PSY 1.10 Social Thinking
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Interpersonal attraction
is what makes people like each other and is influenced by many factors, including physical characteristics, similarity, self-disclosure, reciprocity, and proximity.
physical attractiveness
which is increased with symmetry and proportions close to the golden ratio (1.618:1)
similarities in attitudes
intelligence, education, height, age, religion, appearance, and socioeconomic status
self disclosure
which includes sharing fears, thoughts, and goals with another person and being met with empathy and nonjudgment
Reciprocity
involves an exchange of positive actions between people.
proximity
being physically close to someone
aggression
is a physical, verbal, or nonverbal behavior with the intention to cause harm or increase social dominance.
attachment
Mary Ainsworth
is an emotional bond to another person, and usually refers to the bond between a child and a caregiver.
There are four types of attachment:
secure
avoidant
ambivalent
disorganised
secure attachment
is a caregiver who is consistent, available, comforting, and responsive.
requires a consistent caregiver so the child is able to go out and explore, knowing there is a secure base to return to; the child will show strong preference for the caregiver.
avoidant attachment
occurs when a caregiver has little or no response to a distressed, crying child; the child shows no preference for the caregiver compared to strangers.
ambivalent attachment
occurs when a caregiver has an inconsistent response to a child’s distress, sometimes responding appropriately, sometimes neglectfully; the child will become distressed when the caregiver leaves and is ambivalent when the caregiver returns.
disorganised attachment
occurs when a caregiver is erratic or abusive; the child shows no clear pattern of behavior in response to the caregiver’s absence or presence and may show repetitive behaviors.
social support
is the perception or reality that one is cared for by a social network.
emotional support
includes listening to, affirming, and empathizing with someone’s feelings.
esteem support
affirms the qualities and skills of the person.
material support
is providing physical or monetary resources to aid a person.
Informational support
is providing useful information to a person.
network support
is providing a sense of belonging to a person.
foraging
is searching for and exploiting food resources.
primarily a learned behavior.
Young individuals learn through observing how to find and consume food and how to determine what is safe to eat,
mating system
describes the way in which a group is organized in terms of sexual behavior.
monogamy
consists of exclusive mating relationships.
polygamy
consists of multiple exclusive relationships, including polygyny (with multiple females) and polyandry (with multiple males).
promiscuity
means mating without exclusivity.
Mate choice
is the selection of a mate based on attraction and traits.
5 mechanisms of choice
phenotypic benefits
sensory bias
Fisherian selection
indicator traits
genetic compatibility
altruism
is a form of helping behavior in which people’s intent is to benefit someone else at some cost to themselves.
game theory
attempts to explain decision making between individuals as if they are participating in a game.
characteristics, including strategy, winning and losing, rewards and punishments, and profits and cost
Inclusive fitness
is a measure of an organism’s success in the population. This is based on the number of offspring, success in supporting offspring, and the ability of the offspring to then support others.
Inclusive fitness therefore promotes the idea that altruistic behavior can improve the fitness and success of a species as a whole.
social perception
is the way by which we generate impressions /judgements about people in our social environment. It contains a perceiver, a target, and the situation or social context of the scenario.
implicit personality theory
states that people make assumptions about how different types of people, their traits, and their behavior are related.
Certain cognitive biases impact our perceptions of others
primacy effect
recency effect
reliance on central traits
halo effect
just world hypothesis
self-serving bias
primacy effect
refers to when first impressions are more important than subsequent impressions.
recency effect
is when the most recent information we have about an individual is most important in forming our impressions.
reliance on central traits
is the tendency to organize the perception of others based on traits and personal characteristics that matter to the perceiver.
halo effect
is when judgments of an individual’s character can be affected by the overall impression of the individual.
just world hypothesis
is the tendency of individuals to believe that good things happen to good people and bad things happen to bad people.
self-serving bias
refers to the fact that individuals will view their own successes as being based on internal factors, while viewing their failures as being based on external factors.
influenced by motivational processes such as self enhancement and self verification
attribution theory
focuses on the tendency for individuals to infer the causes of other people’s behavior.
dispositional factors (internal)
situational factors (external)
dispositional factors (internal)
causes are those that relate to the features of the person whose behavior is being considered.
For instance, suppose you hear that a friend has been nominated for an academic award. Believing that the friend has been nominated because of hard work and personal effort would be a dispositional attribution. Contrarily, chalking up the nomination to luck would be a situational attribution.
situational factors
causes are related to features of the surroundings or social context.
such as threats, money, social norms, and peer pressure.

