Elasticity
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Price Elasticity of Demand ε
a measure of the responsiveness of quantity demanded to changes in the price
Always going to have a negative value
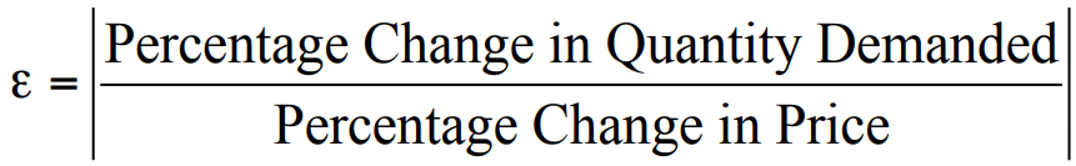
What is Demand when ε > 1?
elastic - consumers fairly responsive to a price change
a small increase in price will decrease quantity demanded by a relatively large amount
an increase in price decreases total revenue
sometimes called a luxury good
What is Demand when ε < 1?
inelastic - consumers fairly unresponsive to a price change
a large increase in price will decrease quantity demanded by a relatively small amount
an increases in price increases total revenue
What is Demand when ε = 1?
unit elastic
What determines the Elasticity of Demand?
Substitutes - if there are no substitutes there is inelastic demand
Perfect Elastic Demand
even the slightest increase in price leads consumers to switch to substitutes
e.g. chewing gum at supermarket till

Perfect Inelastic Demand
consumers can’t switch to substitutes or stop buying when price increases
e.g. life saving drugs - no good substitute
Determinants of ε
The availability of close substitutes
The availability of close substitutes
Share of the budget
What proportion of your budget do you spend on the good in question
Time to adjust
In the short run, consumers may have a difficult time altering their behaviour, in the long run, behavioural changes are easier (e.g. responsiveness to petrol price changes)
Addiction/Habitual
Goods that are addictive tend to be more inelastic
Arc and Point Price Elasticity
the price elasticity of demand between 2 points on the demand curve
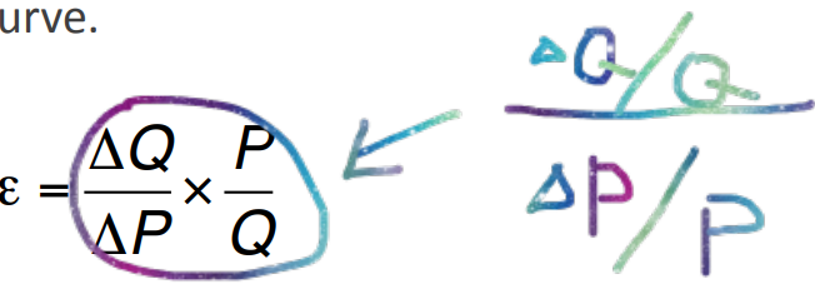
Point Price Elasticity
provides a measure of the elasticity of demand at a particular point on the demand curve
PPE Formula
If we take ΔP to be very small, then the slope of the demand curve at some point is ΔP/ΔQ
So f demand at the point A is:
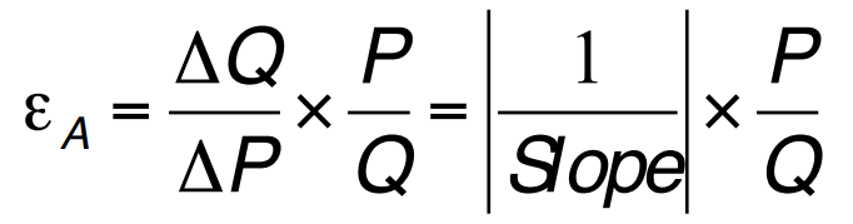
Cross-Price Elasticity of Demand
The percent change in quantity demanded of that good, in response to a 1% change in price of another good
Can be positive or negative:
Positive if substitutes
Negative if complements
Income Elasticity of Demand
The percentage change in quantity demanded associated with a 1% change in consumer income
Describes how responsive demand is the income changes
Positive for normal goods
Its negative for inferior goods
Price Elasticity of Supply
Measures sellers sensitivity to changes in price
E = price change in quantity supplied / percentage change in price
Determinants of Supply Elasticity
Flexibility of inputs
Mobility of inputs
Ability to produce with substitute=ute inputs
Time