exercise 26 KTTK: Eosin methylene blue agar (Micro. lab)
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Eosin methylene blue (EMB) agar is
complex, enriched, selective, and differential medium
complex
• Chemically undefined
• Due to digest of gelatin which provides nitrogen and organic carbon
selective
due to inhibition of most Gram-positive bacteria by
• Eosin Y
• Methylene blue
differential
• Organisms able to ferment lactose produce acidic end products
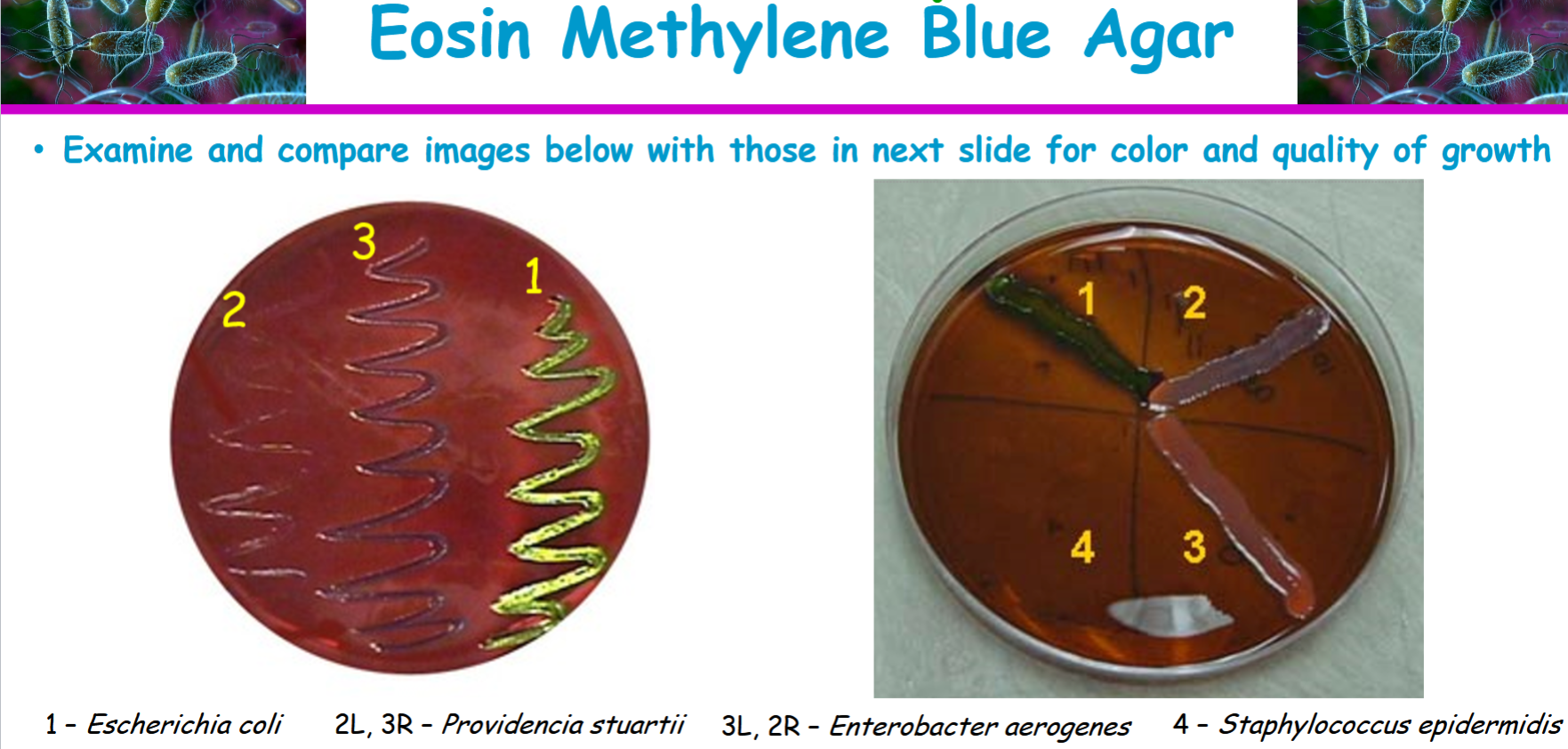
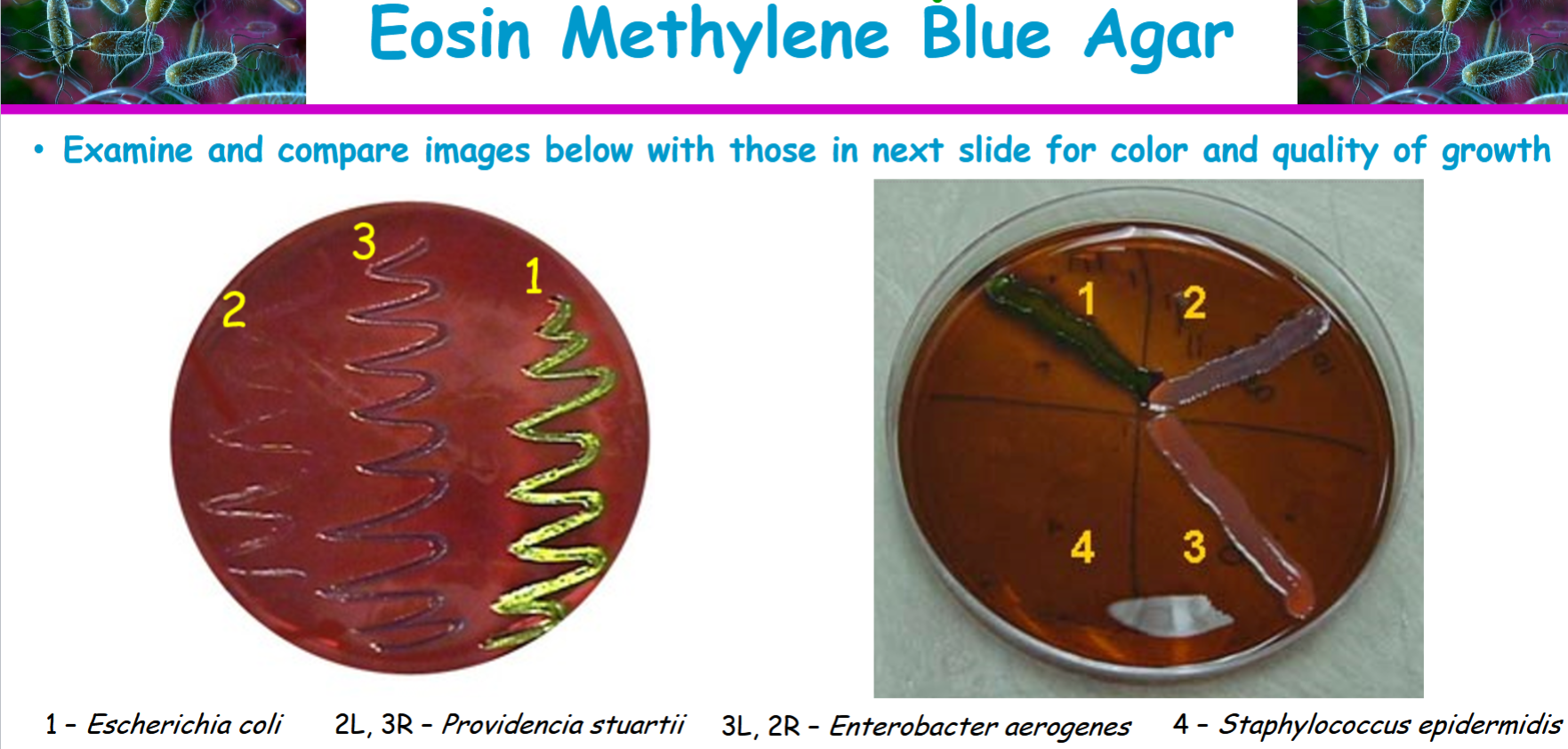
