APES UNIT 7
1/52
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
🌍 Air Pollution
Occurs when harmful substances enter Earth's atmosphere.
📏 Parts per Million (ppm)
Most common unit for measuring air pollutants.
⚠ Primary Pollutants
Emitted directly into the air.
🔄 Secondary Pollutants
Formed when primary pollutants react in the atmosphere.
🏭 Point Source Pollution
Comes from a single, identifiable source (e.g., a factory smokestack).
🌎 Non-Point Source Pollution
Comes from widespread, multiple sources (e.g., car emissions).
🧪 Criteria Air Pollutants
A set of 8 pollutants causing smog, acid rain, & health hazards.
Emitted from industry, mining, transportation, power, & agriculture.
🌫 Industrial Smog (Gray Smog)
Sulfur-based smog from burning coal/oil.
🛠 Formation of Industrial Smog
Coal/oil combustion → CO₂, CO, & soot (PM).
Sulfur compounds react to form sulfuric acid & ammonium sulfate
🚨 Carbon Monoxide (CO)
Colorless, odorless, tasteless gas from incomplete combustion.
Sources: Fires, fossil fuel burning, volcanic activity.
Solutions: Public transport, catalytic converters, renewable energy.
🔩 Lead (Pb)
Found in batteries, bullets, radiation shields.
Exposure: Inhalation, contaminated food/water.
Effects: Anemia, cognitive impairment, miscarriage, death.
💨 Nitrogen Oxides (NOx)
Includes nitric oxide (NO) & nitrogen dioxide (NO₂).
Produced in high-temp combustion (cars, industry).
Nitrous oxide (N₂O): Causes ozone depletion.
☁ Ozone (O₃) – Tropospheric (Ground-Level)
Secondary pollutant harmful to localized areas.
Effects: Lung irritation, asthma, heart disease, immune suppression.
🧪 Peroxyacyl Nitrates (PANs)
Secondary pollutants that travel far from source.
Effects: Eye irritation, respiratory issues, crop damage.
Reduction methods: Reduce fossil fuels, limit wood-burning, improve smokestack filters.
🌋 Sulfur Dioxide (SO₂)
From power plants, refineries, fossil fuel burning.
Effects: Acid rain, respiratory issues, crop damage, stonework erosion.
Reduction methods: Use scrubbers, wash coal, fluidized gas combustion.
🌎 Suspended Particulate Matter (PMx)
Microscopic solid or liquid particles in the air.
Effects: Acidification of lakes, ecosystem damage, soil depletion, respiratory problems.
Reduction: Improve emissions standards, reduce energy use, limit burning.
🌪 Sources of PMx Pollution
🔹 Natural: Dust storms, wildfires, sea spray, volcanoes.
🔸 Human-caused: Fossil fuel burning, waste incineration, deforestation.
🧪 Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
Organic chemicals with high vapor pressure (evaporate easily).
Health effects: Cancer, nerve damage, headaches, nausea, eye/throat irritation.
☁ Photochemical Smog (Brown Smog)
Catalyzed by UV radiation
Nitrogen-based pollution
Appears brown due to nitrogen oxides
🌅 Formation Timeline of Photochemical Smog
6 A.M.–9 A.M. 🚗
Morning traffic increases nitrogen oxides (NOx) & VOCs.
9 A.M.–11 A.M. 🔄
NO & VOCs react → forming nitrogen dioxide (NO₂).
11 A.M.–4 P.M. ☀
Intense sunlight breaks down NO₂ → Ozone (O₃) increases.
NO₂ reacts with water vapor → Nitric acid (HNO₃) & Nitric oxide (NO).
NO₂ reacts with VOCs → forming Toxic PANs.
4 P.M.–Sunset 🌇
Sunlight decreases → ozone production stops.
