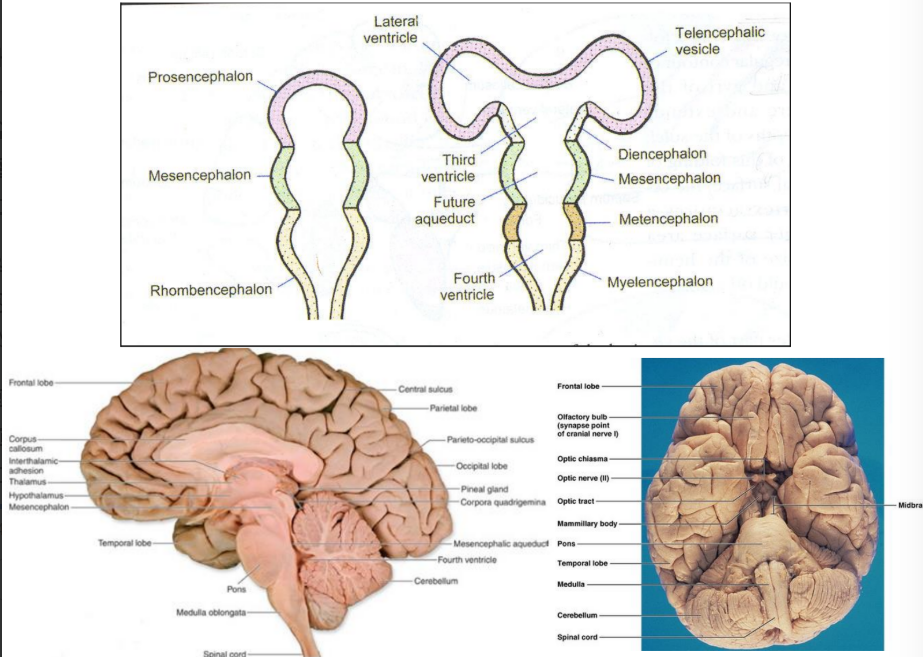
Midbrain
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Features of the midbrain
Connects the pons and cerebellum with the forebrain
Traverses the tentorial notch
Lies in the posterior cranial fossa and overlaps with the parahippocampal gyrus
Cerebral aqueduct communicates the third ventricle with the fourth
Develops from the mesencephalon
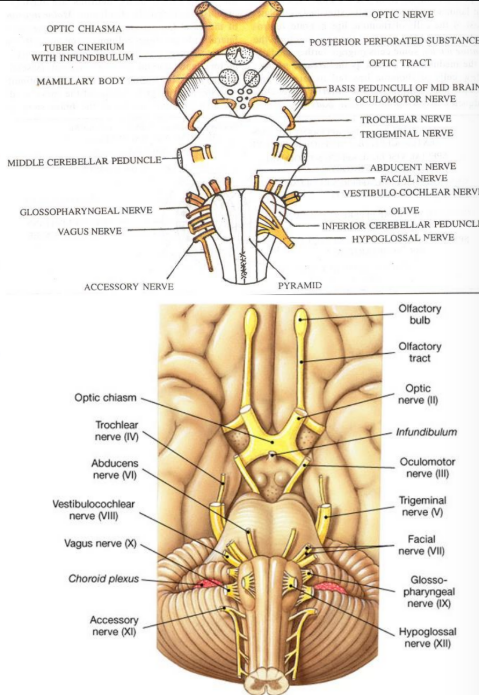
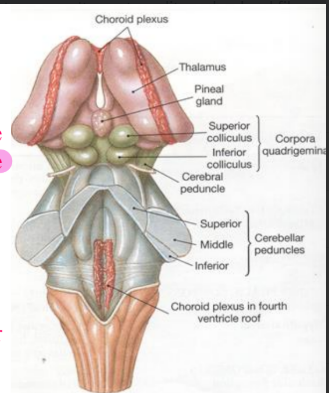
External features of the midbrain
Crura cerebri
Extends from the cranial border of pons to the undersurface of the cerebral hemisphere
Forms posterolateral boundary of the interpeduncular fossa
Medial sulcus separates the crus cerebri from the interpeduncular fossa
Ventral surface crossed by:
Optic tract
Posterior cerebral artery
Superior cerebellar artery
Teniae pontis
Oculomotor and trochlear nerves pass through pontine branches and superior cerebellar artery
Dorsal surface presents:
Superior and inferior colliculus
Pineal gland
Superior medullary velum
