BOC: 226-308 III. Acid-Base, Blood Gases & Electrolytes
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
226.) The expected blood gas results for a patient in chronic renal failure would match the pattern of:
A. metabolic acidosis
B. respiratory acidosis
C. metabolic alkalosis
D. respiratory alkalosis
A
227.) Severe diarrhea causes:
A. metabolic acidosis
B. metabolic alkalosis
C. respiratory acidosis
D. respiratory alkalosis
A

228.) The patient's results are compatible with which of the following?
A. fever
B. uremia
C. emphysema
D. dehydration
C
230.) An emphysema patient suffering form fluid accumulation in the alveolar spaces is likely to be in what metabolic state?
A. respiratory acidosis
B. respiratory alkalosis
C. metabolic acidosis
D. metabolic alkalosis
A
231.) At blood pH 7.40, what is the ratio for bicarbonate to carbonic acid?
A. 15:1
B. 20:1
C. 25:1
D. 30:1
B
233.) The reference range for the pH of arterial blood measured at 37C is:
A. 7.28-7.34
B. 7.33-7.37
C. 7.35-7.45
D. 7.45-7.50
C
234.) A 68-year-old man arrives in the emergency room with a glucose level of 722 mg/dL (39.7 mmol/L) and serum acetone of 4+ undiluted. An arterial blood gas form this patient is likely to be:
A. low pH
B. high pH
C. low pO2
D. high pO2
A
235.) A patient is admitted to the emergency room in a stage of metabolic alkalosis. Which of the following would be consistent with this diagnosis?
A. high TCO2, increased HCO3
B. low TCO2, increased HCO3
C. high TCO2, decreased H2CO3
D. low TCO2, decreased H2CO3
A
236.) A person suspected of having metabolic alkalosis would have which of the following laboratory findings?
A. CO2 content and PO2 elevated, pH decreased
B. CO2 content decreased and pH elevated
C. CO2 content, PCO2, and pH decreased
D. CO2 content and pH elevated
D
237.) Metabolic acidosis is described as a(n):
A. increase in CO2 content and pCO2 with a decreased pH
B. decrease in CO2 content with an increased pH
C. increase in CO2 with an increased pH
D. decrease in CO2 content and pCO2 with a decreased pH
D
238.) Respiratory acidosis is described as a(n):
A. increase in CO2 content and pCO2 with a decreased pH
B. decrease in CO2 content with an increased pH
C. increase in CO2 content with an increased pH
D. decrease in CO2 content and pCO2 with a decreased pH
A
239.) A common cause of respiratory alkalosis is:
A. vomiting
B. starvation
C. asthma
D. hyperventilation
D
240.) Acidosis and alkalosis are best defined as fluctuations in blood pH and CO2 content due to changes in:
A. Bohr effect
B. O2 content
C. bicarbonate buffer
D. carbonic anhydrase
C
241.) A blood gas sample was sent to the lab on ice, and a bubble was present in the syringe. The blood had been exposed to room air for at least 30 minutes. The following change in blood gases will occur:
A. CO2 content increased/pCO2 decreased
B. CO2 content and pO2 increased/pH increased
C. CO2 content and pCO2 decreased/pH decreased
D. pO2 increased/HCO3 decreased
D
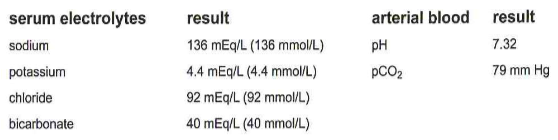
242.) These results are most compatible with:
A. respiratory alkalosis
B. respiratory acidosis
C. metabolic alkalosis
D. metabolic acidosis
B
264.) Select the test which evaluates renal tubular function:
A. IVP
B. creatinine clearance
C. osmolarity
D. microscopic urinalysis
C

