1.4 Polymer processes
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
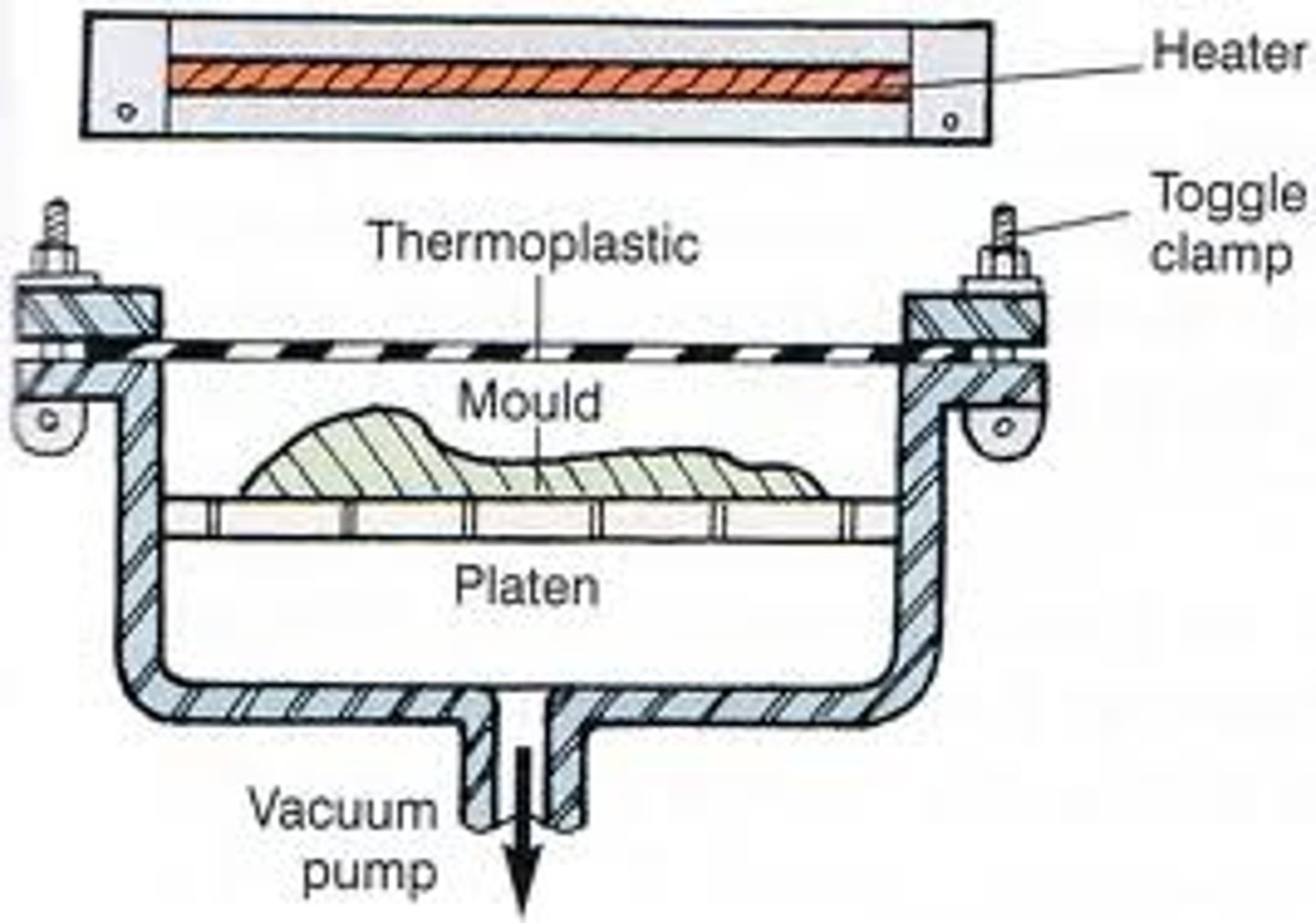
Vacuum forming
1.The mould is placed on a platen and is then lowered into the machine
2.Polymer sheet is clamped over the mould and a heater is pulled over a polymer sheet
3.when the polymer sheet has softened the platen is raised into the polymer and the heat is removed
4.the vaccum pump is switched on which sucks the polymer onto the mould
5.Once the polymer has cooled and returned to a solidified state the platen is lowered and the vacuum switched off
6.The mould is removed from the moulding. Excess polymer is then trimmed off
thermoforming
Plastic sheets are heated over an open mold to a working temperature. Once workable, a vacuum is applied to the mold, forcing the plastic sheet to take the shape of the mold.
