Lab 3 reflexes and peripheral nerves
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Dura Mater
_ most superficial layer of brain
Arachnoid
Middle layer (Between dura and pia)
Pia Mater
Deepest meningeal layer
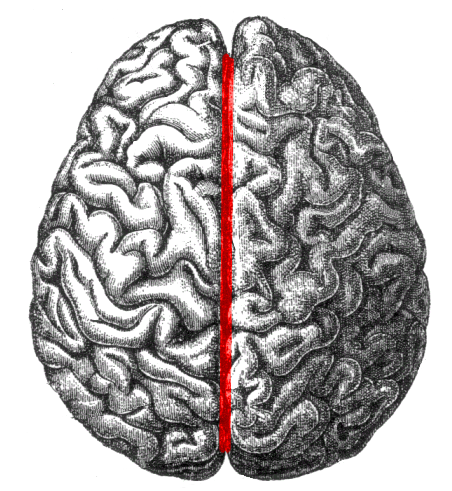
Longitudinal fissure
Separates the left and right hemispheres
Convulsions
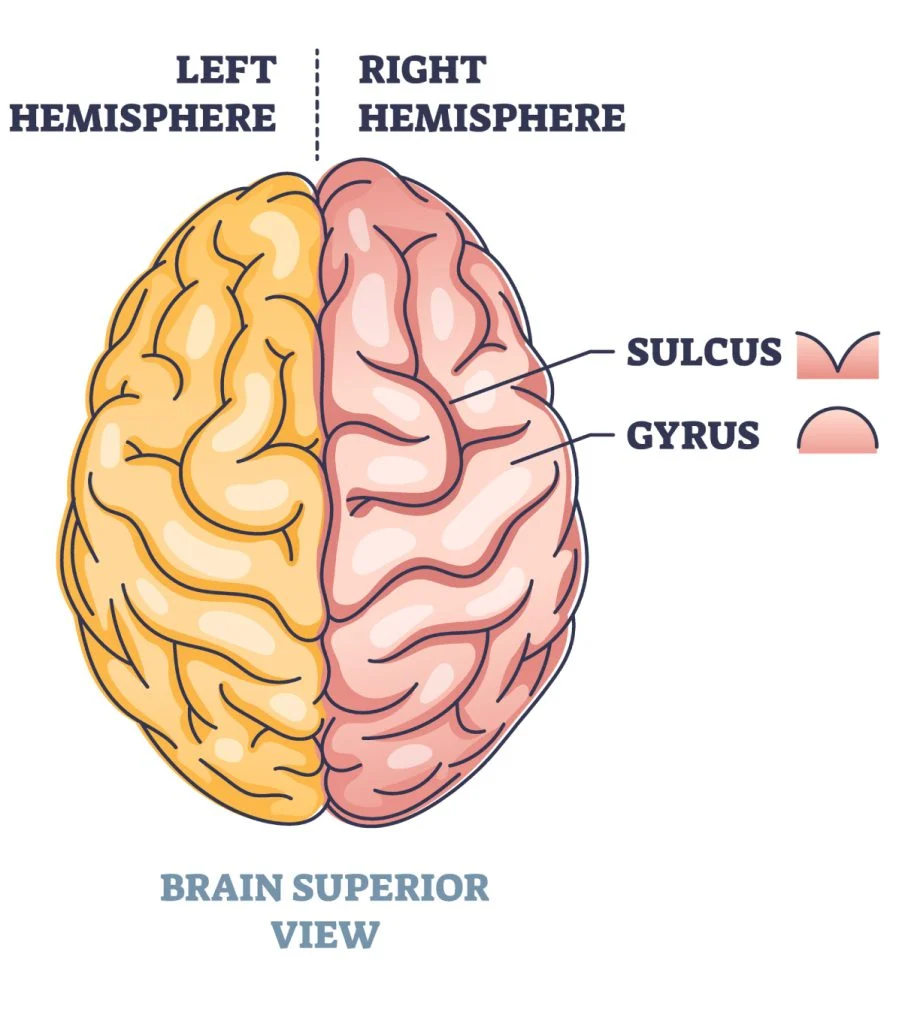
Gyri (ridges) of brain
Sulci (grooves) of brain
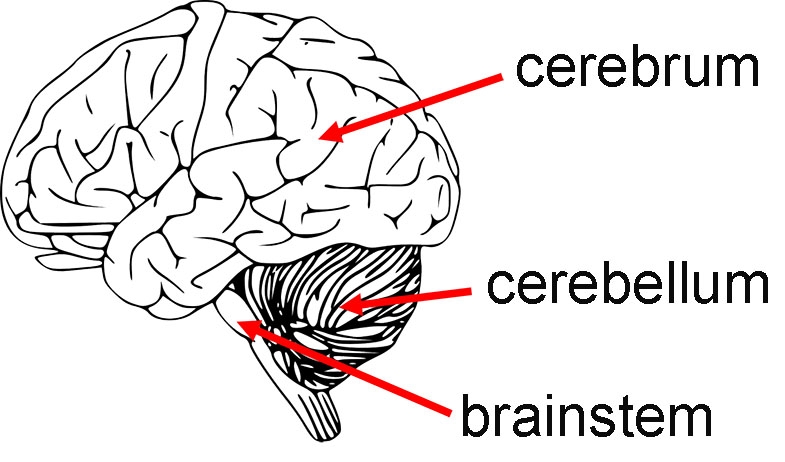
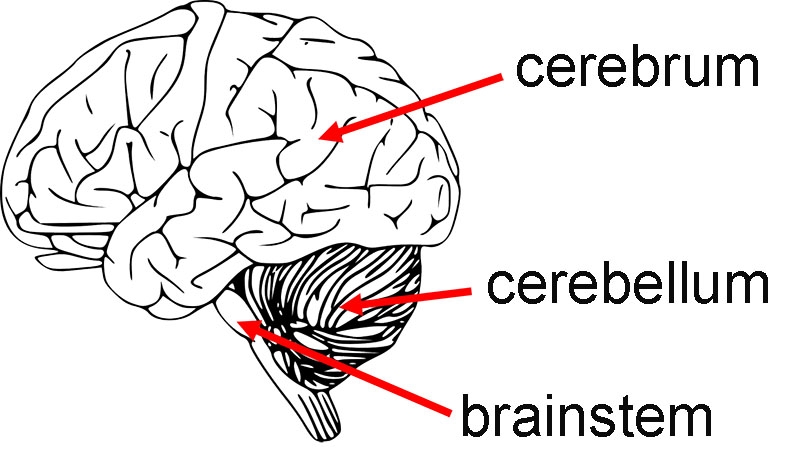
Cerebrum
Large front portion of the brain
Responsible for higher brain functions EX: Thought, Action, and sensory processing
Cerebral hemispheres
Left and right hemispheres
Cerebellum
Inferior to cerebrum, behind the brainstem
Coordination, balance, and fine motor control
Superior Corpora Quadrigemina
- Involved in visual processing and reflexes
- Help coordinate head and eye movements in response to visual stimuli
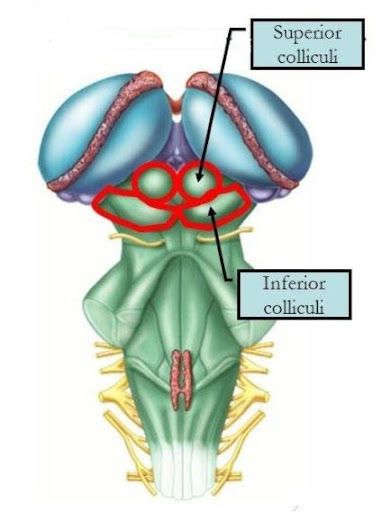
Inferior corpora quadrigemina
- Involved in auditory processing
- Relay auditory information from the ear to the thalamus and help with reflexive responses to sound
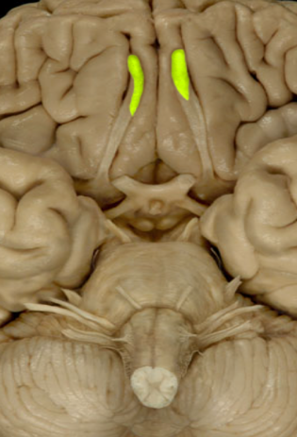
Olfactory Bulbs (1)