265.) A patient had the following serum results. Which osmolality is consistent with these results?
A. 188
B. 204
C. 270
D. 390
C
266.) The degree to which the kidney concentrates the glomerular filtrate can be determined by:
A. urine creatine
B. serum creatinine
C. creatinine clearance
D. urine to serum osmolality ratio
D
267.) Osmolal gap is the difference between:
A. the ideal and real osmolality values
B. calculated and measured osmolality values
C. plasma and water osmolality values
D. molality and molarity at 4C
B
243.) The most important buffer pair in plasma is the:
A. phosphate/biphosphate pair
B. hemoglobin/imidazole pair
C. bicarbonate/carbonic acid pair
D. sulfate/bisulfate pair
C
268.) Quantitation of Na+ and K+ by ion-selective electrode is the standard method because:
A. dilution is required for flame photometry
B. there is no lipoprotein interference
C. of advances in electrochemistry
D. of the absence of an internal standard
C
275.) A potassium level of 6.8 mEq/L (6.8 mmol/L) is obtained. Before reporting the results, the first step the technologist should take is to:
A. check the serum for hemolysis
B. rerun the test
C. check the age of the patient
D. do nothing, simply report out the result
A
276.) The solute that contributes the most to the total serum osmolality is:
A. glucose
B. sodium
C. chloride
D. urea
B
269.) What battery of tests if most useful in evaluating an anion gap of 22 mEq/L (22 mmol/L)?
A. Ca++, Mg++, PO-4, and pH
B. BUN, creatinine, salicylate and methanol
C. AST, ALT, LD and amylase
D. glucose, CK, myoglobin and cryoglobulin
B
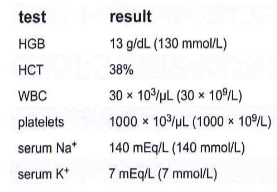
270.) A patient with myeloproliferative disorder has the following lab results. The serum K+ should be confirmed by:
a. repeat testing of the original serum
b. testing freshly drawn serum
c. testing heparinized plasma
d. atomic absorption spectrometry
C
244.) Most of the carbon dioxide present in blood is in the form of:
A. dissolved CO2
B. carbonate
C. bicarbonate ion
D. carbonic acid
C
271.) Serum "anion gap" is increased in patients with:
A. renal tubular acidosis
B. diabetic alkalosis
C. metabolic acidosis due to diarrhea
D. lactic acidosis
D
The anion gap is useful for quality control of laboratory results for:
A. amino acids and proteins
B. blood gas analyses
C. sodium, potassium, chloride, and total CO2
D. calcium, phosphorus and magnesium
C
245.) In respiratory acidosis, a compensatory mechanism is:
a. increased respiration rate
b. decreased ammonia formation
c. increased blood pCO2
d. increased plasma bicarbonate concentration
D
277.) A sweat chloride result of 55 mEq/L (55 mmol/L) and a sweat sodium of 52 mEq/L (52 mmol/L) were obtained on a patient who has a history of respiratory problems. The best interpretation of these result is:
A. normal
B. normal sodium and an abnormal chloride test should be repeated
C. abnormal results
D. intermediate results
D
278.) Which of the following is true about direct ion selective electrodes for electrolytes?
A. whole blood specimens are acceptable
B. elevated lipids cause falsely decreased results
C. elevated proteins cause falsely decreased results
D. elevated platelets cause falsely increased results
A
279.) Sodium determination by indirect ion-selective electrode is falsely decreased by
A. elevated chloride levels
B. elevated lipid levels
C. decreased protein levels
D. decreased albumin levels
B
280.) A physician requested that electrolytes on a multiple myeloma patient specimen be run by direct ISE and not indirect ISE because:
A. excess protein binds Na in indirect ISE
B. Na is falsely increased by indirect ISE
C. Na is falsely decreased by indirect ISE
D. excess protein reacts with diluent in indirect ISE
C
281.) Which percentage of total serum calcium is nondiffusible protein bound?
A. 80%-90%
B. 51%-60%
C. 40%-50%
D. 10%-30%
C
283.) The regulation of calcium and phosphorous metabolism is accomplished by which of the following glands?
A. thyroid
B. parathyroid
C. adrenal glands
D. pituitary
B
284.) A hospitalized patient is experiencing increased neuromuscular irritability (tetany). Which of the following tests should be ordered immediately?
A. calcium
B. phosphate
C. BUN
D. glucose
A
Which of the following is most likely to be ordered in addition to serum calcium to determine the cause of tetany?
A. magnesium
B. phosphate
C. sodium
D. vitamin D
A
287.) Fasting serum phosphate concentration is controlled primarily by the:
A. pancreas
B. skeleton
C. parathyroid glands
D. small intestine
C
288.) A low concentration of serum phosphorus is commonly found in:
A. patients who are receiving carbohydrate hyperalimentation
B. chronic renal disease
C. hypoparathyroidism
D. patients with pituitary tumors
A
286.) A reciprocal relationship exists between:
A. sodium and potassium
B. calcium and phosphate
C. chloride and CO2
D. calcium and magnesium
B
290.) Total iron-binding capacity measures the serum iron transporting capacity of:
A. hemoglobin
B. ceruloplasmin
C. transferrin
D. ferritin
C
291.) The first step in the quantitation of serum iron is:
A. direct reaction with appropriate chromogen
B. iron saturation of transferrin
C. free iron precipitation
D. separation of iron from transferrin
D
292.) A patient's blood was drawn at 8 am for a serum iron determination. The result was 85 ug/dL (15.2 umol/L). A repeat specimen was drawn at 8 PM; the serum was stored at 4 C and run the next morning. The result was 40 ug/dL (7.2 umol/L). These result are most likely due to:
A. iron deficiency anemia
B. improper storage of the specimen
C. possible liver damage
D. the time of day the second specimen was drawn
D
293.) A low serum iron with low iron binding capacity is most likely associated with:
A. iron deficiency anemia
B. renal damage
C. anemia of chronic infection
D. septicemia
C
294.) Decreased serum iron associated with increased TIBC is compatible with which of the following disease states?
A. anemia of chronic infection
B. iron deficiency anemia
C. chronic liver disease
D. nephrosis
B

