Paediatric Trauma III- Permanent Dentition Luxation Injuries:
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What is concussion and what are the features?
Injury to supporting tissues with NO loosening or displacement of the tooth.
TTP, Bleeding or bruising at gingival margin
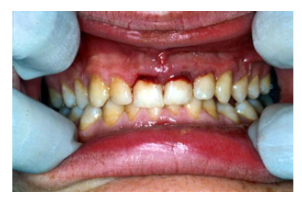
What is subluxation and what are the features?
Injury to the tooth’s supporting tissues WITH abnormal loosening
Tooth will feel mobile, NO displacement, bleeding or bruising at gingival margin
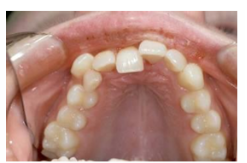
What is Lateral Luxation and what are the features?
Bodily movement of the tooth within the socket - crown moves in one direction (usually direction of force) and root moves in opposite.
Apex displacement - rupture of neurovascular bundle and crushing of PDL cells in palatal cervical region
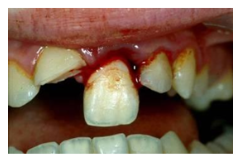
What is extrusion?
Axial displacement partially out of the socket
Mobile tooth, looks elongated
What is intrusion and what are the features?
Tooth forced upwards into the socket
(in developing dentition – may be difficult to tell if teeth were partially erupting anyway
Crushing of PDL cells and neurovascular bundle
If complex or severe - needs specialist management
What is avulsion?
Tooth completely lost from the socket
Ischaemia of pulp, PDL cell death
Emergency management in practice
What structures do we need to consider regarding luxation injuries?
Impact on PULP
Impact on PDL - ruptured tissues may repair but crushed tissue cannot be repaired
Regarding the pulp after trauma, what factors affect prognosis? (3)
Type of injury
Intrusion and avulsion have worst prognosis (blood supply cut off)
Age of PT (stage of apical development)
Open apex (younger pts) = higher chance of revascularisation
An additional hard tissue injury
E.g complicated crown fracture (where pulp exposed) - worsens prognosis
How will pulp healing present? (3)
Complete Healing- vitality maintained.
Pulp Canal Obliteration
Pulpal Necrosis- which can cause inflammatory resorption of the root.
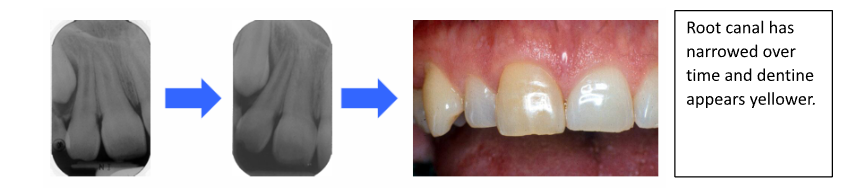
What is pulpal canal obliteration?
Tertiary dentine laid down in canal in response to injury
Shows pulp is alive but chance it may become necrosed in future
Root canal narrowed over time and dentine yellower
How does pulp necrosis cause root resorption?
Pulp death → toxins from pulp leach into PDL space → inflammatory response → inflammatory cells attempt to destroy debris but destory root in process
= inflammatory resorption aka infection related resorption
Can occur 2 weeks after injury
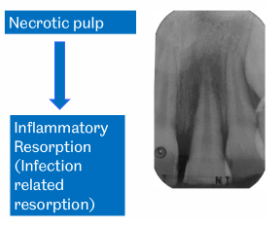
What to do as GDP if you see any inflammatory root resorption?
Attempt extirpation place CaOH + refer to paeds
What are the three types of root resorption related to trauma?
Inflammatory (infection related)- can either be internal or external.
Replacement (ankylosis related)
Internal (infection related)
How does inflammatory (external) resorption occur?
Same as mentioned b4 → toxins from necrotic pulp leach into PDL space → inflammatory response
Will progress until bacteria removed
On healing → resorbed tissue filled with cementum or bone
How does inflammatory (internal) resorption occur?
toxins from necrotic pulp → inflammatory response → ballooning of canals
Tx → extirpation and dress with CaOH otherwise will lead to perforation
How does replacement resorption occur?
From extensive PDL damage (from extrusion or intrusion)
Many PDL cells die to damage → repair response not fast enough to stop osteoclasts from resorbing tooth → eventually tooth root replaced by bone
Occurs more readily in children during puberty (as rapid bone turnover) → thats why avulsion in adults has better prognosis