correspondence inference theory
is used to describe attributions made by observing the intentional (especially unexpected) behaviors performed by another person.
fundamental attribution error
is the bias toward making dispositional attributions rather than situational attributions in regard to the actions of others.
attribute substitution
occurs when individuals must make judgments that are complex but instead substitute a simpler solution or heuristic.
Attributions are highly influenced by the culture in which one resides.
stereotypes
occur when attitudes and impressions are made based on limited and superficial information about a person or a group of individuals.
Stereotypes can lead to expectations of certain groups, which can create conditions that lead to confirmation of the stereotype, a process referred to as self-fulfilling prophecy.
expectations, impressions, and opinions about the characteristics of members of a group
stereotype threat
is concern or anxiety about confirming a negative stereotype about one’s social group.
prejudice
is defined as an irrational positive or negative attitude toward a person, group, or thing prior to an actual experience.
Propaganda is a common way by which large organizations and political groups attempt to create prejudices in others.
social factors that influence prejudice
power
prestige
class
ethnocentrism
refers to the practice of making judgments about other cultures based on the values and beliefs of one’s own culture.
cultural relativism
refers to the recognition that social groups and cultures should be studied on their own terms.
discrimination
is when prejudicial attitudes cause individuals of a particular group to be treated differently from others.
differences in actions toward different groups.
individual discrimination
refers to one person discriminating against a particular person or group.
institutional discrimination
refers to the discrimination against a particular person or group by an entire institution.
reciprocal liking
phenomenon whereby people like others better when they believe the other person likes them.
mere exposure effect
the tendency for people to prefer stimuli that they have been exposed to more frequently.
amygdala
part of the brain responsible for associating stimuli and their corresponding rewards or punishments.
it is responsible for telling us whether or not something is a threat. If the amygdala is activated, this increases aggression.
prefrontal cortex
critically important to managing the limbic system, which is important in managing emotion and stress
Reduced activity in the prefrontal cortex has been linked to increased aggressive behavior.
cognitive neoassociation model
states that we are more likely to respond to others aggressively whenever we are feeling negative emotions, such as being tired, sick, frustrated, or in pain.
Bobo doll experiment
Albert Bandura
viewing violent behavior indeed correlates to an increase in aggressive behavior.
mate bias
refers to how choosy members of the species are while choosing a mate. This bias is an evolutionary mechanism aimed at increasing the fitness of the species.
has direct and indirect benefits
[mating] direct benefits
providing material advantages, protection, or emotional support
[mating] indirect benefits
by promoting better survival in offspring.
phenotypic benefits
observable traits that make a potential mate more attractive to the opposite sex. Usually, these traits indicate increased production and survival of offspring. For example, males that appear more nurturing are more likely to care for, and promote the survival of, their offspring.
sensory bias
development of a trait to match a preexisting preference that exists in the population. For example, fiddler crabs are naturally attracted to structures that break up the level horizon because they may indicate a food source; male crabs take advantage of this fact by building pillars around their territory to attract mates.
fisherian selection
a positive feedback mechanism in which a particular trait that has no effect or a negative effect on survival becomes more and more exaggerated over time. In this model, a trait is deemed sexually desirable and thus is more likely to be passed on. This increases the attractiveness of the trait, which in turn increases the likelihood that it continues to be passed on. The bright plumage of the peacock
indicator traits
traits that signify overall good health and well-being of an organism, increasing its attractiveness to mates. Notably, these traits may or may not be genetic in origin. For example, female cats are more attracted to male cats with clean and shiny coats; a dirty and dull coat may be related to an underlying genetic problem, or to malnutrition or infection.
genetic compatibility
the creation of mate pairs that, when combined, have complementary genetics. This theory provides a mechanism for the reduced frequency of recessive genetic disorders in the population: attraction to others who have starkly different genetic makeups reduces the probability of offspring being homozygotic for a disease-carrying allele.
empathy
ability to vicariously experience the emotions of another, and it is thought by some social psychologists to be a strong influence on helping behavior.
