Exam 2: Chapter 11 and 12
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
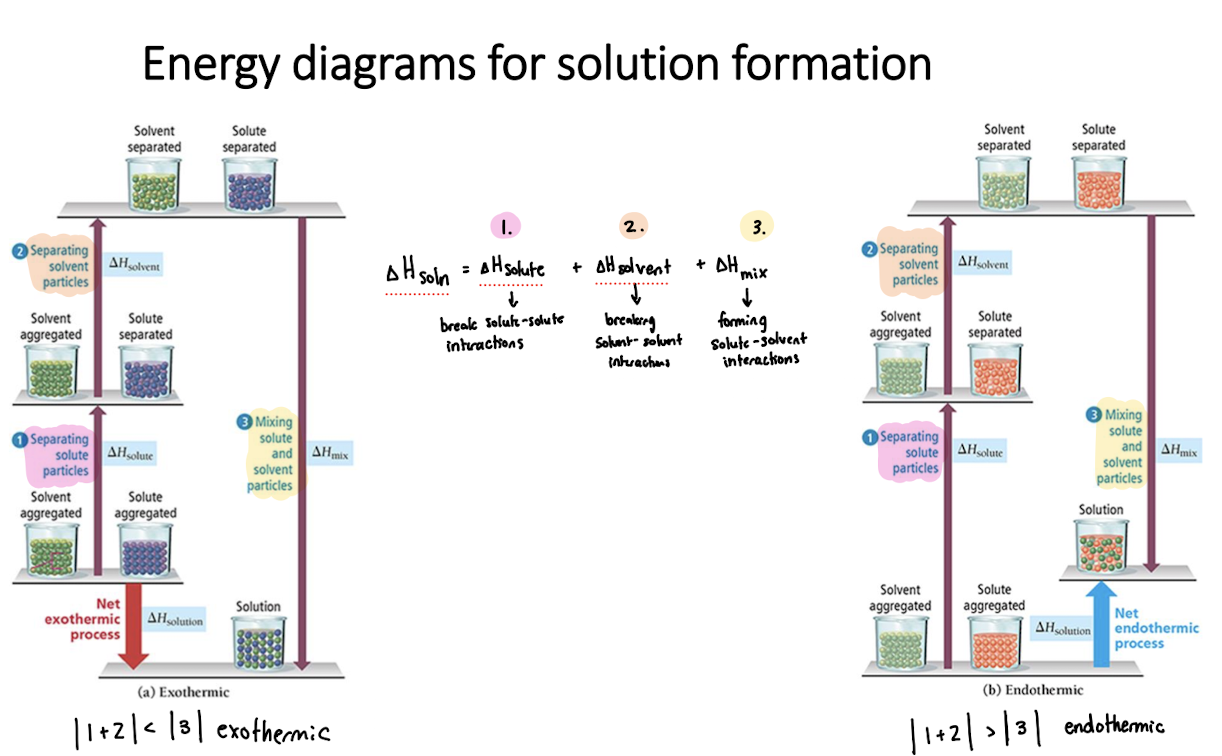
If solvent-solute interactions > solvent-solvent and solute-solute interactions
ΔHsoln< 0 (exothermic)
Solution forms
If solvent-solute interactions = solvent-solvent and solute-solute interactions
ΔHsoln = 0
Solution forms
If solvent-solute interactions < solvent-solvent and solute-solute interactions
ΔHsoln > 0 (endothermic)
Solution may form
ΔHsoln=
break solvent-solvent interactions (endo) + break solute-solute interactions (endo) + form solute-solvent interactions (exo)
DRIVING FORCE IS ENTROPY
Entropy
measurement of matter or energy dispersal in a system
more arrangements, more entropy
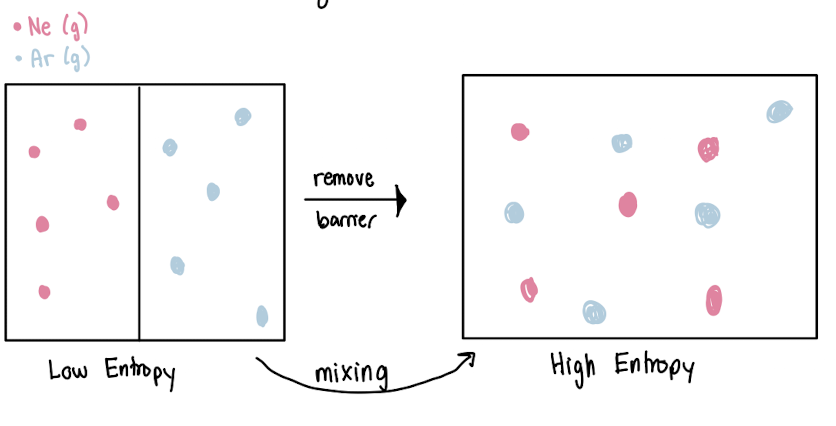
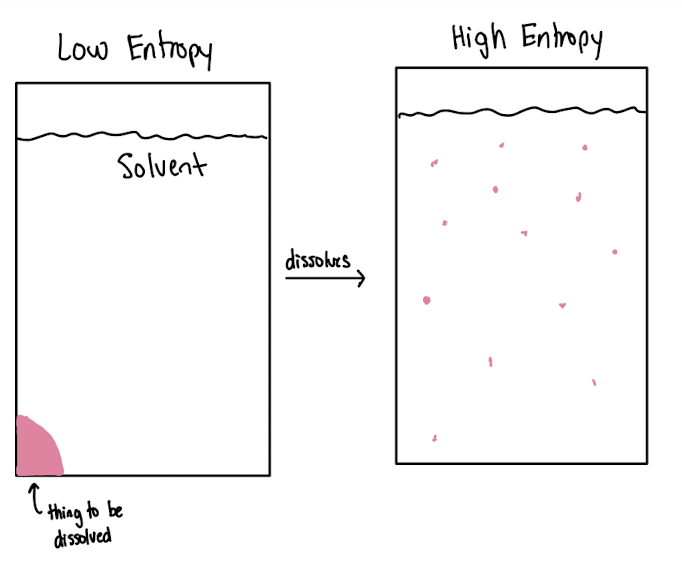
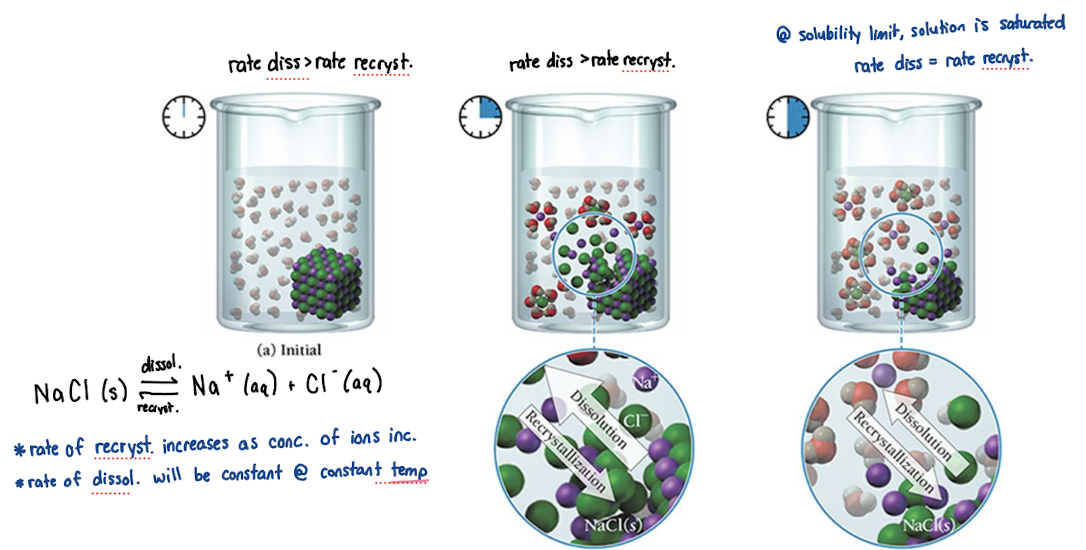
solubility