Involve sense of smell (Sensory)
Optic Nerves (II)
Sense of vision (Sensory)
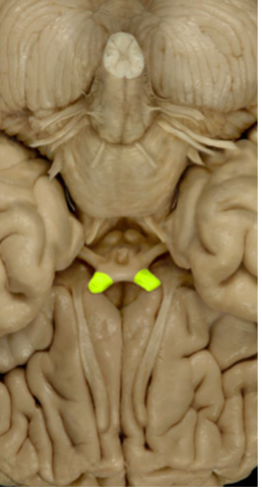
Oculomotor (III)
Eye Movement
Eye dilation/Tracking (parasympathetic)
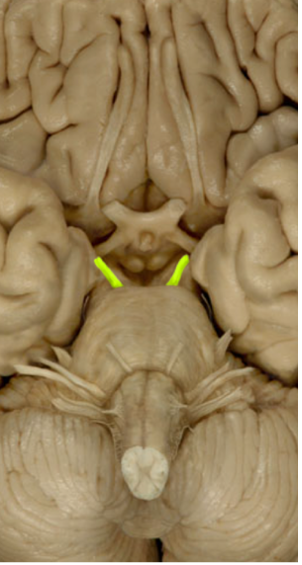
Trochlear nerve (IV)
Eye Movement Up/Down (Motor)
Adduction/Abduction of Eye
Trigeminal (V)
Sensation of the face (sensory)
Chewing muscles (Motor)
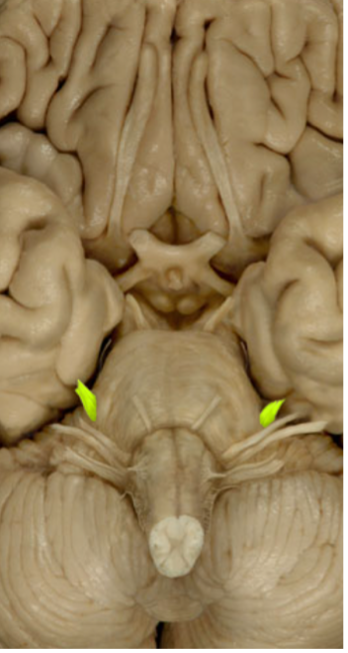
Abducens nerve (VI)
Adduct/ Abduct eye
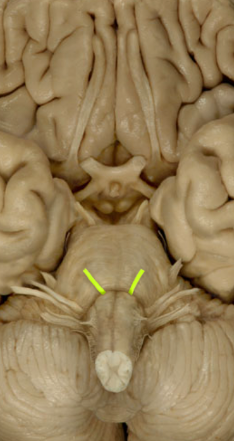
Facial Nerve
Controls facial expression (Motor)
Salivary glands
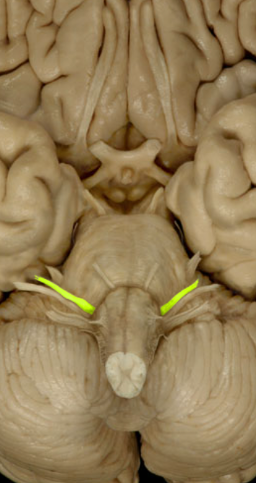
Vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII)
Hearing and Balance (Sensory)
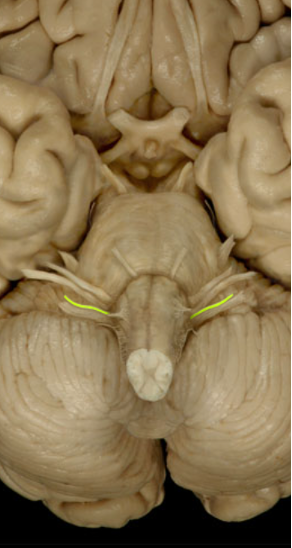
Glossopharyngeal (IX)
Sense of taste (Sensory)
Muscles that help swallow (motor)
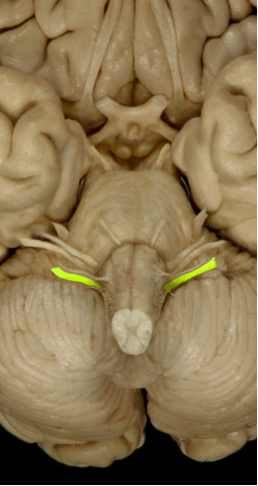
Vagus (X)
Innervates all internal organs
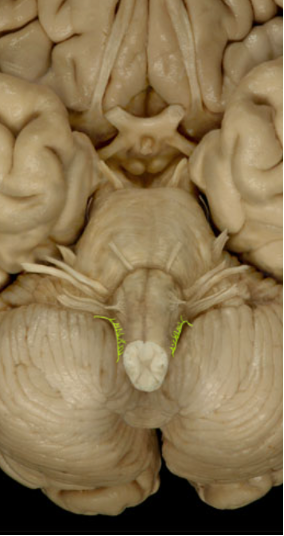
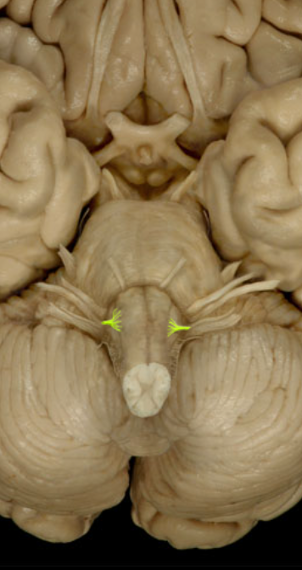
Accessory Nerve (XI)
Controls neck muscles (sternocleidomastoid/trapezius)
Hypoglossal Nerve (XII)
Tongue Movement
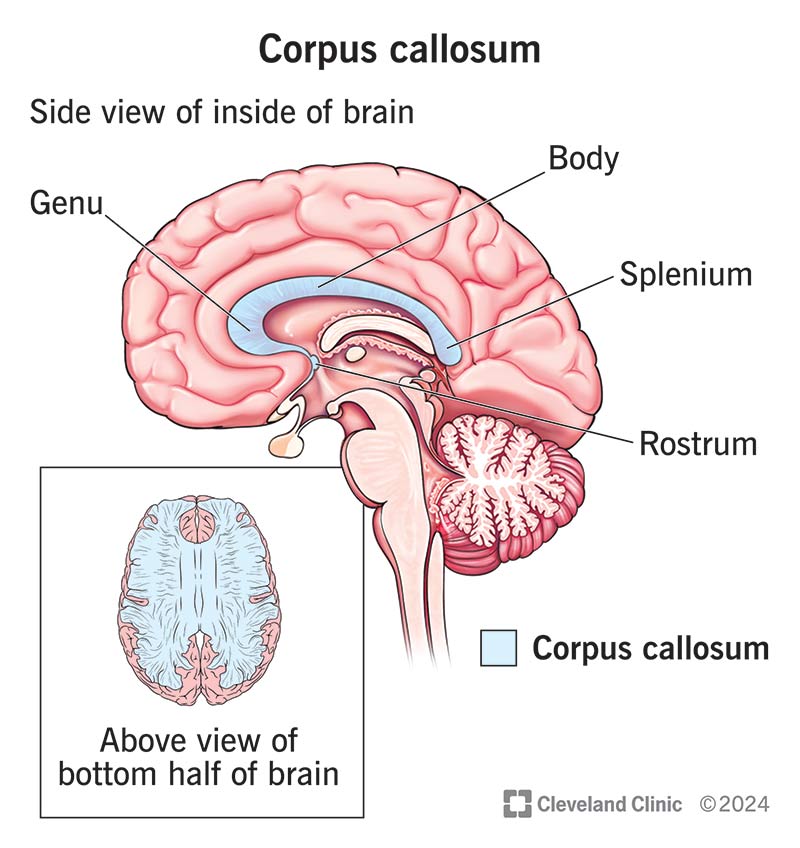
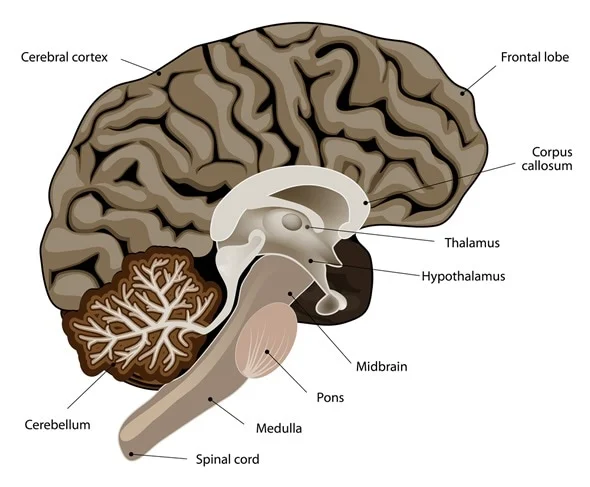
