Memory Systems
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Includes: - Memory Taxonomy
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Working Memory
Long-Term Memory
What 2 types of memory is Memory split into?
Short-term
less effort (can recall without trying)
absorbing information through the senses
vs.
Working memory
more effort (takes active effort to recall)
stores info longer
manipulation of info
ex. rehearsal
What is the difference between short-term memory and working memory?
Declarative (Explicit) Memory
Nondeclarative (Implicit) Memory
What 2 types of memory is Long-term memory split into?
Episodic Memory (events)
Semantic Memory (facts)
What 2 types of memory is Declarative memory split into?
Declarative Memory
with conscious recall
AKA explicit memory
processed in the hippocampus
includes semantic and episodic memory
Procedural Memory
without conscious recall
AKA implicit memory
processed by other brain regions like cerebellum
includes motor/cognitive skill memory and classical conditioning memory
Priming
a memory phenomenon
= exposure to stimulus influences your response to subsequent stimulus
Semantic Memory
memory of facts and general knowledge
Episodic Memory
memory of personally experienced past events
Hippocampus
brain region that
processes everyday new memories
ex. “what did I eat yesterday?”
processes spatial memory
Amygdala
brain region that’s responsible for threat detection
tends to process negative emotions (anger, aggression, fear)
PTSD patients show lots of activity in this region when having flashbacks
fear memory
Cerebellum
Brain region responsible for balance, coordination, movement. (it’s the first part of the brain affected by alcohol)
plays a role in 2 types of memory:
memory in classical conditioning
procedural memory
Acetylcholine
a neurotransmitter involved in muscle control, learning and memory
Serotonin
a neurotransmitter involved with sleep, mood, and hunger
Neural Networks
a collection of neurons that fire together
Long-term Potentiation (LTP)
process by which synaptic connections between neurons become stronger w/frequent activation
thought to be crucial mechanism involved in learning and memory formation
Flashbulb memory
a vivid, enduring memory associated with a personally significant and emotional event, often including such details as where the individual was or what he or she was doing at the time of the event
ex. people remember vivid snapshot of what they were doing when they heard about
the 9/11 attacks
Retrograde Amnesia
a type of amnesia where you can't recall memories that were formed before the event that caused the amnesia. It usually affects recently stored past memories, not memories from years ago.
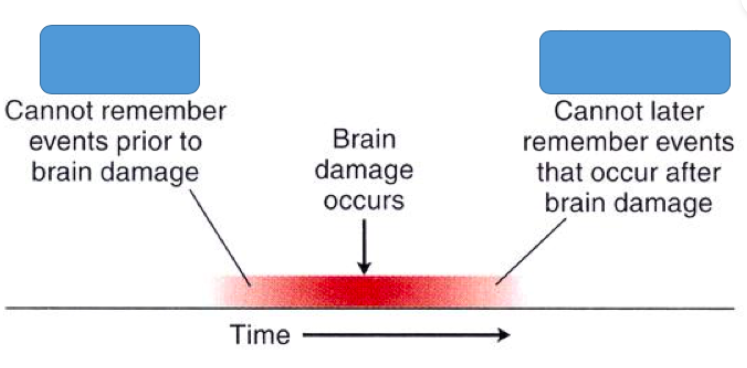
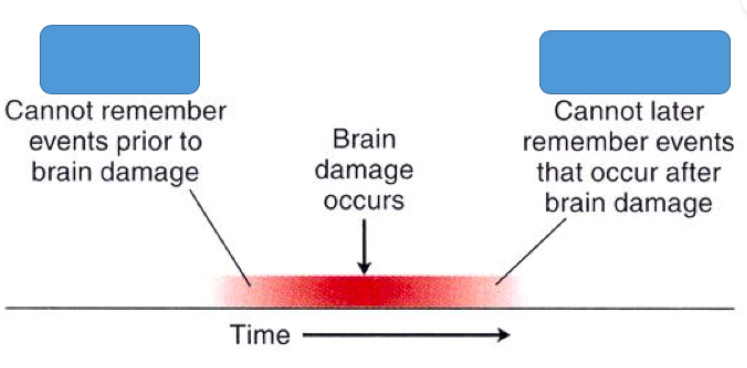
Anterograde Amnesia
a type of memory loss that occurs when you can't form new memories
Alzheimer’s
A progressive disease where brain cell connections and the cells themselves degenerate and die,
destroys memory and other mental functions
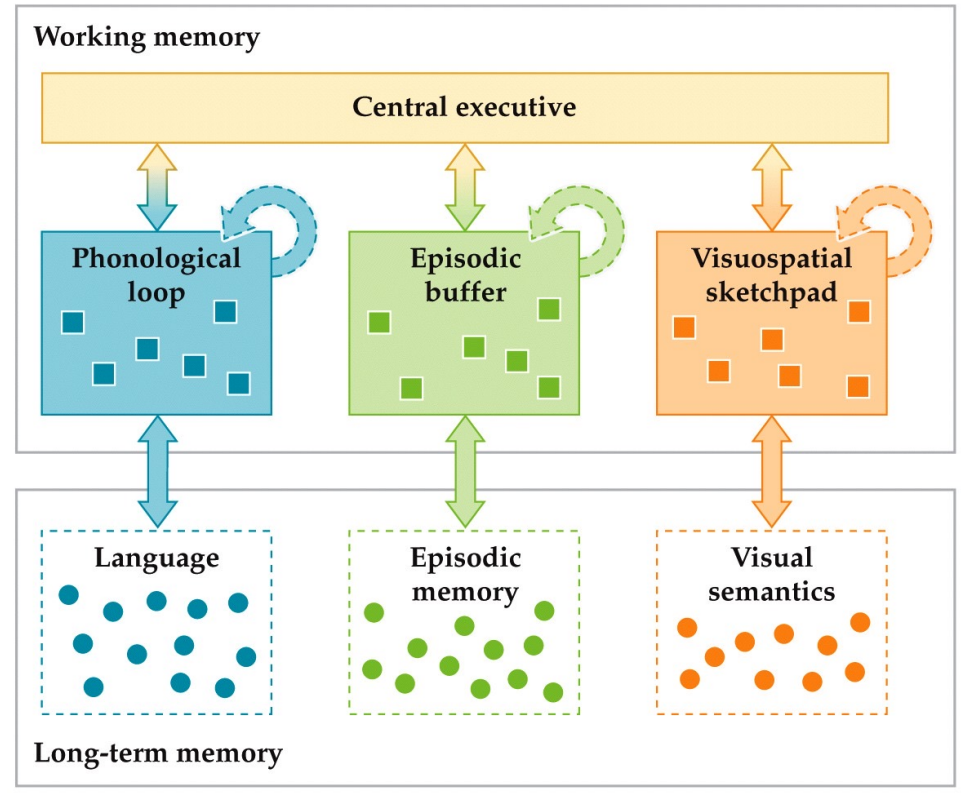
Working Memory
The ability to hold in mind and manipulate information
The Baddeley model of working memory
Working memory has
a central executive = controls what we’re keeping in mind
3 content-specific subsystems
Visuospatial = (visual)
ex. trying to visualize something not in front of you while closing your eyes
dorsal fronto-parietal
Phonological = (audio) rehearsal
ex. trying to remember phone # by repeating it
left frontal cortex = language production
Episodic = remembering our own memories
Medial temporal lobes
Striatum
set of brain regions involved in motor systems
Neocortex
part of cortex involved in sight and hearing