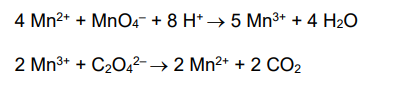Chemistry - 3.2.5: Transition Metals
1/102
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
103 Terms
4 characteristics of transition metals
Complex formation
Formation of coloured ions
Variable oxidation state
Catalytic activity
With the transition elements, where are electrons lost from first when ions are formed?
4s orbital
In the redox reaction between Fe (II) ions and MnO4 - ions, why does the colour of the solution change from colourless to pink?
Just after the end-point, MnO4- ions are in excess
Transition element
An element that forms at least one stable ion with an incomplete d-shell of electrons
Why are scandium and zinc not transition elements?
They do not form ions with partly full d-shells (Sc3+ = 3d0, Zn2+ = 3d0)
Complex ion
A central metal ion surrounded by co-ordinately bonded ligands
Ligand
An atom, molecule or ion which can donate a lone pair of electrons to form a co-ordinate bond
Co-ordination number
The number of co-ordinate bonds to the central metal atom or ion
Possible shapes of complexes
Octahedral if co-ordination number = 6
Tetrahedral or Square planar if co-ordination number = 4
Linear if co-ordination number = 2
Aqua ions
Ions that form when the salt of a transition metal is dissolved in water, so the positively charged metal ion is surrounded by (usually 6) water molecules acting as ligands
Multidentate ligands
Molecules or ions that have more than one atom with a lone pair of electrons which can bond to a transition metal ion
3 examples of monodentate ligands
H2O, NH3 and Cl-
Monodentate ligand
A molecule or ion that has one atom with a lone pair of electrons
2 examples of bidentate ligands
Ethane-1,2-diamine (H2NCH2CH2NH2) or ethanedioate ion C2O42-
Ethane-1,2-diamine abbreviation
en
Give an example of a mutlidentate ligand
EDTA4-
Chelate
A complex ion with multidentate ligands
What are chelates used for?
To remove d-block metal ions from solution
Why does the chelate effect take place? (3)
In a ligand substitution reaction,
- Enthalpy change is negligible (same number of bonds broken and formed)
- Entropy change is positive (more molecules in products)
So as ΔG = ΔH - TΔS,
- ΔG decreases and the reaction becomes more feasible
Compare the NH3 and H2O ligands (2)
Similar in size and uncharged
What happens to the co-ordination number when NH3 and H2O ligands are exchanged?
The co-ordination number does not change-
Why might a transition metal not be a good heterogenous catalyst? (2)
They adsorb too strongly so active sites blocked
They adsorb too weak so they are not held long enough for a reaction to occur
What transition metals are used in catalytic converters and how are they constructed to maximise their effect? (3 metals + 2)
Pt, Pd, Rh - deposited on ceramic honeycomb to increase surface area
Compare the Cl-, NH3 and H2O ligands and explain the impact on the co-ordination number
Cl- is larger than the other two (as uncharged) so fewer ligands can fit around the central metal ion - this means it has a co-ordination number of 4 rather than 6
What is haem?
An iron (II) complex with a multidentate ligand - has co-ordination number of 6.
What is haemoglobin’s function and how does it carry it out?
Transports oxygen around the body as oxygen forms a co-ordinate bond to the Fe2+ in haem
Why is carbon monoxide toxic?
It replaces the oxygen co-ordinately bonded to the Fe (II) in haemoglobin and binds more strongly to it
Describe the structure of haem
4 of the co-ordination sites are taken up by porphyrin (a tetradentate ligand), and another is taken up by a nitrogen of another protein
Give an example of a linear complex
Tollens’ reagent - [Ag(NH3)2]+
What type of isomerism can transition metal complexes form?
Geometrical isomers and optical isomers
What isomerism can octahedral complexes form?
Cis-trans isomerism with monodentate ligands and optical isomerism with bidentate ligands
With complexes, how do you determine which one is the cis isomer and which one is the trans isomer?
Cis = the ligands are next to each other
Trans = the ligands are on opposite sides of the central metal ion
Alternate name for cis isomer
Z isomer
Alternate name for trans isomer
E isomer
What isomerism can square planar complexes form?
Cis-trans isomerism
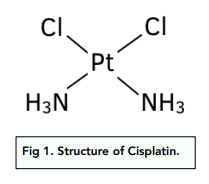
Cisplatin structure
How does colour arise?
Some of the wavelengths of visible light are transmitted / reflected into the eyes, while the remaining wavelengths are absorbed
Why are transition metal complexes coloured? (3)
The complex absorbs some wavelengths of light energy
This causes the d electrons move from a ground state to an excited state (i.e. to a higher energy level)
You therefore see the remaining wavelengths of light
What is the frequency of light related to? (2)
The energy difference between the d electron’s ground and excited state as well as the colour of light
What frequency of light is violet?
High frequency
What frequency of light is red?
Low frequency
What are the equations for the energy difference between the d electron’s ground and excited state?
