Brain and Cranial Nerves
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
CNS- Central Nervous System
Made up of the Brain and Brain Stem
2 Types of Nerves
Cranial and Spinal
The signaling pathway
Stimulus > Receptor > Sensory Neuron > CNS (Spinal Cord > Brain)
Awareness
When signal gets sent to Brain, it gains ___
Motor Neurons
Signal sent back from brain when stimulus needs a response.
2 Types of motor neuron systems
Somatic and Autonoumic
Somatic division
Controls skeletal muscles and things you consciously think about. Voluntary actions.
Autonomic Division
Controls invoulentary actions. Internal organs and glands Sympathetic and Parasympathetic divisions.
Sympathetic and Parasympathetic
Divisions of Autonomic Division of Motor Neurons
Sympathetic Division
Fight or Flight responses- for stressful and imediate solutions
Parasympathetic
Rest and Digest Responses- promotes relax and repair responses
PNS- Peripheral Nervous System
Nerves
Gyrus
Surface Ridges on the brain
Sulcus
the shallow lines on the brain. Central __ is largest
Fissure
Deep lines on surface of brain. Longitudinal __ is most important. Like a sulcus, but deeper.
4 main regions of the Brain
Cerebrum (Cerebral Cortex), Cerebellum, Brain Stem, Diencephalon
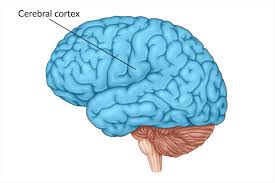
Cerebrum (Cerebral cortex)
Processes information related to sensation and motor Response
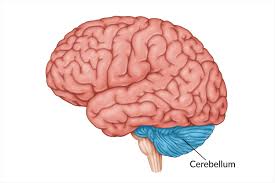
Cerebellum
Keeps balance of the body and equilibrium. Separated by the Transverse fissure. Posterior Region
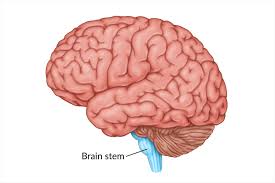
Brainstem
Ventral side of the brain. The most important part of the Brian, where life centers are. You can’t survive without it. 3 regions
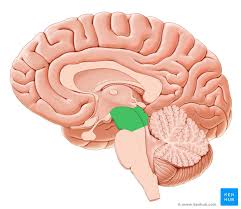
Midbrain
Processes visuals, the head of the brainstem
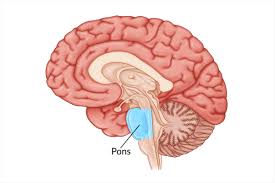
Pons
Center for respiration in the brainstem
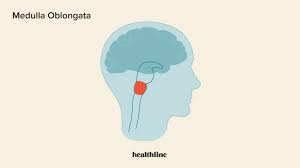
Medula
Center in the brainstem that controls the heart and Veins
Diencephalon
Deepest region in the brain. Autonomic regulation and nervous anatomy. 3 regions
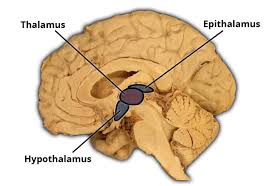
Epithalimus
Penial Gland, produces melatonin. Dorsal part of Diencephalon
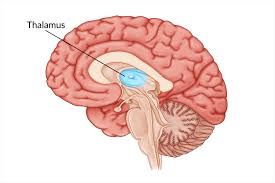
Thalamus
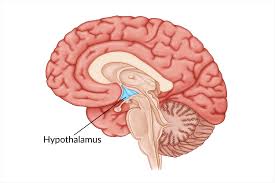
Hypothalamus
Neuroendocrine structure- gives the ___ a lot of power because it controls 2 structures
Longitudinal Fissure
Separates the left and right lobe
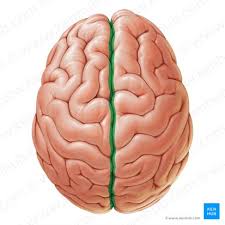
Central Sulcus
Separates the Frontal and Parietal lobes
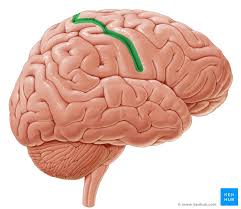
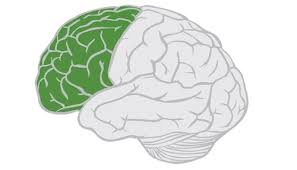
Frontal Lobe
Most anterior lobe of the brain. largest and most crucial containing the language center, personality, judgement and decision making
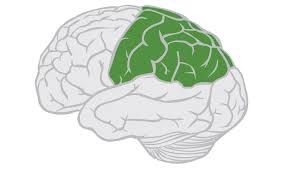
Parietal lobe
medial lobe in the Brain, sensory center of the brain. Reading, math, and writing center
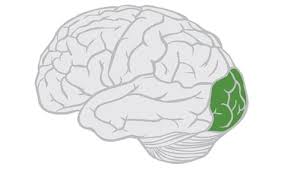
Occipital lobe
most posterior lobe of the Brain. Visual processing center of the brain
Precentral gyrus
the Ridge on the frontal lobe right before the Central Sulcus
Post Central Gyrus
The ridge on the Parietal lobe right after the Central Sulcus
Temporal Lobe
Right below the temporal bones, the Lobes that control auditory and language information
Olfactory bulb
Plays a large roll in the sense of smell. Olfactory tract is connected
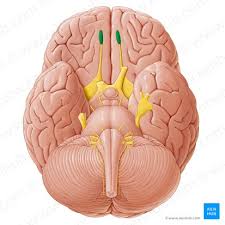
Optic Chiasm
The x shaped structure that is crucial to the visual pathway and optic nerve
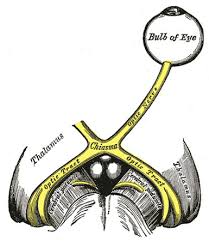
Optic Nerve
A bundle of Nerve fibers that transmit information from the eyes to the brain
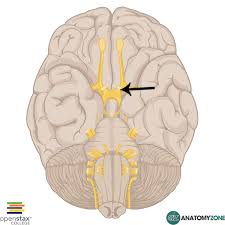
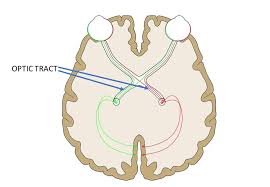
Optic Tract
The back 2 stems of the optic chasm. Part of the visual passageway
Mammillary Body
Play a role in memory and spacial navigation