Unit 7 - Thoracic Spine and Ribs
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
The Thorax Consists of…
Rigid Rib Cage
Thoracic Vertebrae
Sternum
Rigidity provides:
Stable base for muscles to control craniocervical region
Protection for intrathoracic organs
Mechanical bellows for breathing
Thoracic Articulations
24 Apophyseal Joints (12 pairs)
Costocorporeal Joints
Costotransverse Joints
24 Apophyseal Joints (12 pairs)
Mild forward slope in frontal plane
15-25 degrees from vertical (65-75 from horizontal)
Limited by immobility of costocorporeal and costotransverse joints (rib attachments)
Ribs indirectly attach thoracic vertebrae to fixed sternum
Costocorporeal Joints
Connect Head of Rib to Vertebral Body via demifacets
Slightly ovioid with capsule and radiate ligaments
Intervenes with adjacent Disc
Costotransverse Joints
Articular Tubercle of most ribs to costal facet of transverse process of same T-vertebra
Synovial joint —> capsule
Costotransverse Ligament attaches neck of rib to transverse process of same T-vertebra
Superior Costotransverse Ligament stabilizes by attaching superior neck of one rib to inferior margin of transverse process of above T-vertebra
Ribs 11 & 12 lack these joints (“Floating”)
Thoracic Region
Second only to sacroiliac joints as most mechanically stable portion of vertebral column
Attachments of thoracic vertebrae to rib cage to sternum
Thoracic Kinematics: Influenced by…
Resting posture of region
Orientation of apophyseal joints
“Splinting” action of rib cage
Relative heights of intervertebral discs
Smallest disc-to-vertebral body height ratio
Thoracic Kinematics: Decreased Mobility —>
Increased Mechanical Stability
Kinematics: Flexion
30-40 degrees
Bilateral Facet Upglide (slide)
Limited by:
Apophyseal joint capsule
Supraspinous ligaments
Interspinous ligaments
Posterior Longitudinal Ligament
Compression of anterior Annulus Fibrosus
> Movement in caudal regions
Free-floating ribs 11 & 12
Kinematics: Extension
15-20 degrees
Bilateral Facet Downglide (slide)
Limited by:
Apophyseal joint approximation
Supraspinous Processes
Laminae
Anterior Longitudinal Ligament
Compression of posterior Annulus Fibrosus?
Arthrokinematics same as Mid-Cervical region
Kinematics: Axial Rotation
25-30 degrees in horizontal plane
Cumulative throughout region
Very little slide at each facet
Freedom of Axial Rotation decreases in lower regions
Orientation of Facets becomes more vertical and shift toward sagittal plane orientation
Kinematics: Lateral Flexion
25-30 degrees in region
45 degree thoracolumbar arc
Ipsilateral downglide of inferior facet of superior vertebra ON superior facet of inferior vertebra; opposite for contralateral
Limited by
Rib attachments
Intertransverse ligament
Approximation of ipsilateral facets
Joint capsule of contralateral facets
Pathoanatomy: Thoracic Spine Mobility Deficits
What is the proposed underlying cause for mobility deficits?
Spondylosis
Sprain/strain
Pathoanatomy: Thoracic Spine Mobility Deficits
What is the proposed underlying cause for mobility deficits?
Spondylosis
Gradual progression of age-related joint changes
Adaptive shortening of the joint connective tissue and periarticular soft tissue
Pathoanatomy: Thoracic Spine Mobility Deficits
What is the proposed underlying cause for mobility deficits?
Sprain/strain
Acute onset sudden awkward movement
Gradual onset repetitive postural loading
Muscle strain and/or ligament sprain
Medical Screening: Thoracic Spine Mobility Deficits
What other conditions should be considered with this patient presentation?
Viscerogenic
Neoplastic conditions
Inflammatory or systemic disease
Spinal infection
Cardiopulmonary conditions
Medical Screening: Thoracic Spine Mobility Deficits
What other conditions should be considered with this patient presentation?
Neuromusculoskeletal
Spinal fracture
Cervical myelopathy
Differential Diagnosis: Thoracic Spine Mobility Deficits
What other conditions should be considered with this patient presentation?
Neuromusculoskeletal
Neck pain with mobility deficits
Neck pain with movement coordination deficits
Neck pain with radiating pain
Thoracic movement coordination impairments
Thoracic outlet
Subjective Examination: Thoracic Spine Mobility Deficits
What system, structure, pain mechanism, and phases of healing are unique to this patient presentation?