Escherichia coli and Enterobacter aerogenes ferment lactose
Proteus, Shigella, and Salmonella do not ferment lactose
• Aggressive lactose fermenters interact with Eosin Y and methylene blue
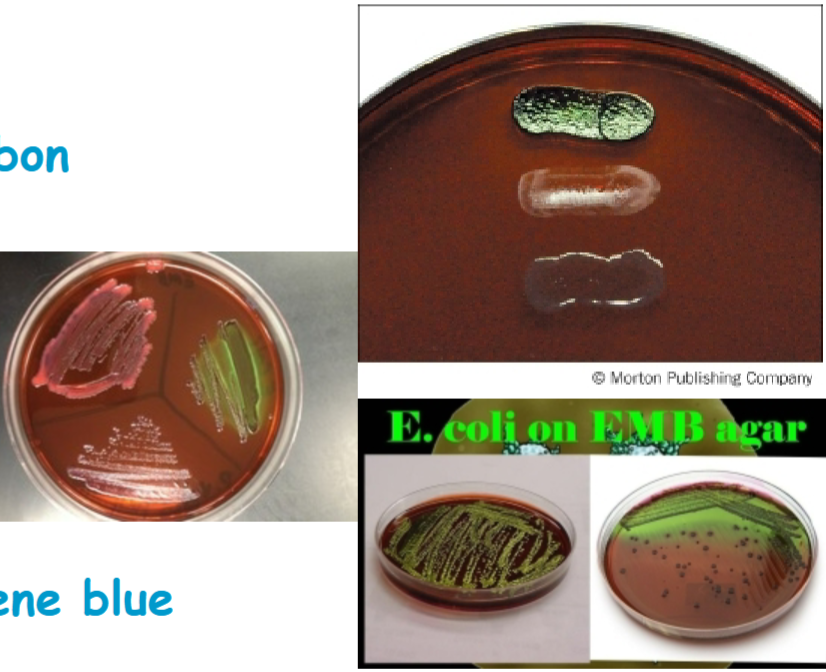
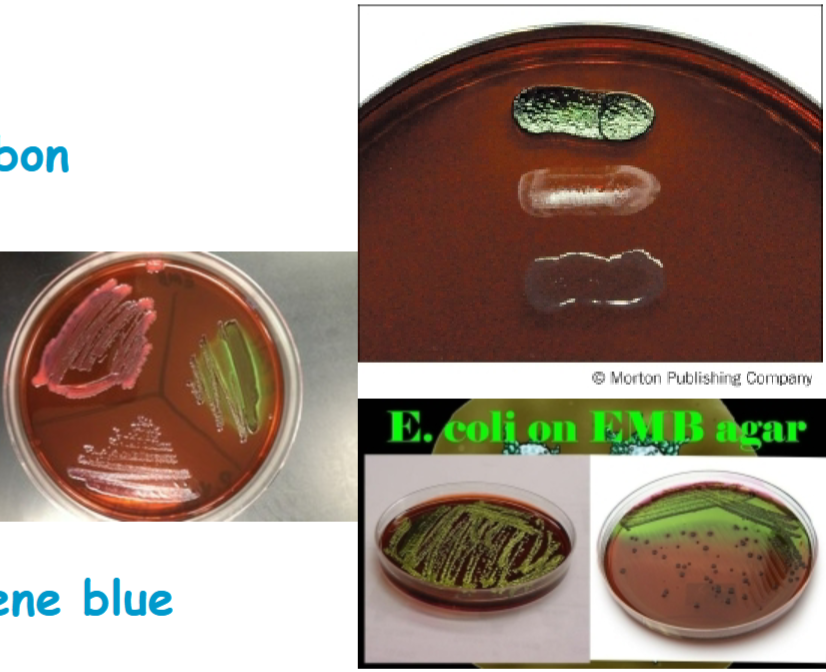
Produce dark purple to black colonies
E. coli usually has distinctive green metallic sheen
• Less aggressive lactose fermenters
Produce pink to dark purple colonies
Enterobacter or Klebsiella species would be examples
• Non-fermenters retain normal color or take on medium’s coloration
EMB agar contains
pancreatic digest of gelatin, lactose, dipotassium phosphate, methylene blue,
eosin Y, sucrose, distilled/deionoized water
the purposes of the dyes eosin Y and methylene blue are
render the media selective and allow us to differentiate lactose fermenters from non-fermenters. Because the dyes inhibit the growth of most Gram-positive organisms (some Enterococcus and Staphylococcus species are exceptions), these media are selective for Gram-negative bacteria.
