Exam 2 REPRO PHYSIO
1/349
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
350 Terms
Can oogenesis happen without folliculogenesis
no
Reproduction
series of physiological and psychological events that must be properly timed
T/F: we can define reproduction as needing a functional male and a willing female
true
T/F: rate-limiting factor in farm animals, and most mammals is the male
false; it’s the female
What are the 2 breeding patterns in mammals (include examples of species for each)
once per cycle desire to mate (exhibit a standing heat)
ex: domestic mammals
breed. whenever they want (Ab Libitum: At will)
ex: humans and dolphins
[1.] is defined as standing heat, one event; [2.] is the progressive accomplishments of alterations in repro tract characterisitcs of estrus, metestrus, diestrus, and proestrus produced by changes in ovarian hormones, entire cycle
Estrus
Estrous Cycles
T/F: the structures on the ovary control what cycle female is in and how structure works
true
Breeding Exhaustion
point where male has mated too many times and is producing too few sperm to allow for a reasonable chance for pregnancy
What controls where a female is in her cycle
a) brain
b) muscles
c) structures on her mammary glands
d) structures on her ovary
d) structures on her ovary
T/F: Breeding Exhaustion is GREAT for optimizing repro/fertilization
false
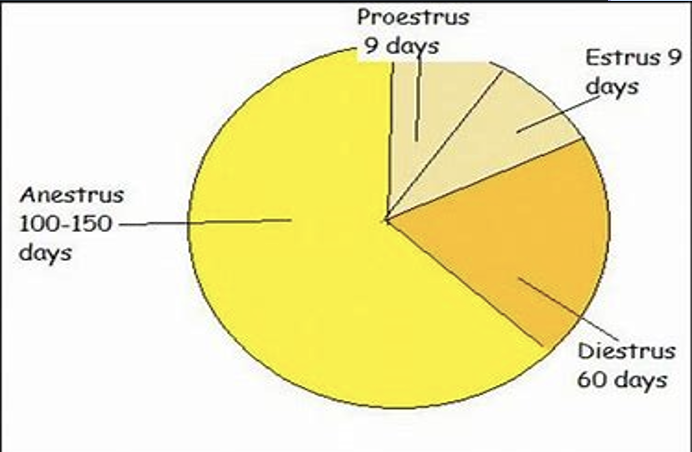
List out the whole Estrous Cycle (hint: 4 phases)
proestrus → estrus → metestrus → diestrus
Do Estrous Cycles occur in non primate females
yes
T/F: The estrous cycle is the period from the beginning of estrus to the beginning of next estrus
true
Estrous cycles are the growth of [?], ovulation of [?] around the time of standing heat, and formation of a corpus luteum
a) hormones
b) follicles
c) corpus hemorrhagicum
d) P4
b) follicles
If the animal is NOT pregnant, the estrous cycle (will or will not?) start over
will
Cycles begin at [What]
ovulation occurs in this phase
start of cycle
clear and observable signs in this phase
a) Estrus
b) Proestrus
c) Metestrus
d) Diestrus
a) estrus
T/F: Estrus and Estrous length varies bt species
true
Animals will ovulate during or just after estrus, the ovary will switch gears and go from growing follicles to creating [what]
a) more follicles
b) none of these
c) corpus luteum
c) corpus luteum
corpus hemorrhagicum, which is a major anatomical feature on ovary during what phase
metestrus
corpus luteum occurs in what phase
diestrus (longest phase of cycle)
If you see follicular growth on the ovary, what phase of the cycle is this
proestrus
Anestrus
(in some species) period bt diestrus and proestrus when nothing is happening
NOT part of the cycle
period when ovary and hormones are quiet like they were before puberty
Ewe
length of cycle “estrous” :
length of heat “estrus” :
length of cycle “estrous” : 16-17 d
length of heat “estrus” : 24-36 hrs
Goat
length of cycle “estrous” :
length of heat “estrus” :
length of cycle “estrous” : 21 d
length of heat “estrus” : 32-40 hrs
Sow
length of cycle “estrous” :
length of heat “estrus” :
length of cycle “estrous” : 19-21 d
length of heat “estrus” : 48-72 hrs
Cow
length of cycle “estrous” :
length of heat “estrus” :
length of cycle “estrous” : 20-22d
length of heat “estrus” : 18-24 hrs
Mare
length of cycle “estrous” :
length of heat “estrus” :
length of cycle “estrous” : 19-25 d
length of heat “estrus” : 4-7d
Days 17 to 21 of estrous cycle of cow is considered apart of what phase of cycle
proestrus (follicular)
which phase do these describe
ovarian follicles are growing rapidly
increase in estrogen secretion by growing follicles
decrease in P4 from corpus luteum (CL)
mucosal layers of vagina and uterus multiply
a) proestrus
b) anestrus
c) diestrus
d) none
a) proestrus
T/F: proestrus must occur first in order to have an ovulation
true
Proestrus begins as CL from previous cycle becomes atretic (closure), stops function → no more P4
What effect will this have
no more negative feedback on GnRH, FSH, LH → follicular development due to estrogen
in 3-4 days, some follicles go primary to secondary to tertiary, estrogen peaks which causes a transition from proestrus → ?
