interprofessional: global health midterm notes
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
vulnerable population
populations that are wounded by social forces that place them at a disadvantage with respect to their health
social groups being compared are differentiated by
their underlying social position including but not limited to demographics, identity, orientation, wealth, power, and/or prestige
health disparities
denotes a specific kind of health difference between more and less privileged groups
health equity
the attainment of the highest level of health for all people
healthcare disparities
systematic differences in health care received by people based on these same social characteristics
a reduction in health disparities is…
evidence of making progress toward greater health equity
what shows a strong association with health and longevity
social class
higher ____ provides individuals with more material, psychological, and social resources, which can benefit their health
socioeconomic status (SES)
analyses of the SES gradient generally reveal
a sharp drop in mortality as income increases
in contrast to the relationship between income and health, which demonstrates a continued drop in mortality as income increases, the association between mortality and education is more…
discontinuous
the concept of race as commonly used tends to evoke differences in skin color and other superficial secondary charcateristics, whereas ethnicity…
incorporates the concept of culture
the concept of race is
a predominantly social construct
it is important to recognize that the forces producing health disparities function in a more ____, involving interactions and feedback loops among all the elements displayed
dynamic, multidirectional manner
genetic endowment and epigenetic processes
offers relative protection against, or vulnerability to certain conditions
epigenetics describe
physical environment, social environment, behavior and lifestyle, chronic stress, healthcare
for health professionals to successfully attend to the health needs of vulnerable populations, they must recognize…
how vulnerability manifests itself
a public health perspective compels health professionals to not only heal the wounds of vulnerability but also…
eradicate the primary causes of those wounds
list the contexts for effective intervention
assessing vulnerabilities and strengths
eliciting the pt’s story
building the therapeutic alliance
what is therapeutic alliance?
when pt and clinician develop mutual trusting, caring, and respectful bonds that allow collaboration in care and treatment
what are the four main components of successful therapeutic alliance
empathy, trust, respect, agreement/collaboration
what is direct vulnerability?
the vulnerability in and of itself which leads to poor health
what is indirect vulnerability
vulnerability which affects components of the clinician/patient relationship or the therapeutic alliance
what is effect modification vulnerability
vulnerability which weakens or impedes the benefits of medical treatment on coexisting medical conditions
what are the results of the absence of a therapeutic alliance
mistrust, poor care, disrespect, and poor collaboration
what are the goals of a therapeutic alliance
set a climate of interest, concern, and calm
empathetic communication
allow for the humanity of the patient and clinician to emerge
what does CAPTURES stand for
C = curiosity/ interest
A = appreciate/admire
P = point of view
TU = timing/use of body language
RE = react
S = support
what is inequality?
the condition of being unequal
what is inequity?
a disparity due to differences in social, economic, environmental, or healthcare resources
how is health equity achieved?
when every person has the opportunity to “attain his or her full potential” and no one is “disadvantaged from achiving this potential because of social position or other social determined circumstances”
what are common causes of inequity
income, education, access, environment
what is health policy?
decisions, plans, and actions that are undertaken to achieve specific health care goals within a society
an explicit health policy…
defines a vision for the future
establishes targets and points of reference for the short and medium term
outline priorities and the expected roles of different groups
builds consensus and informs people
what are the five steps of CDC policy process
problem identification, policy analysis, strategy and policy development, policy enactment, policy implementation
what is problem identification?
clarify and frame the public health problem to determine where to go in your policy journey
what is policy analysis?
use quantitative and qualitative methods to identify effective and efficient policy solutions
what is strategy and policy development?
identify and strategize for getting the policy adopted and how the policy will operate
what is policy enactment?
following internal or external procedures for getting a policy enacted or passed
what is policy implementation?
translating the enacted policy into action, monitoring uptake, and ensuring full implementation
what was true of public perceptions?
impacts that are less tangible and more narrow had less support
T/F: equity down resolves underlying issues of inequities
false
what is true of inequity up
outcomes get better but inequity remains
policies that exacerbate inequity do not:
define a vision for the future
establish targets and points of reference for the short and medium terms term
outline priorities and expected roles of different groups
builds consensus and informs people
what are luxury beliefs?
ideas and opinions that confer status on the rich at very little cost, while taking a toll on the lower class
describe the healthy people 2030 initiative
plans on building a healthier nation for all
data-driven national, measurable objectives
359 core objectives as well as developmental and research objectives
started in 1979, every 10 years
what are the social determinants of health
economic stability, education access and quality, health care access and quality, neighborhood and built environment, social and community context
according to the united nations universal declaration of human rights says…
health and medical care is a human right t
according to the WHO regarding universal health coverage policies
universal coverage means that all people can use health services, while being protected against financial hardship associated with paying for them
poverty and health have what type os association
bidirectional
what are causes of medical vulnerability worldwide?
poverty
malnutrition and food insecurity
environmental risk
fragile states and destabilized societies
displacement and homelessness
violation of human rights
countries with greater relative income inequality….
have worse measures of health and social problems
what is food insecurity?
the absence of enough, safe, nutritious, and socially acceptable food
may be chronic, seasonal, or temporary and may occur at the household, regional, or national level
high food security
household had no problems, or anxiety about consistently accessing adequate food
marginal food security
households had problems at times, or anxiety about, accessing adequate food, but the quality, variety, and quantity of their food intake were not substantially reduced
low food security
households reduced the quality, variety, and desirability of their diets, but the quantity of food intake and normal eating patterns were not substantially disrupted
very low food security
at times during the year, eating patterns of one or more household members were disrupted and food intake reduced because the household lacked money and other resources for food
what are some health system challenges
lack of documentation
workforce shortages
unaffordability of care
lack of documentation is termed in literature as ?