maximum amount of solute able to be dissolved in a solvent under given conditions
solubility = max amt of solute / amt solvent
unsaturated solution
concentration < solubility
rate dissolution > rate of recrystallization
saturated solution
concentration = solubility
rate dissolution = rate of recrystallization
oversaturated solution
concentration > solubility
rate dissolution < rate recrystallization
miscible
mix in any ratio (no solubility limit)
solubility: gases with gases
always miscible
solubility: liquids with liquids
like dissolves like (in terms of polarity)
concentration
amt solute / amt solution
molarity: mol/L
mass %: mass/mass x 100%
mole fraction: moles/total moles
Energy diagrams for solution formation
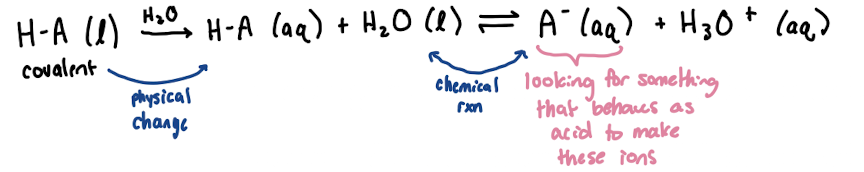
Dissolution of Ionic and Covalent Compounds
Ionic: dissociate into individual ions which are surrounded by solvent
Covalent: dissolve as whole molecules (not breaking covalent bond)