estrus
Diagram of Proestrus (I made this so chill)
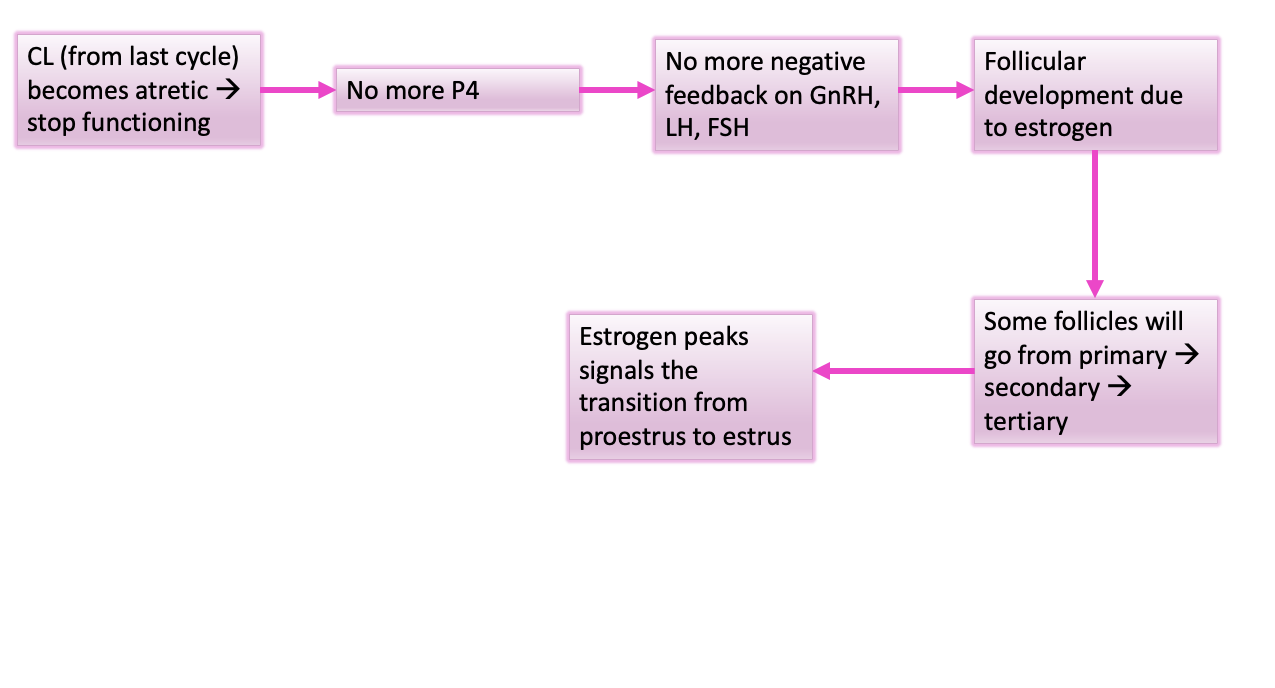
Describe the uterine changes during proestrus
increase in number of cells in both the uterus and vagina, and uterus is in follicular phase
Estrogen during proestrus
mucus in uterus, vagina, and cervix will begin to thin out and become watery (helps sperm transport)
Estrous Cycle Diagram
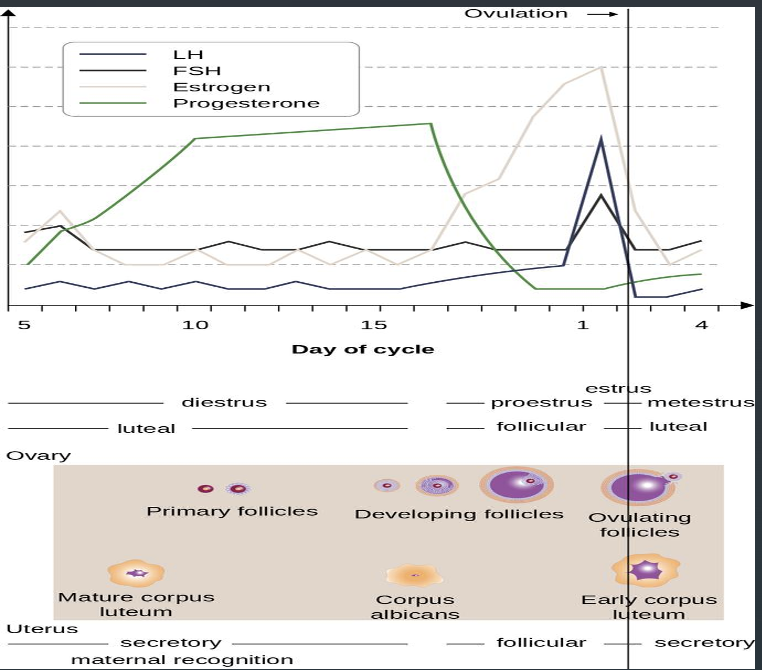
What phase do the following characteristics describe
period of sexual receptivity in female
called heat
first day of standing heat is day 1
a) proestrus
b) anestrus
c) diestrus
d) estrus
d) estrus
T/F: Estrus is the end of follicular phase
true
When does ovulation occur