scandal of invisibility
what are some health system solutions
building primary care systems
improving healthcare accessibility and affordability
caring for displaced populations
educating health professionals
understand these sectors of covered groups:
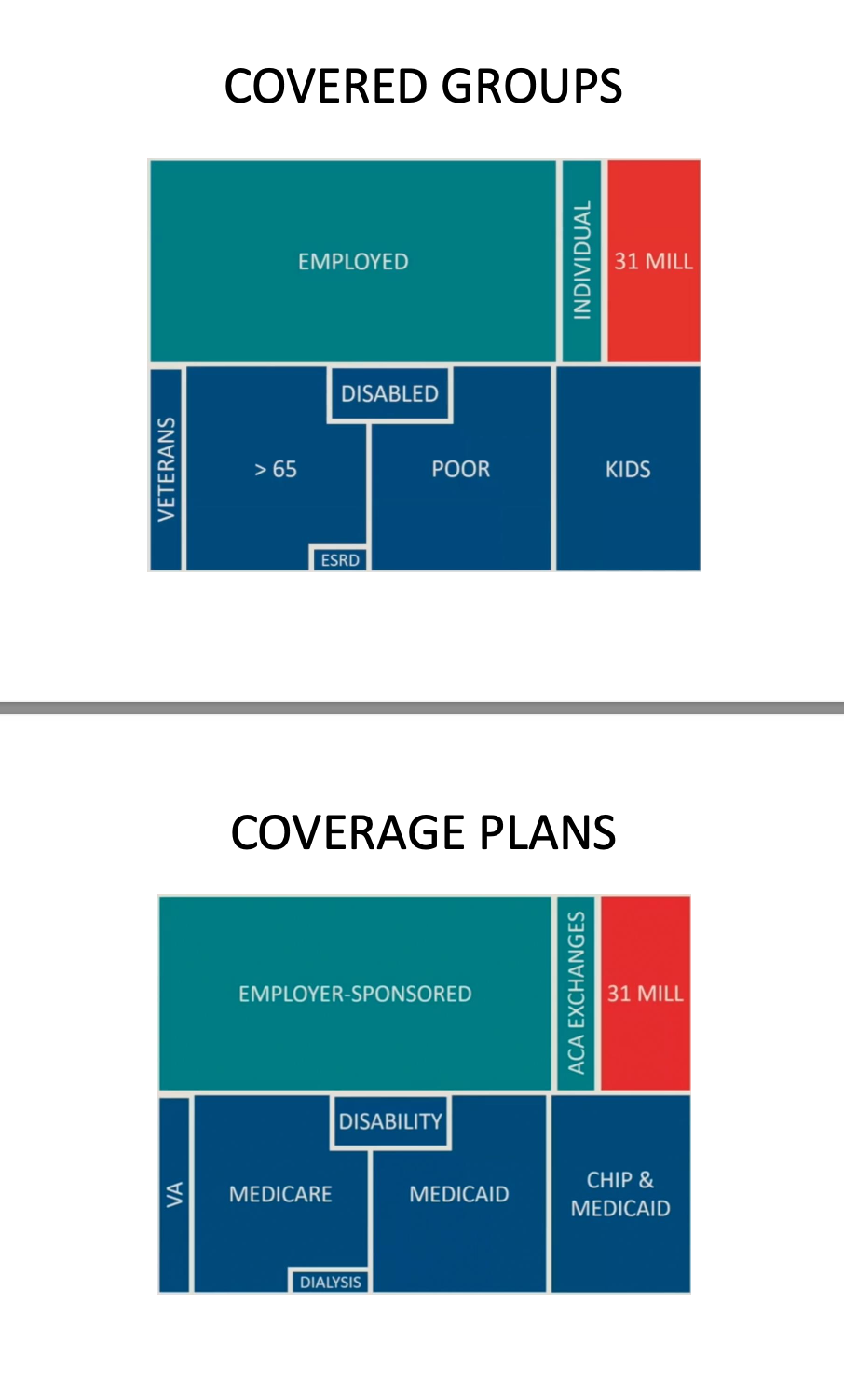
what is the difference between medicare and medicaid
medicare = generally for people who are 65 and olderr, or who have a qualifying disability
medicaid = for individuals, families, and children with limited income and resources
what is medicare?
national health insurance which began in 1965, paid by federal tax dollars (from payroll taxes)
what is medicaid? (medical in california)
federal and state program that helps with healthcare costs for some people with limited income and resources
financed by both state and federal government. benefits are determined by state or need federal rules if using expansion funds
what is commercial pt insurance?
health insurance provided and administered by nongovernmental entities, often paid by employer and employee
what did the affordable care act do?
allowed for medicaid expansion option to states
what are the results of medicaid expansion?
medicaid expansion provides more low-income adults with access to healthcare services, resulting in improved health outcomes
medicaid expansion would benefit people from communities of color because many work in low wage jobs that do not offer health benefits
provides funding and federal requirements to participating states
what is the most stated reason a state would choose ‘not’ to accept federal fund and adopt medicaid expansion?
they would have to follow ACA medicaid rules (especially those targeting medicaid coverage and services)
medicaid spending will increase significantly
provider will drop out or limit access due to lower payment rates
existing pts will compete with newly added pts
states will be hit with increased costs as federal matches are recalculated, but still must meet federal requirements