empathy altruism hypothesis one explanation for the relationship between empathy and helping behavior. one individual helps another person when feeling empathy for the other person, regardless of the cost
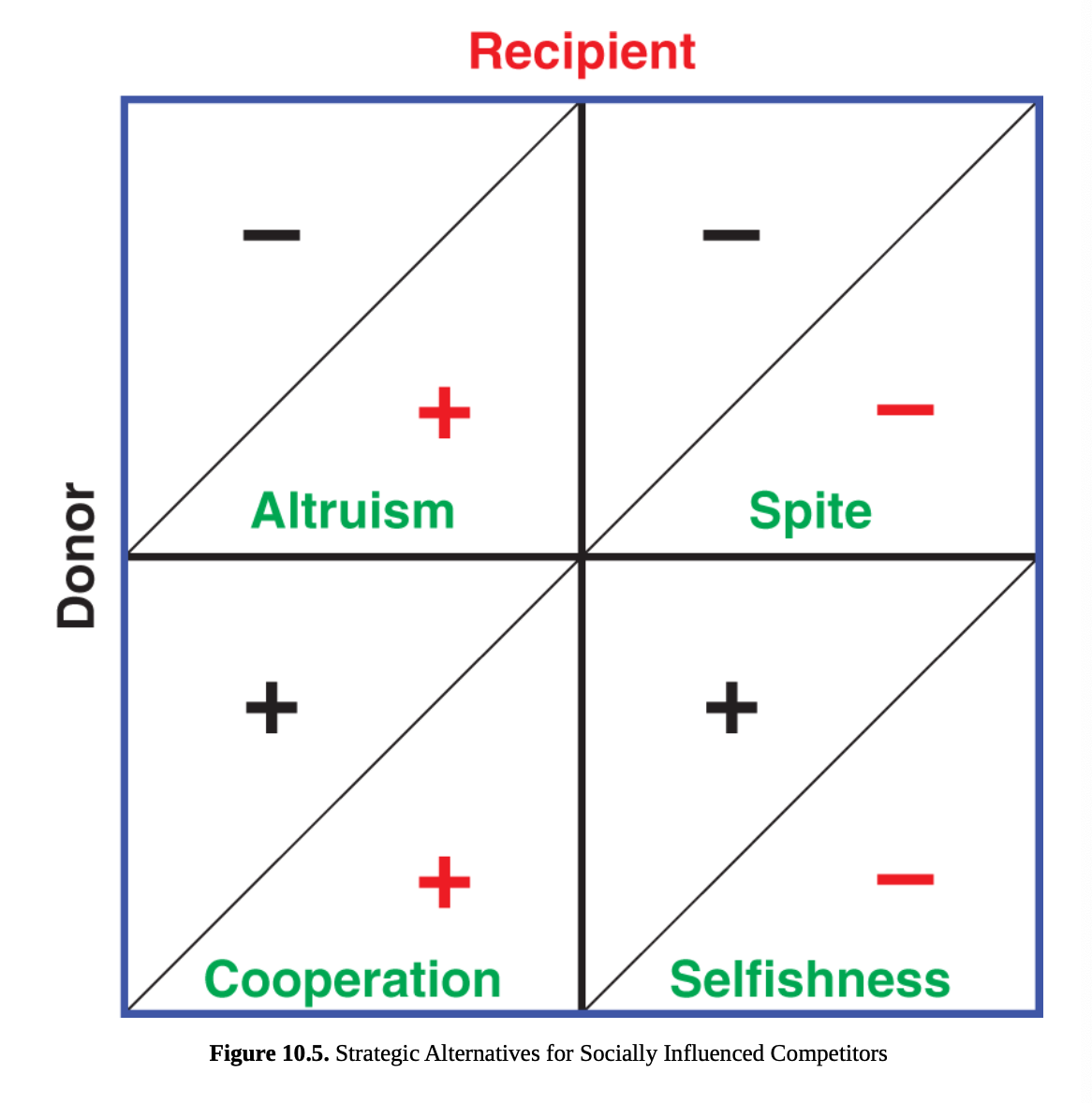
strategic alternative for socially influenced competitors
Altruism: the donor provides a benefit to the recipient at a cost to the donor
Cooperation: both the donor and recipient benefit by cooperating
Spite: both the donor and recipient are negatively impacted
Selfishness: the donor benefits while the recipient is negatively impacted
components of social perception
perceiver (influenced by experience, motives, and emotional state. Past experiences affect our attitudes toward current and future experiences and can lead to particular expectations of event)
target (refers to the person about which the perception is made. Knowledge of the target can include past experiences or specific information that affect perception.)
situation (important in developing perception. A given social context can determine what information is available to the perceiver.)
self enhancement
focuses on the need to maintain self-worth, which can be accomplished in part by the self-serving bias.
self verification
suggests people will seek the companionship of others who see them as they see themselves, thereby validating a person’s self-serving bias.
in group
refers to the inclination to view members in one’s group more favorably
out group
refers to the inclination to view individuals outside one’s group harshly.
cues
used to understand behaviour of others
consistency cues
consensus cues
distinctiveness cues
consistency cues
cues are signals, either from the environment or internal states, that trigger a specific behavior or habit
eg Placing a book on your pillow: A cue to read before sleep
consensus cues
are statements about how others generally responded to a product, service, or idea, and can be used to influence decision-making
eg Rated 4.5 out of 5 stars by customers"
distinctiveness cues
are cues that help determine whether a person's behavior is unique to a specific situation or is a general characteristic of their personality.
high distinctiveness is attributed to situational factors
actor observer bias
results from the self-serving bias (by the actor) and the fundamental attribution error (by the observer).