electrolyte
ions in solution conduct electricity (produce ions when put in water)
ionic species and dissolves —> strong electrolyte
strong electrolyte
100% of products form
weak electrolyte
< 100% of products form
non-electrolyte
no products form (aka pathetic)
some molecular solutes form ions by reacting
Solution equilibrium
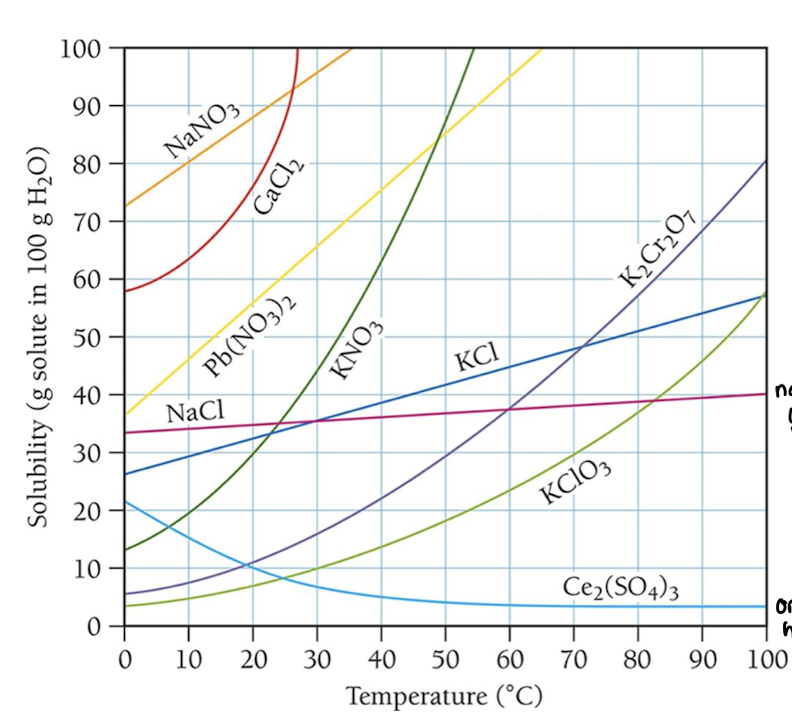
solubility curves for solids
solubility of a substance v. temperature
With Increased Temperature:
increased rate of dissolution (by a lot)
increased rate of recrystallization (by a smaller factor)
so, solubility typically increases for solids at higher temperatures
temperature dependence of solubility of gases in water
increase of temperature, decrease of solubility
With Increased Temperature:
increased rate of dissolution (by a smaller factor)
increased rate of gas bubbling out (by a lot!)