ΔE = hv
ΔE = energy difference, h = Planck’s constant, v = frequency
OR
ΔE = hc/λ
ΔE = energy difference, h = Planck’s constant, c = speed of light, λ = wavelength
What does the colour of a transition metal complex depend on?
The energy gap ΔE
What does the energy difference (ΔE) depend on? (3)
The oxidation state of the metal ion
The co-ordination number
The ligand
What happens if the energy difference (ΔE) changes?
The colour of the complex changes
How does a simple colorimeter work?
It uses a light source and a detector to measure the amount of light of a particular wavelength that passes through a coloured solution
In colorimetry, what happens as the concentration of the solution increases?
The amount of light transmitted through the solution decreases
How can you use colorimetry to determine the concentration of an unknown solution? (3)
Make some known concentrations of the coloured solution and measure the absorbance of each one with a colorimeter
Plot a graph of absorbance against concentration
Read unknown concentration from graph
Why can co-ordinate bonds form between transition metal ions and ligands? (2)
The ligand donates a lone pair - the transition metal ion accepts it
Write out the reactions involved in the redox titration of Fe2+ by MnO4- (3)
MnO4- + 8H+ + 5e- → Mn2+ + 4H2O
Fe2+ → Fe3+ + e-
MnO4- + 8H+ + 5Fe2+ → Mn2+ + 5Fe3+ + 4H2O
How do you find the concentration of an oxidising / reducing agent?
By carrying out a redox titration
Ratio of Fe2+ to MnO4-?
5:1
Describe what happens in the redox titration of Fe2+ by MnO4- (3)
Add iron (II) sulfate tablets dissolved in sulfuric acid into a conical flask
Using a burette, gradually add potassium manganate solution (VII)
Stop when the colour of the mixture changes from colourless to pink
In the redox titration of Fe2+, why can’t you use hydrochloric acid instead of sulfuric acid?
Hydrochloric acid contains Cl- ions, which would also be oxidised by the MnO4- ions - the MnO4- ions should only be used to oxidise Fe2+ ions
In the redox titration of Fe2+, why is sulfuric acid used?
MnO4- ions do not oxidise sulfate ions
What affects the redox potential of a transition metal ion? (2)
The pH and the ligand
What happens if transition metal ions are in acidic solution?
They are reduced
How are transition metal ions with low oxidation states kept and why?
In acid solution to stabilise them against oxidation by air
What happens if transition metal ions are in alkaline solution and why?
Lower oxidation states of transition metal ions tend to be oxidised - because the solution is alkaline, there is a tendency to form negative ions and it is easier to lose electrons from negatively charged species than positively charged or neutral ones
What substitution occurs when transition metal ions are in alkaline solution?
One H2O ligand is replaced by an OH- for each positive charge of the metal ion
How are vanadium species in oxidation states IV, III and II formed?
By the reduction of vanadate (IV) ions by zinc in acidic solution
Write out the equations for the formation of each vanadium species with different oxidation states + the reduction of zinc. (4)
Zn → Zn2+ + 2e-
VO2+ + 2H+ + e- → VO2+ + H2O
VO2+ + 2H+ + e- → V3+ + H2O
V3+ + e- → V2+
How is Tollens’ reagent used to distinguish between aldehydes and ketones?
Aldehydes reduce [Ag(NH3)2]+ to metallic silver:
[Ag(NH3)2]+ + e- → Ag + 2NH3
Write out the reactions involved in the redox titration of C2O42- by MnO4- (3)
MnO4- + 8H+ + 5e- → Mn2+ + 4H2O
C2O42- → 2CO2 + 2e-
5C2O42- +2MnO4- +16H+ -> 10CO2 +2Mn2+ + 8H2O
Ratio of C2O42- to MnO4-?
5:2
2 types of catalysts
Heterogeneous and homogeneous
Heterogeneous catalysts
Catalysts that are in a different phase from the reactants
How do heterogeneous catalysts work? (3)
Normally, they’re solids and the reaction takes place on the solid surface
Reactants pass over the surface
The reaction takes place on active sites on the surface of the catalyst
How can heterogenous catalysts be made more efficient? (2)
Increasing their surface area
Spreading the catalyst onto an inert support medium to increase the surface-to-mass ratio
Why do heterogenous catalysts not last forever? (2)
Poisoning - the surfaces may become covered with unwanted impurities, blocking the catalsyt’s active sites
The catalyst may gradually be lost from the support medium
Give two examples of heterogeneous catalysts
Fe (s) in the Haber process
V2O5 in the contact process
How does V2O5 act as a catalyst in the contact process?
SO2 + V2O5 → SO3 + V2O4 (or 2VO2)
2V2O4 + O2 → 2V2O5
What is the contact process? Include the overall equation.