System
Neuromusculoskeletal
Structure
Zygapophyseal joint and periarticular soft tissue
Pain mechanism
Nociceptive
Phase of healing
Muscle strain 2-4 weeks, ligament sprain and cartilage injuries 10-12 weeks
Subjective Examination: Thoracic Spine Mobility Deficits
What are common subjective reports for patients with mobility deficits?
General symptoms
Central or unilateral symptoms
Possible somatic referred along the ribs and into the upper extremity (T4 syndrome)
Dull ache at rest that becomes sharp with movement
Subjective Examination: Thoracic Spine Mobility Deficits
What are common subjective reports for patients with mobility deficits?
Spondylosis
Gradual onset with progressive loss of motion
Subjective Examination: Thoracic Spine Mobility Deficits
What are common subjective reports for patients with mobility deficits?
Sprain/strain
Immediate onset of pain and loss of motion
Recent unguarded/awkward movement or position
Progressive onset with repetitive postural loading
Subjective Examination: Thoracic Spine Mobility Deficits
What are common subjective reports for patients with mobility deficits?
Aggravating factors
Dull ache and stiffness with inactivity
Symptoms reproduced with active movements
Subjective Examination: Thoracic Spine Mobility Deficits
What are common subjective reports for patients with mobility deficits?
Easing factors
Staying active and changing positions
Progressive thoracic spine movement
Subjective Examination: Thoracic Spine Mobility Deficits
What are common subjective reports for patients with mobility deficits?
24-hour pain behavior
Morning
May have pain and stiffness that upon waking that eases with activity and movement
Noon to evening
Symptoms may vary throughout the day depending on the patient’s activities, may have increased pain and stiffness after being sedentary
Night
Symptoms may disrupt sleep with changing positions depending on symptom irritability
Objective Examination: Thoracic Spine Mobility Deficits
What are the key examination procedures for patients with mobility deficits?
Systems Review: Cardiopulmonary
Vitals – BP, HR, auscultate
Assess for mechanical reproduction of symptoms and/or adverse response to movement
AROM, PIVM, compression/distraction
Objective Examination: Thoracic Spine Mobility Deficits
What are the key examination procedures for patients with mobility deficits?
Systems Review: Neuromusculoskeletal
Reflexes/pathological reflexes
Dermatomes/myotomes
Objective Examination: Thoracic Spine Mobility Deficits
What are the key examination procedures for patients with mobility deficits?
Movement and provocation examination
Cervical clearing examination
Neurodynamic testing
Active range of motion
Passive intervertebral motion (PIVM)
Objective Examination: Thoracic Spine Mobility Deficits
What are the key examination procedures for patients with mobility deficits?
Cervical clearing examination
Active range of motion
Passive intervertebral motion
Objective Examination: Thoracic Spine Mobility Deficits
What are the key examination procedures for patients with mobility deficits?
Neurodynamic testing
ULTTA/ULND1
Objective Examination: Thoracic Spine Mobility Deficits
What are the key examination procedures for patients with mobility deficits?
Active range of motion
Thoracic range of motion limitations and symptom provocation consistently reproduced at end range
Symptom provocation with the addition of overpressure and/or combined motions
Objective Examination: Thoracic Spine Mobility Deficits
What are the key examination procedures for patients with mobility deficits?
Passive intervertebral motion (PIVM)
Hypomobility throughout the thoracic spine and ribs
Hypomobility of the involved segment(s) with local and/or somatic referred symptom reproduction
Objective Examination: Thoracic Spine Mobility Deficits
What are the key examination procedures for patients with mobility deficits?
Muscle performance examination
Muscle coordination, endurance, strength, and length testing
Palpation
Objective Examination: Thoracic Spine Mobility Deficits
What are the key examination procedures for patients with mobility deficits?
Muscle coordination, endurance, strength, and length testing
Deep neck flexors/extensors, middle/lower trapezius, rhomboids, serratus anterior
Upper trapezius, levator scapulae, scalenes, suboccipitals, SCM, pec minor/major
Objective Examination: Thoracic Spine Mobility Deficits
What are the key examination procedures for patients with mobility deficits?
Palpation
Palpation of the cervicothoracic musculature may reveal active or latent myofascial trigger points and increase resting tone
Interventions: Thoracic Spine Mobility Deficits
What are interventions recommended for mobility deficits?
Education
Exercise
Manual therapy
Interventions: Thoracic Spine Mobility Deficits
What are interventions recommended for mobility deficits?