why (application) eosin methylene blue agar is used
• Used for isolation of fecal coliforms
• Can either be streaked for isolation or used in Membrane Filter Technique
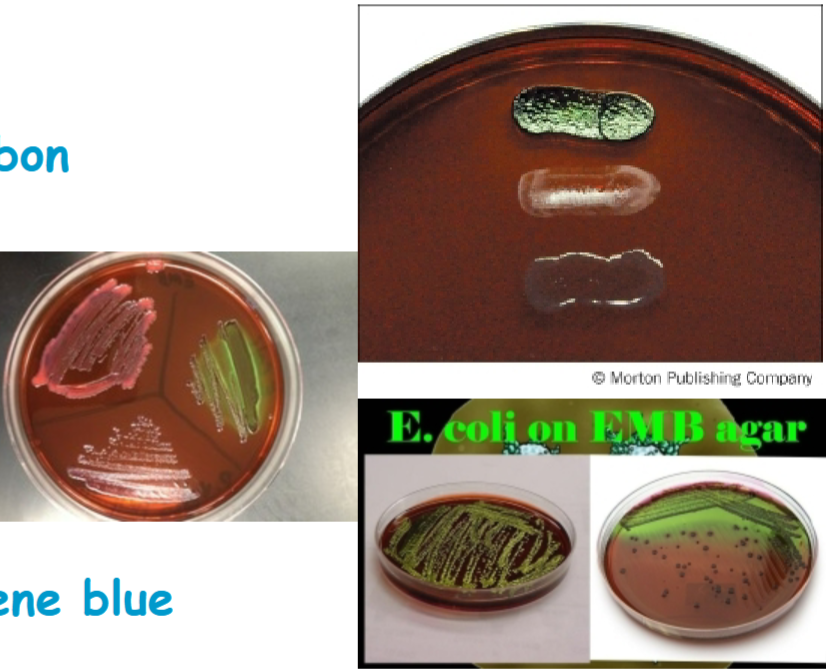
Know how Escherichia coli should have grown on the EMB agar
dark blue black colonies with a distinctive metallic green sheen
providencia stuartii
appears colorless or pale colored colonies and non lactose fermenter
