Chapter 6: Marketing Strategy - nog niet af
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
5 steps in strategy development
1) Develop a goal
2) Set the objectives
3) Select major Market / Segment
4) Set policy: courses of action
5) Assemble & implement
Strategic context
Facets of Marketing Strategy
Product
Place
Price
Promotion
Strategy development: Marketing goals (1)
= Statements of purpose / Mission statement
General guideline for employees
Usually rather general and abstract statement
Eg. “Become a leading brand worldwide”
Strategy development: Operational objectives (2)
Near-term / Long-term
Usually more specific and concrete than goals
Eg. “Realise 5% growth next year in Europe”
The growth-gain matrix
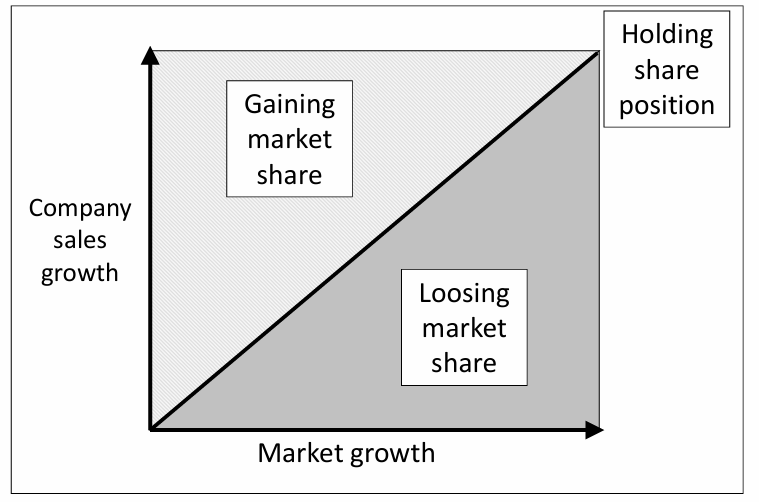
Strategy development: Selecting major markets (3) - where growth can be realised
Consumer home food market = consumption at home
Food service market = catering, restaurant
Institutional food market = organisations, e.g. schools
Government food market = e.g. for food aid purpose
Industrial food market = business-to-business
Each of these markets can be
National
International
Strategy development: Courses of action (4) = ANSOFF growth matrix
Alternative product / market strategies for realising growth
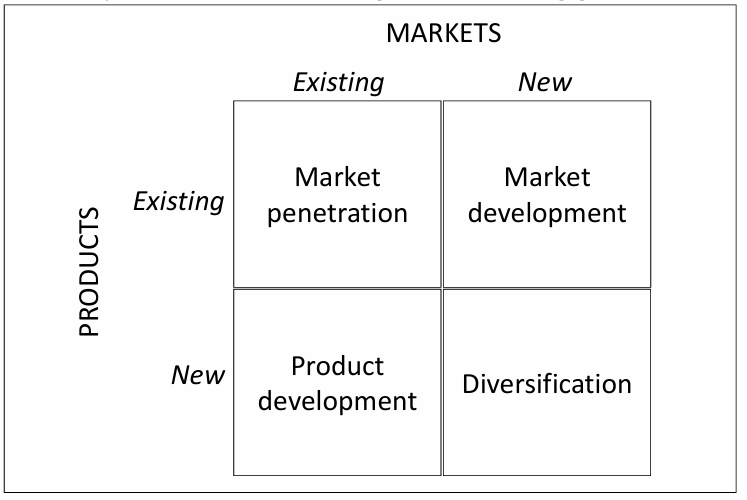
Market penetration strategies
Current market + current products
Increase market share
Increase product share
Increase frequency of use
Increase quantity used
Stimulate adoption of new applications
Product development strategies
Current market + New products
Product improvement
Product line extensions
New products for same market
Innovations
Market development strategies
New markets + current products
Expand markets for existing products
Geographic expansion
New target segments
Diversification strategies
New markets + new products
Vertical integration
Forward integration (eg. dairy company merges with ice cream company)
Backward integration (eg. ice cream company merges with dairy company)
Horizontal integration
Diversification into related businesses = concentric diversification (eg. dairy company merges with meat company)
Diversification into unrelated businesses = conglomerate diversification (eg. dairy company merges with insurance company)