Education
Active lifestyle and general exercise including aerobic and strength training
Interventions: Thoracic Spine Mobility Deficits
What are interventions recommended for mobility deficits?
Exercise
Exercises that promote range of motion and mobility of the cervicothoracic spine and ribs
Impairment-based approach to address cervicoscapulothoracic mobility, flexibility, endurance, neuromuscular control, and strength
Interventions: Thoracic Spine Mobility Deficits
What are interventions recommended for mobility deficits?
Manual therapy
Mobilization and manipulation of the cervicothoracic spine and ribs
Regional Interdependence: Thoracic Spine Mobility Deficits
What other conditions respond favorably to treatment in the thoracic spine?
“Impairments in one region of the body can influence the musculoskeletal system and neuromuscular function and in symptoms in other, remote region of the body
Biomechanical and anatomical relationships
“Kinetic chain”
Regional neurophysiological effects
Regional Interdependence: Thoracic Spine Mobility Deficits
What other conditions respond favorably to treatment in the thoracic spine?
Thoracic mobility impairments with shoulder pain
Mobility of the thoracic spine is necessary for full; shoulder range of motion
Mechanisms of manual therapy in neurophysiologic effect that may help explain
Mintken et al. CPR 3/5 (+LR 5.3, 61% to 89%)
Pain free shoulder flexion <120*, shoulder internal rotation <53* at 90* abduction, not taking medications for shoulder pain, and symptoms <90 days
Regional Interdependence: Thoracic Spine Mobility Deficits
What other conditions respond favorably to treatment in the thoracic spine?
Thoracic mobility impairments with neck pain
Thrust and non-thrust cervicothoracic manipulation combined active cervicothoracic range of motion exercises
Impairment-based approach
Interventions: Thoracic Spine Mobility Deficits
When should we consider interprofessional or intraprofessional referral and what are other treatment options?
Imaging
Medications/injections
Interventions: Thoracic Spine Mobility Deficits
When should we consider interprofessional or intraprofessional referral and what are other treatment options?
Imaging
In the absence of red flag signs and for those classified as low risk, imaging is not indicated
Interventions: Thoracic Spine Mobility Deficits
When should we consider interprofessional or intraprofessional referral and what are other treatment options?
Medications/injections
NSAIDs
Facet joint injections
Radiofrequency ablation
Pathoanatomy: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
What is the proposed underlying cause for thoracic outlet?
Neurovascular entrapment
Three sites of compression
Subclavian artery and lower roots between the anterior and middle scalene
Subclavian artery and vein and lower trunk in the costoclavicular space
Axially artery and vein and cords in subcoracoid tunnel
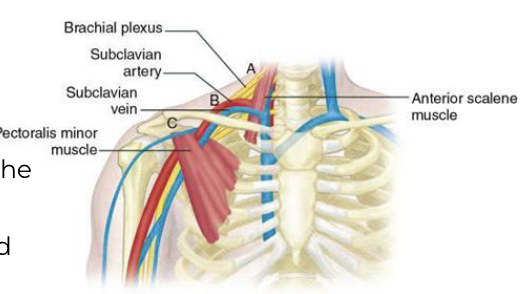
Pathoanatomy: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
What is the proposed underlying cause for thoracic outlet?
Classification
Vascular thoracic outlet; arterial TOS (aTOS)
Vascular thoracic outlet; venous TOS (vTOS)
Neurogenic thoracic outlet; true neurologic TOS (tnTOS)
Neurogenic thoracic outlet; symptomatic TOS (sTOS)
Pathoanatomy: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
What is the proposed underlying cause for thoracic outlet?
Vascular thoracic outlet; arterial TOS (aTOS)
Compression of the subclavian-axillary artery
Pathoanatomy: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
What is the proposed underlying cause for thoracic outlet?
Vascular thoracic outlet; venous TOS (vTOS)
Compression of the subclavian-axillary vein
Pathoanatomy: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
What is the proposed underlying cause for thoracic outlet?
Neurogenic thoracic outlet; true neurologic TOS (tnTOS)
Traction or compression injury to the brachial plexus
Pathoanatomy: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
What is the proposed underlying cause for thoracic outlet?
Neurogenic thoracic outlet; symptomatic TOS (sTOS)
Repetitive compression and tensioning causing neural irritation of the brachial plexus
Pathoanatomy: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
What is the proposed underlying cause for thoracic outlet?
Double crush syndrome
Nerve entrapment that occurs at multiple sites
Cervical, thoracic outlet, elbow, forearm, and wrist
Medical Screening: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
What other conditions should be considered with this patient presentation?