295.) A patient has the following results. The best conclusion is that the Pt has:
A. normal iron status
B. iron deficiency anemia
C. chronic disease
D. iron hemochromatosis
D

296.) Serum and urine copper levels are assayed on a hospital patient with the following results. This is most consistent with:
A. normal copper levels
B. Wilms tumor
C. Wilson disease
D. Addison disease
C
248.) Blood received in the laboratory for blood gas analysis must meet which of the following requirements?
A. on ice, thin fibrin strands only, no air bubbles
B. on ice, no clots, fewer than 4 air bubbles
C. on ice, no clots, no air bubbles
D. room temperature, not clots, no air bubbles
C
297.) After a difficult venipuncture requiring prolonged application of the tourniquet, the serum K+ was found to be 6.9 mEq/L (6.9 mmol/L). The best course of action is to:
A. repeat the test using the same specimen
B. adjust the value based on the current serum Na+
C. repeat the test using freshly drawn serum
D. cancel the test
C

298.) Serum from a patient with metastatic carcinoma of the prostate was separated form the clot and stored at room temperature. The following results were obtained. The technician should repeat the:
A. LD using dilute serum
B. acid phosphatase with freshly drawn serum
C. LD with fresh serum
D. test using plasma
B

249.) Arterial blood that is collected in a heparinized syringe but exposed to room air would be most consistent with the changes in which of the following specimens?
A. specimen A
B. specimen B
C. specimen C
D. specimen D
A
251.) Unless blood gas measurements are made immediately after sampling, in vitro glycolysis of the blood causes a:
A. rise in pH and pCO2
B. fall in pH and a rise in pO2
C. rise in pH and a fall in pO2
D. fall in pH and a rise in pCO2
D
An arterial blood specimen submitted for blood gas analysis was obtained at 8:30 AM but was not received in the laboratory until 11 AM. The technologist should:
A. perform the test immediately upon receipt
B. perform the test only if the specimen was submitted in ice water
C. requires a venous blood specimen
D. request a new arterial specimen be obtained
D
253.) If the pKa is 6.1, the CO2 content is 25 mM/L, the salt equals the total CO2 content minus the carbonic acid; the carbonic acid equals 0.03 x PCO2 and PCO2- 40 mmHg, it may be concluded that:
A. pH=6.1 + log [(40-0.03)/(0.03)]
B. pH=6.1 + log [(25-0.03)/(0.03)]
C. pH=6.1 + log [(25-1.2)/(1.2)]
D. pH= 6.1 + log [(1.2)/(1.2-25)]
C
250.) Specimens for blood gas determination should be drawn into a syringe containing:
A. no preservative
B. heparin
C. EDTA
D. oxalate
B
254.) The bicarbonate and carbonic acid ratio is calculated from an equation by:
A. Siggaard-Andersen
B. Gibbs-Donnan
C. Natelson
D. Henderson-Hasselbalch
D
299.) The osmol gap is defined as measured Osm/kg minus the calculated OSm/kg. Normally, the osmol gap is less than:
A. 10
B. 20
C. 40
D. 60
A
256.) Normally the blood bicarbonate concentration is about 24 mEq/L and the carbonic acid concentration is about 1.2, pK=6.1, log 20= 1.3. Using the equation pH= pK + log [salt]/[acid], calculate the pH.
A. 7.28
B. 7.38
C. 7.40
D. 7.42
C
300.) In the atomic absorption method for calcium, lanthanum is used:
A. as an internal standard
B. to bind calcium
C. to eliminate protein interference
D. to prevent phosphate interference
D
301.) Which of the following methods is susceptible to the solvent displacing effect that results in falsely decreased electrolyte values?
A. indirect ion-selective electrodes
B. direct ion-selective electrodes
C. alkaline electrophoretic separation of ions
D. fluorescence
A
257.) An electrode has a silver/silver chloride anode and a platinum wire cathode. It is suspended in KCl solution and separated form the blood to be analyzed by a selectively permeable membrane. Such an electrode is used to measure which of the following?
A. pH
B. pCO2
C. pO2
D. HCO3
C
258.) Hydrogen ion concentration (pH) in blood is usually determined by means of which of the following electrodes?
A. silver
B. glass
C. platinum
D. platinum-lactate
B
303.) Coulometry is often used to measure:
A. chloride in sweat
B. the pH in saliva
C. bicarbonate in urine
D. ammonia in plasma