Colliculi separated by cruciform sulcus
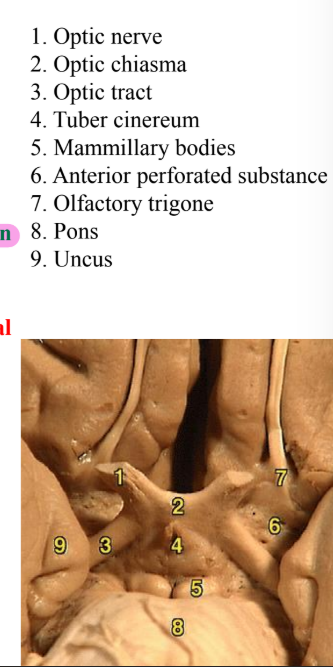
Interpeduncular fossa
Anteriorly- optic chiasma
Anterolaterally- optic tracts
Posterolaterally- crus cerebri
Posteriorly- cranial border of pons
Laterally overlapped by parahippocampal gyrus
Floor presents:
Infundibulum
Tuber cinereum
Median eminence
Mamillary bodies
Posterior perforated substance
Colliculi of midbrain
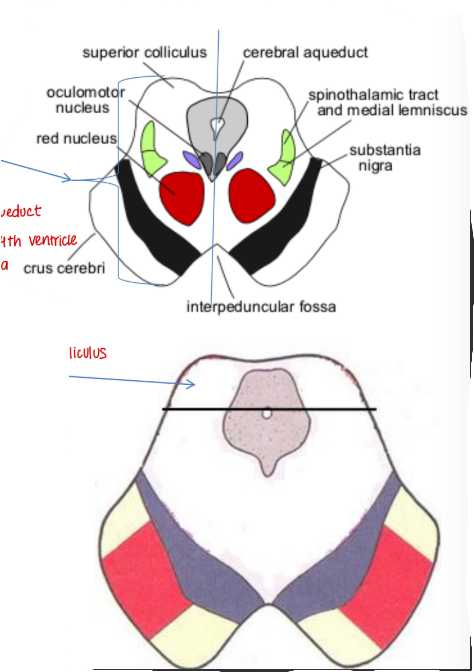
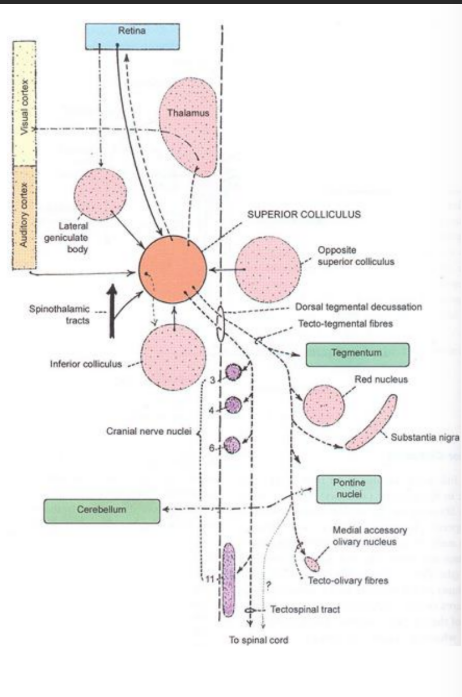
Superior colliculus
Larger and darker than inferior
Concerned with optic senses
Connected to lateral geniculate body
Inferior colliculus
Smaller but more prominent
Concerned with auditory senses
Connected to medial geniculate body
Internal structure
Demarcated into:
Ventral crus cerebri
Substantia nigra
Dorsal tegmentum
Tectum
Studied at the level of:
At the level of superior colliculus
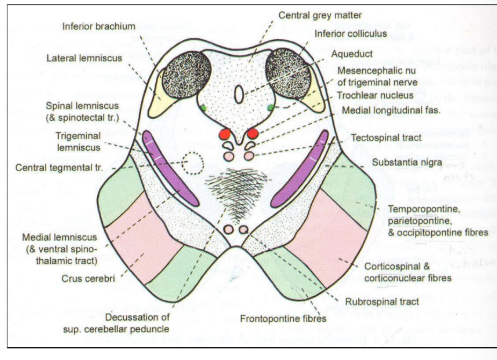
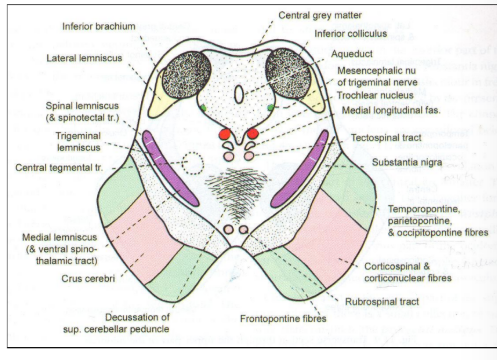
At the level of inferior colliculus
*Tegmentum differs but crus cerebri remains the same