during estrus or a few hours after it ends
Reproductive receptivity
time when female in estrus stands to be mated
Estrus induces behaviors conducive to what
a) sleeping
b) social bonding
c) mating
d) none
c) mating
T/F: estrogen-induced contraction will move the sperm away from the tract (AIJ- site of fertilization)
false: moves the sperm up to AIJ
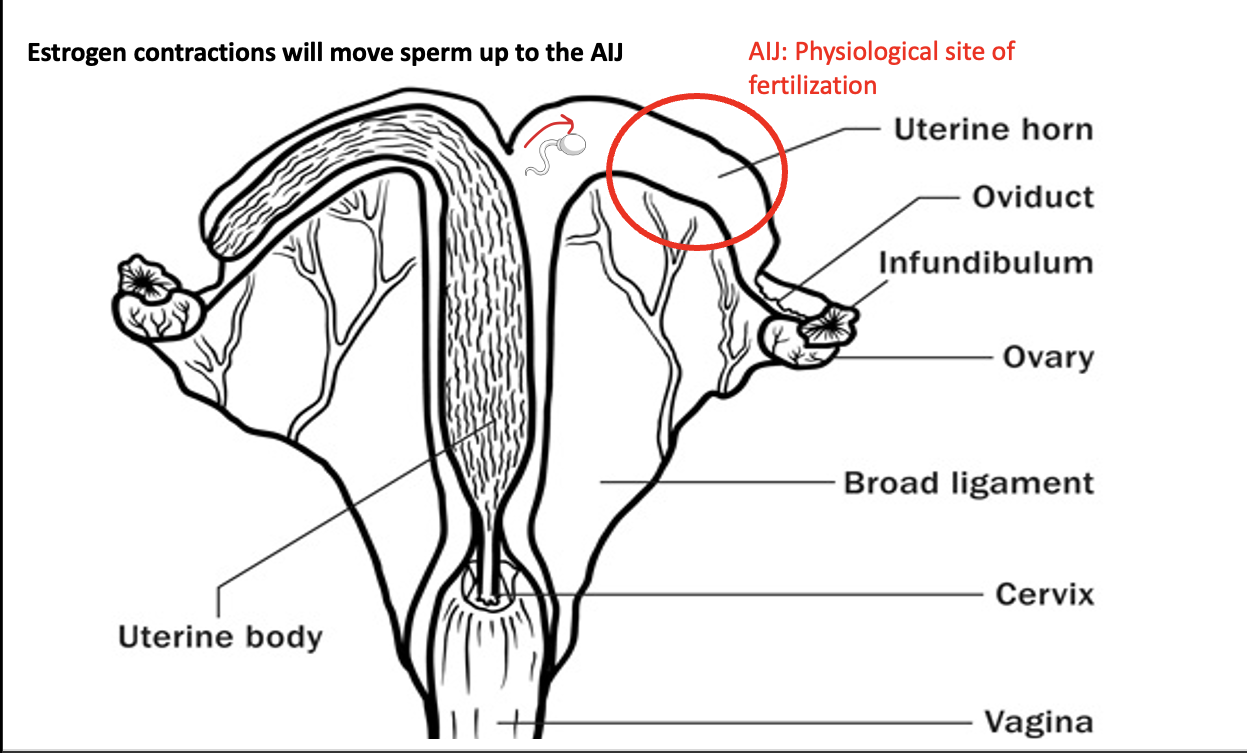
Estrogens (during estrus) will lead to a surge of what 2 hormones
FSH and LH
LH surge triggers ovulation and begins transformation of theca and granulosa of follicle into what
P4-producing luteal cells of corpus luteum
T/F: (Estrus) Uterus will remain in follicular phase until ovulation
true