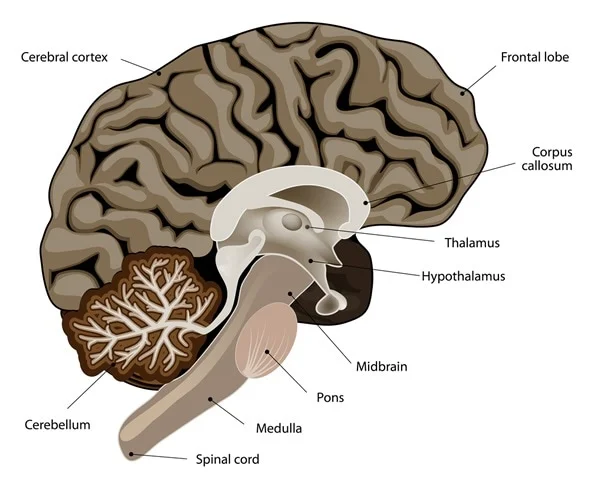
Corpus Callosum
Location: Deep within the brain, connecting the left and right cerebral hemispheres.
Function: Facilitates communication between the two hemispheres, integrating motor, sensory, and cognitive performances.
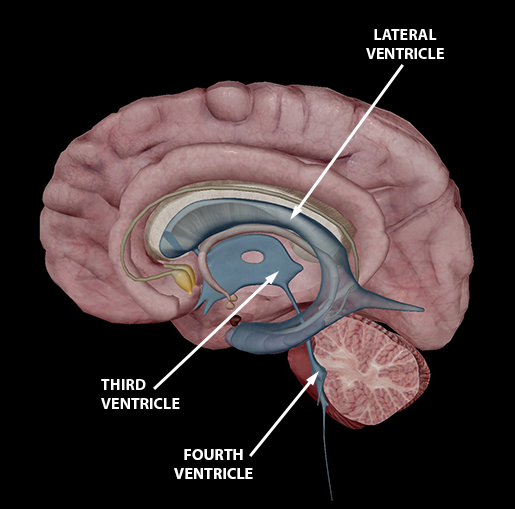
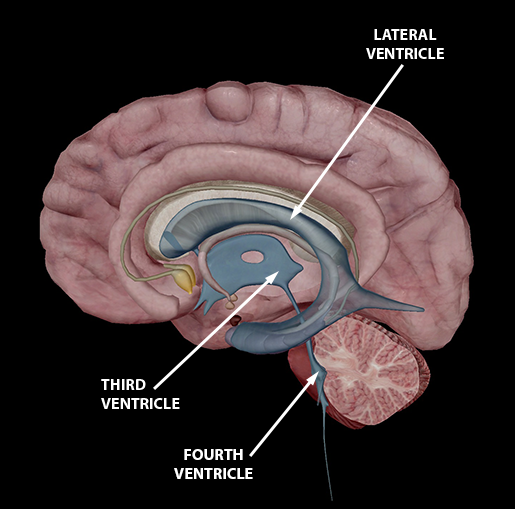
Lateral ventricle
Location: C-shaped cavities located within each cerebral hemisphere.
Function: Contain cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) that cushions the brain and removes waste.
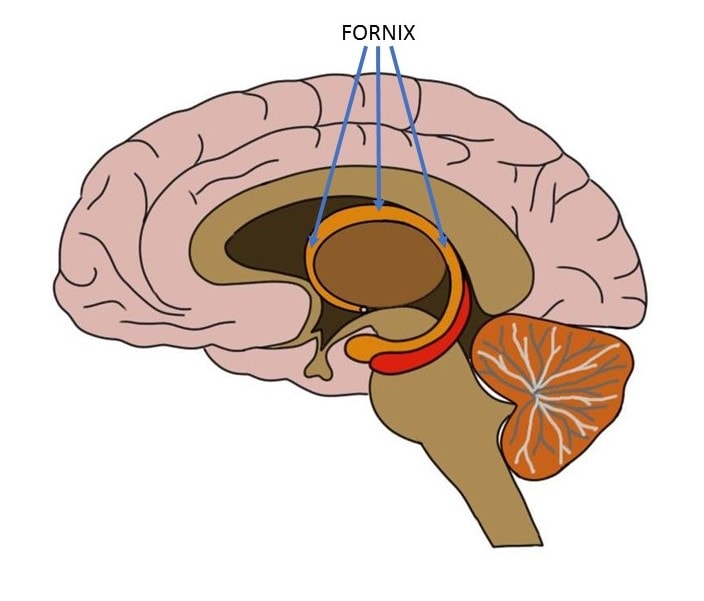
Fornix
Location: beneath the corpus callosum.
Function: Connects the hippocampus to other brain regions, playing a role in memory formation.
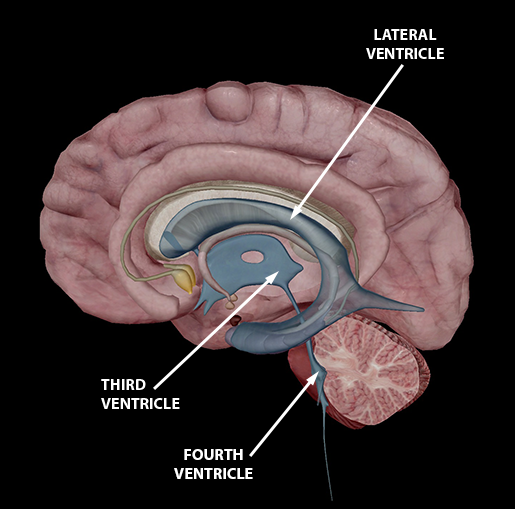
Third Ventricle
Location: A narrow cavity located in the midline between the two halves of the thalamus.
Function: Circulates CSF and connects the lateral ventricles to the fourth ventricle via the cerebral aqueduct.
Thalamus
Location: Situated above the brainstem, between the cerebral cortex and midbrain.
Function: Acts as a relay station, transmitting sensory and motor signals to the cerebral cortex.