so, solubility typically decreases for gases at higher temperatures
impact of temperature on solubility of solids v. gas

pressure dependence of solubility of gases in water
(refers to the partial pressure of that gas above water: not dependent on pressures of other gases)
as pressure of that gas increases, solubility increases (more will end up dissolves in the water)
Henry’s Law
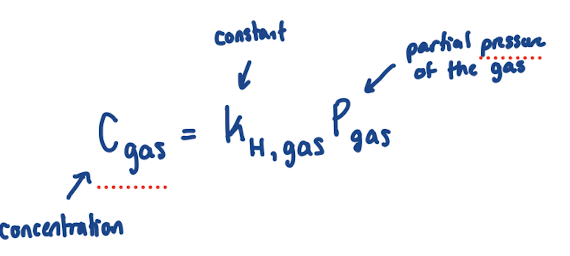
Concentration: molarity of gas in aqueous solution
Pgas: pressure of gas above liquid
molarity (M)
moles solute / L solution
molality (m)
moles solute / kg solvent
mole fraction (x)
moles solute / moles solution
(then multiply this by 100% for mole percent)
colligative properties
Nothing to do with the identity of the solute, only dependent on the amount
Boiling Point Tb
Freezing Point Tf
Vapor Pressure (Pvap)
Osmotic Pressure
Freezing Point Depression: ΔTf=
i x m x kf
i: Van’t Hoff Coefficient (for electrolytes), moles of particles formed in solution / moles solute added
m: molality of particles
kf : freezing point constant (unique to the solvent)
Boiling Point Elevation: ΔTb=
i x m x kb
i: Van’t Hoff Coefficient (for electrolytes), moles of particles formed in solution / moles solute added
m: molality of particles
kb : boiling point constant (unique to the solvent)
Equation for vapor pressure after dissolution of a compound (when solutes are nonvolatile)
Pvap, soln = xsolvP°vap,solv
xsolv: mole fraction (aka how much of the surface is still solvent particles)
P°vap,solv : vapor pressure of pure solvent
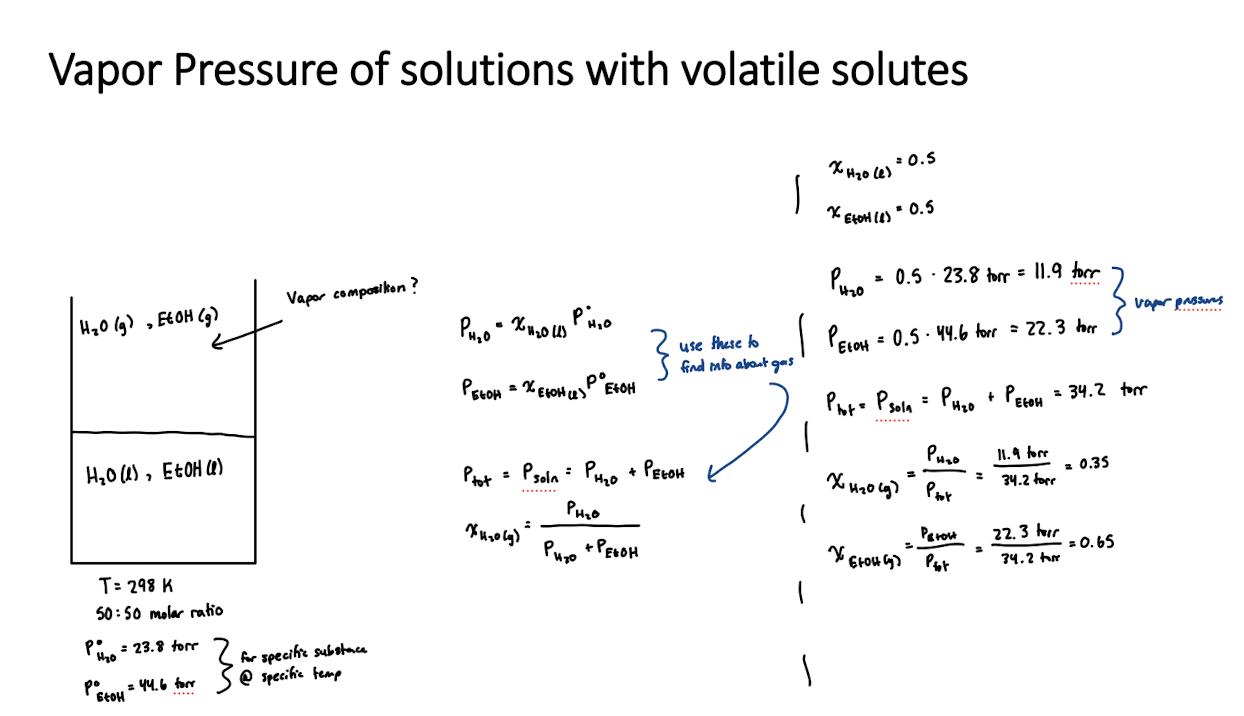
Equation for vapor pressure after dissolution of a compound (when solutes are volatile)
This means that evaporation of solute must be accounted for!