Diagram of Estrus that I made
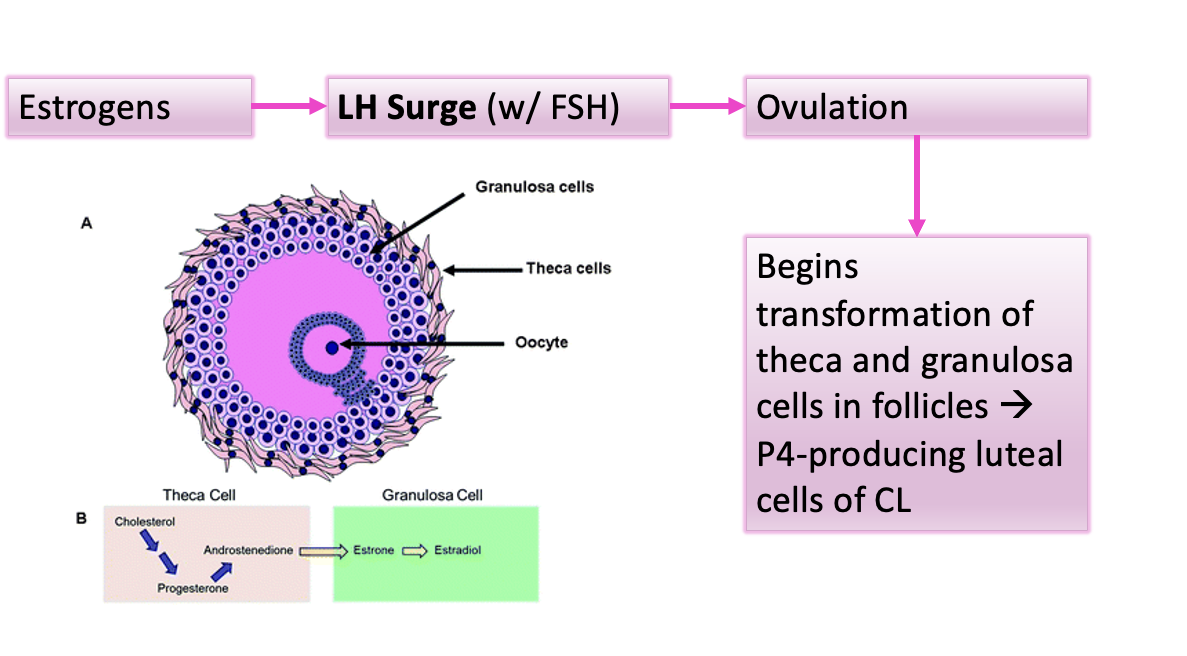
Metestrus (luteal phase)
short transition period, within the luteal phase, that transforms repro system from estrogen dominated system to a P4 dominated system attempting to support a preg
after ovulation, ovary will enter what phase, while the uterus enters the secretory phase of development
luteal
after ovulation, follicle collapses into what structure, blood clot, non functioning
corpus hemorragicum
the blood clot (corpus hemo.) is replaced by functional cells, P4. By what day does the corpus hemorrhagicum transformed to corpus luteum
a) day 5
b) day 2
c) day 10
d) day 1
a) day 5
What phase are we in according to these characteristics
