final marketing exam
1/162
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
163 Terms
Buyers
people in an organization's buying center who make an actual purchase
The Importance of Price to Buyers
consumers consistently rank price as one of the most important variables driving purchase decisions
Revenue
The price charged to
customers multiplied by the
number of units sold.
Profit
Revenue minus expenses.
Price
Price is that which is given up in an exchange to acquire a good or service.
profit oriented
pricing strategy focused on profits
sales oriented
Companies emphasized widespread distribution and promotion in order to sell products and services
status quo pricing
a pricing objective that maintains existing prices or meets the competition's prices
demand schedule
a table that shows the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded
demand curve
a graph of the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded
price elasticity of demand
a measure of how much the quantity demanded of a good responds to a change in the price of that good, computed as the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price
inelastic demand
A situation in which an increase or a decrease in price will not significantly affect demand for the product
elastic demand
A situation in which consumer demand is sensitive to changes in price
break even analysis
a method of determining what sales volume must be reached before total revenue equals total costs
fixed cost
a cost that does not change, no matter how much of a good is produced
variable cost
a cost that rises or falls depending on how much is produced
total cost
fixed costs plus variable costs
markup pricing
the cost of buying the product from the producer, plus amounts for profit and for expenses not otherwise accounted for
list price
The retail price listed in a catalog or on an Internet site
quantity discount
a price reduction offered to buyers buying in multiple units or above a specified dollar amount
seasonal discounts
discounts offered to encourage buyers to buy earlier than present demand requires
cash discounts
reductions in price to encourage buyers to pay their bills quickly
odd-even pricing
setting prices a few dollars or cents under an even number
loss leader pricing
the pricing policy of setting prices very low or even below cost to attract customers into a store
What is Customer Value?
the relationship between benefits and the sacrifice necessary to obtain those benefits
What is Demand?
the quantity of
product that will be sold in the market at
various prices for a specified period.
determines the upper limits or
ceiling of the selling price.
unitary elasticity
a situation in which total revenue remains the same when prices change
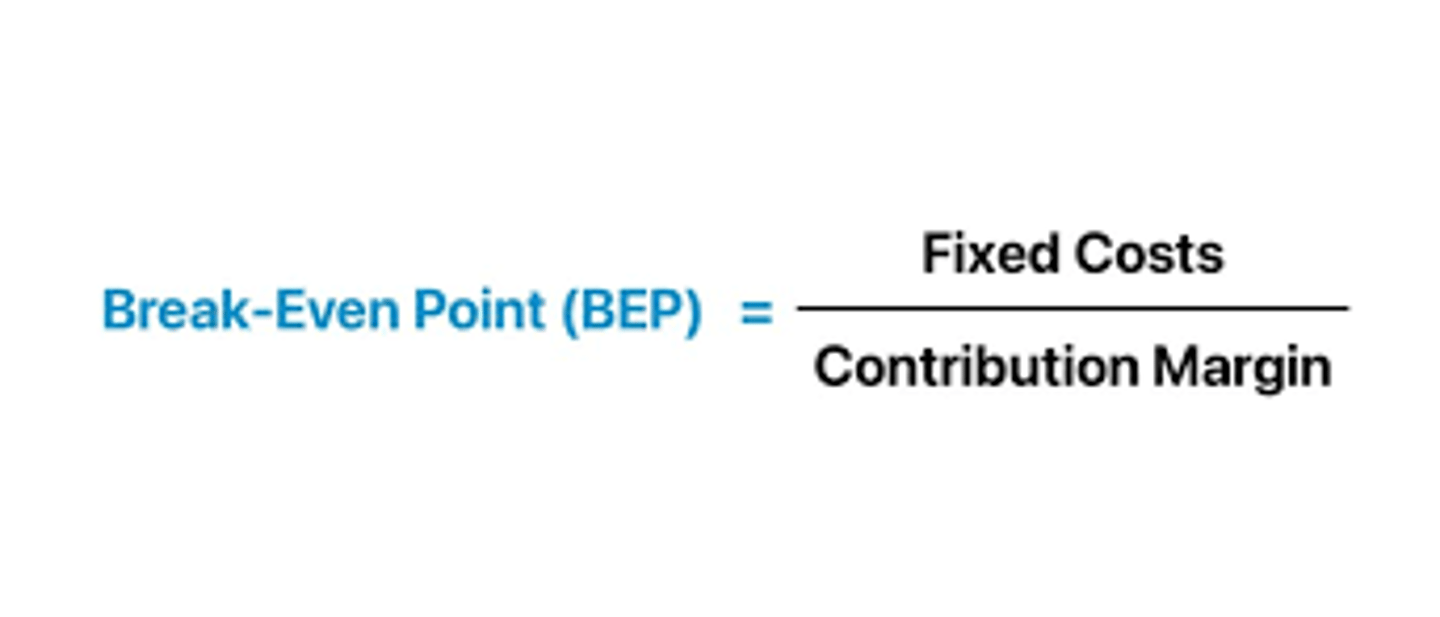
elasticity of demand formula
percentage change in quantity demanded/percentage change in price
What are Costs?
the production and
marketing costs associated with selling
a product.
determine the lower limit or floor
of the selling price.