Crus cerebri
Contains:
Corticospinal fibres
Corticonuclear fibres
Corticopontine fibres
Frontopontine fibres (medial 1/6)
Temporoponitne, parietopontine and occipitopontine (lateral 1/6)
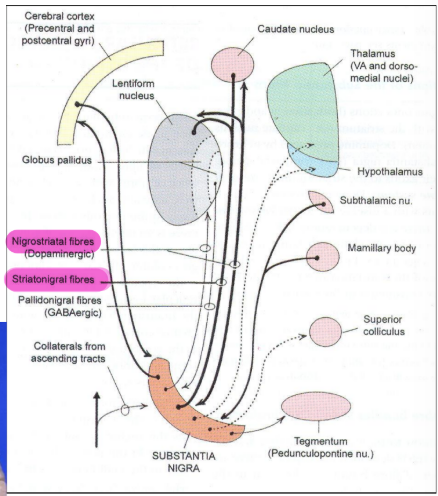
Substantia nigra
Pigmented sheet of multipolar motor neurons associated with the production of dopamine
Extends from the cranial border of the pons to the subthalamic region
Divided into:
Dorsal pars compacta (rich in melanin, cells small)
Ventral pars reticularis (rich in iron, larger cells)
Pars lateralis insignificant in man
Afferents
Nigro-stiratal fibres from putamen and caudate nucleus which convey GABA to the pars reticularis
Also connected to the cerebral cortex, hypothalamus, subthalamus, spinal cord, thalamus (VA, VL, DM nucleus)
FUNCTION: Help in smooth and skillful performance of voluntary movements
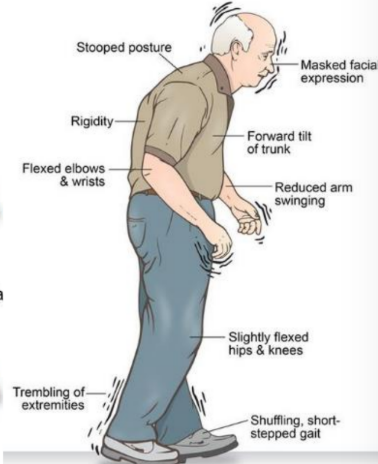
Parkinson’s disease
Dopamine levels of the substantia nigra and corpus striatum dramatically decrease

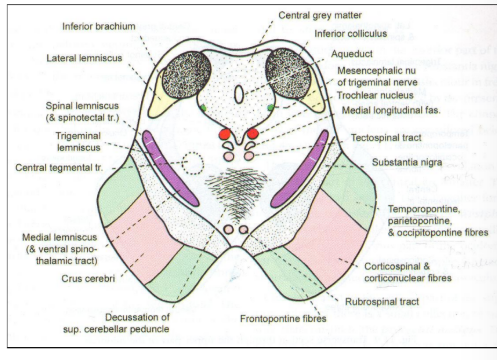