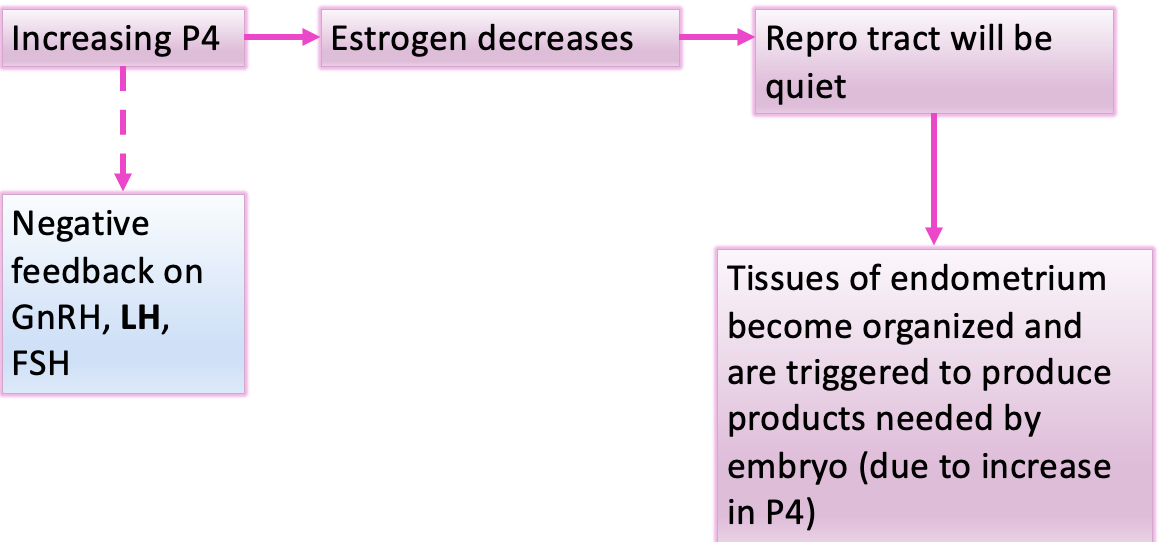
P4 lvls rise and estrogen lvls drop
repro tract is going quiet
increasing P4 conc. induces tissues of endometrium to become organized and trigger them to produce products needed by embryo
ex: cow, this will be period of ovulation, occuring a few hours after animal finishes standing heat
a) proestrus
b) diestrus
c) anestrus
d) metestrus
d) metestrus
the rising P4 occurring in metestrus causes a (positive or negative?) feedback on GnRH, FSH, and LH (esp LH)
negative feedback
Diagram of Metestrus that I made
what phase is during/start of day 1 of cycle
a) estrous
b) estrus
c) proestrus
d) none
b) estrus
what event triggers ovulation?