Break-Even Point
the point at which the costs of producing a product equal the revenue made from selling the product
Formulas for Calculating
Selling Price with Markup
When markup is stated as a percent of cost:
Selling Price = Cost + Markup% (Cost)
When markup is stated as a percent of retail:
Selling Price = Cost__
1 - Markup %
Trade discounts
A reduction from the
base or list price offered to channel
members.
Net Price
The remainder when the
amount of discount is subtracted from
the base or list price.
Pricing Terminology
-at-the-money
-in-the-money
-out-of-the-money
-deep in-the-money
-deep out-of-the-money
P&G offered a 5% reduction in the list
price of Pantene Shampoo to Walmart.
This is an example of a:
Trade Discount
Cumulative Quantity Discount
uses the amount purchased over a specified time period and usually involves several transactions
Noncumulative Quantity Discount
a deduction from list price that applies to a single order rather than to the total volume of orders placed during a certain period
Geographic Pricing
The setting of different prices depending on a geographical division of the delivery areas.
Establishes when ownership of the freight
transfers from the seller to the buyer
• FOB Origin
- Title to the goods passes to the buyer at the
point of loading shipment onto the mode of
transportation
• FOB Destination
- Title to the goods passes to the buyer once
the shipment is delivered to the buyer
Price Bundling
the practice of offering two or more different products or services for sale at one price
Prestige Pricing
charging a high price to help promote a high-quality image
Deceptive Pricing
occurs when a seller states prices or price savings that mislead consumers or are not actually available to consumers
Predatory Pricing
The practice of charging very low
prices for products with the intent of
driving competitors out of business.
price fixing
An agreement between two
or more firms on the price they
will charge for a product.
Price Discrimination
Occurs when a seller knowingly charges
different prices to competitive resellers
or industrial buyers of commodities of
like grade and quality when the effect
may be to injure competition.
The Robinson-Patman Act of 1936
Prohibits any form of price discrimination that has the effect of reducing competition among wholesalers or retailers
Five Most Common Deceptive Pricing Practices
1. bait and switch
2. bargains conditional on other purchases
3. comparable value comparisons
4. comparisons with suggested prices
5. former price comparisons
bait and switch
A store advertises bargains that do not really exist to lure customers in, in hopes that they will buy more expensive merchandise.
bargains conditional on other purchases
This practice may exist when a buyer is offered "1-Cent Sales," "Buy 1, Get 1 Free," and "Get 2 for the Price of 1." Such pricing is legal only if the first items are sold at the regular price, not a price inflated for the offer. Substituting lower quality items on either the first or second purchase is also considered deceptive.
comparable value comparisons
Advertising such as "Retail Value $100.00, Our Price $85.00" is deceptive if a verified and substantial number of stores in the market area do not price the item at $100.
comparisons with suggested prices
a claim that a price is below a manufacturer's suggested or list price may be deceptive if few or no sales occur at that price in a retailer's market area
former price comparisons
When a seller represents a price as reduced, the item must have been offered in good faith at a higher price for a substantial previous period. Setting a high price for the purpose of establishing a reference for a price reduction is deceptive
You just opened a specialty lemonade stand/kiosk in the local mall. You wish to identify how many cups of lemonade you must sell to cover your fixed cost and break-even. Customers are willing to pay $3 per cup. Fixed cost equal $2,000 per month for rent, insurance, advertising and loan payment. The unit variable cost is $2 per cup for labor, ingredients, and supplies. Compute total variable cost, fixed cost, total cost, total revenue, and profit at the following quantity levels (0, 1000, 2000, 3000, 4000). What is the breakeven point?
Selling price per cup: $3
Fixed costs: $2000
Variable cost per cup: $2
Quantity levels: 0, 1000, 2000, 3000, 4000
2000 units
Yesterday, the price of envelopes was $3 a box, and Julie was willing to buy 10 boxes. Today, the price has gone up to $3.75 a box, and Julie is now willing to buy 8 boxes. Is Julie's demand for envelopes elastic or inelastic? What is Julie's elasticity of demand?
Initial price: $3 per box, Initial quantity: 10 boxes, New price: $3.75 per box, and New quantity: 8 boxes.