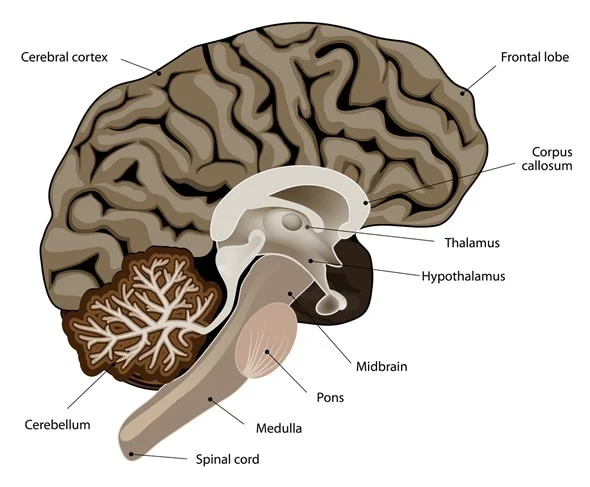
Hypothalamus
Location: Below the thalamus, forming the floor of the third ventricle.
Function: Regulates vital bodily functions, including temperature, hunger, thirst, and hormone production.
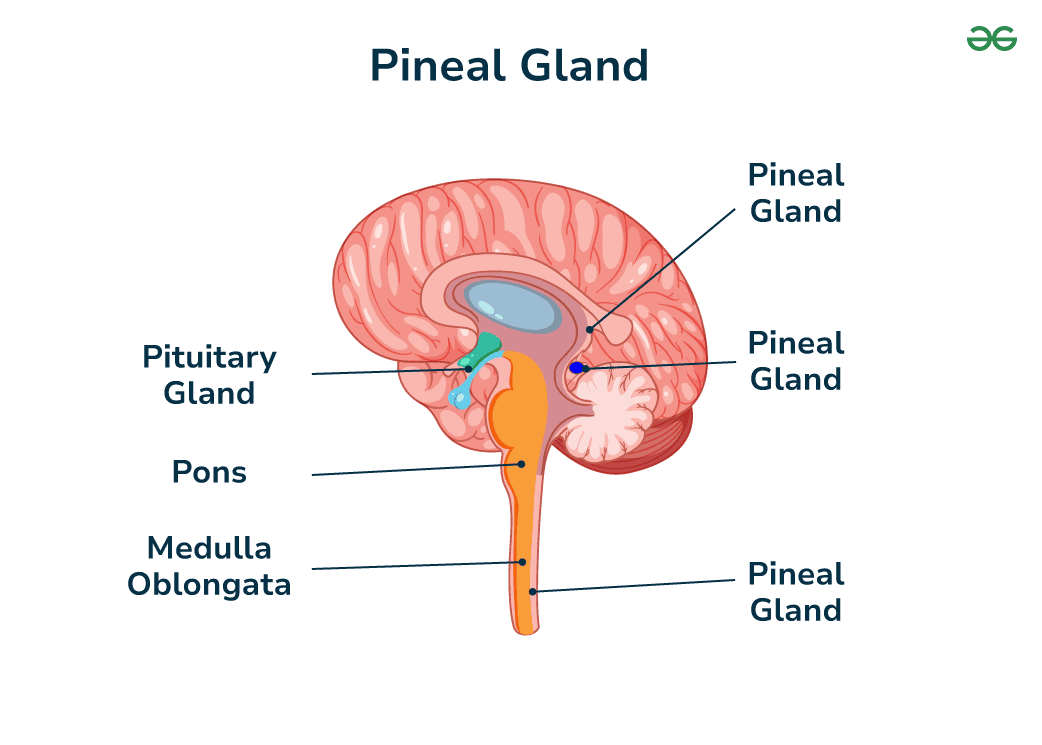
Pineal Body
Location: Near the center of the brain, between the two hemispheres, in a groove where the two halves of the thalamus join.
Function: Secretes melatonin, regulating sleep-wake cycles.
Midbrain
Location: Upper part of the brainstem, connecting the forebrain to the hindbrain.
Function: Involved in vision, hearing, motor control, sleep/wake, arousal, and temperature regulation.
Cerebral aqueduct
Location: A narrow channel running through the midbrain.
Function: Connects the third and fourth ventricles, allowing CSF to flow between them.
Fourth ventricle
Location: Located between the pons and the cerebellum.
Function: Continues the flow of CSF from the cerebral aqueduct to the central canal of the spinal cord.
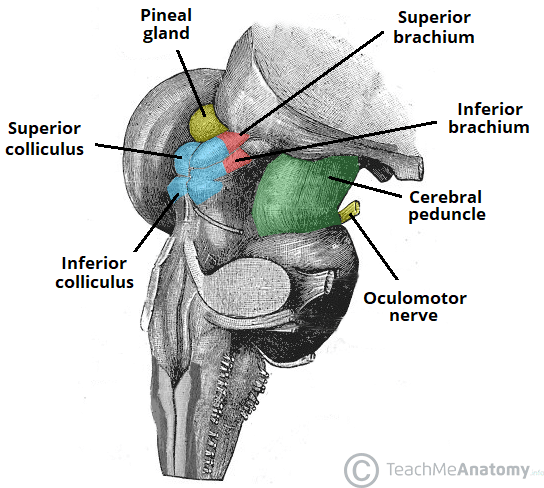
Cerebral peduncles
Location: Structures on the front of the midbrain.
Function: Contain motor tracts that convey information from the cerebral cortex to the brainstem and spinal cord.
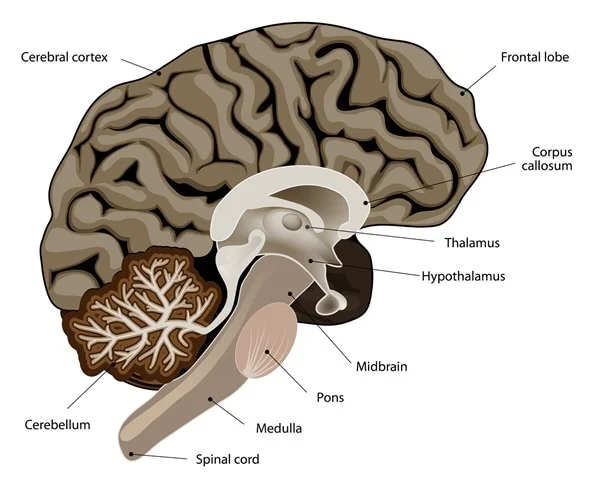
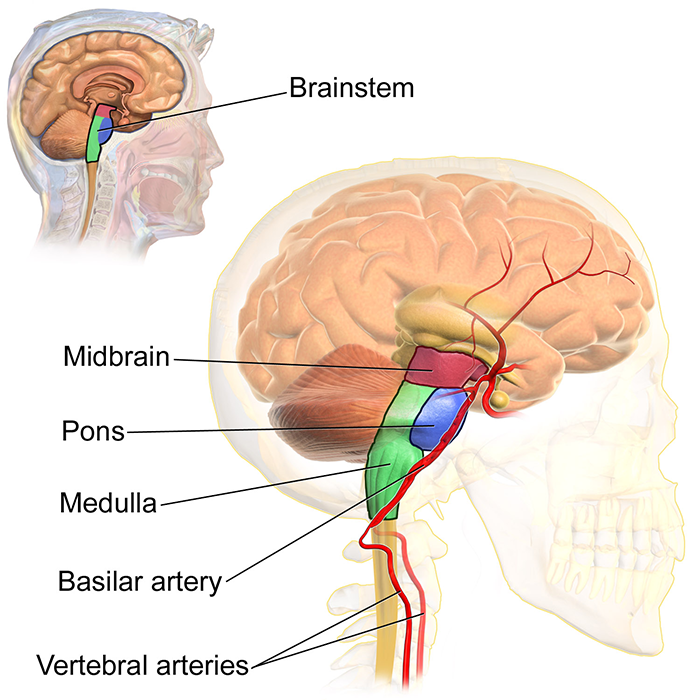
Pons
Location: Part of the brainstem, situated above the medulla oblongata and below the midbrain.
