Care of clients with problems in Oxygenation: Gas Exchange
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/156
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
157 Terms
1
New cards
Movement of air in and out of the lungs (alveoli)
Ventilation
2
New cards
Movement of air between the alveoli (O2) and pulmonary capillaries (CO2)
Diffusion
3
New cards
This is dependent on airway resistance and lung compliance
Ventilation
4
New cards
Transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood and body fluids to body cells
Perfusion
5
New cards
It is also called internal respiration
Perfusion
6
New cards
Give the possible chief complaints for patients with problems in gas exchange
\
* Shortness of breath - respiratory patterns
* Labored breathing
* Activity intolerance
* Easy fatigability
* Cough
* Chest pain
* Difficulty moving (doing ADL)
* Shortness of breath - respiratory patterns
* Labored breathing
* Activity intolerance
* Easy fatigability
* Cough
* Chest pain
* Difficulty moving (doing ADL)
7
New cards
Who is often at risk of experiencing problems in gas exchange, and explain why?
* Older adults or extremes of age since they are immunocompromised
* Pediatric patients because they are smaller and have narrower airways
* Pediatric patients because they are smaller and have narrower airways
8
New cards
Process of breathing in and breathing out
Ventilation
9
New cards
Two questions frequently asked regarding smoker patients are:
* Packs per day
* For how many years has the patient been smoking, or at what age did the patient start smoking
* For how many years has the patient been smoking, or at what age did the patient start smoking
10
New cards
It refers to non modifiable factors that has been there with the patient ever since.
Predisposing factors
11
New cards
It refers to the events or activities that triggered the attack to the patient
Precipitating factors
12
New cards
Problem of developing or third world countries
Tuberculosis
13
New cards
The number one reason why tuberculosis is one of the leading respratory diseases in the country.
Non-compliance leading to resistance
14
New cards
Triggers of dyspnea
* Activity
* Allergens
* Change in temperature
* Allergens
* Change in temperature
15
New cards
Difficulty of breathing during supine position
Orthopnea
16
New cards
Position of relief
upright position
17
New cards
Another term for dry or nonproductive cough
hacking
18
New cards
It is also called the barking cough
Brassy
19
New cards
Sputum present with bacterial infection
Purulent yellowish/pus
20
New cards
What kind of sputum is present with viral infection
clear, thin, mucoid
21
New cards
Conditions that might result to blood-tinged sputum
* Tuberculosis
* Lung cancer
* Laryngeal cancer
* Throat irritation (harmless)
* Lung cancer
* Laryngeal cancer
* Throat irritation (harmless)
22
New cards
Condition where sputum is profuse, frothy or pink.
pulmonary edema
23
New cards
Possible conditions where sputum is already foul-smelling.
* abscess
* rotten tissue
* necrotic tissue
* rotten tissue
* necrotic tissue
24
New cards
What are the triggers of chest pain in a patient with respiratory problem
* Coughing
* Breathing
* Breathing
25
New cards
Characterized by __sudden and intense sharp__, stabbing, or burning pain in the chest when inhaling and exhaling.
Pleuritic pain
26
New cards
In what type of condition is pleuritic pain present?
Pneumonia
27
New cards
Inflammation of the lungs
Pneumonia
28
New cards
TRUE or FALSE:
\
It is not always necessary for a person with chest pain to undergo an ECG.
\
It is not always necessary for a person with chest pain to undergo an ECG.
FALSE
29
New cards
When assessing the general appearance of a patient, what factors should you take into consideration?
* Color
* Nails
* Respiratory Pattern
* Nails
* Respiratory Pattern
30
New cards
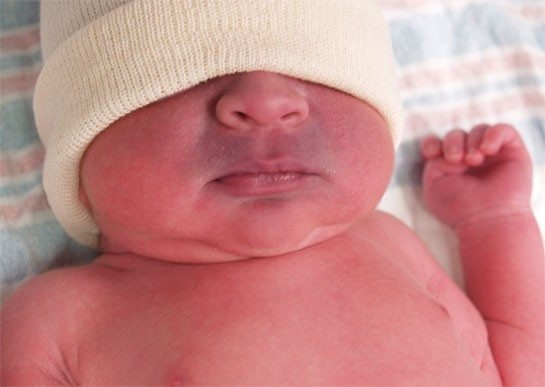
What do you call this type of cyanosis
Circumoral or central
31
New cards
What happens to the nails of patients with respiratory problem?