A process used to produce sulfuric acid:
2SO2 + O2 ⇌ 2SO3
Homogeneous catalyst
A catalyst that is in the same phase as the reactants
Give an example of a homogeneous catalyst
Fe2+ in the reaction between I- and S2O82-
How does Fe2+ act as a catalyst in the reaction between I- and S2O82-? (2)
S2O82- + 2Fe2+ → 2SO42- + 2Fe3+
2Fe3+ + 2I- → 2Fe2+ +I2
What is the overall equation in the reaction between I- and S2O82-?
S2O82- + 2I- → 2SO42- + I2
Why is a catalyst needed in the reaction between I- and S2O82-? (4)
Both the ions are negatively charged so would repel each other
So there is a high activation energy
The Fe ions are positively charged, so can attract each ion
This means they can provide an alternative route with a lower activation energy
Autocatalysis
When one of the products of the reaction is a catalyst for the reaction
Give an example of an autocatalysed reaction
The oxidation of ethanedioic acid by manganate (VII) ions
In redox reactions, what happens to Cr2O72- ions?
They are reduced to Cr3+
In redox reactions, what happens to Fe2+ ions?
They are oxidised to Fe3+
Why is a catalyst needed in the reaction between ethanedioic acid and acidified potassium dichromate solution? (3)
There is no/little catalyst at the start
There are two negative ions, which repel
So the reaction has a high activation energy
Sketch and describe a graph of how one of the reactants of an autocatalysed reaction (e.g. MnO4-) varies with time (2)
The rate increases as the catalyst forms
Then, the rate decreases as the MnO4- concentration decreases and is used up
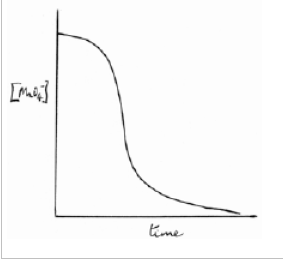
Why can transition metal ions be used as catalysts? (3)
They can exist in variable oxidation states
Include equations showing how each oxidation state is formed
This then lowers the activation energy (state effect)
How is the risk associated with the use of cisplatin as a drug minimised?
By being used in small amounts
How does the ligand / coordination number / oxidation state affect the colour of a complex? (3)
Different energies of d-electrons
Different wavelengths of light absorbed by the d-electrons
Different wavelengths of light transmitted
When carrying out colorimetry, why must the container for each sample have the same dimensions?
Absorption depends on the path length / distance travelled through solution
When carrying out colorimetry, why is a coloured filter used?
To select the wavelength most absorbed by the sample
Why might you use colorimetry instead of a titration? (2)
Quicker to analyse extracted samples than by titration / uses smaller volumes of solution
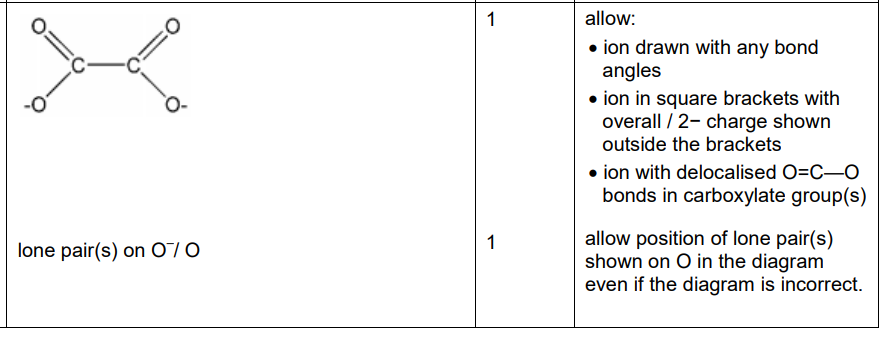
Draw an ethanedioate ion
Give 2 metal ions that do not change coordination number when in ligand substitution reactions with neutral ligands
Co2+ and Cu2+
Give 3 metal ions that change coordination number when in ligand substitution reactions where neutral ligands are replaced by charged ones (e.g. Cl-)
Co2+, Cu2+ and Fe3+
Why are Cu / Cr complexes not coloured? (2)
It has a full d orbital
So cannot absorb frequencies of visible lights
In a ligand substitution reaction, why is the enthalpy change close to 0? (2)
The bonds being broken and formed are similar, so have similar enthalpy
The same number of bonds are being broken and made.
What process does cisplatin inhibit during cell division?
DNA replication
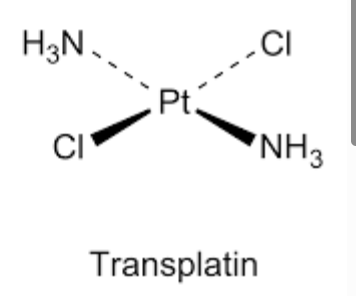
Transplatin structure
This is the equation for the reaction between C2O42- ions and MnO4- ions.
5C2O42- +2MnO4- + 16H+ -> 10CO2 + 2Mn2+ + 8H2O
Write out two equations showing how the Mn2+ ions catalyse this reaction.
4Mn2+ + MnO4- + 8H+ → 5Mn3+ + 4H2O
2Mn3+ + C2O42- → 2Mn2+ + 2CO2