a) P4 rise
b) PGF2 alpha
c) none
d) LH surge
d) LH surge
T/F: metestrus and diestrus are in the luteal phase of the estrous cycle
true
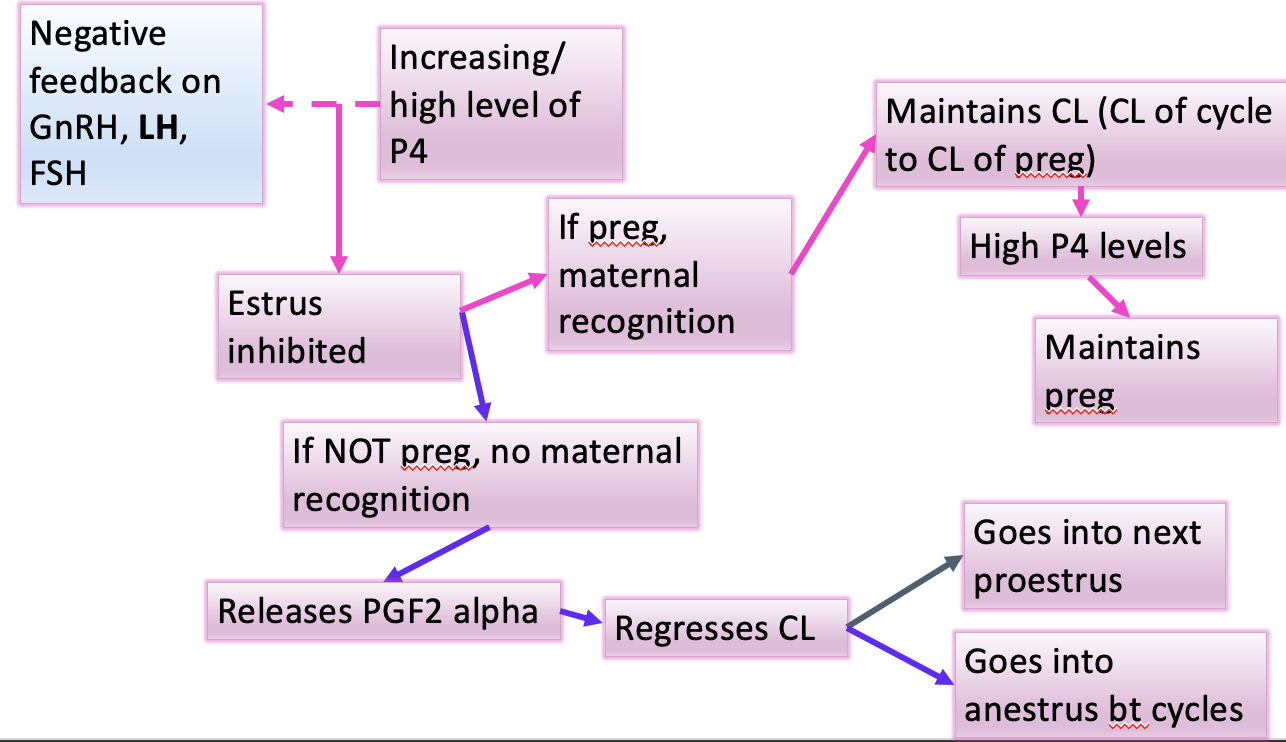
What phase are we in according to these characteristics?