A
302.) An automated method for measuring chloride which generates silver ions in the reaction is:
A. coulometry
B. mass spectroscopy
C. chromatography
D. polarography
A
259.) In a pH meter reference electrodes may include:
A. silver-silver chloride
B. quinhydrone
C. hydroxide
D. hydrogen
A
260.) Amperometry is the principle of the:
A. pCO2 electrode
B. pO2 electrode
C. pH electrode
D. Ionized calcium electrode
B
262.) Blood PCO2 may be measured by:
A. direct colorimetric measurement of dissolved CO2
B. a self-contained potentiometric electrode
C. measurement of CO2-saturated hemoglobin
D. measurement of CO2 consumed at the cathode
B
261.) Most automated blood gas analyzers directly measure:
A. pH, HCO3 and % O2 saturation
B. pH, pCO2 and pO2
C. HCO3, pCO2 and pO2
D. pH, pO2 and % O2 saturation
B
304.) Valinomycin enhances the selectivity of the electrode used to quantitate:
A. sodium
B. chloride
C. potassium
D. calcium
C
306.) Which of the following calcium procedures utilizes lanthanum chloride to eliminate interfering substances?
A. o-cresolphthalein complexone
B. precipitation with chloranilic acid
C. chelation with EDTA
D. atomic absorption spectrophotometry
D
307.) The osmolality of a urine or serum specimen is measured by a change in the
A. freezing point
B. sedimentation point
C. midpoint
D. osmotic pressure
A
308.) Which of the following applies to cryoscopic osmometry?
A. temperature at equilibrium is a function of the number of particles in solution
B. temperature plateau for a solution is horizontal
C. freezing point of a sample is absolute
D. initial freezing of a sample produces an immediate solid state
A
255.) Calculate the blood pH given a pCO2 of 60 mm Hg and a bicarbonate of 18 mmol/L
A. 6.89
B. 7.00
C. 7.10
D. 7.30
C
263.) Which blood gas electrode is composed of a semi-permeable membrane, a silver/silver chloride reference electrode and glass electrode?
A. pO2
B.% O2 Sat
C. pCO2
D. HCO3
C
282.) The best method for ionized calcium involves the use of:
A. valinomycin incorporated into a semipermeable membrane that allows for change in current
B. ion selective electrode that detects change in potential when Ca2+ binds reversibly to the membrane
C. 8-hydroxyquinoline selective membrane that binds with Ca2+ to prevent other ions which may change potential
D. biuret reaction that removes protein prior to binding with arsenazo ions to cause change in voltage
B

289.) The following serum laboratory results were obtained. These results are most compatible with:
A. multiple myeloma
B. primary hyperparathyroidism
C. chronic renal failure
D. secondary hyperparathyroidism
C
The total CO2 concentration is comprised of which components?
a. H2CO3 + HCO3
b. pCO2 + HCO3
c. H2CO3 + pCO2
d. tCO2 + H2CO3
A
Carbonic acid concentration can be calculated as follows:
a. HCO3/2.8
b. HCO3/H2CO3
c. pCO2 × 0.03
d. tCO2 × 0.03
C

Specimens from a patient with chronic lung disease show the following results. These results indicate:
a. metabolic compensation by renal retention of bicarbonate
b. metabolic compensation by renal excretion of bicarbonate
c. respiratory compensation by retention of CO2
d. combined retention by excretion of CO2
A

A serum sample from an unconscious Pt in the ED has the following lab results. This indicates the need to investigate for:
a. chronic respiratory disease
b. milk-alkali syndrome
c. methanol or other organic poisoning
d. renal compensation for respiratory alkalosis
C
How do you calculate blood pH/What is the Henderson-Hasselbach equation?
pH = pK’ + log([HCO3]/[.03 x pCO2])
pK’ = negative log of the dissociation constant for dissolved CO2 + HCO3
Magnesium carbonate is added in an iron binding capacity determination in order to:
a. allow color to develop
b. precipitate protein
c. bind with hemoglobin iron
d. remove excess unbound iron
D
The anion gap is useful for quality control of laboratory results for:
a. amino acids and proteins
b. blood gas analyses
c. sodium, potassium, chloride, and total CO2
d. calcium, phosphorus and magnesium
C
Which of the following electrolytes is the chief plasma cation whose main function is maintaining osmotic pressure?
a. chloride
b. calcium
c. potassium
d. sodium
D