Pvap, soln = xAP°vap,A + xBP°vap,B
same as Ptot = PA + PB
Osmotic Pressure
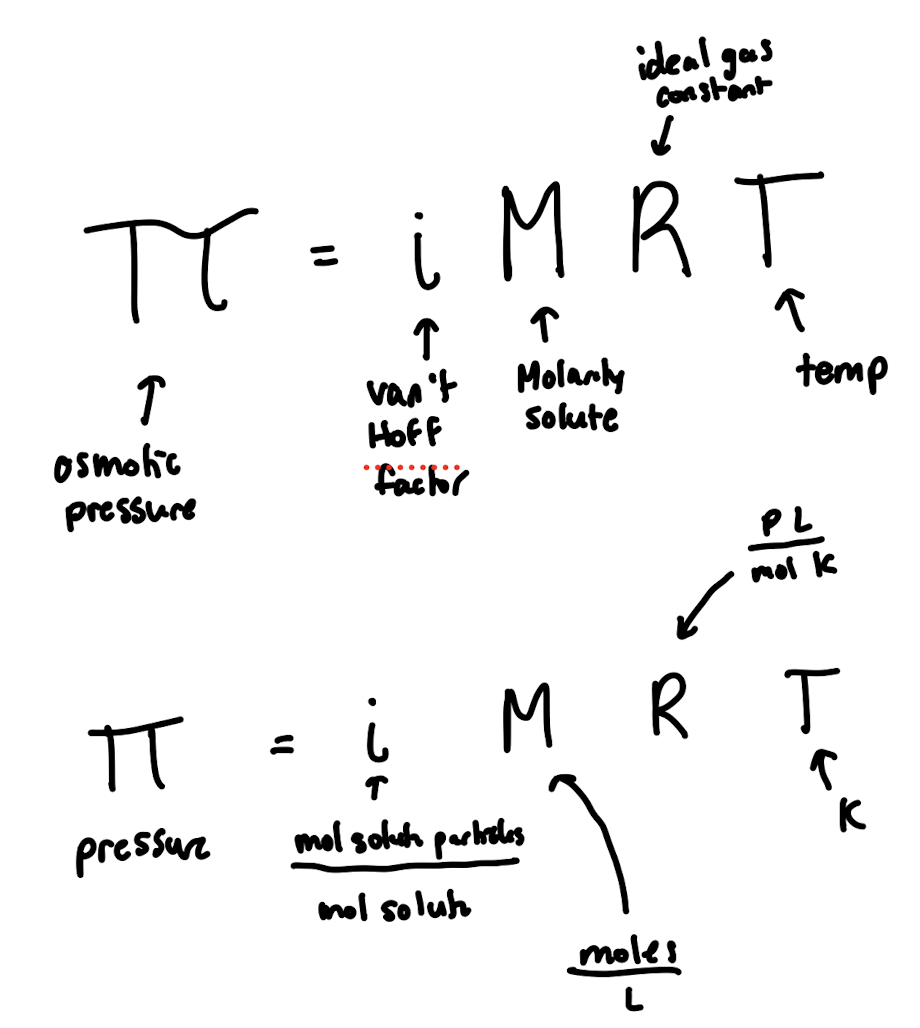
Important Equations to Consider with Ch. 11 Questions
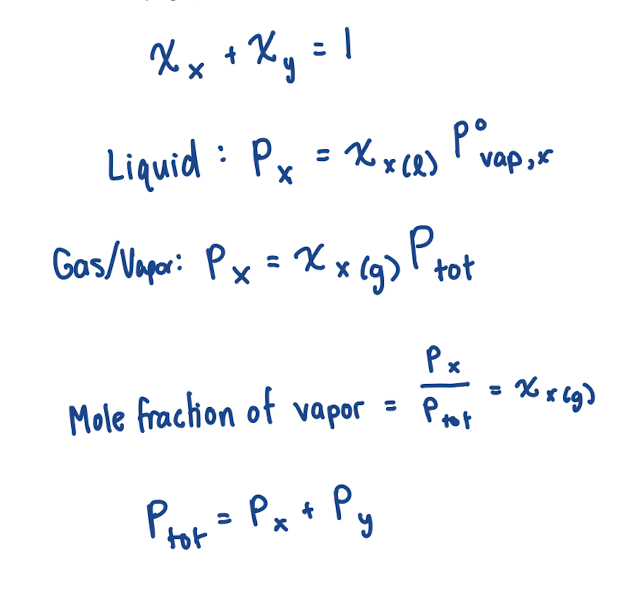
Equation for average rate of consumption or production of a substance, A
Δ[A] / Δt
NOT ON EQUATION SHEET: For aA + bB —> cC + dD, the Rate of the Reaction =
Rate= -1/a Rate A = -1/b Rate B = 1/c Rate C = 1/d Rate D
Rate of Reaction is NEVER regative
Higher concentration = ______ Rate
Higher Rate: since things have to collide for a reaction to occur and things are more likely to collide at higher concentrations
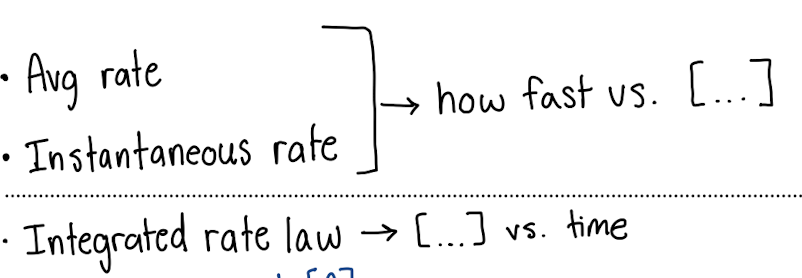
Differential rate laws tell us about
rate versus concentration
instantaneous rate (rate at some specific time)
Equation for differential rate law
Raterxn= k [A]x[B]y
k: rate constant
x: order of reaction with respect to [A]
y: order of reaction with respect to [B]
x and y are NOT determined by stoichiometric coefficients