0.8
The cost to the manufacturer to produce the product is $80. It marks up the price by 40% to sell to the wholesaler. The wholesaler then marks up the price another 10% to sell to the retailer. The retailer adds a 50% mark-up to arrive at the price charged to the consumer. What is the price paid by the wholesaler, retailer, and consumer if the markup up percentages are based on cost?
Manufacturer's cost: $80, Manufacturer's markup: 40, Wholesaler's markup: 10, and Retailer's markup: 50.
wholesaler: $112
Consumer: $184
Retailer: $123.20
Compute the missing value (cost or selling price) for the following:
(a) Cost of an item is $48; markup is 40%. What is the selling price if markup is based on cost? What is the selling price if markup is based on retail?
(b) The selling price of the item is $24; markup is 300%. What is the cost of the item if markup is based on cost?
(c) The retailer's selling price of the item is $168; the desired markup is 40% on retail. What should the retailer be willing to pay the vendor?
A: Cost of item: $48
Markup: 40%
B: Selling Price: $24
Markup: 300%
C: Selling Price: $168
Markup: 40%
A: $67.20 and $80
B: $6
C: $100
An invoice for $1,230 is dated July 16 with terms, 2/10, net 30. What is the amount due if the invoice is paid on July 26?
$1230
Promotion
Communication by marketers that informs,
persuades, and reminds potential buyers
of a product in order to influence an
opinion or elicit a response.
Five Promotional Elements
1. Advertising
2. Personal Selling
3. Public Relations
4. Sales Promotion
5. Direct Marketing
Advertising
Impersonal, one-way
communication about a
product or organization that is
paid for by a marketer.
Personal Selling
Direct interaction between a
company representative and a
customer that can occur in
person, by phone, or even over
an interactive computer link.
Public Relations
Describes a variety of
communication activities that seek
to create and maintain a positive
image of an organization and its
products among various publics,
including customers, government
officials, and shareholders
Sales Promotion
Short term incentives
used to arouse interest in
buying a good or service
Direct Marketing
direct communication between a seller and an individual customer using a promotion method other than face-to-face personal selling
What are the three goals of promotion?
inform, persuade, remind
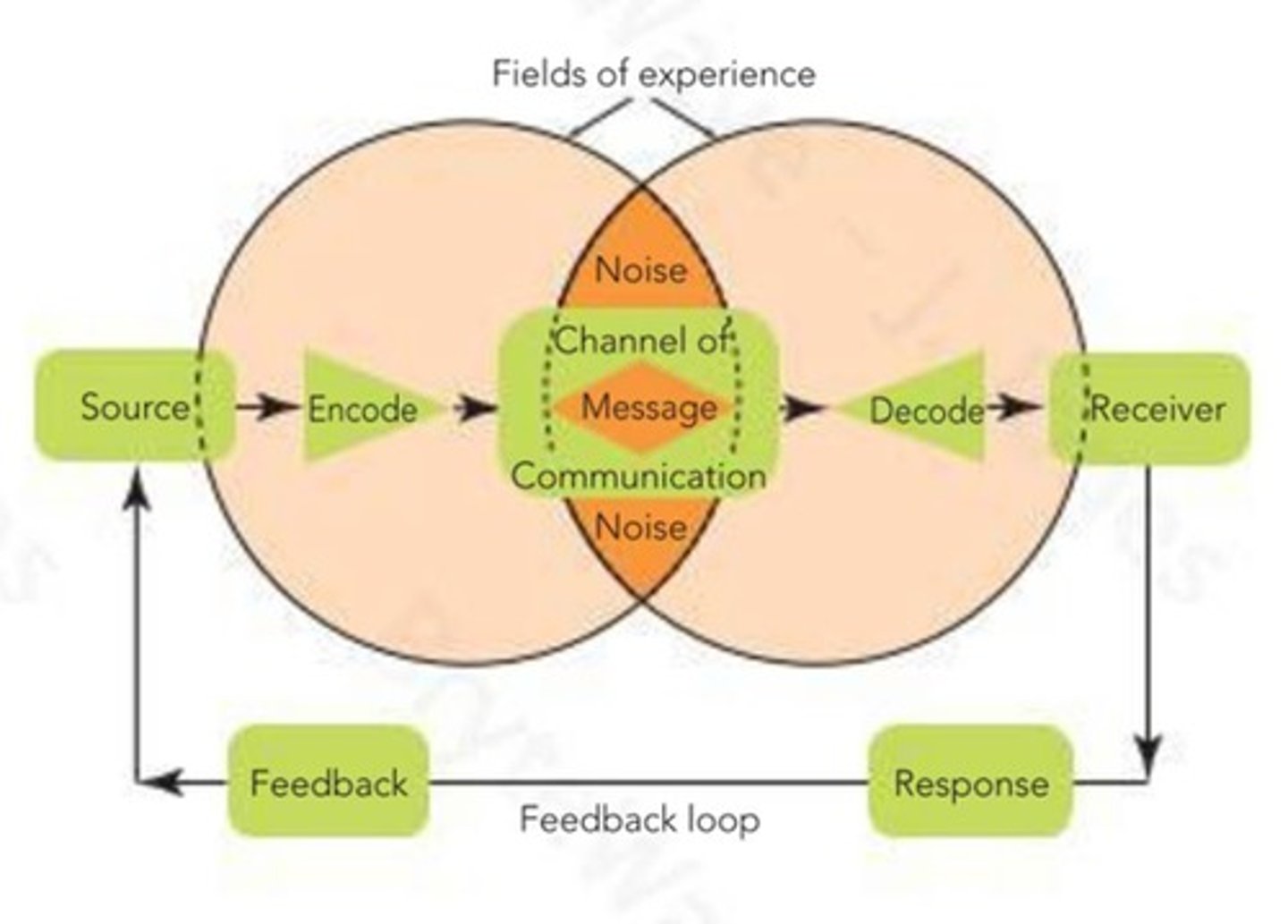
elements of the communication process
sender, encoding, message, media, decoding, receiver, response, feedback, noise
What is Integrated Marketing Communications?
