ch4 global supply chain management
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
supply chain
= network of activities to deliver finished products to customers
supplier provides raw materials and components
manufacturers transform these materials into finished products
products are distributed to retailers via distribution centers and or wholesalers
retailers sell the finished products to the end customer
suppliers
provide raw materials and components
manufacturers
transform these materials into finished products
distribution centers / wholesalers
distribue the products to the retailers
supply chain management SCM
coordination and management of all the activities of the supply chain → prime example of OM
supply chain components : internal functions
processing : transforming raw materials into finished products, packaging
purchasing : selecting suppliers, monitoring perofrmance, developing and maintaining relationships
production : planning and controling
quality assurance : overseeing quality
shipping : selecting carriers/ fleet
supply chain components : external distributors
logistic function
traffic management : selecting and monitoring of carriers/ fleet
distribution management : packaging, labelling, storing and handling at warehouses and at stores
major issues in supply chain management
E-commerce
globalization
infrastructure issues
government regulation
green supply chain management
green supply chain management
impact of supply chain on living environment and climate change ?
→ meeting present needs without compromising abilities of future generations
sourcing
is the proces of selecting suppliers to provide goods and services
important cosiderations during sourcing
how to choose between suppliers
availability
cost
quality
speed and reliability
one or more suppliers per item ?
partnership with a supplier ?
→ decisions must be in accordance with business strategy
vertcial integration
extent to which a suppy chain is owned/operated by the manufacturer
backwards integration : owning or controling sources of raw materials and components
forward integration : owning or controlling the channels of distribution
insourcing :
the manufacturer provides products and services in house
outsourcing
the manufacturer pays suppliers or third parties for their products and services
→ a product or service should not be outsourced if its
a company’s core competence
critical to the company’s success or survival
make or buy decisions based on
volume : indifference point
quality and functionality
required skills
available capital for investment
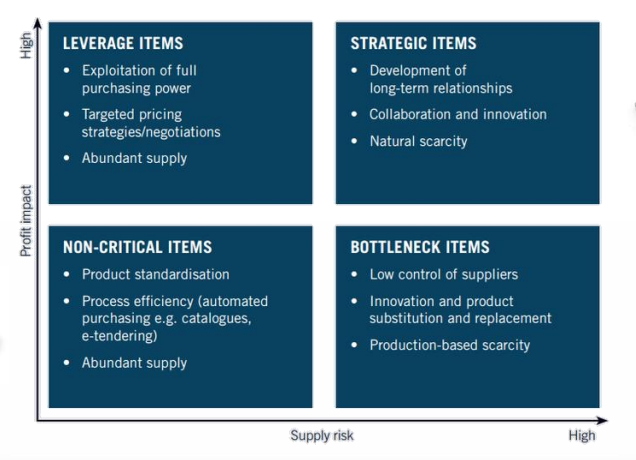
Kraljic matrix
→ 4 different sourcing strategies
strategic item
high profit impact and high supply risk
leverage items
high profit impact and low supply chain risk
non-critical items
low profit impact and supply risk
bottleneck items
high supply risk and low profit impact
partnering
developing a long-term relationship with a supplier based on mutual trust, shared vision, shared information, and shared risks
strategic in nature
driven by-end customer expectations
earrly supplier involvemenet (ESI)
critical suppliers are part of a cross-functional product design team (shared expertise, shorter time to market)
critical success factors of partnering
impact : attaining higher levels of productivity and competitiveness
elimination of duplicate and waste
leveraging core competencies
creating new opportunities
intimacy : trust to share all information on sales, operations ext
vision : agreement on the goals of the partnership and the role of each partner
benefits of partnering : manufacturer’s benefit
reduces costs
reduce duplication of effort
improve quality
reduce lead time
implement cost reduction program
involve suppliers earlier
reduce time to market
reduce inevntory
benefits of partnering ; supplier’s benefit
increases in sales volume
increase customer loyality
reduce costs
improve demand data
imrpove profitability
reduce inventory