ECF , ICF, Osmosis
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
What is intra and extracellular fluid
Fluid inside and outside the cell , separated by cell membrane.
Which part of a phospholipid is hydrophobic?
lipid tail
Which part of a phospholipid is hydrophilic?
phosphate head
What is the function of cholesterol in the cell membrane
Structural integrity, more cholesterol = stronger/ridgid
Functions of cell membrane
Selectively Permeable, separates the interior of the cell from the outside environment. regulates the transport of materials entering and exiting the cell.
What pathways allow movement across membranes
pores
channels
carriers (transporters)
pumps
Pore pathways + types
non selective
- porins
-perforins
channel pathways
Allow movement of solutes (ions), simple diffusion. there are non gated and gated pathways.
what are gated channels controlled by
voltage, ligand (something needs to bind), second messenger
examples of gated channels
Na+ channels
K+ Channels
Ca2+ channels
anion channels
what are carrier pathways
facilitate passive transport of smaller molecules.
what are pump pathways
active transport of ions, uses ATP
Exocytosis
Process by which a cell releases large amounts of material
Endocytosis
process by which a cell takes material into the cell by infolding of the cell membrane
difference between transporters and channel proteins
Channel proteins transport ions and molecules only down a concentration gradient, no energy. use simple diffusion.
Carrier protein (transporters) transport solutes across the membrane both down and up - energy required - the concentration gradient. facilitated diffusion
how do solutes move across membrane
Active transport
Facilitated diffusion
Simple diffusion
endo and exocytosis
how does fluid and solutes balance across a membrane
By diffusion of water or solutes, osmotic balance ensures balance.
Solutes or water move across a semi-permeable membrane
What is an electrochemical gradient
What does it involve
It is the difference in charge and chemical concentration across a membrane.
movement of ions through open channel. in or out of cell
potassium concentration in cells clinical relevance
hypokalaemia - muscle weakness , cardiac arrhythmias
hyperkalemia - bradycardia, reduced reflexes and power
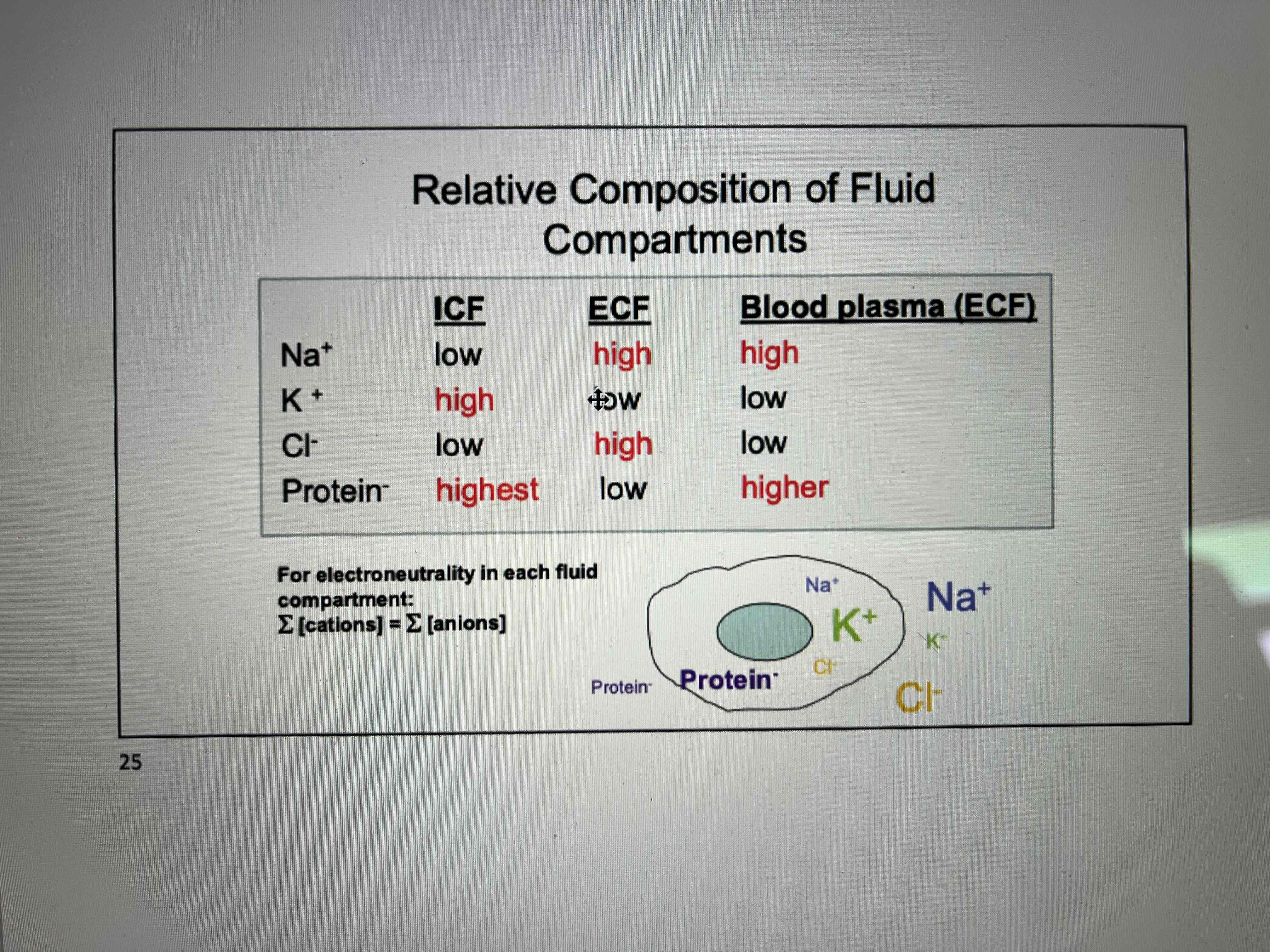
What does cellular fluid consist of?
Sodium - Na+
Potassium - K+
Chlorine - Cl-
Protein-
Components high or low in ICF and ECF
sodium
potassium
chlorine
protein
Sodium - high ECF low ICF
Potassium - low ECF high ICF
Clorine - high ECF low ICF
Protein - low ECF high ICF
what are the main electrolytes
Sodium, potassium, chloride
What do electrolytes do?
regulate nerve and muscle function
hydrate the body,
balance blood acidity and pressure,
help rebuild damaged tissue.
What can dehydration cause?
UTI
Kidney failure / stones
Hypovolemic shock
