4.2 marketing planning
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
market segmentation
dividing a broad market into various consumer groups according to psycho-socio demographics
segments are made up of consumers with similar needs and tastes → respond to trends and market forces in similar ways.
types
geographic
demographic
psychographic
market segmentation advantages
target specific market → increased sales
identify gaps in market → exploit
differentiated promotion strategies → avoid promoting to consumers with no intention of buying
specialisaton → smaller firms able to compete
market segmentation disadvantages
differentiated promotion strategies → no marketing EOS → promotional costs high
different products → R&D and production costs high
many products → production and stock-holding costs high
excessive specialisation if only focus on a few market segments → will be affected if consumer tastes change
product positioning
the process of designing the products and image to occupy a distinctive place in the perceptions of consumers in the target market
analyses how brand will relate to competitors, illustrated by perception map
perception map
diagram that analyses consumer perceptions of competing brands with respect to two product characteristics
allows businesses to identify how competitors are positioned relative to its own products (how saturated/diverse)
identifies gaps in market
position in gaps → differentiate
position with other products → lower risk, less profitable
allows business to be aware of key features that should be promoted heavily
can see if need to reposition existing product → using new promotional campaigns etc

niche market
small part of a larger market. customers have very specialised needs or wants that are different from the larger market
products sold in niche markets are more expensive than in mass markets, not suitable for mass production and sale.
mass market
A market for goods that are standardised and produced in very large quantities.
Less expensive due to economies of scale
niche marketing
identifying and exploiting a small segment of a larger market by developing products to suit it
not yet exploited by competitors
niche marketing advantages
small business → can survive
large business → can create status and image which mass-market products lack
if unexploited by competitor, exclusive → can use premium pricing for high profit margin
niche marketing disadvantages
cannot exploit EOS → higher unit cost of production
high risk: small no. of consumers so if buying change will cause rapid decline in sales → therefore need diversify
mass marketing
selling the same products to the whole market with no attempt to target groups within it
due to more competitors in the market and increased consumer choice, use mass marketing to expand range of products and number of potential customers
mass marketing advantages
can exploit EOS → lower unit cost of production
lower risk: large no. of consumers so unlikely for sudden change in buying habits
mass marketing disadvantages
small businesses → cannot survive
large businesses → unable to create status and image using mass products
since many competitors, not exclusive → cannot charge premium pricing
marketing planning
process of developing appropriate strategies and preparing marketing activities to meet marketing objectives
market plan is a formal document which outlines how the business intends to achieve marketing objectives derived from business objectives.
elements of a marketing plan
SMART objectives
budget → finance
sales forecast → to monitor progress
startegies
tactics → action plan
purpose of a marketing plan
provide focus → roadmap of strategies
link strategies and tactics to SMART objectives → increase chances of success
plan budget in advance
integrates different business departments in the plan
ensures marketing mix is appropriate and aligned and fully integrated
limitations of a marketing plan
outdated if not revised → changing internal/external conditions
needs to be based on up to date market research
constant process, final outcome must be judged against original objectives → to aid future decision-making
target market
particular group of customers or potential customers that a company is trying to reach
helps to shape marketing strategies, well-targeted product needs less advertising and promotional support since it meets needs
consumer profile
quantified picture of consumers of a business’ products, showing proportions of psycho-socio demographics
competitive advantage
an edge a business has over its rivals gained by offering customers greater value. Leads to customer loyalty. → in contrast to first-mover advantage: just the first, value doesn’t matter
either by low prices or by providing greater benefits and service to justify higher price
unique selling point
special feature of a PRODUCT that differentiates it from competitors and attracts customers. can be based on any aspect of marketing mix.
Leads to competitive advantage → leads to customer loyalty.
types
low prices
trust
ethical stance
purchase convenience
innovation
adv/disadv of USP: low prices
advantages
consumer limited spending power, high proportion attracted
disadvantages
lower profit margin → total profit falls
brand may be perceived as poor quality
may not integrate well with rest of marketing mix
difficult to differentiate: globalisation → more low-cost countries producing
adv/disadv of USP: trust
advantages
customers careful with spending → do research to make safe decisions
if successfully build consumer relations → high loyalty
disadvantages
new businesses → difficult to gain
can be lost → difficult to regain
adv/disadv of USP: ethical stance
advantages
consumers share values, will be loyal even if prices are high
disadvantages
consumers prioritise cost over ethical stance
false show of ethics, not genuine → loss of trust
adv/disadv of USP: purchase convenience
advantage: consumers lack time/dislike experience of shopping
disadvantage: difficult to differentiate since methods are widespread
adv/disadv of USP: innovation
advantages
if patented, competitors cannot copy
brand image → command premium prices
disadvantages
R&D expensive and time-consuming
R&D success not guaranteed
need constant R&D to stay competitive → continuous investment
porter’s generic strategies [HL ONLY]
how to gain long-term competitive advantage over rivals
relate to scope of market (mass/niche) and competitive advantage (unique product/cost of production)
cost leadership: mass market, low cost of production
differentiation: mass market, unique product (due to quality/brand image)
cost focus: niche market, low cost of production
differentiation focus: niche market, unique product
BCG matrix
analysing product portfolio of a business in terms of market share and market growth. size of circles represents total revenue earned by the product.
