Investigative Interviewing and Eyewitness Memory: Techniques, Biases, and Legal Guidelines
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
What is the primary goal of investigative interviewing?
To gather as much complete and accurate information as possible about what someone experienced.
What are the stages of memory involved in the memory process?
Encoding, storage, and retrieval.
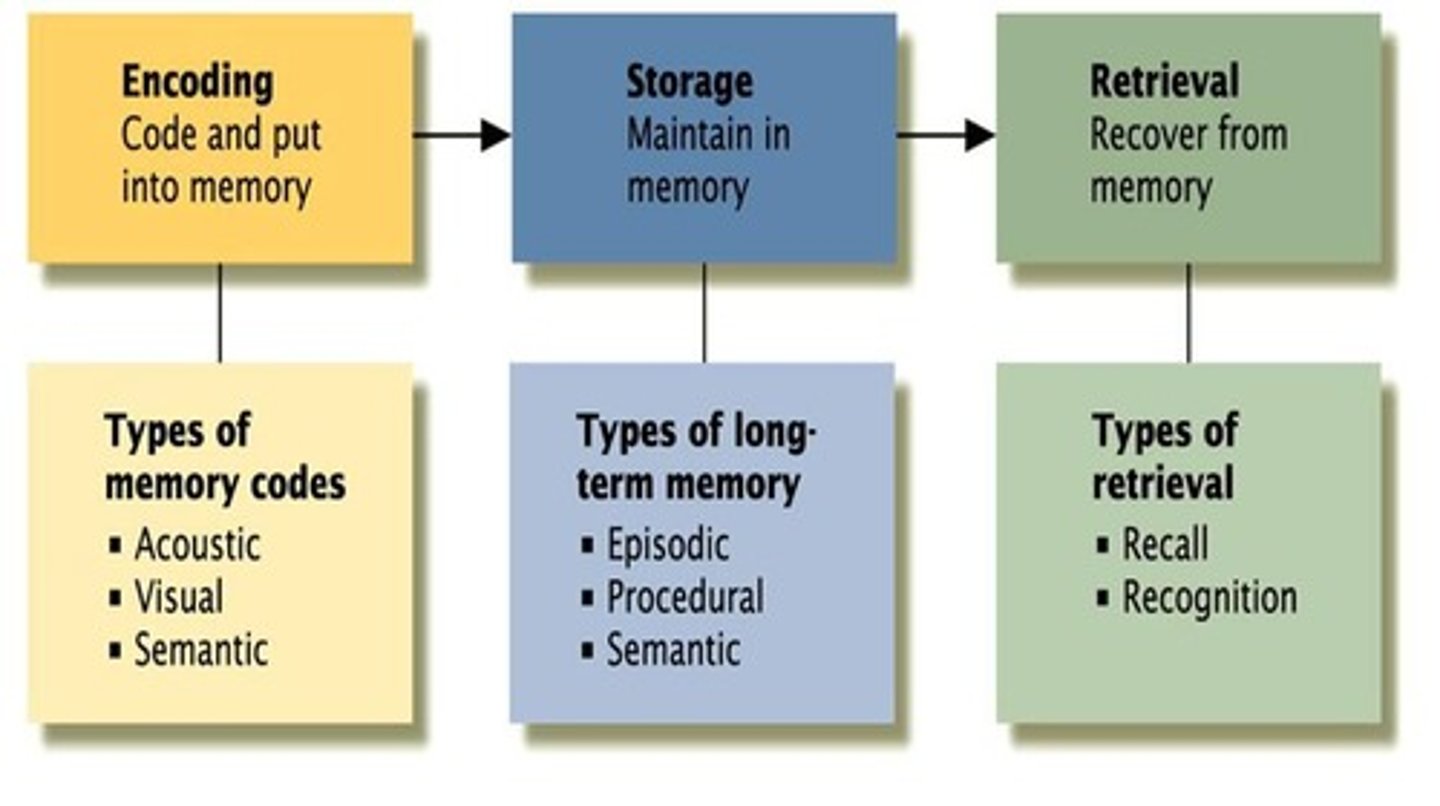
What does the term 'encoding' refer to in memory?