Strategy development: Assemble and implement the strategy (5) - STP analysis
STP-analysis
Segmentation
Targetting
Positioning
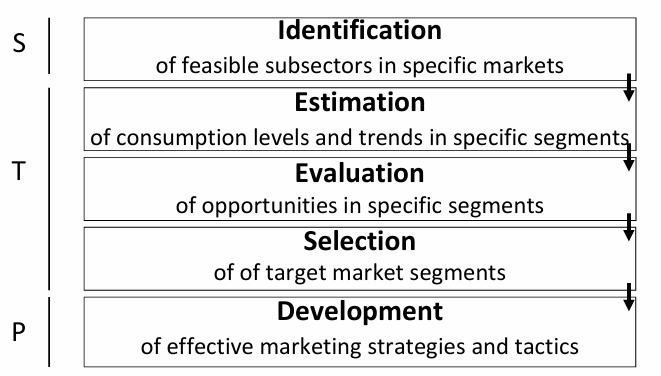
Strategy development: Assemble and implement the strategy (5) - STP analysis: Segmentation
Types of segmentation
1) Homogenous
2) Diffused
3) Concentrated
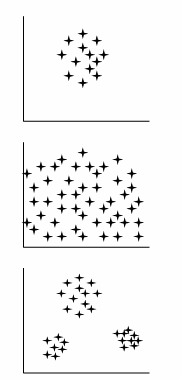
Good segments should be …
Homogenous preferences within segments
Heterogenous preferences between segments
Demand differences between segments
Accessible: can be reached
Stable: exist now and later
Substantial: size or purcchasing power
Segmention criteria
Identifiable
Measurable
Relevant
Segmentation Variables
Socio-economic
…
Macro segmentation variables | Micro segmentation variables |
|
|
Market Segmentation Process

Strategy development: Assemble and implement the strategy (5) - STP analysis: Targeting
Evaluate segments: in terms of …
Attractiveness
size: now and in the future
spending power
stability over time
accessibility
Fit with objectives and means of the company
Growth potential
And select the most promising one(s) as target(s)
Targeting outcomes
Single-segment concentration concentrate on 1 section with 1 product & design that product targetted to that 1 section disadvantage: if the segment starts shrinking → you are losing market | Selective specialisation Develop 3 products, each specialised for a segment Disadvantage: you have to put much effort to develop 3 products | Market specialisation People from 1 segment can choose between 3 products (eg. 3 lactose free products) Advantage: you offer choice to people from a certain segment and they will know your product good |
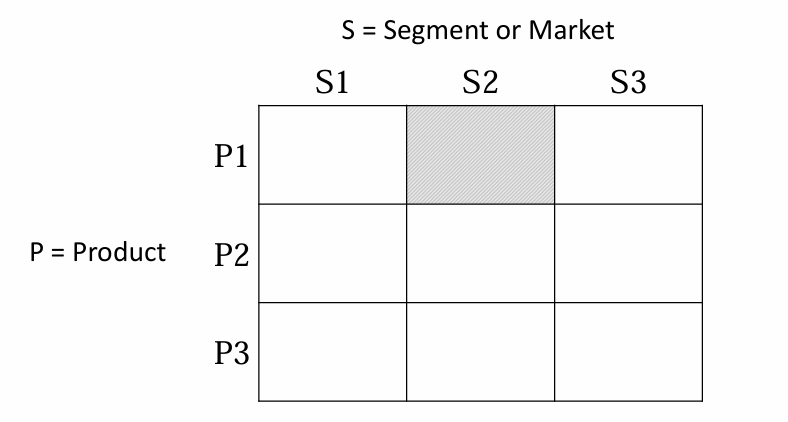 | 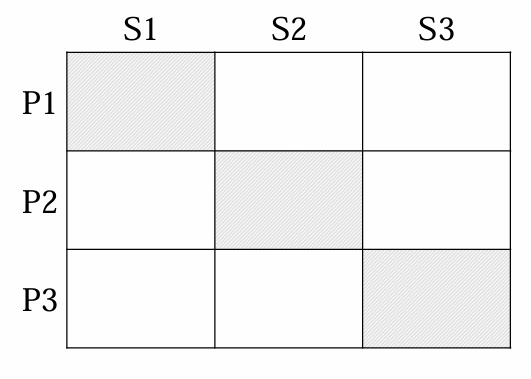 | 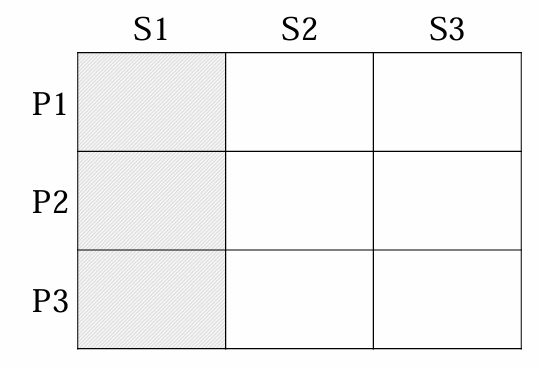 |
Product specialisation specialize in 1 product and make it available for different segments | Full coverage | |
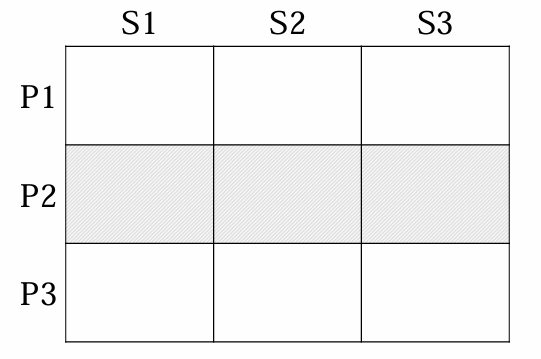 | 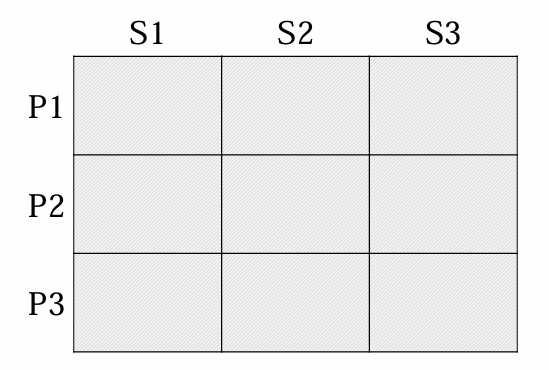 |

Strategy development: Assemble and implement the strategy (5) - STP analysis: Positioning
Placing or positioning the product in the market
choosing a position in the market through giving the product specific characteristics