gram negative bacterium
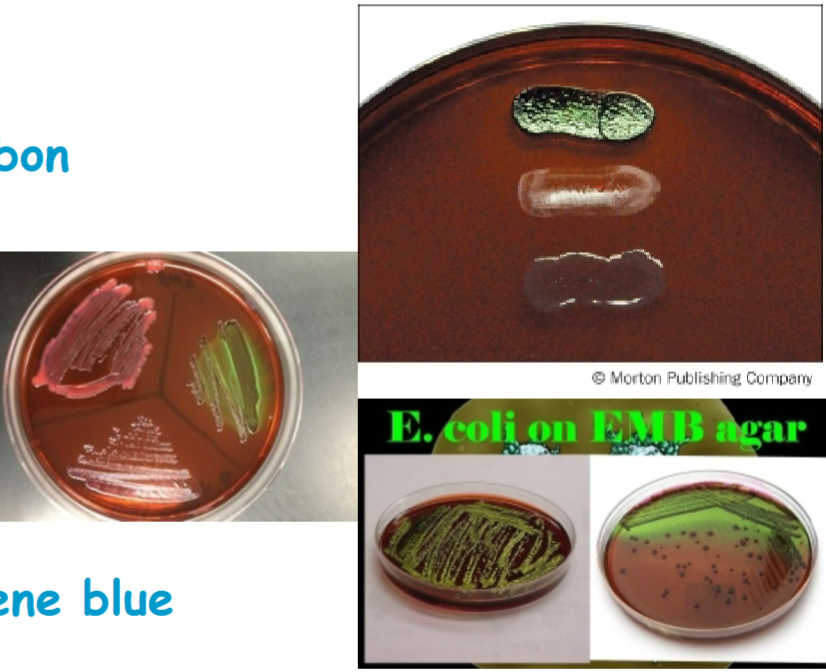
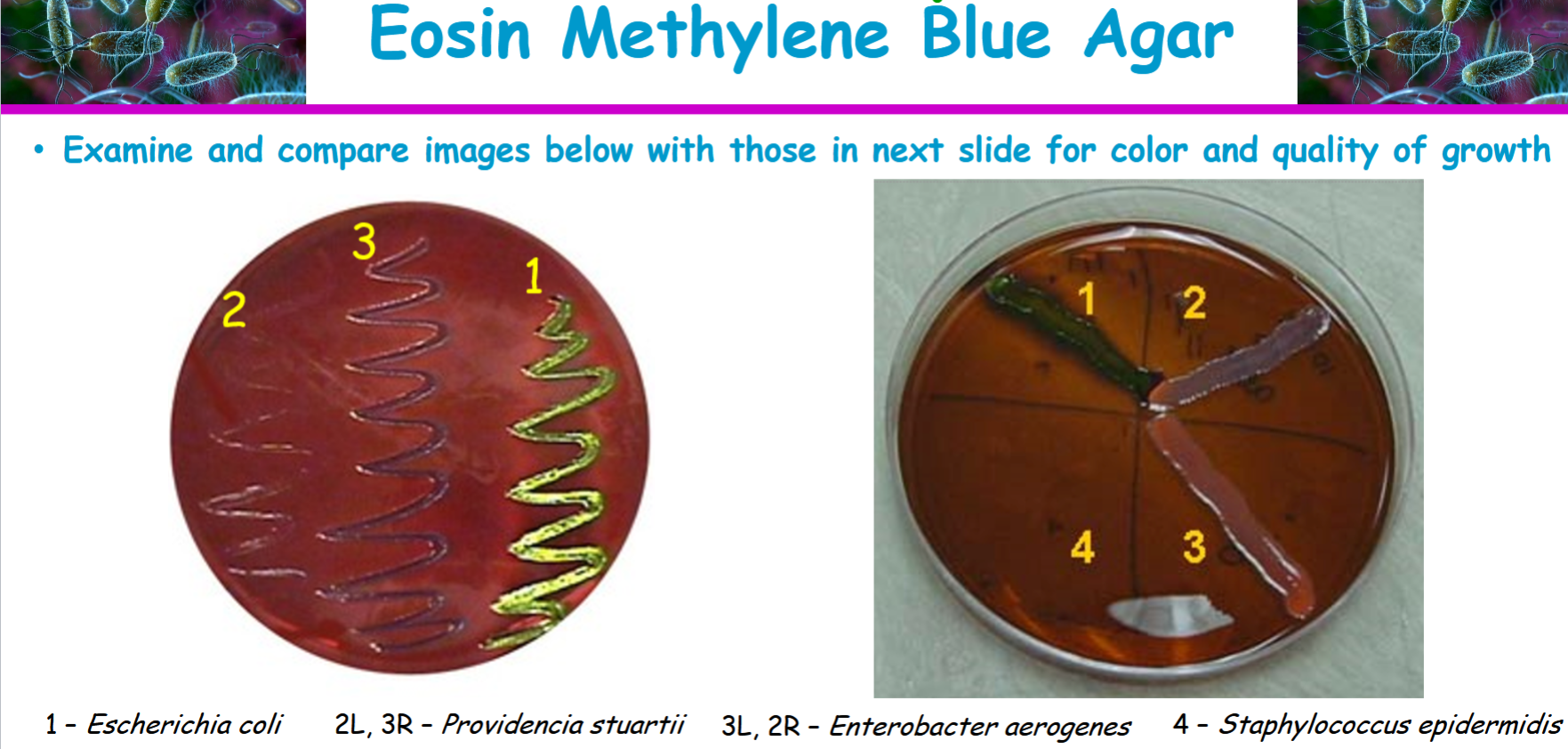
enterobacter aerogenes
a large pinkish to purple mucoid colony with a dark center but without metallic sheen. weakly ferments lactose. gram negative
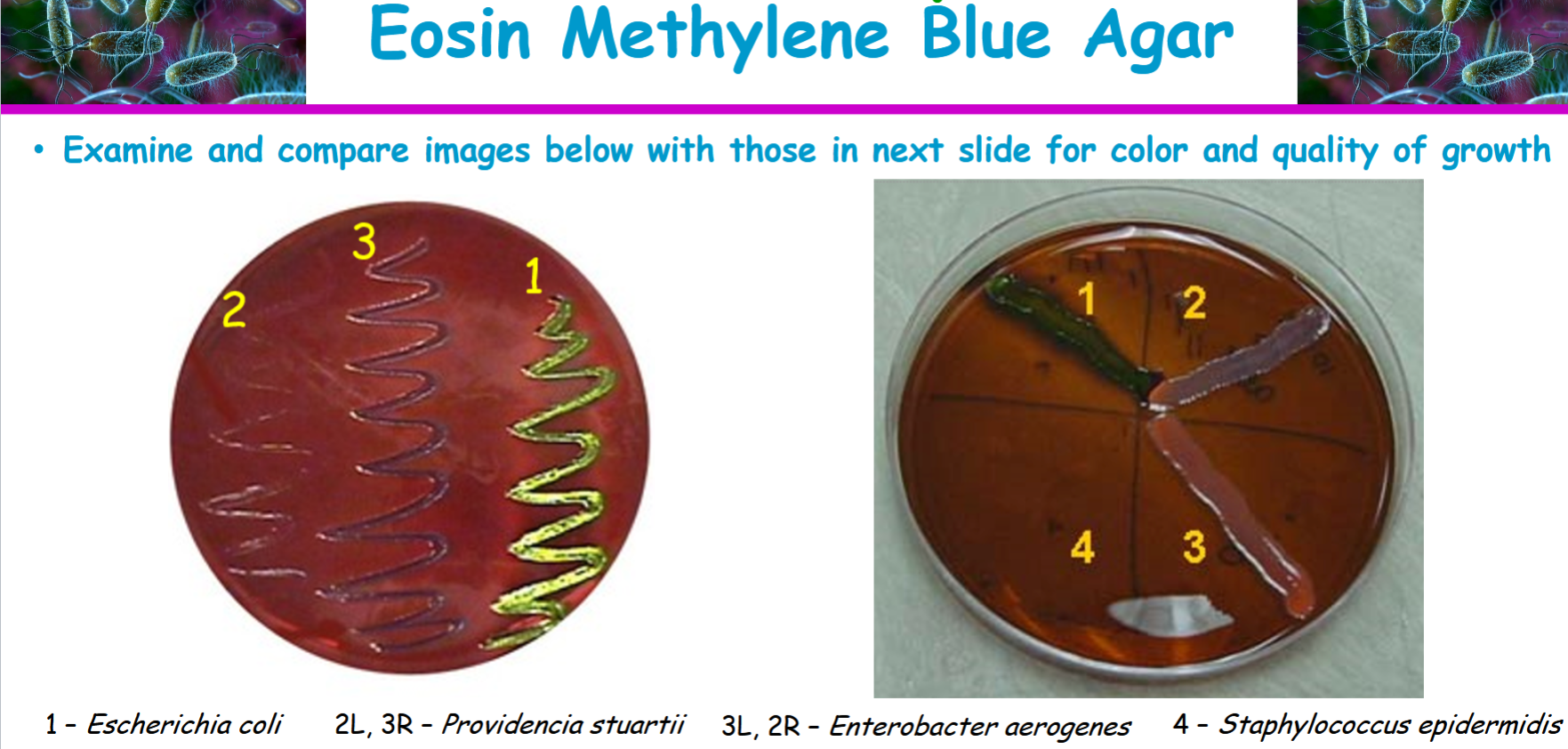
staphylococcus epidermidis
little to no growth, gram positive, non lactose fermenter