Function: Relays signals between the forebrain and the cerebellum; involved in sleep, respiration, swallowing, and facial expressions.
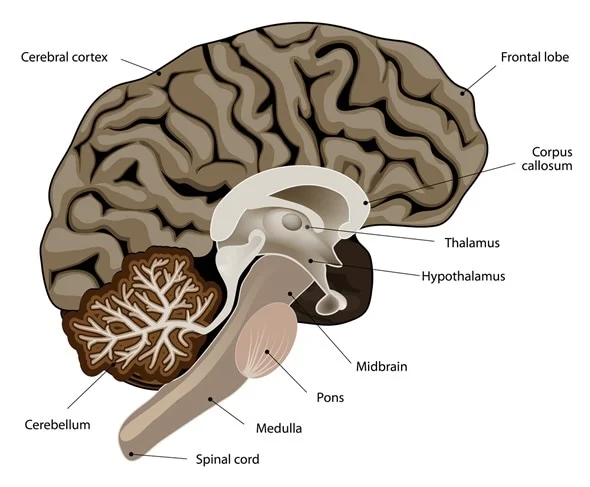
Medulla Oblongata
Location: Lowest part of the brainstem, connecting the brain to the spinal cord.
Function: Controls autonomic functions such as breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure.
Cerebellum
Location: Located at the back of the brain, beneath the occipital lobes.
Function: Coordinates voluntary movements, balance, and posture.
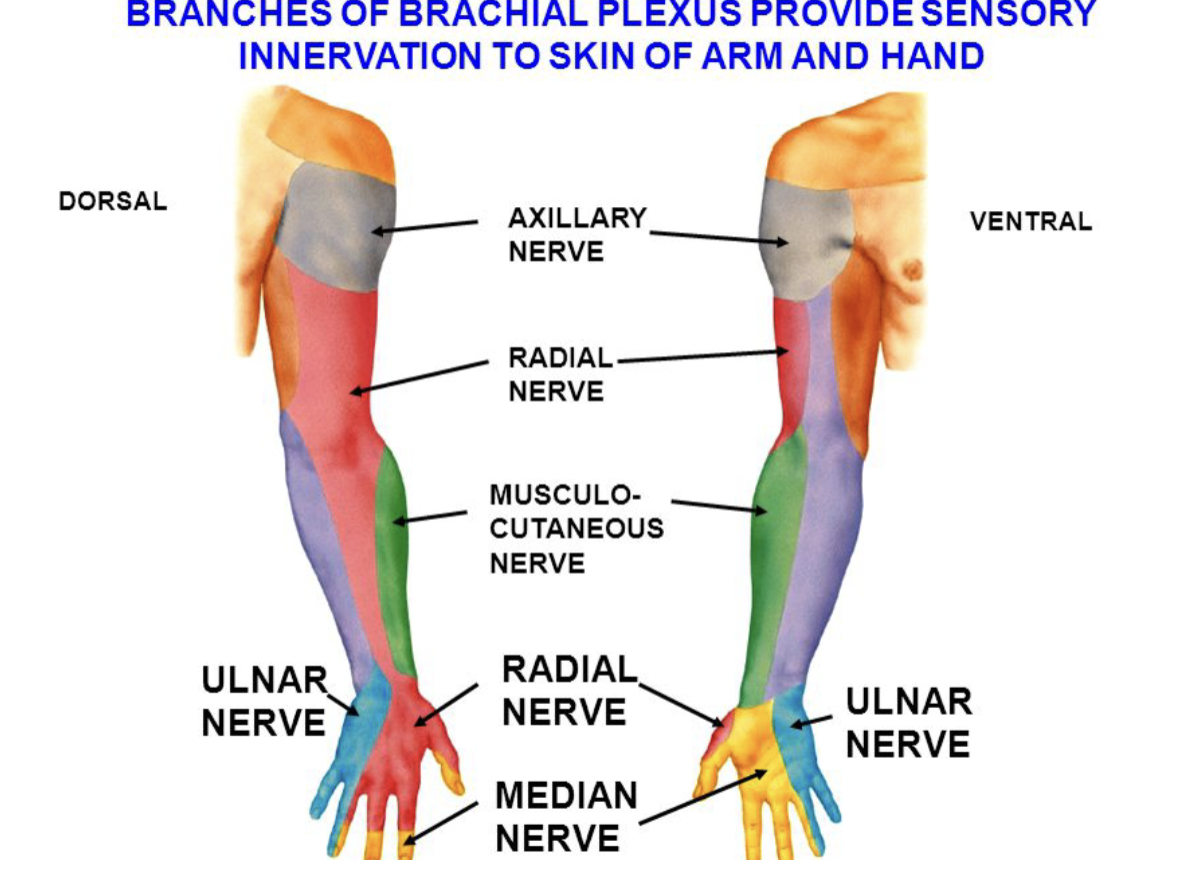
Musculotaneous nerve
Motor Function: Innervates the anterior compartment of the arm: biceps brachii, brachialis, and coracobrachialis.
Sensory Function: Provides sensation to the lateral forearm via the lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm.
Radial Nerve
Motor Function: Supplies the posterior compartments of the arm and forearm, including triceps brachii, extensor muscles of the wrist and fingers.
Sensory Function: Innervates the posterior arm, forearm, and dorsolateral hand.
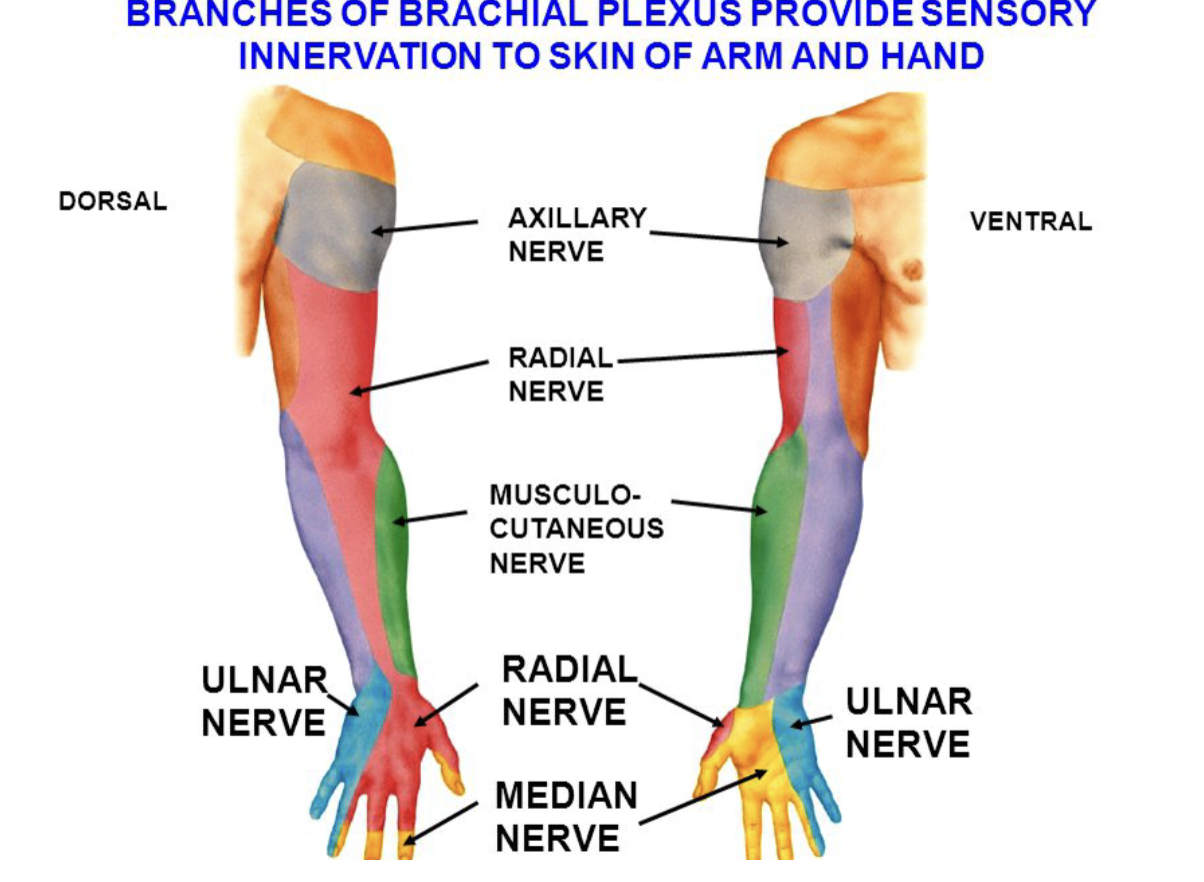
Median Nerve
Motor Function: Innervates most of the anterior forearm muscles (except flexor carpi ulnaris and part of flexor digitorum profundus) and thenar muscles in the hand.
