AP Precalculus Unit 1a
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Increasing
a < b
then f(a) < f(b)
Decreasing
a < b
then f(a) > f(b)
positive graph quality
if a graph is ______ it means all of it’s y values are above the y-axis
negative graph quality
if a graph is ______ it means all of it’s y values are below the y-axis
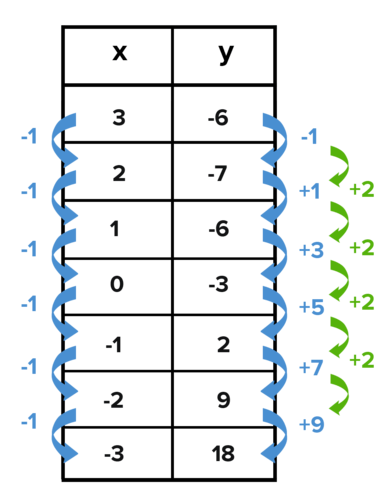
Determine if the table represents a linear function, quadratic function, or neither.
Quadratic; the average rate of change is changing at a constant rate
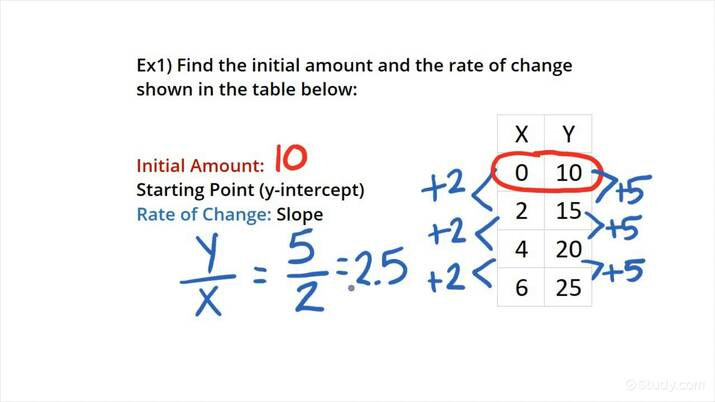
Determine if the table represents a linear function, quadratic function, or neither.
Linear; the average rate of change is constant
Concave up?
increasing rate of change
Concave down?
Decreasing rate of change
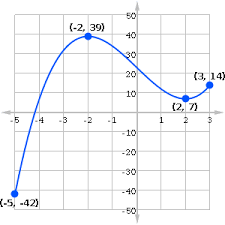
What is the Absolute Max?
-2
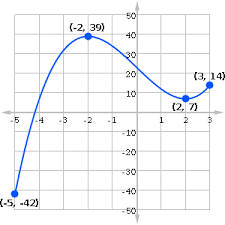
What is the Absolute Max value?
39
When does a point of inflection occur?