Eosin methylene blue agar results and interpretations
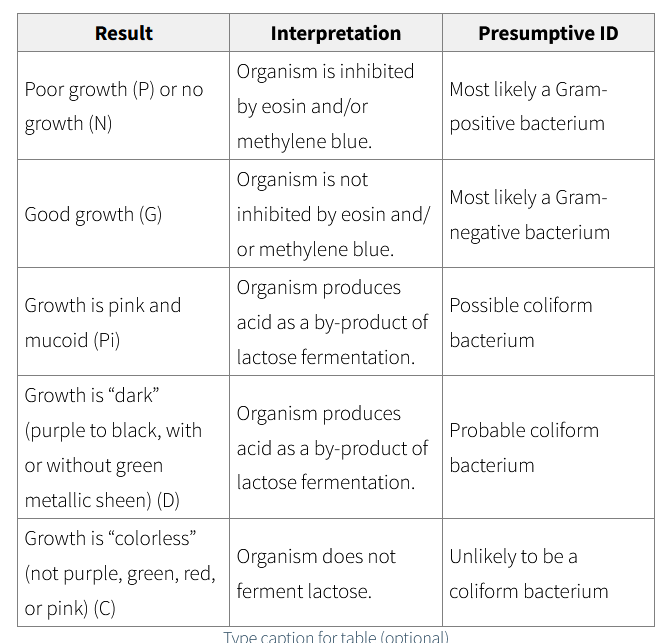
Role of methylene blue in EMB agar
It is important for differentiating lactose fermenters from non-fermenters.
It has a role in inhibiting gram positive bacteria from growing
Roles can be tied to eosin Y in EMB agar
It helps us visually differentiate lactose fermenters from non-fermenters.
It inhibits the growth of most gram positive bacteria