Clubbing or there is increased convexity
32
New cards
Clubbing is a response to ___________
chronic hypoxia
33
New cards
Conditions where clubbing of nails is usually present
* Pediatric - Congenital heart defects
* Adult - Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
* Adult - Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
34
New cards
One of the common position of individuals experiencing respiratory distress, aiming to expand their chest cavity
Orthopneic or tripod position
35
New cards
It means that accessory muscles are being used
Retractions
36
New cards
Possible areas where we can observe retractions
* Supraclavicular
* Suprasternal
* Intercostal
* Subcostal
* Suprasternal
* Intercostal
* Subcostal
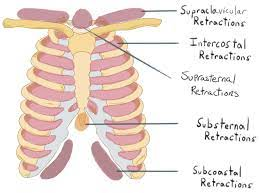
37
New cards
In pediatric patients, where can we observe retrations
subcostal
38
New cards
Barrel chest is expected among patients with what condition
Patients with COPD because there is an enlargement in lungs.
39
New cards
What factors do we take into account when palpating a patient's chest?
* Chest expansion
* Fremitus
* Tenderness
* Fremitus
* Tenderness
40
New cards
In percussing the patient’s chest, you noticed that it is hyperresonant. This means that there is _______
too much air in the lungs
41
New cards
Hyperresont lungs usually occur in patients with ___________
COPD
42
New cards
Dull sound during percussion is usually heard in patients with ______
Pneumonia because there is too much sputum
43
New cards
This auscultation sound means that there is fluid in the lungs.
Crackles
44
New cards
Specific conditions where you expect crackles in the lungs
* Pneumonia
* Pulmonary edema
* Pulmonary edema
45
New cards
What lung sound do you expect when the fluid is in the airways
Rhonchi (low pitch)
46
New cards
It is lung sound also called as a snoring sound usually during expiration
Rhonchi
47
New cards
It is the common breath sound heard in patients with bronconstriction (e.g. asthma)
Wheezing sound
48
New cards
TRUE or FALSE: There could be a wheezing sound in patients with pneumonia
TRUE
49
New cards
What should be taken into consideration before conducting Pulmonary Function Tests?
* Don’t exercise before the test
* Avoid using bronchodilators before
* Avoid too much food intake
* Avoid using bronchodilators before
* Avoid too much food intake
50
New cards
This pertains to the unit used for measuring oxygen saturation, also called the saturation of peripheral oxygen.
SpO2 or SaO2
51
New cards
Limitation of measuring the saturation of peripheral oxygen
When the patient has poor peripheral blood flow, specifically when he is on:
* Cardiac arrest/shock
* Severe anemia
* Vasoconstricting medications
* Nail polish
* High carbon dioxide
* Cardiac arrest/shock
* Severe anemia
* Vasoconstricting medications
* Nail polish
* High carbon dioxide
52
New cards
Two culture/antigen test for Tuberculosis Testing
* PPD: Purified Protein Derivative (skin test)
* **TST**: Tuberculin Skin Tests
* **TST**: Tuberculin Skin Tests
53
New cards
How would you guide a patient to provide a good specimen?
Instruct the patient to take a deep breath, and at the highest point of inhalation, initiate a cough.
54
New cards
Nursing care before bronchoscopy
* NPO for 6 hours or night before the procedure
* Remove dentures
* Administer pre-operative medications
* Remove dentures
* Administer pre-operative medications
55
New cards
Why is anticholinergic drugs usually prescribed before bronchoscopy?
Anticholinergic medications act against parasympathetic reduce secretions that might interfere with the procedure.
56
New cards
Which medication inhibits the patient's gag reflex?
Lidocaine
57
New cards
Nursing care after bronchoscopy
* Watch out for bleeding/DOB
* NPO until gag reflex restores
* NPO until gag reflex restores
58
New cards
Before permitting the patient to consume food following bronchoscopy, what initial assessment should the nurse perform?
Check for gag reflex
59
New cards
TRUE or FALSE: Atropine increases the salivation of the patient.
FALSE
60
New cards
Normal value of partial pressure of oxygen
PO2: 80 -100 mmHg
61
New cards
Most harmful effect of getting the ABG of the patient.