Seizures
What do the following mean (relate to dehydration).
Hypovolemic shock
Seizures
Hypovolemic shock - dehydration complication. Low blood volume causes drop is BP. Amount of oxygen decreases.
Seizures - electrolytes regulate electrical signals in the body. If electrolytes are unbalanced (caused by dehydration) messages can be messed up.
Why are ICF and ECF concentrations important?
overall cellular homeostasis.
nerve signaling
muscle contraction
osmotic regulation.
Define osmosis
process by which water moves between body compartments from an area of high to low concentration, no energy is required
osmotic pressure
the pressure needed to stop osmosis, hydrostatic pressure is applied.
Reflection coefficient meaning
how permeable the membrane is the a solute
Reflection coefficient of one
membrane is not permeable to solute
Reflection coefficient of zero
Freely permeable
Reflection coefficient between one and zero
semipermeable to solute
what is tonicity
The effect of a solution on cell volume
how do isotonic solutions effect cell
no net movement
no volume change
pressure is same in ECF and ICF
How do hypotonic solutions effect cell
movement of water inward
volume increases
potential lysis
How do hypertonic solutions effect cell
outward water movement
cell volume decreases
cell shrinkage
What is a osmole?
Depends on number of particles rather than molecules
What is osmolarity
Osmolarity is a measure of osmotic pressure exerted by a solution across a perfectly semi-permeable membrane. measure of activity of solvent. increase in osmolarity means decrease of solvent activity.
how to calculate osmolarity
G X Molar concentration of osmolyte particles
g = osmotic coefficient
What does oncotic mean
pressure exerted by large molecules in solution
Why is osmosis clinically relevant?
ECF is usually isotonic to ICF. Imbalance can lead to oedema (swelling) or cell shrinkage
Gibbs-donan effect
build of ions inside the cell leading to movement into the cell. countered by action of sodium potassium pump. 2 positive potassium in, 3 sodium negative out
ICF and ECF components
what is osmoregulation? why is it important?
control of solute and water balance within an organism.
maintain osmotic balance and prevent the cell from losing or gaining too much water.
example of osmotic regulation
sodium-potassium pump
what is the movement of water in and out of capillaries determined by
oncotic pressure and hydrostatic pressure
why is the movement of water clinically relevant
disturbances can lead to issues such as oedema
what is osmotic pressure determined by?
number of dissolved particles in a solution
What is hydrostatic pressure
pressure that any fluid in a confined space exerts.
What is oncotic pressure
type of osmotic pressure induced by the plasma proteins, in a blood vessel's plasma that causes a pull on fluid back into the capillary.