Tegmentum at the level of the inferior colliculus
Trochlear nerve nucleI
Nucleus extends throughout the caudal half of the midbrain
Fibres pass dorsally to mesencephalic nucleus of V
Thinnest cranial nerve and only one that exits from the dorsal aspect
Only nerve that decussates before its target (expect optic)
Mesencephalic nucleus of trigeminal nerve
Extends from main sensory nucleus of pons
Cells of pseudounipolar
Mesencephalic nucleus receives proprioceptive sensation
Chief nucleus receives touch and pressure
Spinal nucleus receives pain and temperature
Decussation of superior peduncle
Efferents derived from dentate, globose and emboliform nucleus
After decussation divide into ascending and descending fibres
Ascending fibres terminate in VL nucleus and red nucleus (uncrossed end at midbrain and periaqueductal gray matter)
Descending fibres terminate at reticular nuclei of pons and inferior olivary complex
Also present:
Rubrospinal tract
Tectospinal tract
Median longitudinal fasciculus
Medial lemniscus
Lateral lemniscus (ends at inferior colliculus)
Trigeminal lemniscus
Spinal lemniscus
Tegmentum at the level of the superior colliculus
Oculomotor nucleus
Red nucleus
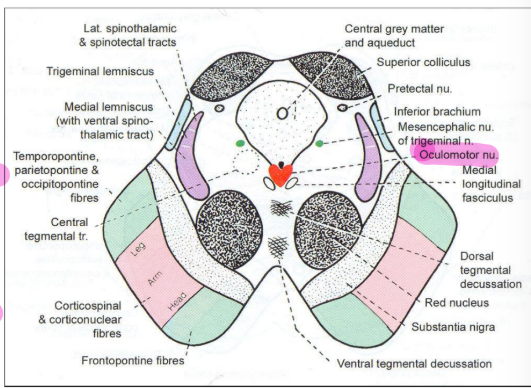
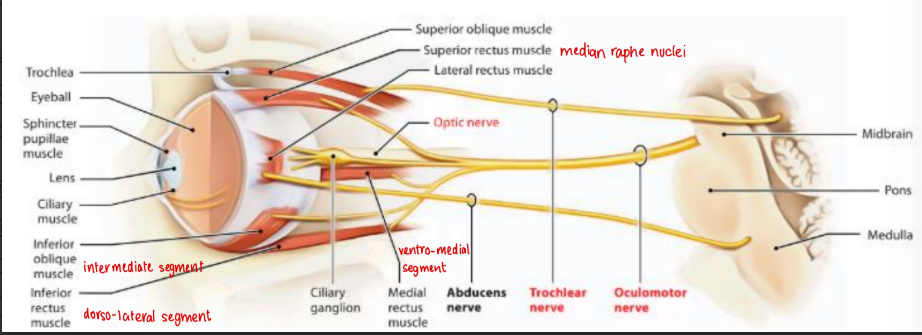
Occulomotor nucleus
Consists of somatomotor and visceromotor nuclei (Edinger Westphal)
Dorsolateral segment supplies inferior rectus
Intermediate segment supplies inferior oblique
Ventromedial segment supplies medial rectus
Cuadal centre supplies levator palpebrae superioris
Median raphe nucleus supplies superior rectus
Nucleus of Darkschewitsch is an accessory nucleus that is concerned with eye movements and reflex gaze movements
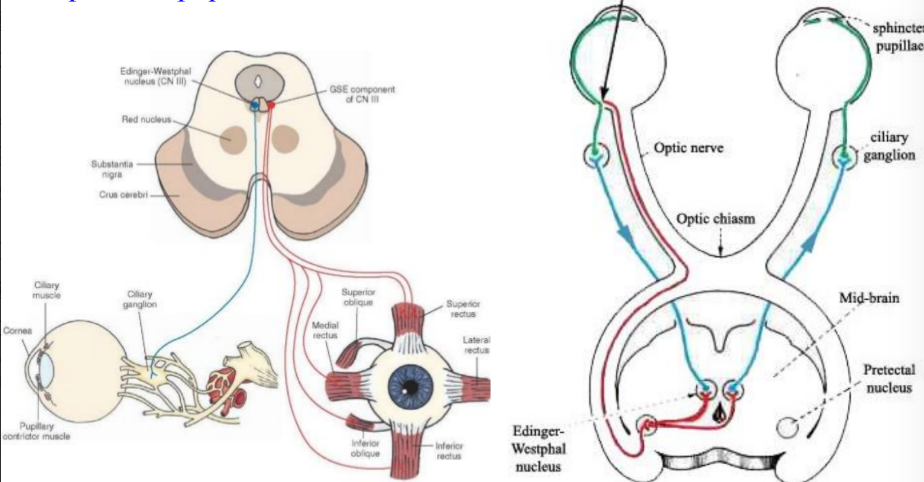
Edinger Westphal nucleus concerned with parasympathetic supply of ciliaris and sphincter pupillae
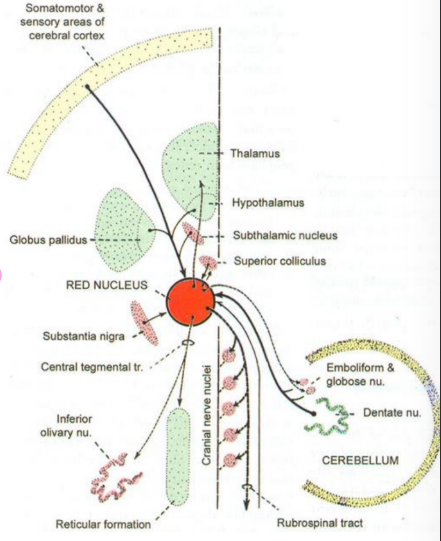
Red nucleus
Ovoid mass containing iron
Contains mostly multipolar cells
Made up of caudal pars magnocellularis and cranial pars parvocellularis
Afferents