The process of converting external stimuli into memory.
What is the difference between short-term and long-term memory?
Short-term memory has limited capacity and requires rehearsal, while long-term memory is more permanent and can be easily retrieved.
What is the misconception about memory as stated in the notes?
Memory is not a recorder; it is malleable and can be reconstructed.
What factors can affect the encoding of memory?
State of witness, stress level, attention, and witness involvement.
What are some factors affecting memory retrieval?
Inference, stereotypes, bias, emotional factors, and context effects.
What are the two types of memory retrieval?
Recall and recognition.
What is the 'misinformation effect'?
The phenomenon where post-event information can influence a witness's memory of the event.
What was the main finding of Loftus & Palmer's 1974 study?
The wording of questions can significantly affect eyewitness memory, as shown by different speed estimates based on verb choice.
What are 'independent variables' in eyewitness research?
Variables that can be manipulated, such as time and illumination.
What are 'dependent variables' in eyewitness research?
Variables that measure the outcome, such as recall of the event or recognition of the perpetrator.
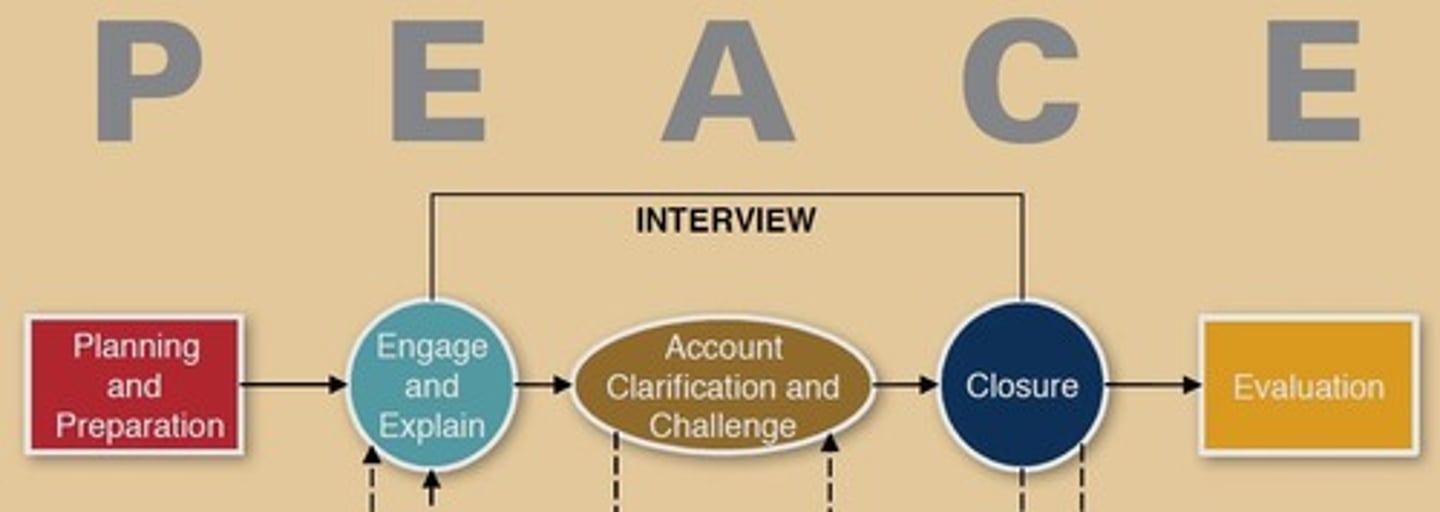
What is a cognitive interview?
A technique used to enhance witness memory by encouraging detailed recall.
