NEUROLOGIC EXAMINATION p2
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Normal respons to babinski
downward contraction of toes
upgoing big toe and fanning of other toes with or without triple flexion (ankle dorsiflexion, hip and knee flexion)
Babinski sign
(+) UMN lesion
Babinski sign is normal up to how many years old
2 y/o
Tap glabella rapidly 10 times
N: lid remains open
Abn: continuous reflex blinking with or without lid closure (orbicularis oris)
Glabellar Blink or Tap
With patient’s eyes closed, tap the philtrum or press the tip of a test tube firmly compressing the upper lip against the gum
N: no response
Abn: puckering or pursing or the lips (orbicularis oris)
Snout Reflex
Stroke patient’s hypthenar eminence
N: no contraction of mentalis
Abn: ipsilateral or bilateral mentalis contraction
Palmomental Reflex
Use index and middle finger to stroke patient’s palm from the hypothenar eminence towards junction of finger and thumb
N: no response
Abn: grasping fingers
Grasp Reflex
Normal response is the umbilicus twitches towards stimulated quadrant
Abdominal (Beevor’s) Reflex
Elevation of ipsilateral testicle in relation to thigh stimulus
Cremasteric Reflex
Pricking the glans penis causes reflex contraction of the bulbocavernosus muscle, detected by pressing a finger against the perineum
Bulbocavernosus Reflex
Pricking or scratching the perianal skin causes a quick constriction of the anal sphincter
Anocutaneous (Anal Wink) Reflex
Nerve roots of the beevor’s reflex below the umbilicus
T10-12
Nerve roots of the bulbocavernosus reflex
S2-4
Nerve roots of the Cremasteric reflex
L1-2
Nerve roots of the beevor’s reflex above the umbilicus
T8-10
Nerve roots of the anal wink reflex
S2-4
Abnormal movements in coordination disorders
Ataxia
lesion on ipsilateral cerebellar hemisphere causes?
Appendicular ataxia
lesion on the vermis causes?
Truncal ataxia
Rapid alternating movement
dysdiadochokinesia
Finger-to-nose test is used to test for?
dysmetria
Other tests and signs of appendicular ataxia:
Overshoot (hypermetria)
Finger tapping test
Heel-shin test
Foot tapping
Ipsilateral limb intention tremor
Ipsilateral limb ataxia
Signs of Truncal Ataxia
Wide-based, unsteady, drunkard-like gait
May have difficulty sitting up without support
Romberg Test uses which senses?
Vision, proprioception, vestibular senses
Stand with feet together, eyes closed
instability due to impaired proprioceptive and vestibular systems
Gait where patient walks in straight line while toughing the heel of one foot to toe of the other with each step
Tandem gait
Sensations
Light touch → cotton
Pain → pinprick
Temperature → cool piece of metal (i.e. tuning fork)
5-10 deg C and 40-45 deg C
Vibration sense
Joint position sense
Two-point discrimination (using a caliper)
Which tract is responsible for light touch?
anterior spinothalamic tract
Which tract is responsible for pain sense?
lateral spinothalamic tract
Objectives of Both Light Touch and Pain
Performed in all extremities including face and trunk
Eyes closed
Reproducible
Correlate and recheck to improve objectivity
Which tract is responsible for temp sense?
lateral spinothalamic tract
Which tract is responsible for vibration sense
posterior-column medial lemniscal pathway (DCML)
Which tract is responsible for proprioception / joint sense
DCML
Which tract is responsible for two point discrimination?
DCML
Review this
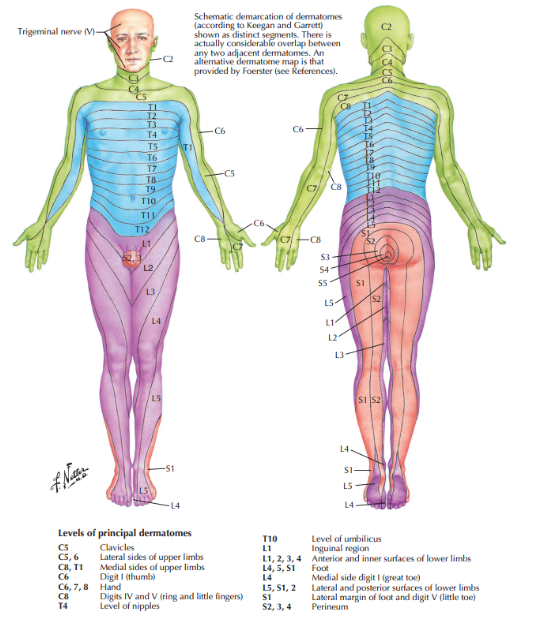
Dermatome distribution of C5
Clavicles
Which nerve roots are the dermatomes for the lateral sides of upper limbs?
C5-6
Dermatome distribution of C8-T1
Medial sides of upper limbs
Nerve roots of the dermatome of digits IV and V
C8
Nerve roots of the dermatome of digit 1
C6
Nerve roots for the dermatome at the level of the nipples
T4
Nerve roots for the dermatomes of the hand
C6,7,8
Dermatome distribution of T10
umbilicus
Dermatome distribution of S2,3,4
Perineum
The inguinal region’s dermatome is supplied by which nerve root?
L1
Dermatome distribution of L4
Medial side of great toe
Nerve root of dermatome that supplies the lateral margin of foot and digit V (little toe)
S1
Dermatomes of the anterior and inner surfaces of lower limbs are supplied by which nerve roots?
L1,2,3,4
Dermatomes of the lateral and posterior surfaces of the lower limbs are supplied by which nerve roots?
L5, S1,2
What is the distribution of the dermatome with the nerve roots L4,5 and S1
Foot
Neither patient nor examiner can flex the patient’s head because of reflex spasm of nuchal (extensor) muscles
Nuchal Rigidity
Adduction and flexion of legs as head is flexed
Neck flexion places tension on the entire cord and roots
Flexion of legs reduces stretch on nerve root
Brudzinski
Bend knee leg raising tests; knees cannot extend due to pain
Kernig