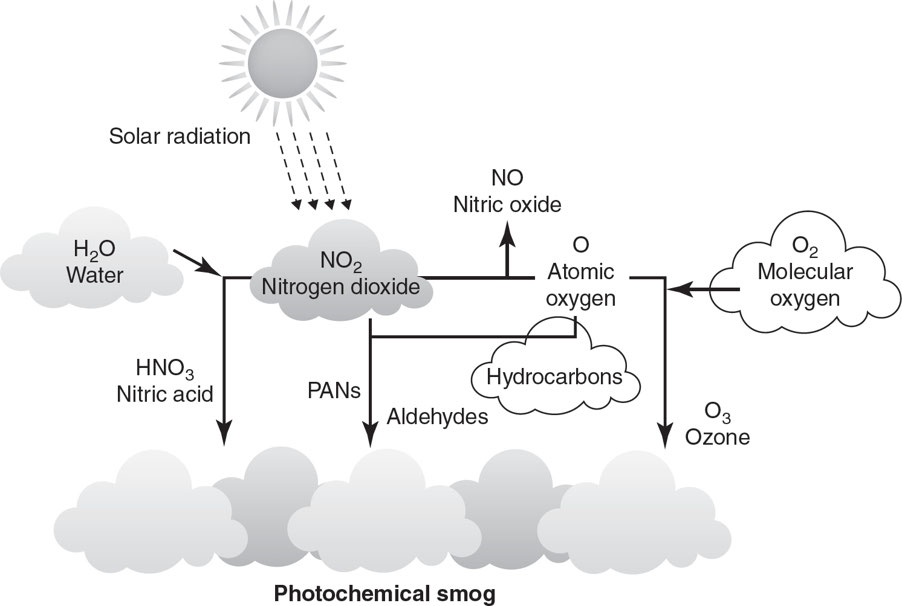
🌍 Effects of Photochemical Smog
Irritates eyes & lungs
Reduces visibility
Damages crops & vegetation
🚦 Ways to Reduce Photochemical Smog
Reduce vehicle emissions
Use alternative fuels
Implement stricter industrial regulations
🌡 Thermal Inversion
Occurs when air temperature increases with height instead of decreasing.
Traps pollutants like smog close to the ground, worsening air quality.
🌙 When Does It Happen?
At night, when the surface cools, cooling the air above it.
When a warm air mass moves over colder air, trapping pollutants
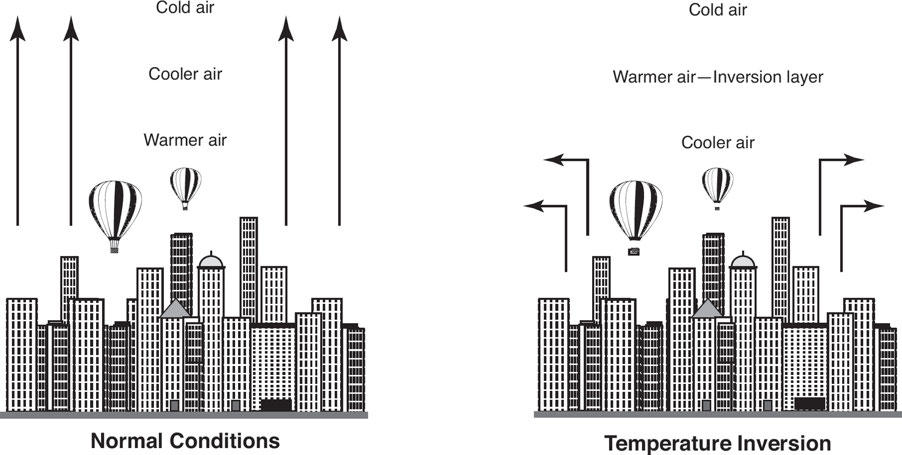
🌍 Effects of Thermal Inversion
Increases air pollution concentrations
Harms human health (respiratory issues, irritation, asthma attacks)
Reduces visibility
❄ Example:
Antarctica has a nearly constant temperature inversion.
🚦 Ways to Reduce Harmful Effects
Limit emissions during inversion events
Improve urban ventilation
Reduce vehicle & industrial pollution
🏢 “Sick Building” Syndrome (SBS)
A combination of health issues linked to poor indoor air quality in workplaces or homes.
🧱 Asbestos
Properties: Inexpensive, durable, flexible, fireproof, and insulating.
Health Risk: Can cause lung diseases, including mesothelioma.
🚗 Carbon Monoxide (CO) Poisoning
Most common fatal indoor air poisoning.
Danger: CO binds to hemoglobin, blocking oxygen transport in the blood.
⚠ Formaldehyde
A carcinogenic organic chemical found indoors.
Linked to: Lung cancer.
🛑 Radon
Invisible radioactive gas from radium decay.
Health Risk: Can cause lung cancer.
🚬 Cigarette Smoke
Contains 5,000+ chemicals, including 60 carcinogens like dioxin.
Major cause of indoor air pollution.
🛠 Remediation Steps to Reduce Indoor Air Pollutants
✅ Add plants that absorb toxins
✅ No smoking indoors
✅ Install air purification systems
✅ Maintain filters and vents
✅ Monitor humidity to prevent mold
✅ Test for radon gas
✅ Use "green" cleaning products
✅ Apply natural pest control techniques
🚗 Catalytic Converter
Function: Converts toxic chemicals in vehicle exhaust into less harmful substances.