longest period of estrous cycle in domestic species (short cycle animals lack this phase completely if NOT preg)
rising or high lvls of P4
GnRH, FSH, LH inhibited
estrus inhibited
maternal recognition signal must occur in this phase if animal is preg
maintains CL; CL of cycle to CL of preg
a) estrus
b) proestrus
c)diestrus
d) anestrus
c) diestrus
Maternal recognition
physiological recognition of preg, by female adults’ system due to a chemical signal from embryo
If there is no maternal recognition signal during diestrus, what hormone will be released (Hint: think of the main structure on ovary we need to get rid of)
a) Lactogen
b) GnRH
c) P4
d) PGF2 alpha
d) PGF2 alpha
(Diestrus) No maternal recognition signal → release of PGF2 alpha → regresses CL → what will happen in these species
cow and pig
horse and sheep
cow and pig: goes into immediately into next proestrus (repeating cycles)
horse and sheep: leave estrous cycle from diestrus and goes through anestrus period (anestrus occurs bt cycles)
Diagram of Diestrus that I made
What is occurring according to the following
period bt diestrus and proestrus in monoestrous and seasonal polyestrous animals
non-breeding season of ewe and mare
varies in length
quiet of repro tract
ends when proestrus begins
NOT a phase OF ESTROUS CYCLE
a) estrus
b) anestrus
c) luteal
d) ovulation
b) anestrus
Continuous Estrus
estrous animal w/ constant desire to mate and whose ovulation is triggered by act of mating
T/F: follicles are constantly developing then regressing → no luteal phase in continuous estrus
true
In diff types of estrous cycles, who does the continuous type occur in
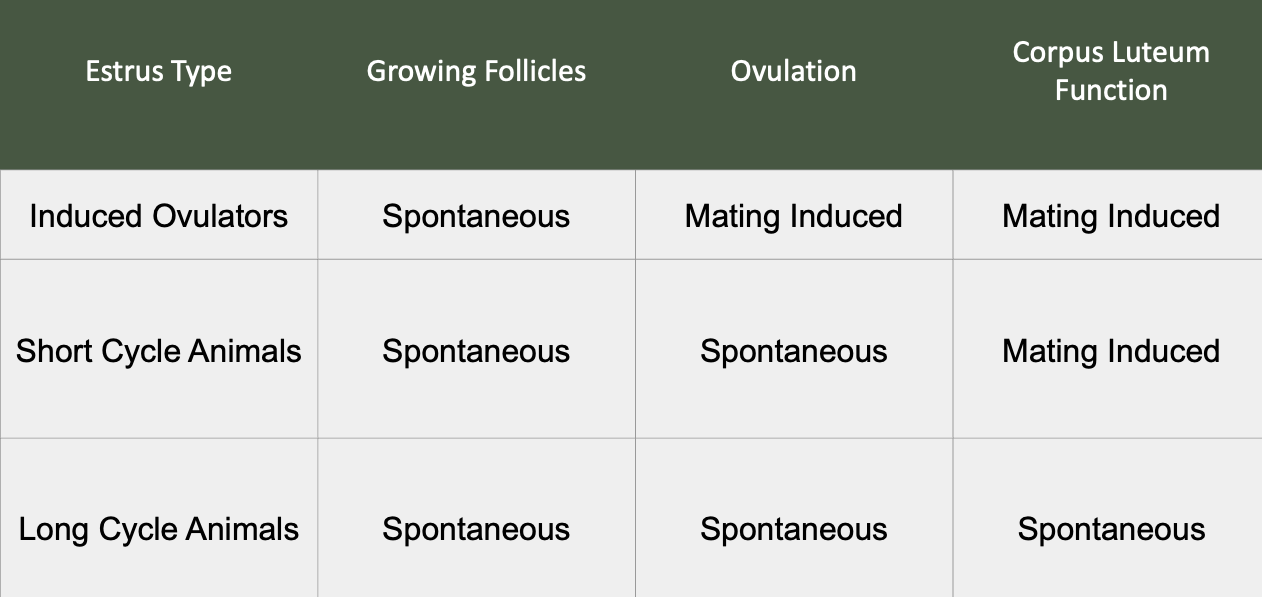
rabbits and other induced ovulators
In continuous estrus cycles:
LH release is induced by [what?]
ovulation occurs 8-12 hrs after mating
act of mating sends a nervous impulse triggers [what?] surge (induced ovulation)
mating
LH
Induced ovulator means ovulation is triggered by what
act of mating
T/F: in induced ovulators:
the nervous impulse, during mating, triggers LH surge
extremely high conception rates, sperm in tract same time as ovulation
true
Monoestrous
single cycle per year
ex: bears, wolfs, foxes and many dog breeds
single cycle → anestrus → single cycle
True polyestrous
2 or more estrous cycles per year UNLESS interrupted by preg
composed of proestrus, estrus, metestrus, and diestrus merging into proestrus
what species are true polyestrous
cows and pigs
Seasonal polyestrous
same as true poly. but last diestrus of breeding season would go into anestrus
cycles are exactly like true polyestrous animals when in season
out of season, complete the cycle with diestrus and go into anestrus (melatonin)
what species are seasonal polyestrous
sheep and horses
what are the 2 categories of polyestrous cycle?