Actor-observer bias holds that, due to our unique knowledge about our own actions, we are more likely to make situational attributions for the self as compared to others.
self fulfilling prophecy
These expectations can create conditions that then cause the expectations to become reality
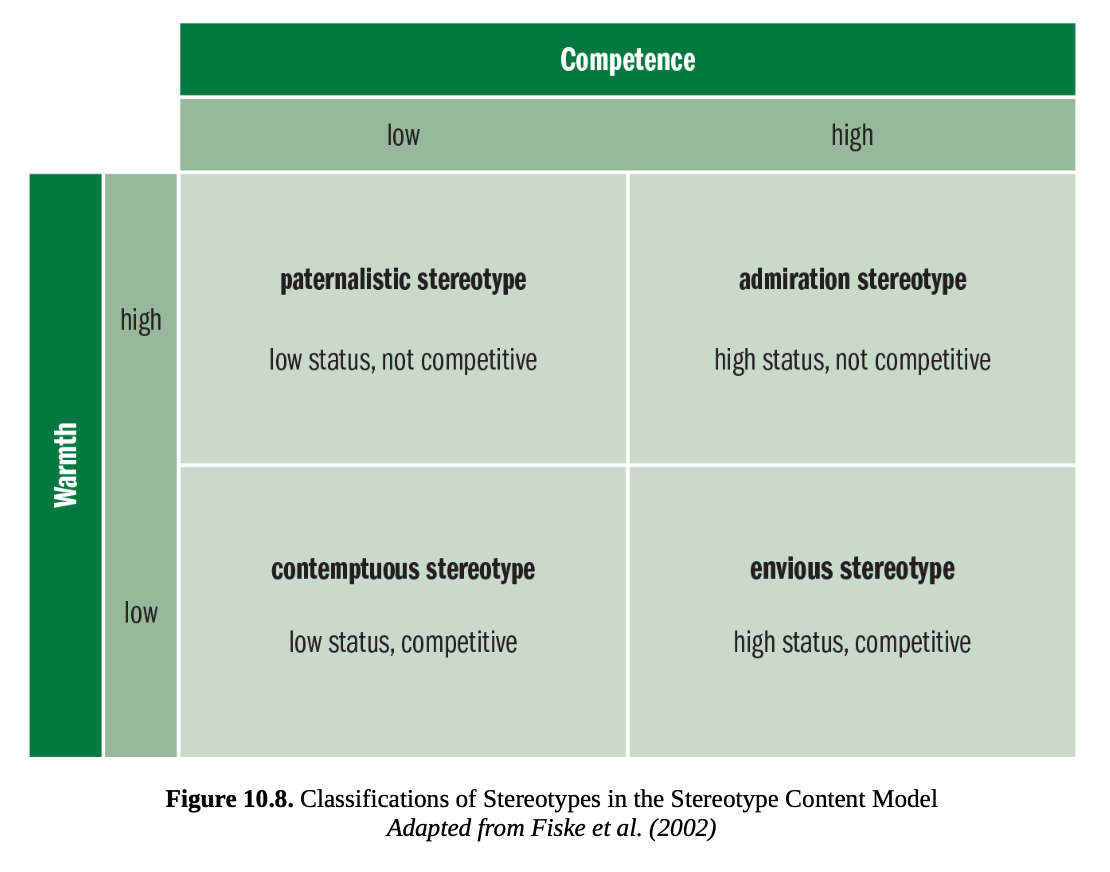
stereotype content model
classify stereotypes with respect to a hypothetical in-group using two dimensions: warmth and competence.
Warm groups are those that are not in direct competition with the in-group for resources; competent groups are those that have high status within society
Paternalistic stereotypes are those in which the group is looked down upon as inferior, dismissed, or ignored.
Contemptuous stereotypes are those in which the group is viewed with resentment, annoyance, or anger.
Envious stereotypes are those in which the group is viewed with jealousy, bitterness, or distrust.
Admiration stereotypes are those in which the group is viewed with pride and other positive feelings