CMD 377- Quiz 7
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
cornea
the main site of refraction (bending light for focusing on the retina)
Iris
regulates the amount of light entering the eye
lens
·elastic structure
o Flattened by the tension of the zonule fibers for far focusing
o During accommodation, the anterior part bulges forward for near-focus
retina
innermost layer of eyes
o Photoreceptors located in the retina
Rods
o Concerned with peripheral vision & vision under conditions of low illumination (night vision)
o Numerous in the periphery
Cones
Concerned with central discriminative vision & detection of color (color vision)
Fovea
center of the retina
o The region of the highest visual acuity
o Made up of cones
Parts of the retina
-retina
-rods
-cones
-fovea
Transduction of photic information
Photoreceptors (rods & cones) convert photic information into electrical charge in the retina action potential info is transmitted down the optic nerves
Visual pathway
Photoreceptors in the retina ganglion cell axons leave the retina optic nerve optic chiasm (partial decussation) optic tract lateral geniculate nucleus (the thalamic relay (nucleus for vision) optic radiation primary visual cortex (calcarine sulcus)
·Some branch off (from the LGN) to synapse on the superior colliculi in the midbrain
The blind spot
a hole in our vision created by the optic disk (where the ganglion cell axons leave the retina)
right nasal retina
looking at right visual field/world (right eye)