Sensory Function: Provides sensation to the lateral palm and the palmar side of the thumb, index, middle, and half of the ring finger.
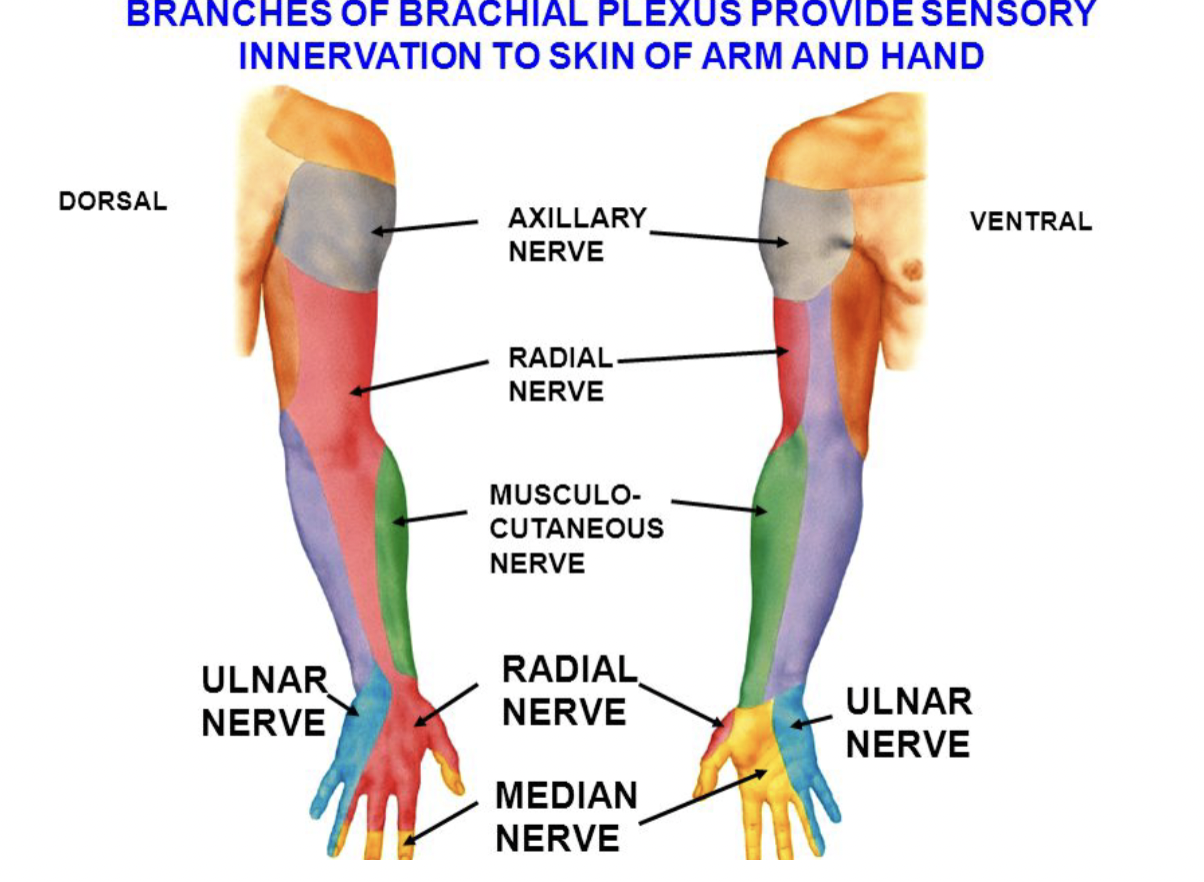
Ulnar Nerve
Motor Function: Supplies flexor carpi ulnaris, the medial part of flexor digitorum profundus, and most intrinsic hand muscles.
Sensory Function: Innervates the medial one and a half fingers on both palmar and dorsal sides.
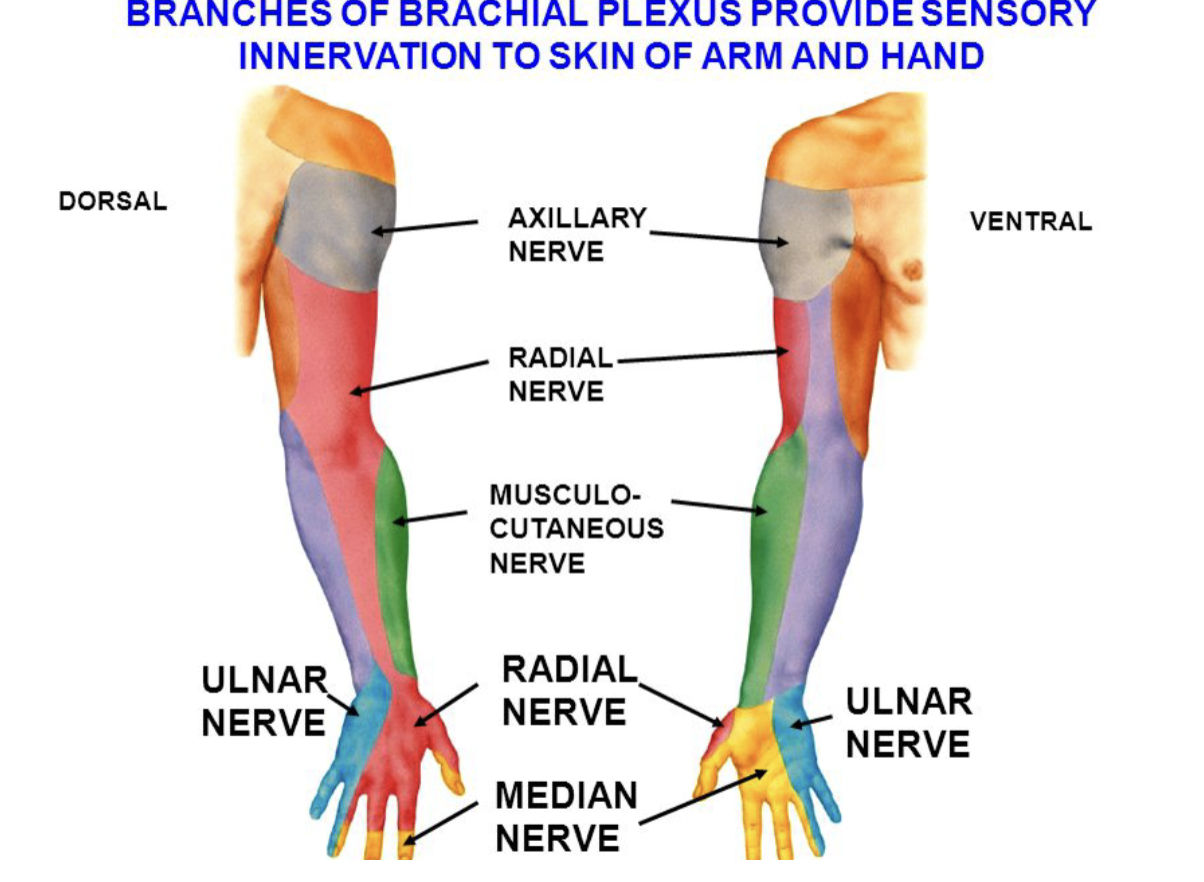
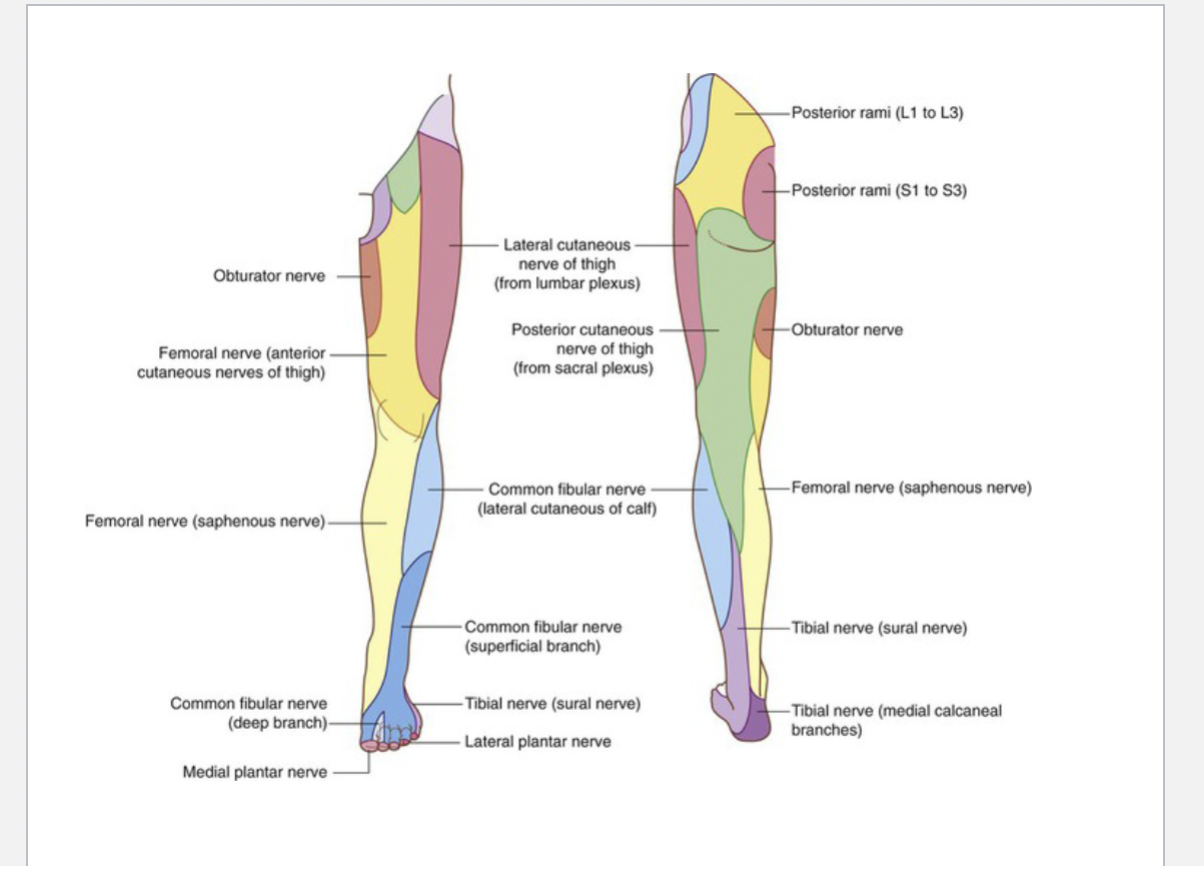
