Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table Overview
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Atomic number
Number of protons
Mass number
Number of protons + neutrons
Relative Atomic Mass (Ar)
An average value that takes account of the abundance of the isotopes of an element
Ar formula
(mass 1 x abundance 1) + (mass 2 x abundance 2)
Radius of atom
10^-10 m
Radius of nucleus
10^-14 m
Electron shell
Each shell can hold a maximum number of electrons
1st shell maximum electrons
2
2nd shell maximum electrons
8
3rd shell maximum electrons
8
Proton
Sub-atomic particle with a relative mass of 1 and a charge of +1
Neutron
Sub-atomic particle with a relative mass of 1 and no charge
Electron
Sub-atomic particle with a relative mass of very small and a charge of -1
Element
Consists of one type of atom only
Compound
Formed from chemically bonding elements
Mixture
Two or more elements or compounds not chemically bonded together
Ion
An atom or molecule which has different number of protons and electrons
Isotope
Atoms of the same element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons
Abundance
How much of something there is (as a percentage)
Periodic table
Lists all the known elements in order of increasing atomic number
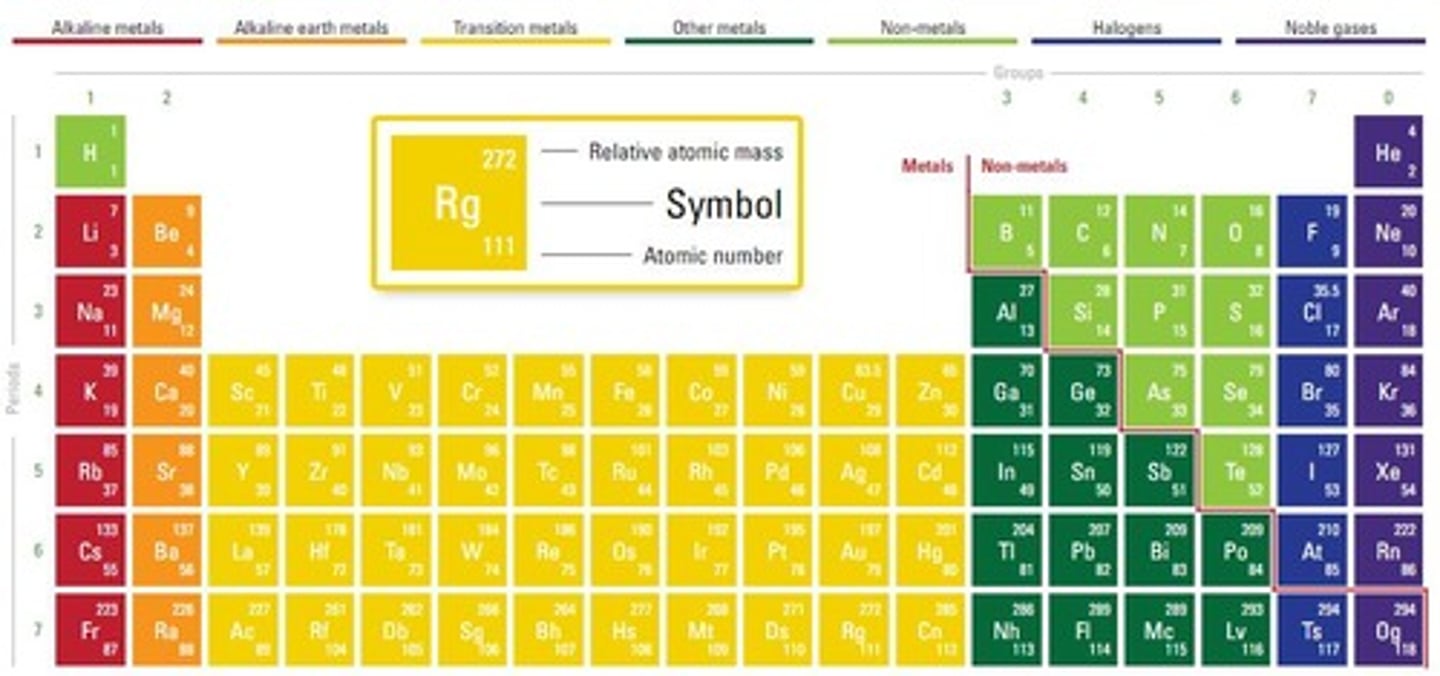
Metals
Elements that react to form positive ions
Alkali metals
A group of metals in the periodic table
Alkali earth metals
A group of metals in the periodic table
Non-metals
Elements that do not form positive ions and typically have properties such as being soft, low density, and having low melting and boiling points.
Metallic properties
Characteristics of metals, including the ability to conduct electricity and heat, and being shiny when cut.
Non-metallic properties
Characteristics of non-metals, including being dull, poor conductors of heat and electricity, and brittle.
Group number
The column number in the periodic table that indicates the number of electrons in the outermost shell.
Period number
The row number in the periodic table that indicates the number of shells containing electrons.
Group
A column of elements in the periodic table with similar chemical properties.
Group 7 Halogens
Elements in Group 7 of the periodic table that have 7 electrons in their outermost shell and increase in reactivity down the group.
Diatomic molecules
Molecules made of two atoms combined, such as F2 and Cl2.
Periodic table development
The arrangement of elements by atomic mass in the early 1800s that revealed a periodic pattern in properties.
Newland's Octaves
A method proposed by Newland in 1863 where every eighth element had similar properties, which was unsuccessful due to gaps left for undiscovered elements.
Dimitri Mendeleev
A scientist who created a periodic table in 1869 ordered by atomic mass, leaving gaps for undiscovered elements whose properties fit the patterns.
Reactivity trend in groups
Reactivity increases down the group for alkali metals and increases up the group for halogens.
Group 0 Noble Gases
Elements in Group 0 that are unreactive/inert due to having a stable arrangement of electrons and a full outer shell.
Displacement reactions
Reactions where a more reactive halogen displaces a less reactive halide ion from its solution.
Boiling point trend
Boiling points increase down the group for noble gases.
Reaction with oxygen
Alkali metals react with oxygen to form alkali metal oxides.
Reaction with water
Alkali metals react with water to form alkali metal hydroxides and hydrogen.
Reaction with chlorine
Alkali metals react with chlorine to form alkali metal chlorides.
alloy
a mixture of two or more elements, at least one of which is a metal
covalent bond
the bond between two atoms that share one or more pairs of electrons
covalent bonding
the attraction between two atoms that share one or more pairs of electrons
delocalised electron
bonding electron that is no longer associated with any one particular atom
dot and cross diagram
a drawing to show only the arrangement of outer shell electrons of the atoms or ions in a substance
fullerene
form of the element carbon that can exist as large cage-like structures, based on hexagonal rings of carbon atoms
gases
substances that have no fixed shape or volume and can be compressed easily
giant covalent structure
a huge 3D network of covalently bonded atoms
giant lattice
a huge 3D network of atoms or ions
giant structure
see giant lattice
intermolecular forces
the attraction between the individual molecules in a covalently bonded substance
ionic bond
the electrostatic force of attraction between positively and negatively charged ions
liquids
substances that have a fixed volume, but they can flow and change their shape
nanoscience
the study of very tiny particles or structures between 1 and 100 nanometres in size - where 1 nanometre = 10-9 metres
particle theory
a theory that explains the properties of solids, liquids and gases based on the fact that all matter is made from tiny particles. It describes the movement of particles and the distance between them
polymer
a substance made from very large molecules made up of many repeating units
solids
substances that have a fixed shape and volume that cannot be compressed
states of matter
the forms in which matter can exist. A substance can be solid, liquid or gas