Viscerogenic
Neoplastic conditions
Inflammatory or systemic disease
Cardiopulmonary conditions
Vascular occlusion
Medical Screening: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
What other conditions should be considered with this patient presentation?
Neuromusculoskeletal
Spinal fracture
Cervical myelopathy
Differential Diagnosis: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
What other conditions should be considered with this patient presentation?
Neuromusculoskeletal
Neck pain with mobility deficits
Neck pain with movement coordination deficits
Neck pain with radiating pain
Thoracic mobility deficits
Rotator cuff related shoulder pain
Medial epicondalgia
Ulnar nerve palsy
Subjective Examination: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
What system, structure, pain mechanism, and phases of healing are unique to this patient presentation?
System
Neuromusculoskeletal, vascular
Structure
Brachial plexus, subclavian-axillary artery and vein
Pain mechanism
Neuropathic, nociceptive
Phase of healing
Nerve 2-3mm/day
Subjective Examination: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
What are common subjective reports for patients with thoracic outlet?
Vascular: Arterial
Upper extremity fatigue/paresthesia with the use of the arm
Cold sensitivity or Raynaud’s
Subjective Examination: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
What are common subjective reports for patients with thoracic outlet?
Vascular: Venous
Upper extremity pain, venous engorgement and edema
Cyanosis and fatigability
Feeling of stiffness
Subjective Examination: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
What are common subjective reports for patients with thoracic outlet?
Neurogenic: Symptomatic
Pain and paresthesia commonly in the ulnar distribution
Provoked with repetitive use of the upper extremity and positioning arm above shoulder height
Subjective Examination: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
What are common subjective reports for patients with thoracic outlet?
Neurogenic: True neurologic
Pain and paresthesia in the neck chest and upper extremity
Weakness and numbness in the distribution of the involved neural structure
Subjective Examination: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
What are common subjective reports for patients with thoracic outlet?
24-hour pain behavior
Morning
May have pain, paresthesia, edema, stiffness that upon waking
Noon to evening
Symptoms may vary throughout the day depending on the patient’s activities, may have increased symptoms with overhead activities
Night
Symptoms may disrupt sleep with changing positions depending on symptom irritability and sleeping position
Objective Examination: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
What are the key examination procedures for patients with thoracic outlet?
Systems Review: Cardiopulmonary
Vitals – BP, HR, auscultate
Visual inspection and palpation
Objective Examination: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
What are the key examination procedures for patients with thoracic outlet?
Systems Review: Neuromusculoskeletal
Reflexes/pathological reflexes
Dermatomes/myotomes
Objective Examination: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
What are the key examination procedures for patients with thoracic outlet?
Movement and provocation examination
Cervical clearing examination
Shoulder examination
Neurodynamic testing
Thoracic spine and ribs
Objective Examination: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
What are the key examination procedures for patients with thoracic outlet?
Cervical clearing examination
Active range of motion
Passive intervertebral motion
Spurling A & distraction test
Objective Examination: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
What are the key examination procedures for patients with thoracic outlet?
Shoulder examination
Active range of motion
Passive range of motion
Objective Examination: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
What are the key examination procedures for patients with thoracic outlet?
Neurodynamic testing
ULND test 1/ULTTA
ULND test 2/ULTTB
ULND test 3/ULTTC
Objective Examination: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
What are the key examination procedures for patients with thoracic outlet?
Thoracic spine and ribs: Active range of motion
Inhalation/exhalation
Thoracic and rib range of motion limitations
Objective Examination: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
What are the key examination procedures for patients with thoracic outlet?
Thoracic spine and ribs: Passive intervertebral motion (PIVM)
Hypomobility throughout the thoracic spine and ribs
Hypomobility and symptom relief with first rib depression
Objective Examination: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
What are the key examination procedures for patients with thoracic outlet?
Muscle performance examination
Muscle coordination, endurance, strength, and length testing
Palpation
Objective Examination: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
What are the key examination procedures for patients with thoracic outlet?
Muscle coordination, endurance, strength, and length testing
Deep neck flexors/extensors, middle/lower trapezius, rhomboids, serratus anterior
Upper trapezius, levator scapulae, scalenes, suboccipitals, SCM, pec minor/major, and diaphragm
Objective Examination: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
What are the key examination procedures for patients with thoracic outlet?
Palpation
Cervicothoracic musculature may reveal active or latent myofascial trigger points and increased resting tone
Supra- and infra- clavicular spaces may present with tenderness, tone or muscle spasm and symptom reproduction
Objective Examination: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
What are the key examination procedures for patients with thoracic outlet?