Femoral Nerve
Motor Function: Innervates the anterior thigh muscles, including quadriceps femoris, sartorius, and pectineus.
Sensory Function: Provides sensation to the anterior thigh and medial leg via the saphenous nerve.
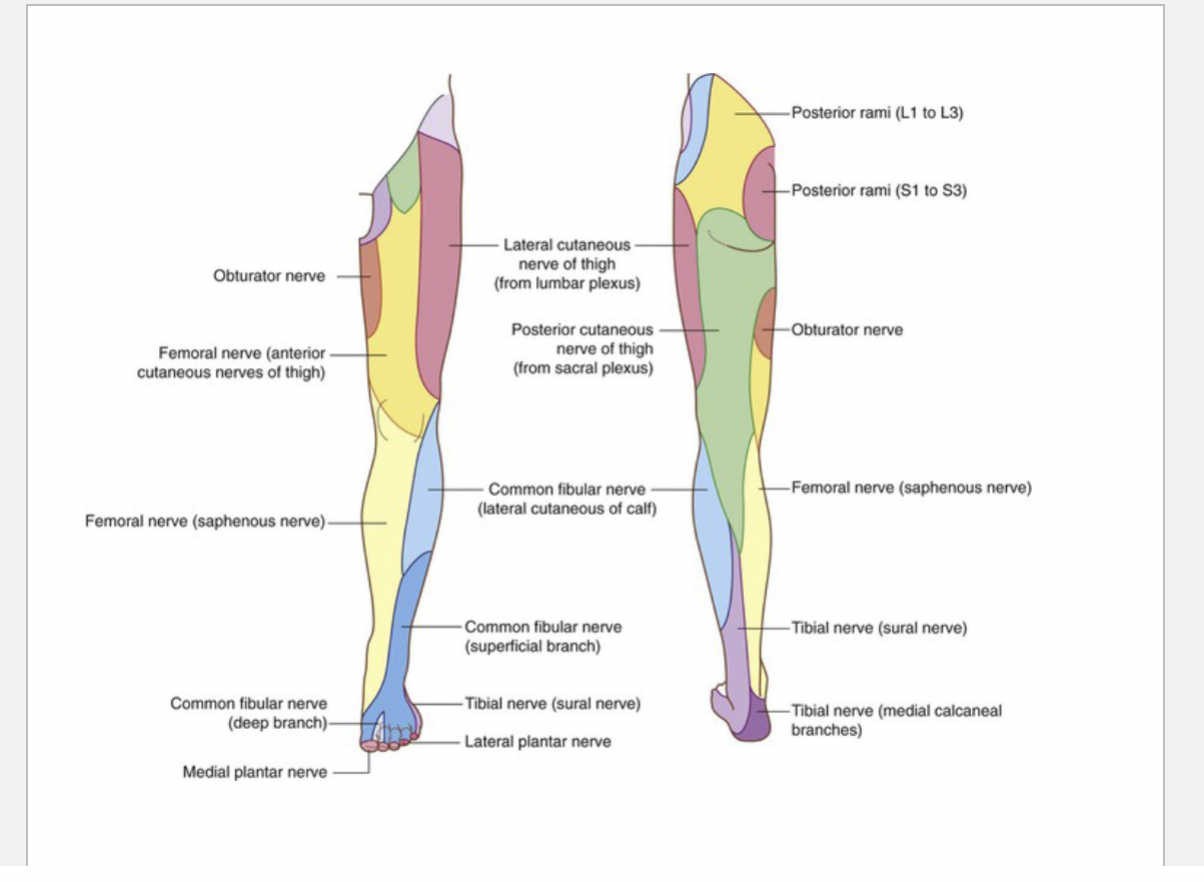
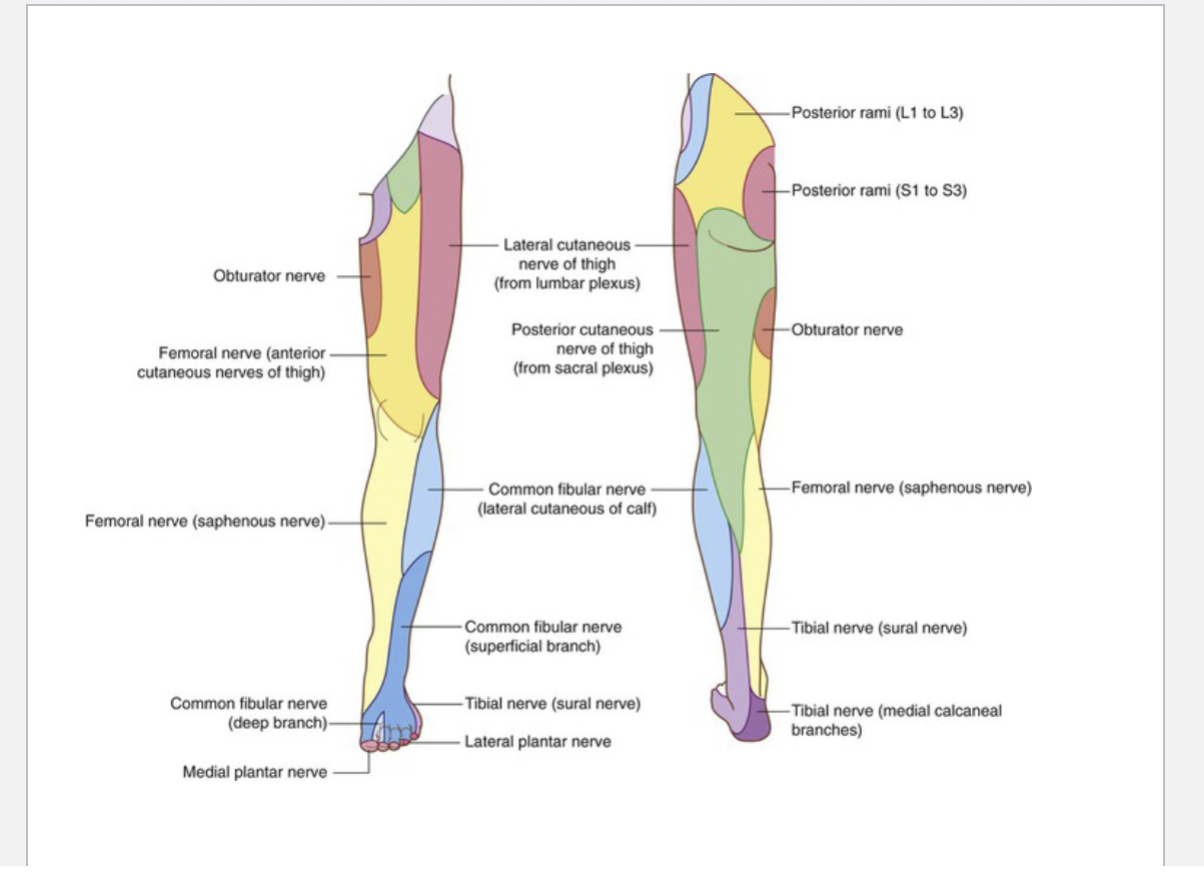
Sciatic Nerve
Motor Function: Innervates the posterior thigh muscles (hamstrings) and all muscles of the leg and foot via its branches.
Sensory Function: Provides sensation to the lateral leg and foot through its branches.