Cerebellorubral (contralateral dentate, emboliform and globose)
Corticorubral (ipsilateral from area 4&6)
Pallidorubral (globus paliidus)
Tectorubral (superior colliculus)
Efferents
Rubrospinal
Rubrobulbar
Rubro-reticular fibres
FUNCTION: Forms a prominent and important motor nucleus concerned with the maintenance of posture and muscle tone
Tectum of midbrain
Situated dorsal to the aqueduct
Consists of inferior and superior colliculus
Colliculi derived from dorsal lamina of the periaqueductal gray matter
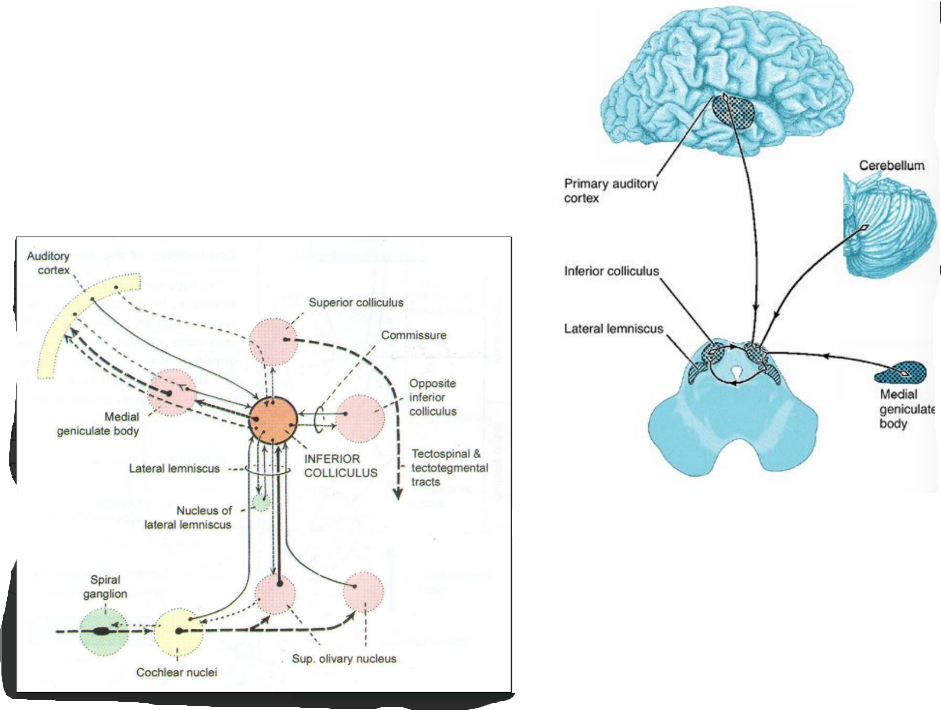
Inferior colliculus
Connected to the medial geniculate body
Afferents
Lateral lemniscus
Contralateral inferior colliculus
Medial geniculate body
Efferents
Medial geniculate body
Opposite inferior colliculus
To cerebellum as tectocerebellar fibres
Ipsilateral superior colliculus
Superior olivary nucleus and cochlear nuclei
FUNCTION: Acts as relay nucleus of auditory pathway
Superior colliculus
Connected to the lateral geniculate body
Afferents
Retinotectal fibres
Corticotectal fibres (to visual asscoiation areas)