Coordination of promotion and marketing efforts for maximum impact
Role of Promotion in the Marketing Mix
Communication by marketers that informs, persuades, and reminds potential buyers of a product in order to influence an opinion or elicit a response
The Promotional Mix
the combination of promotional tools—including advertising, public relations, personal selling, sales promotion, and social media—used to reach the target market and fulfill the organization's overall goals
Advertising Media
the vehicles through which advertising messages are delivered to their intended audiences
Traditional Advertising Media
Television
Radio
Newspapers
Magazines
Books
Direct mail
Billboards
Transit cards
new advertising media
internet, banner ads, viral marketing, email, interactive video
Public Relations Tools
news, special events, written materials, audiovisual materials, corporate identity materials, public service activities
social media
Promotion tools used to
facilitate conversations
among people online
Hannah is responsible for developing a
plan for the optimal use of advertising,
personal selling, sales promotion, and
public relations. Hannah is developing
a(n):
promotional plan
3 multiple choice options
Sender
the originator of the message in
the communication process
- For an advertisement, press release, or social media campaign, the company or organization is the sender
Encoding
the conversion of the sender's
ideas and thoughts into a message,
usually in the form of words or signs
Channel
a medium of communication—such as a voice,
radio, or newspaper—for transmitting a message
Noise
anything that interferes with, distorts, or slows
down the transmission of information
Receiver
the person who decode the message
Decoding
interpretation of the language and symbols
sent by the source through a channel
Feedback
The receiver's response to a message
Informative Promotion
increase awareness, explain how product works, suggest new uses, build company image
Persuasive Promotion
encourage brand switching, change customers' perceptions of product attributes, influence immediate buying decision, persuade customers to call
Reminder Promotion
remind customers that product may be needed, remind customers where to buy product, maintain customer awareness
This promotion task is used to keep a familiar brand name in the public's mind and is prevalent during the maturity stage of the product life cycle
Reminder
In the communications process, this occurs when the receiver interprets the language and symbols used by the sender.
Decoding
This is defined as the communication by marketers that informs, persuades, and reminds potential buyers of a product in order to influence an opinion or elicit a response.
Promotion
This is defined as the originator of the message in the communication process.
sender
Public Relations is defined as impersonal, one-way communication about a product or organization that is paid for by a marketer.
False
1 multiple choice option
What are the three basic tasks of promotion?
informing, persuading, reminding
Campbell's soup has been promoted with television commercials, radio spots, newspaper coupons, and magazine advertisements. In the communications process these media served as ______ during the communication process.
channels
Social media include all of the following EXCEPT:
a pop-up ad on the ESPN Web site
3 multiple choice options
A $1-off coupon for a bottle of dish washing liquid is a form of:
sales promotion.
Advertising
Impersonal, one-way mass
communication about a
product or organization that is
paid for by a marketer.
advertising campaign
A series of related advertisements
focusing on a common theme, slogan,
and set of advertising appeals that
promotes a particular product or
company for a defined period of time.
Major Components of the Advertising Campaign
Review marketing plan, specify advertising objectives, develop creative plan, and develop media plan
Why is it important to review
the marketing plan before
developing the advertising
campaign?
it ensures the campaign aligns with overall marketing goals, targets the right audience, and utilizes resources effectively.
Marketing Plan
a written document that acts as a guidebook of marketing activities for the marketing manager
Specify Advertising Objectives
helps advertises w/ other choices such as selcting media/evaluating campaign.
• Awareness?
• Trial?
What are advertising
objectives and how are they
determined?
specific, measurable goals that a business aims to achieve through its advertising campaigns.