Found using experimental data
units for k for zero order reaction
M/s
units for k for first order reaction
1/s
units for k for second order reaction
1/Ms
What do Avg Rate and Instantaneous Rate tell you vs. Integrated Rate Law?
Integrated Rate Law for Zeroth Order Reaction

Integrated Rate Law for First Order Reaction

NOT ON EQUATION SHEET: Alternate (Exponential) Form of Integrated Rate Law for First Order Reaction
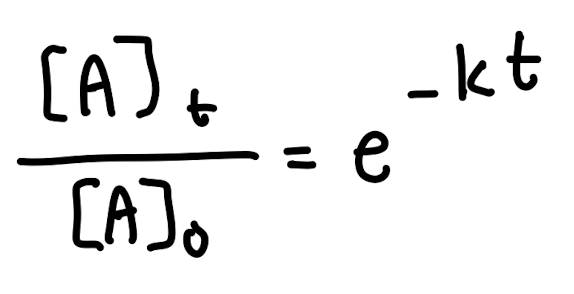
Integrated Rate Law for Second Order Reaction
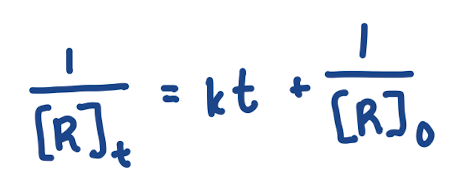
Calculate Half life (for first order reactions)
t1/2= ln2 / k
or k = ln2 / t1/2
Fundamental Relation for Half-Life
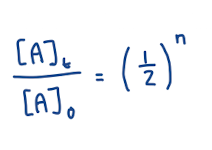
n: number of half lives
Can calulate n by doing t / t1/2
aka time divided by how much time is considered one half life
[A]0: initial concentration, you can choose if told substance has decayed by _%
A graph shows the correct order for a reaction if the data is _____
linear
then slope can be used to determine k