right temporal retina
looking at left visual field (Right eye)
left temporal retina
looking at right visual field (left eye)
left nasal retina
looking at left visual field (left eye)
L visual field
represented in the Right optic tract, LGB & Right in visual cortex
visual field representation
at the level of the optic nerve
Upper half of the visual field
represented in the visual cortex below the calcarine sulcus (lingual gyrus)
Lower half of the visual field
represented in the visual cortex above the calcarine sulcus (cuneus)
lesions of superior optic radiation & cuneus
lower visual field cut
Unilateral optic nerve lesion
ipsilateral (same side) hemianopia
severing of nasal fibers at the optic chiasm
bitemporal hemianopia (tunnel vision)
unilateral lesion of optic tract
contralateral (opposite side) hemianopia
lesions of superior optic radiation and lingual gyrus
upper visual field cut
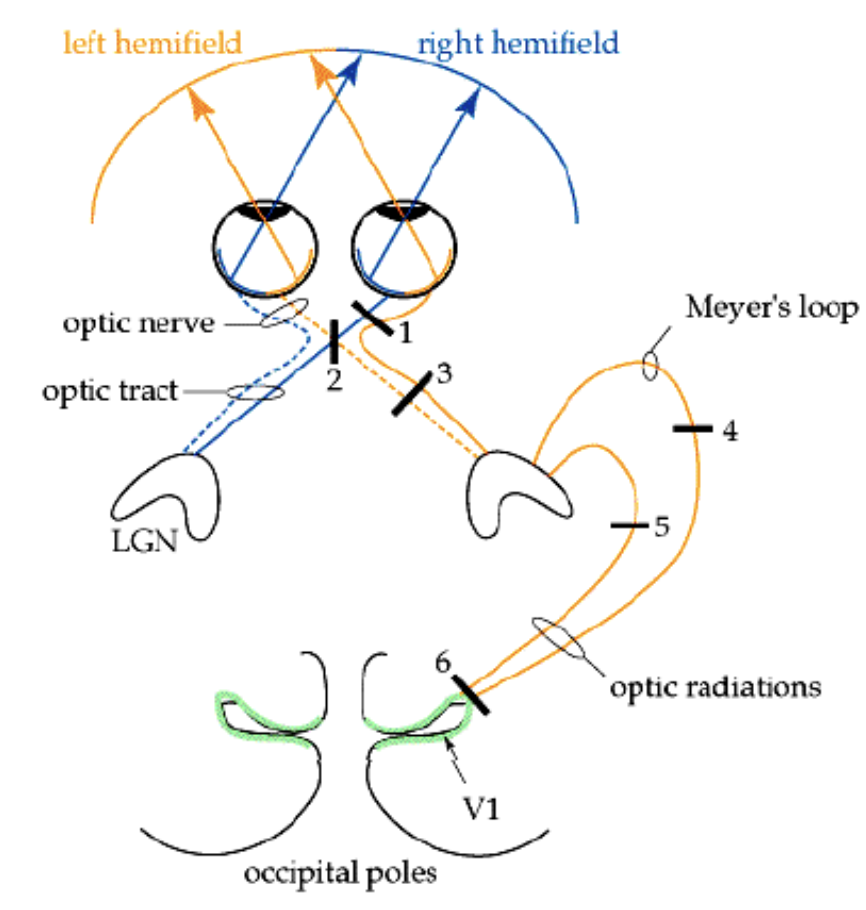
Lesion right eye optic nerve
blindness of right eye
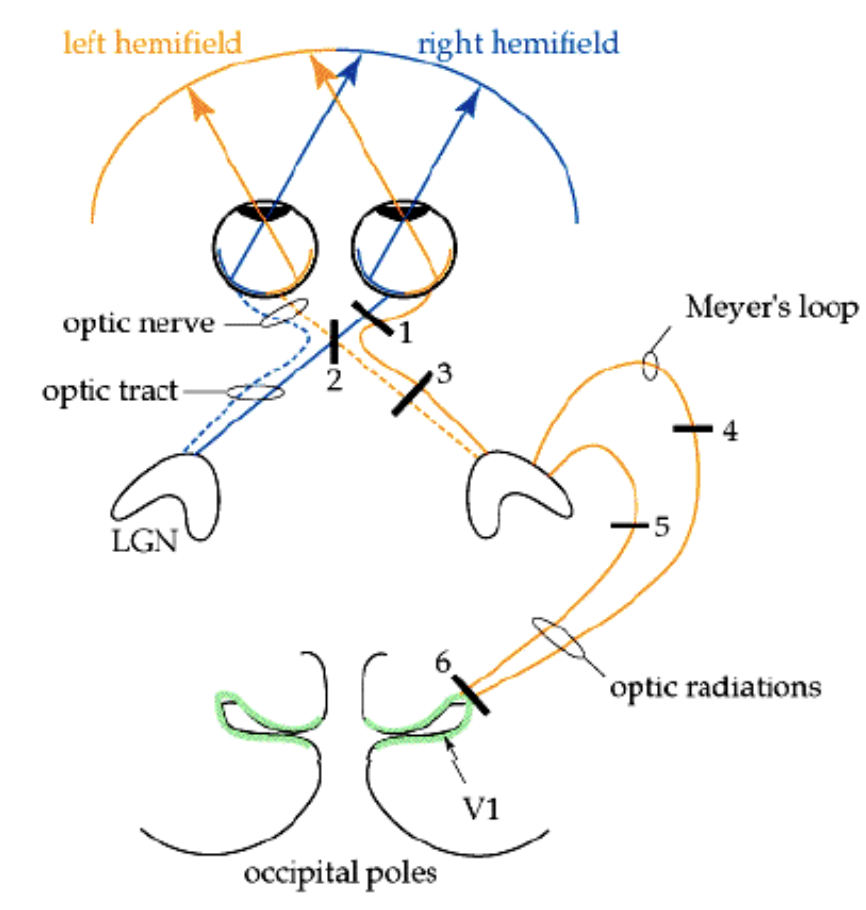
Lesion optic chasm in midline
Bitemporal hemianopsia (outer visual field for both eyes)
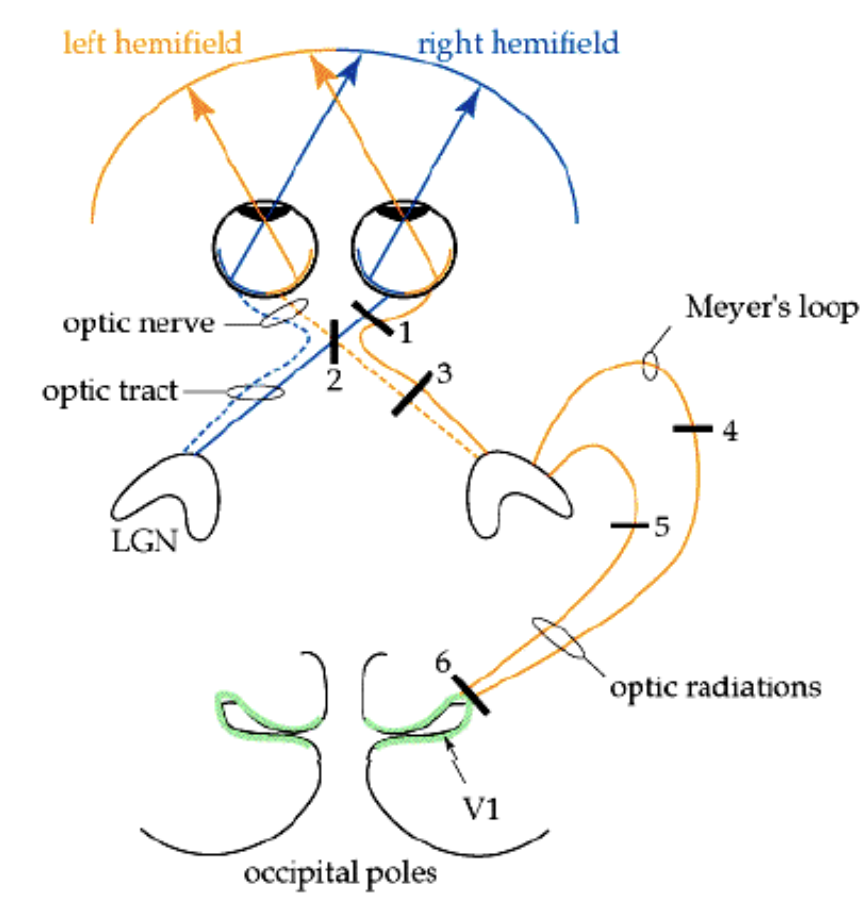
right optic tract
left homonymous heminopsia (left side of visual field in both eyes)
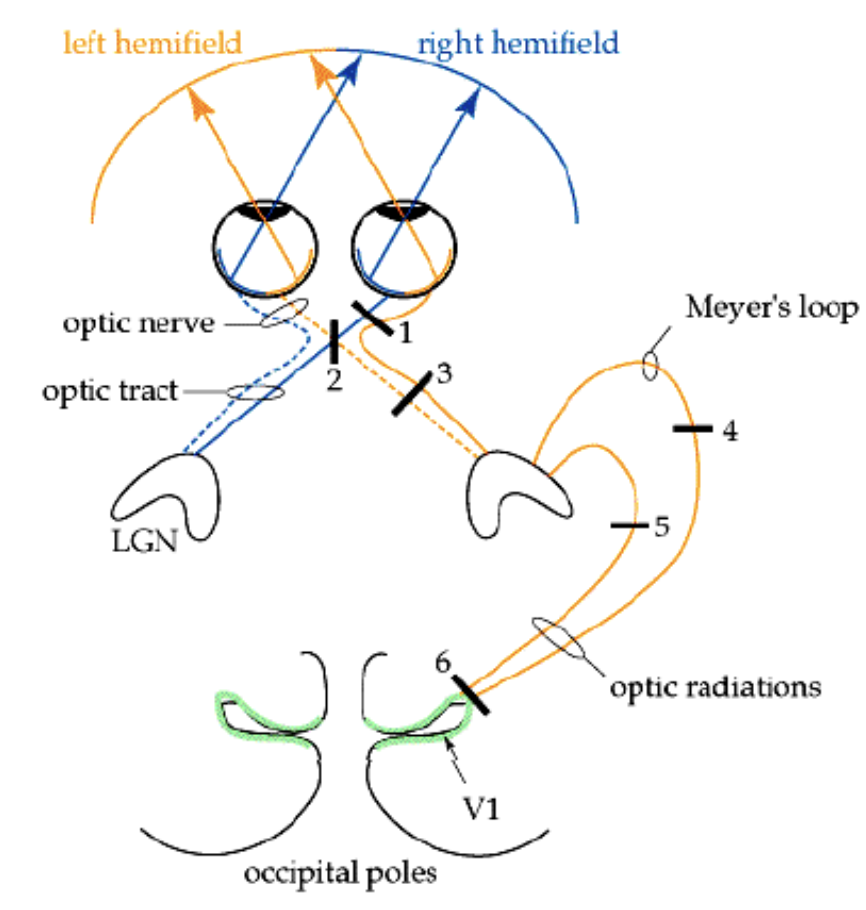
upper left visual field in both eyes
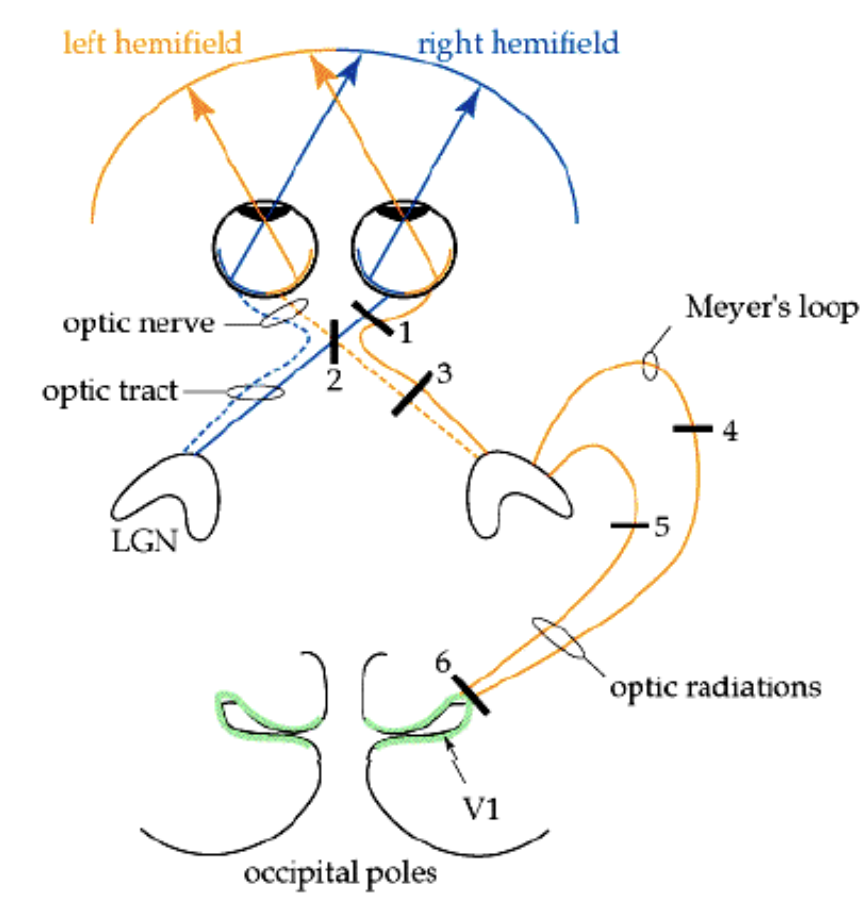
lower left visual field in both eyes
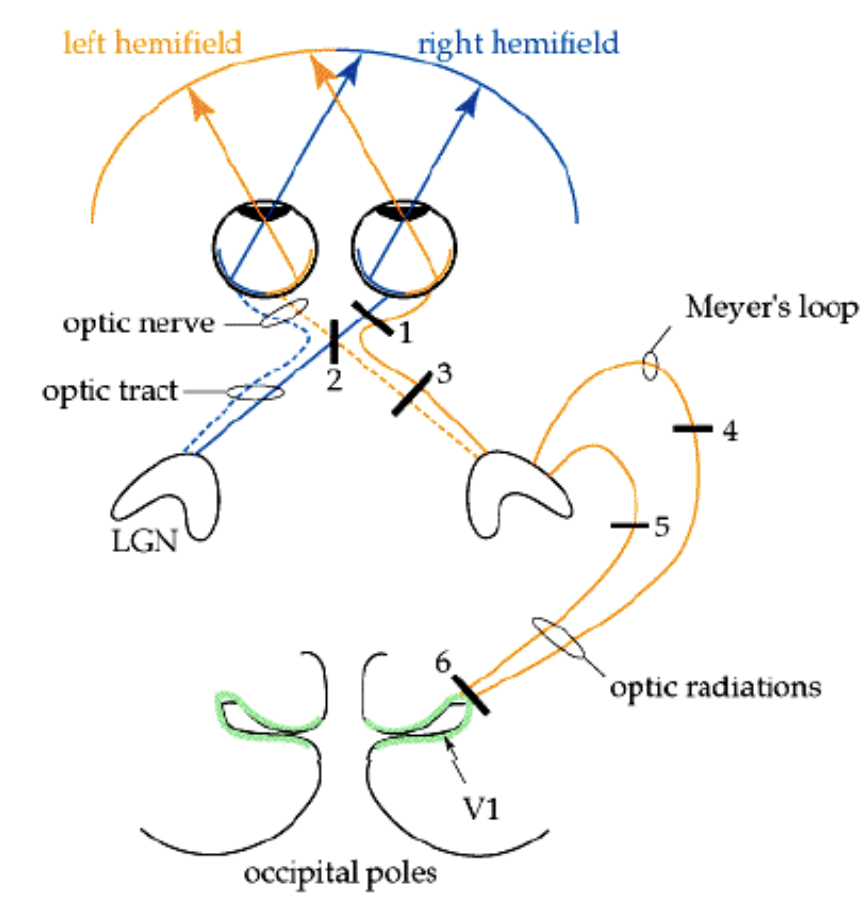
left macular sparing in both eyes visual field