Occurs when a function changes from concave down to concave up OR from concave up to concave down.
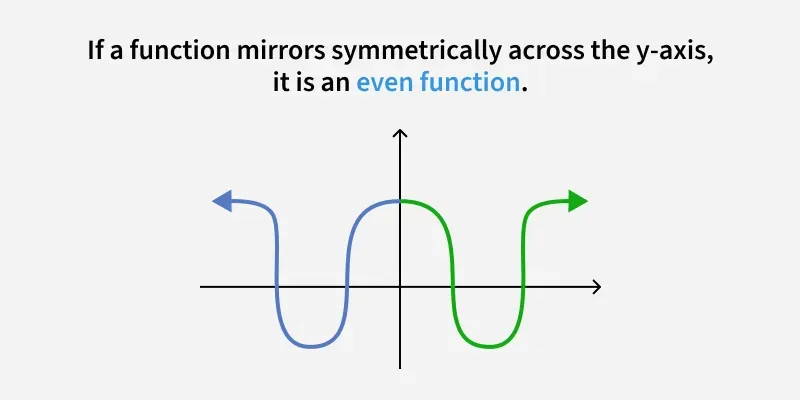
Determine whether the functions are even, odd, or neither
even, symmetric about the y-axis
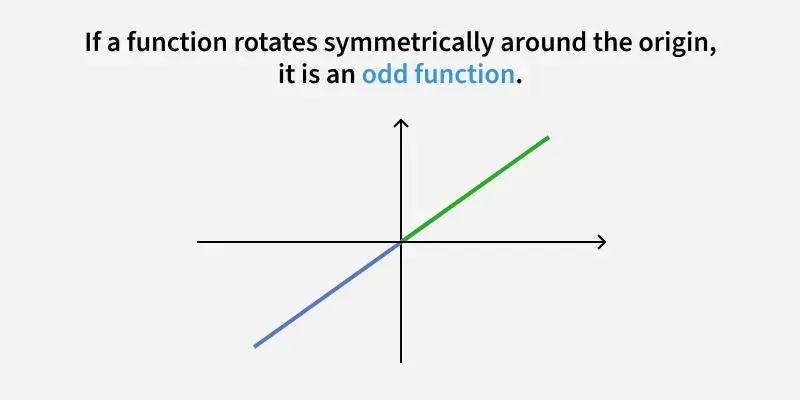
Determine whether the functions are even, odd, or neither
odd, symmetric about the origin
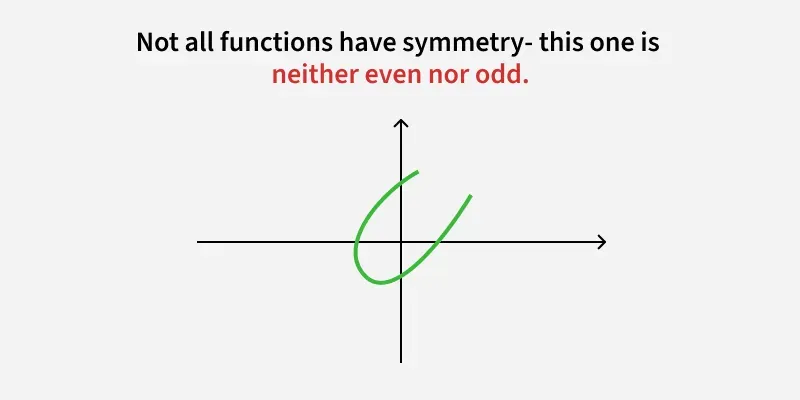
Determine whether the functions are even, odd, or neither
neither, the graph is not symmetric about the origin and is not symmetric across the y-axis.
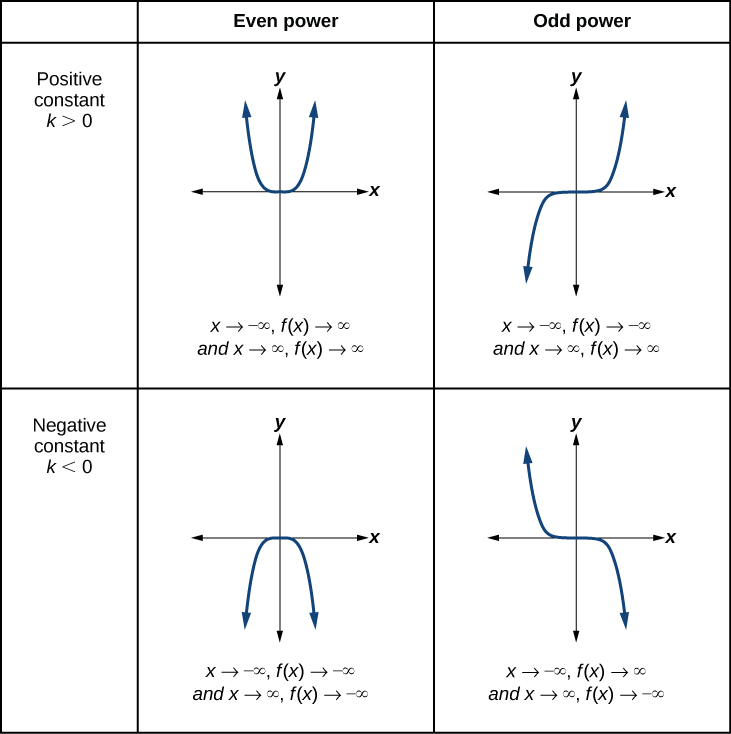
Explain the end behavior verbally for the top left graph
As the x values decrease without bound, the y values increase in that bound.
As the x values increase without bound, the y values increase in that bound.
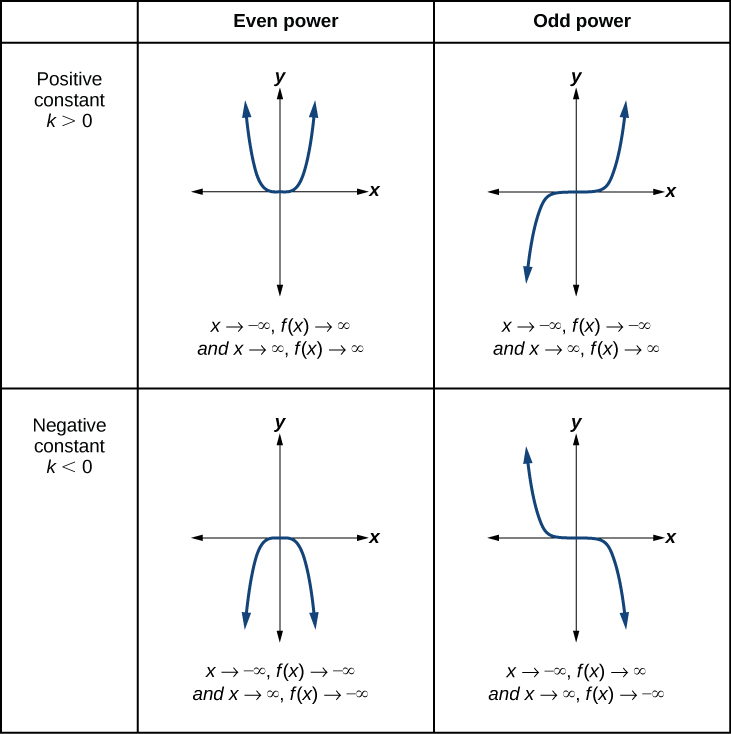
Explain the end behavior verbally for the top right graph
As the x values decrease without bound, the y values decrease in that bound.