What is the role of rapport building in witness interviewing?
To create a comfortable environment that encourages witnesses to share accurate information.
What problematic practice should be avoided in police questioning?
Asking leading questions that suggest a specific answer.
What is the 'source misattribution hypothesis'?
The idea that witnesses may confuse the source of their memories, leading to inaccuracies.
What is the purpose of using hypnosis in witness memory?
To potentially increase the amount of details recalled, though accuracy may be compromised.
What is the 'memory impairment hypothesis'?
The theory that exposure to misleading information can impair the accuracy of a witness's memory.
What are 'estimator variables'?
Variables that cannot be controlled during an investigation, affecting eyewitness reliability.
What is the significance of emotional factors in memory retrieval?
Emotional states can influence how memories are recalled and interpreted.
What does 'context effects' refer to in memory retrieval?
The influence of the environment or context in which information was learned on recall.
What is the 'acceptance hypothesis' in relation to misinformation?
The idea that witnesses may accept misleading information as true, altering their memory.
What is the cognitive interview?
A scientifically validated approach to interviewing witnesses, based on memory storage and retrieval principles.
What principle suggests recall is improved when cues are available?
Encoding specificity.
What is state-dependent memory?
Recall is improved when an individual is in the same state as when the memory was encoded.
What does the 'Report Everything' tool in cognitive interviews aim to achieve?
It prevents witnesses from editing or leaving out details they may feel are unimportant.
What is the Mental Reinstatement of Context (MRC)?
A cognitive interview technique that involves creating a mental picture of the context to aid recall.
How does changing the order of recall help in cognitive interviews?
It disrupts the schema and can lead to more accurate recall.
What is the purpose of changing the perspective in cognitive interviews?
To form a new schema and disrupt the existing one to enhance recall.
What were the findings of Geiselman et al. (1985) regarding cognitive interviews?
Cognitive interviews resulted in more correct details recalled compared to standard interviews.
What is the Enhanced Cognitive Interview?
An improved version of the cognitive interview that includes rapport building and supportive interviewer behavior.
What is a common issue with eyewitness identification?
Descriptions often lack accuracy, particularly for height and weight.
What are the two types of strategies for selecting foils in lineups?
Similarity-to-Suspect Strategy and Match-to-Description Strategy.
What is the difference between target-present and target-absent lineups?
Target-present lineups contain the suspect, while target-absent lineups do not.
What is the purpose of a simultaneous lineup?
All lineup members are presented at once, leading to relative judgment.
What is a sequential lineup?
Lineup members are presented one at a time, requiring absolute judgment before seeing the next member.
What is the recommendation regarding show-ups in eyewitness identification?
Show-ups should be avoided due to higher rates of false identifications.
What are some biases that can affect lineup accuracy?
Foil bias, clothing bias, and instruction bias.
What factors increase accuracy in voice identification?
Longer voice samples and the absence of unfamiliar accents.
What is the relationship between confidence and accuracy in eyewitness testimony?
There is a small positive correlation, but confidence can be influenced by police feedback.
What is the cross-race effect?
Witnesses remember same-race faces better than faces of different races.
What is weapon focus in eyewitness testimony?
Witnesses may focus on a weapon rather than the perpetrator, affecting identification accuracy.
What are the Canadian guidelines for lineup procedures?
Lineups should be videotaped, presented sequentially, and witnesses should be informed that the perpetrator may not be present.
What is the significance of the Innocent Project in relation to eyewitness misidentification?
Up to 75% of DNA exoneration cases involved eyewitness misidentification.
What is the effect of emotional arousal on eyewitness memory?
Increased emotional arousal can decrease attentional capacity, leading to poorer recall.
What is the role of the American Psychology and Law Society in eyewitness testimony?
They provide guidelines for improving eyewitness evidence and lineup procedures.
What is the importance of assessing witness confidence before police feedback?
To ensure that the confidence level is not influenced by the police's suggestions.