* It could puncture the arteries of the patient (through and through)
62
New cards
Test performed to check the patency of ulnar and radial artery
Allen’s Test
63
New cards
Centesis means ________
aspiration
64
New cards
Procedure of aspirating fluids or pus from the patient
Thoracentesis
65
New cards
This refers to a condition where fluid is present within the lungs.
Pulmonary edema
66
New cards
This refers to a condition where fluid is present outside the lungs or within the pleural space
Pleural effusion
67
New cards
Possible complication in performing thoracentesis.
Lung perforation
68
New cards
When conducting a thoracentesis on a patient, what position should the patient be in?
Orthopneic position
69
New cards
What is the recommended patient positioning after a thoracentesis procedure?
Side-lying: Unaffected side
70
New cards
Three basic considerations before performing nursing procedures.
CAN
* Consent
* Allergy
* NPO
* Consent
* Allergy
* NPO
71
New cards
It refers to a condition where there is an airway constriction or bronchoconstriction due to various stimuli
Bronchial Asthma
72
New cards
Give different triggers of asthma attack
\
* Environmental factors
* Change in temperature
* Atmospheric pollutants
* Strong odors
* Allergens
* Stress or emotional upset
* Exercise
* Environmental factors
* Change in temperature
* Atmospheric pollutants
* Strong odors
* Allergens
* Stress or emotional upset
* Exercise
73
New cards
What does BA/AE means
Bronchial Asthma in Acute Exacerbation
74
New cards
Two examples of OBSTRUCTIVE LUNG DISEASES
* Bronchial Asthma
* COPD
* COPD
75
New cards
Wheezing is usually heard during ________
Expiration
76
New cards
When conducting an assessment on a patient with bronchial asthma, what type of lung sounds would be heard during auscultation?
Wheezes
77
New cards
What does anticholinergic medication does with the airway?
Dilates can lead to bronchodilation
78
New cards
Salbutamol is usually combined with ______ to achieve bronchodilation
Ipratropium
79
New cards
Remember: Bronchodilator such as beta 2 agonist and anticholinergics can result to _____________
Tachycardia
80
New cards
Group of disorders characterized by progressive deterioration in pulmonary function
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
81
New cards
Number one risk factor of **Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)**
Smoking
82
New cards
Protein in the lungs responsible for elastic recoil
Alpha1 - Antitrypsin
83
New cards
Two examples/conditions under Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
* Pulmonary emphysema
* Chronic Bronchitis
* Chronic Bronchitis
84
New cards
Condition wherein there is a loss on the elastic recoil of the lungs, leads to alveolar hyperinflation
Pulmonary emphysema
85
New cards
This condition involves inflammation and excessive mucus production in the bronchial passages of the lungs.
Chronic Bronchitis
86
New cards
TRUE or FALSE: Chronic bronchitis and pulmonary emphysema can occur simultaenously
TRUE
87
New cards
Emphysema: ________
Chronic Bronchitis: Inflamed airways
Chronic Bronchitis: Inflamed airways
CO2
88
New cards
TRUE or FALSE: COPD is reversible
FALSE
89
New cards
Possible breath sounds in patients with COPD.
* Wheezes
* Rhonchi
* Crackles
* Rhonchi
* Crackles
90
New cards
TRUE or FALSE: Chest X Ray is utilized to diagnose COPD
FALSE, it is only used as a contributing assessment in severe COPD cases
91
New cards
Elevation in the blood pressure of the patient’s pulmonary artery.
Pulmonary Hypertension
92
New cards
Also called as the right-sided heart failure
Cor pulmonale
93
New cards
This technique involves breathing to elevate pressure for the release of carbon dioxide.
Diaphragmatic pursed-lip breathing
94
New cards
It is the respiratory center of the body and responsible for breathing
Medula oblongata
95
New cards
_______ is the secondary stimulus for breathing
hypoxia
96
New cards
Medulla oblongata: Increased carbon dioxide
__________ : Hypoxia or decreased oxygen levels
__________ : Hypoxia or decreased oxygen levels
Baroreceptors
97
New cards
The stimulus that assumes control when the medulla oblongata is inactive.
Hypoxia
98
New cards
Three cardinal movements of Chest-pulmo physiotherapy
* Percussion
* Vibration
* Drainage
* Vibration
* Drainage
99
New cards
_________ maintains osmotic pressure and keeps the blood or the plasma in the blood vessel
Albumin
100
New cards
Bronchodilators should be given ______ before meal
30 minutes