a) true polyestrous and seasonal polyestrous
b) true polyestrous and false polyestrous
c) real polyestrous and fake polyestrous
d) true polyestrous and multiestrous
a) true polyestrous and seasonal polyestrous
Proposed mechanisms of seasonal polyestrous
retina of eye is sensor for light signals
impulses travel by way of optic nerve to pineal gland
pineal gland releases melatonin
melatonin serves as mediator bt photoreceptors, hypothalamus, and/or anterior pituitary
episodic surges of LH occurs as breeding season begins
Postpartum estrus
estrus occurring within a few days after delivery
rarely seen in cattle or sheep: they have extended postpartum anestrus period to allow repair of repro tract
Sow Heat
postpartum estrus ~3-10 days after farrowing, they rarely ovulate → cycle is sub or infertile
Foal heat
bt 5-15 days after foaling
can ovulate and become preg on these cycles
usually lower fertility due to damage to repro tract
Silent or Quiet Estrus/ Quiet ovulation
during estrus, ovulation occurs but none of physiological signs of standing heat
lack of receptors for estrogen in brain which form in response to having seen P4 from previous cycle
where would you see silent or quiet estrus
seen in farm animals on cycle before first standing heat or after long anestrus period
Will animals going through a silent or quiet estrus stand to be mated
no
Which of these are the cause of silent or quiet estrus
a) heat stress
b) stress
c) iodine limiting
d) predisposed condition
e) all of above
e) all of above
Anovulatory estrus
estrus w/o ovulation
occurs in all farm animals
ex: postpartum estrus in sows
What type of estrus is characterized as a continuous psychological desire to mate by female animal that’s not in heat
a) anovulatory
b) nymphomania
c) silent estrus
d) anestrus
b) nymphomania
T/F: ovulation rarely occurs in nymphomania
true
T/F: Nymphomania most occurs in cows (less in mares and rarely in sheep or pigs)
true
T/F: all individuals w/ cystic ovaries display nymphomania
false; not ALL
cystic ovaries do USUALLY accompany nymphomaniac condition
T/F: during foal heat, mares have a high fertility rate
false
Anovulatory estrus can occur in what animals
a) only sheep
b) only dogs
c) English cows
d) all farm animals
d) all farm animals
spontaneous ovulation is the most common, hormonal, but does this require a male involved
no
What type of ovulation does this explain
repeated ovulation at regular intervals except during preg
LH release is cyclic and independent of mating stimulus
LH release is triggered by increasing conc. of estrogen
a) spontaneous
b) mating induced
c) none of above
a) spontaneous
What animals does spontaneous ovulation occurs in
cow, ewe, sow, mare, rat, hamster, and guinea pig
T/F: in induced ovulation, ovulation occurs after stimulation of vagina and/or cervix, requires mating
true
In induced ovulations, LH release occurs only (before or after?) mating stimulus
after
How induced ovulation works
lacks receptors for estrogen on cells that release LH
nerve connection during mating
nerves set off in vagina, which gives feedback to AP to trigger LH surge and ovulation
absent of mating → follicles don’t ovulate
mating is needed to trigger ovulation and CL
T/F: Continuous estrus animals (rabbits) are induced ovulators
estrus persists for variable time
occurs in rabbit, cat, mink, and llama
true
Long cycle animals: grow follicles → LH surge → ovulates → forms what
corpus hemorrhagicum and functional CL, corpus albicans
Small rodents have fast metabolisms have a physiological strategy that save energy normally assoc. with what phase of estrous cycle
diestrus
Non-preg cycle of rodent
growing follicles → ovulating → forming a corpus hemorrhagicum → not preg → SKIPS forming CL → returns to follicular phase
how: systems require physical stim of vagina and nervous signal, which triggers CL formation and P4 production
no signal, P4 lvls low → no negative feedback on hypothalamus and AP → animal goes right back to metestrus
Chart of Induced Ovulators, Short Cycle, and Long Cycle (KNOW)