleading
Advantages and Disadvantages of using Death Rate
Display quality of countries healthcare system
Good indicator of standard of living
Rich countries may have older people → higher death rates → misleading
Advantages and Disadvantages of using GNI per capita
Only measures economic development
Does not consider standard living
An average → hides information about extremities (very poor/rich)
Advantages and Disadvantages of using HDI
Widely recognised as beneficial
Takes into account both social and economic
What factors influence level of development? (6)
Physical factors
Economic factors
Environmental factors
Historical factors
Political factors
Natural resources
How do Physical Factors affect the level of development?
Some areas have hostile landscapes → development more difficult
Hot climates
Arid climates (lack water)
These make it difficult to grow sufficient food.
How do Economic Factors affect the level of development?
High levels of debt → interest and repayments
Little left over for development projects.
How do Environmental Factors affect the level of development?
Environmental issues → difficult to develop
Extreme flooding
Desertification
Etc.