Spinotectal fibres
Inferior colliculus
Efferents
Tectospinal
Tectobulbar (to oculomotor, abducens and trochlear)
Few tectothalamic
FUNCTION: Reflex and integrating centre of visual system
Pretectal nucleus
Receives fibres from the optic tract
Concerned with the pupillary light reflex
Reticular formation
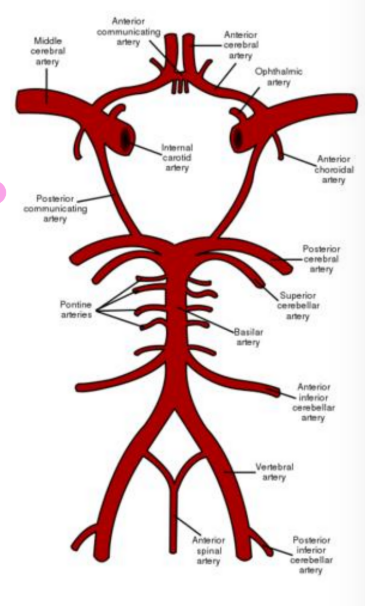
Blood supply of midbrain
Posterior cerebral artery and superior cerebellar artery (branches of basilar artery)
Direct branches from basilar artery
Branches of posterior communicating
Branches from anterior choroidal artery
Venous drainage
Into great cerebral vein and basal vein
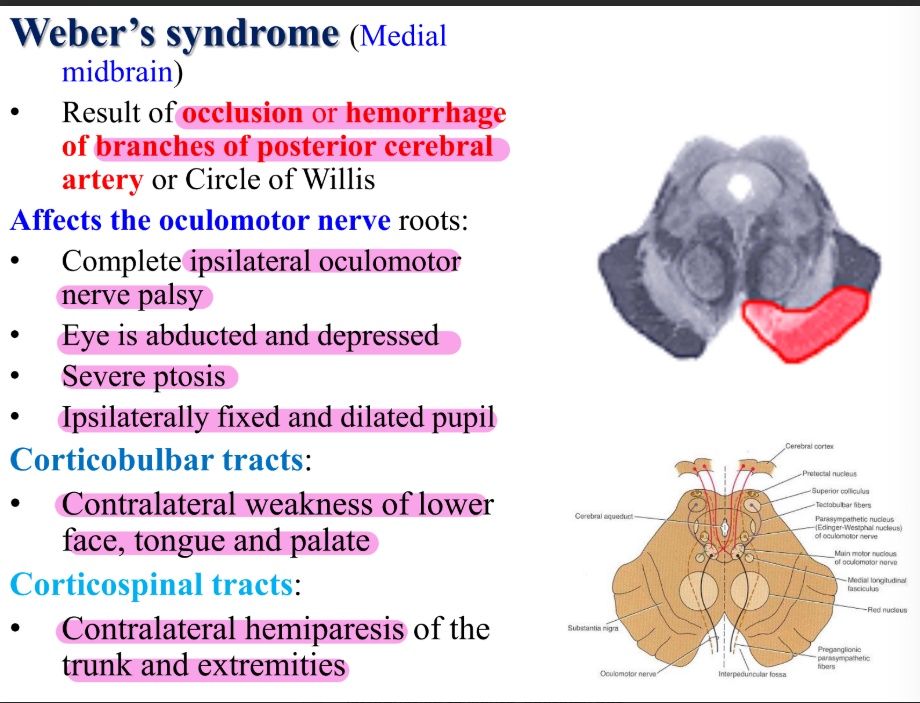
Midbrain lesions
As a result of:
Vascular occlusions of the branches of the posterior cerebral artery
Aneurysm in the posterior part of the Circle of Willis
Tumors of the pineal gland
Hydrocephalus
Perinaud’s syndrome (dorsal midbrain)

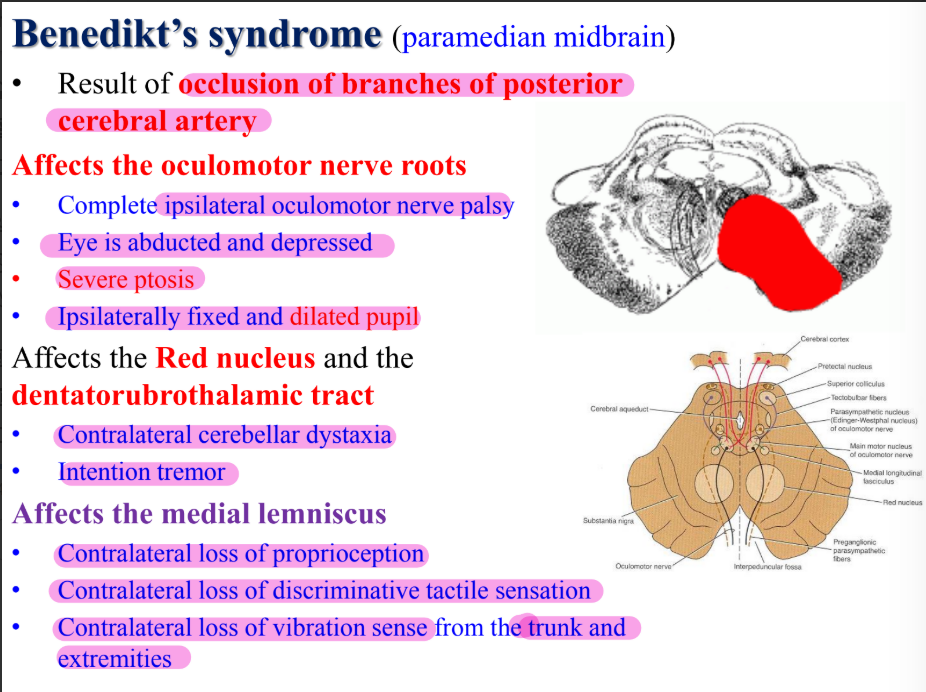
Benedikt’s syndrome (paramedian midbrain)
Weber’s syndrome (medial midbrain)