helps decide marketing strategies to take
quadrants
star: high market share, high market growth
question mark: low market share, high market growth
cash cow: high market share, low market growth
dog: low market share, low market growth
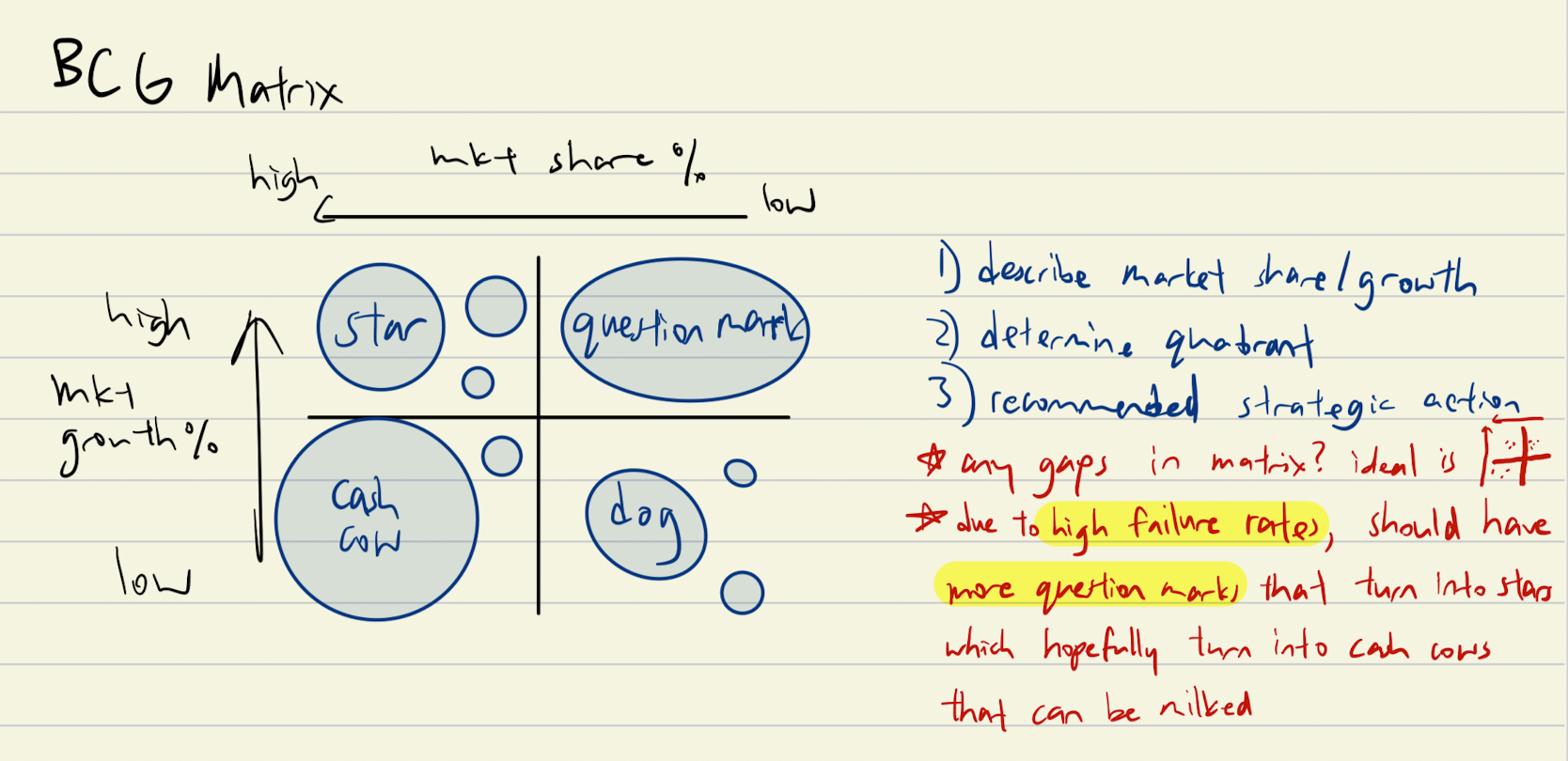
cash cow
well-established product in mature market → high consumer awareness so low promotional costs → promote to remind customers
high sales, high profit
milk: take positive cash flow and invest in question marks
question marks
consumes resources but low sales and profit
high promotion costs → promote to gain awareness
has potential since growing market
build: support with more promotion and distribution outlets. financed by milking cash cows.
stars
performing well in growing market
high promotion costs to differentiate product and reinforce brand image → promote to gain new customers
high sales, high profit
hold: continue support, freshen appearance to sustain growth
dogs
withdraw from market, reposition into faster-growing markets
divest: stop production
impacts workforce
spare capacity should be invested into other quadrant