⚡ Catalyst
Role: Stimulates chemical reactions that convert combustion by-products into less toxic substances.
🔄 Three-Way Catalytic Converter
1⃣ Oxidation of CO → CO₂
2⃣ Oxidation of unburned hydrocarbons → CO₂ & H₂O
3⃣ Reduction of NOₓ → N₂ & O₂
💡 Fact: Catalytic converters remove hydrocarbons & harmful emissions but do not reduce CO₂ from fossil fuels.
🌍 Remediation Steps to Reduce Air Pollution
🚫 Ban open waste burning
🚗 Use smaller, fuel-efficient cars
🛣 Decrease unnecessary travel
☀ Distribute solar cook stoves
⚙ Maintain vehicles (regular tune-ups & oil changes)
🛑 Reduce idling & turn off engines while waiting
🚆 Use mass transit & carpool when possible
⚖ Toughen Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) standards
🛢 Reduce sulfur content in fuels through legislation
💨 Use fans instead of air conditioners
💡 Switch to LED or fluorescent lighting
🔍 Consider fuel efficiency when buying a car
🌧 Acid Deposition
Definition: Transformation of sulfur & nitrogen compounds into acidic wet or dry deposits on Earth.
🌀 Dry Deposition
Acidic chemicals in the air stick to surfaces (buildings, trees, cars).
Rainstorms wash them away, increasing acidic runoff.
💦 Wet Deposition
Includes acid rain, fog, & snow.
Affects plants, animals, and soil by increasing acidity.
🌲 Effects of Acid Rain
Acidifies lakes & streams.
Damages high-elevation forests & soils.
Harms decomposers & mycorrhizal fungi.
⚠ Acid Shock
Cause: Rapid melting of acidic snowpacks.
Effect: Raises acid concentration in lakes & streams 5-10x higher than acidic rainfall.
🔬 Acid Deposition from Sulfur Dioxide (SO₂)
Sources: Burning coal & oil, smelting metals, ocean spray, organic decay.
Process:
SO₂ + H₂O → Sulfurous Acid (H₂SO₃)
H₂SO₃ + O₂ → Sulfuric Acid (H₂SO₄)
🔬 Acid Deposition from Nitrogen Oxides (NOₓ)
Sources: Burning fossil fuels, volcanic gases, forest fires, lightning, soil bacteria.
⚠ Effects of Acid Deposition
🌊 Acid shock & fish kills.
🐾 Changes in animal life due to vegetation shifts.
🌱 Soil nutrient loss & reduced buffering capacity.
☠ Increased solubility of toxic metals (methyl mercury, lead, cadmium).
🔄 Ecosystem & food web disruptions.
🏙 Urban Heat Islands
Definition: Metropolitan areas warmer than surroundings.
🌧 Effect: Increased rainfall (up to 30% more downwind of cities).
🔥 Causes of Higher Urban Temperatures
🚗 Transportation, AC, & lighting generate heat.
🏢 Buildings block thermal radiation.
🌳 Lack of vegetation & water reduces cooling.
🚧 Black asphalt absorbs heat instead of reflecting sunlight.
🏙 Street Canyon Effect
Definition: Narrow streets flanked by tall buildings trap heat & pollution.
🌡 Localized Greenhouse Effect
Urban pollution traps heat, worsening warming effects.
⚕ Impact on Residents
Health risks for people who cannot afford AC.
🔊 Noise Pollution
Definition: Unwanted human-created sound that disrupts the environment.
Main Source: Transportation (cars, planes, trains).
⚠ Effects of Noise Pollution
🦻 Hearing Loss
Sensory hearing loss from inner ear damage is most common.
🧠 Cognitive & Emotional Effects
Reduced alertness & memory.
Increased anxiety & nervousness.
💓 Physical Health Effects
Cardiovascular issues (high blood pressure, rapid heartbeat).
Gastrointestinal problems (stomach issues).
🚗 Techniques to Reduce Roadway Noise
🛣 Traffic flow devices to reduce braking & acceleration.
🛑 Noise barriers along highways.
🏎 Improved tire designs & new road surfaces.
⏳ Restricted heavy-duty vehicle hours.
🚦 Lower speed limits.
✈ Techniques to Reduce Aircraft Noise
🛩 Develop quieter jet engines.
📅 Reschedule takeoff & landing times.
🏭 Techniques to Reduce Industrial Noise
⚙ New noise-reducing industrial technology.
🏢 Noise barriers in workplaces.
🚫 Local laws to control residential noise (power tools, loud music).