Orthopaedic examination tests
Adson’s (+LR 3.29, -LR 0.27)
Roos (+LR 1.2, -LR 0.53)
Hyperabduction – pulse (+LR 1.49, -LR 0.56)
Hyperabduction – symptoms (+LR 0.69, -LR 0.34)
Tinel sign – supraclavicular space (+LR 1.04, -LR 0.96)
Adson’s Maneuver

Roos Stress Test
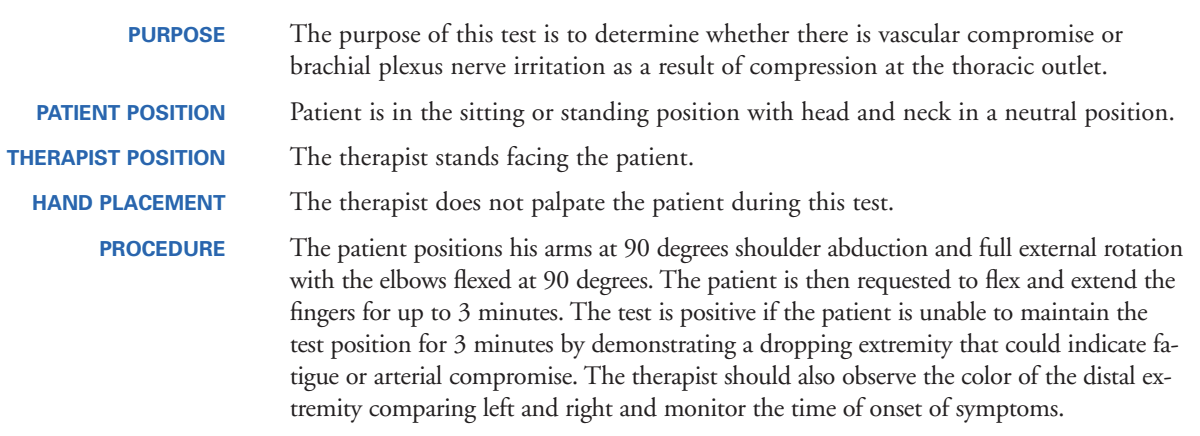
Hyperabduction Test

Tinel Sign
It is performed by lightly tapping (percussing) over the nerve to elicit a sensation of tingling or "pins and needles" in the distribution of the nerve.[3]
The Tinel sign is elicited by the percussion of an injured nerve trunk at or distal to the site of the lesion.
Positive test: The test is positive when a tingling or prickling sensation is felt in the distribution of the nerve.
Sign indicates nerve regeneration.
Objective Examination: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
What are the key examination procedures for patients with thoracic outlet?
Diagnostic test-item cluster
5/5 (+LR 5.25, -LR 0.19)
Adson’s
Roos
Hyperabduction – pulse
Hyperabduction – symptoms
Tinel signs (supraclavicular space)
Interventions: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
What are interventions recommended for thoracic outlet?
Education
Exercise
Manual therapy
Interventions: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
What are interventions recommended for thoracic outlet?
Education
Active lifestyle and general exercise including aerobic and strength training
Temporary reduction of repetitive overhead movements
Sleep hygiene, nutrition, stress reduction
Diaphragmatic breathing
Edema management
Interventions: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
What are interventions recommended for thoracic outlet?
Exercise
Exercises that promote range of motion and mobility of the cervicothoracic spine and ribs
Impairment-based approach to address cervicoscapulothoracic mobility, flexibility, endurance, neuromuscular control, and strength
Interventions: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
What are interventions recommended for thoracic outlet?
Manual therapy
Mobilization and manipulation of the cervicothoracic spine and ribs
Upper quarter nerve mobilization procedures
Interventions: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
When should we consider interprofessional or intraprofessional referral and what are other treatment options?
Imaging
Medical Interventions
Interventions: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
When should we consider interprofessional or intraprofessional referral and what are other treatment options?
Imaging
Electromyography/nerve conduction
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (cervical)
Magnetic Resonance Angiography
Venography
Doppler ultrasound
Brachial plexus block
Chest x-ray
Interventions: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
When should we consider interprofessional or intraprofessional referral and what are other treatment options?
Medical Interventions
Medications/injections
NSAIDs, muscle relaxants
SSRIs/SNRIs, antiepileptics
Botulinum toxin injections
Anticoagulants
Surgical
Decompression