Tibial Nerve
Motor Function: Supplies the posterior compartment of the leg and the plantar muscles of the foot.
Sensory Function: Innervates the sole of the foot.
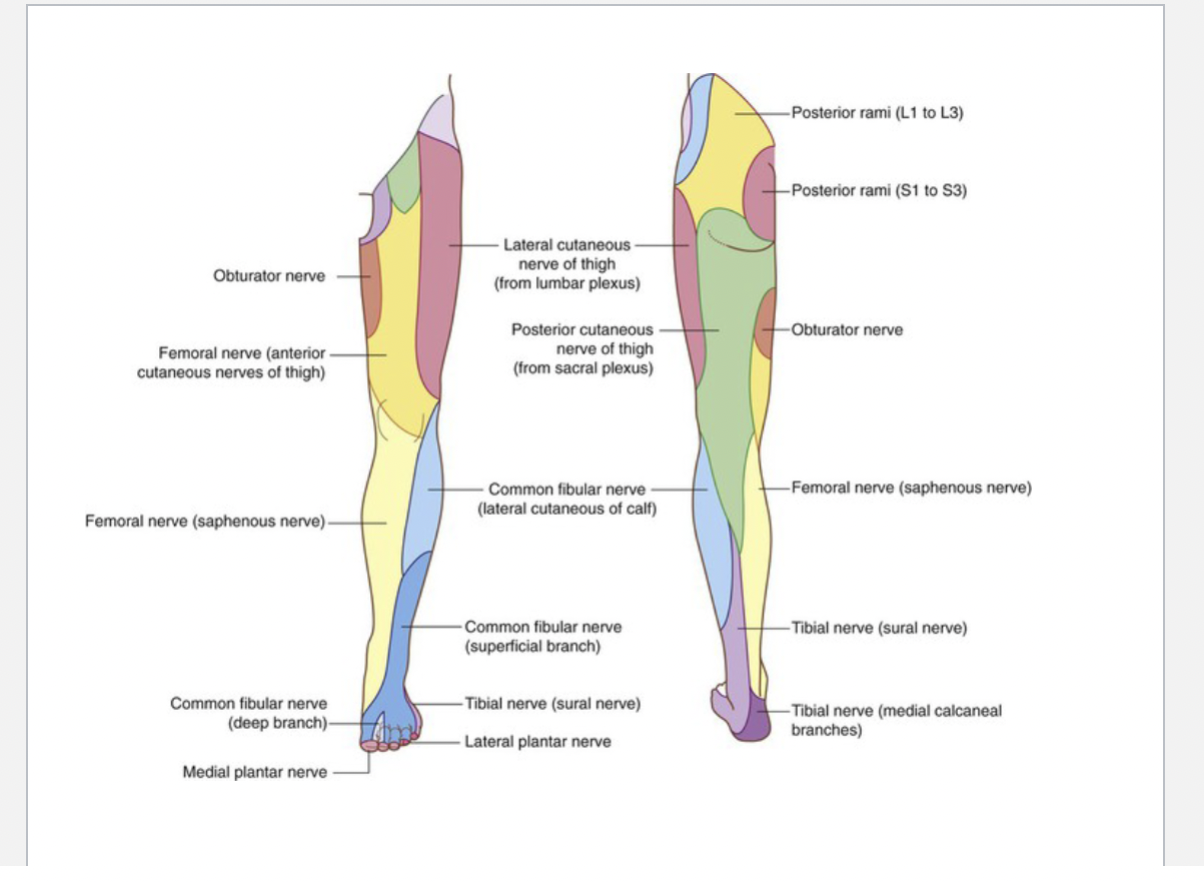
Common fibular nerve
Motor Function: Divides into:
Superficial Peroneal Nerve: Innervates the lateral compartment of the leg (fibularis longus and brevis).
Deep Peroneal Nerve: Supplies the anterior compartment of the leg (tibialis anterior, extensor muscles).