As the x values increase without bound, the y values increase in that bound.
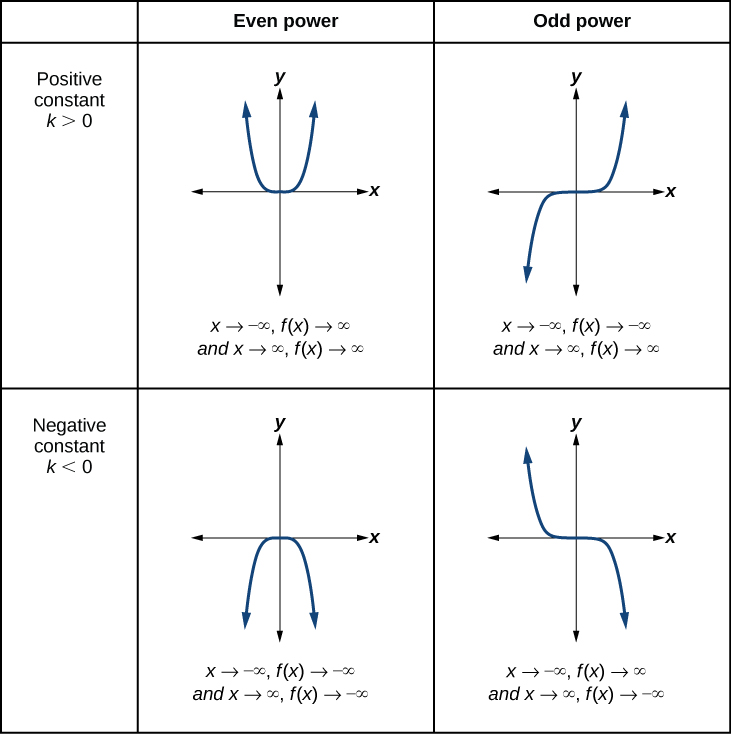
Explain the end behavior verbally for the bottom left graph
As the x values decrease without bound, the y values decrease in that bound.
As the x values increase without bound, the y values decrease in that bound.
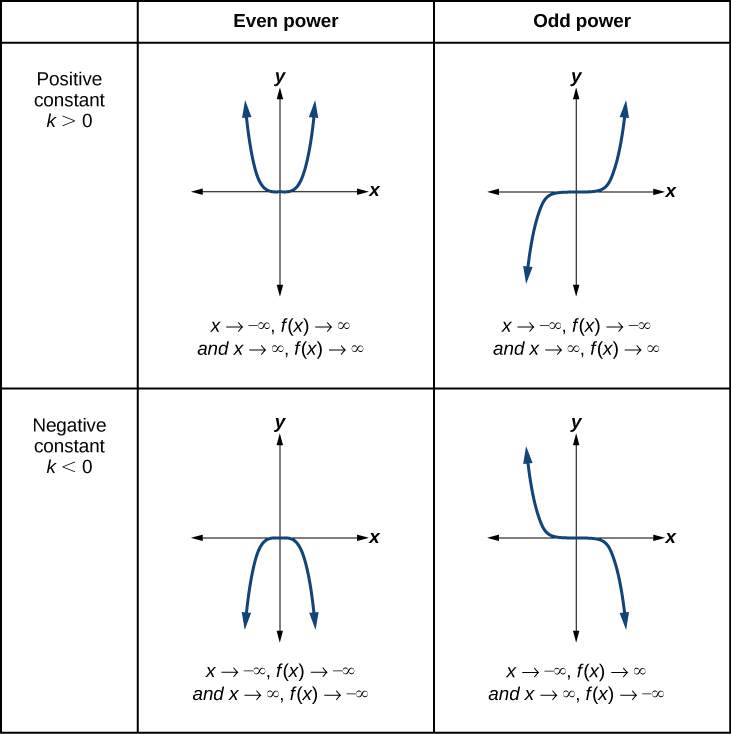
Explain the end behavior verbally for the bottom right graph
As the x values decrease without bound, the y values increase in that bound.
As the x values increase without bound, the y values decrease in that bound.
Table k(x) has a constant rate of change
Determine whether the function would be concave up, down, or neither over its domain.
k(x) is neither concave up or conave down because the rates of change are constant.
Fundamental Theorem of Algebra
A polynomial of degree n has exactly n complex roots when counting multiplicities.