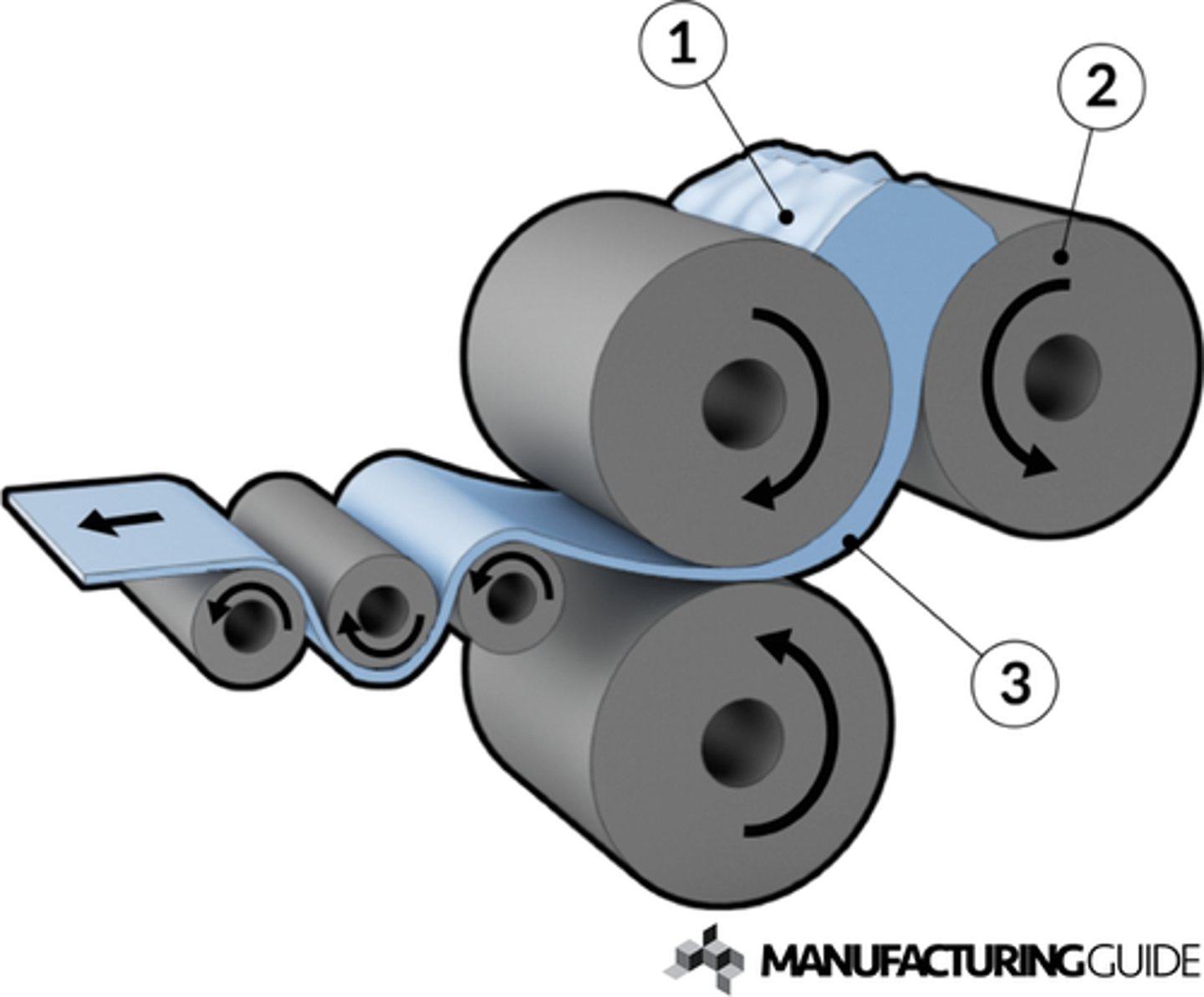
calendaring
A polymer process which smooths and rolls polymers to make sheet and film
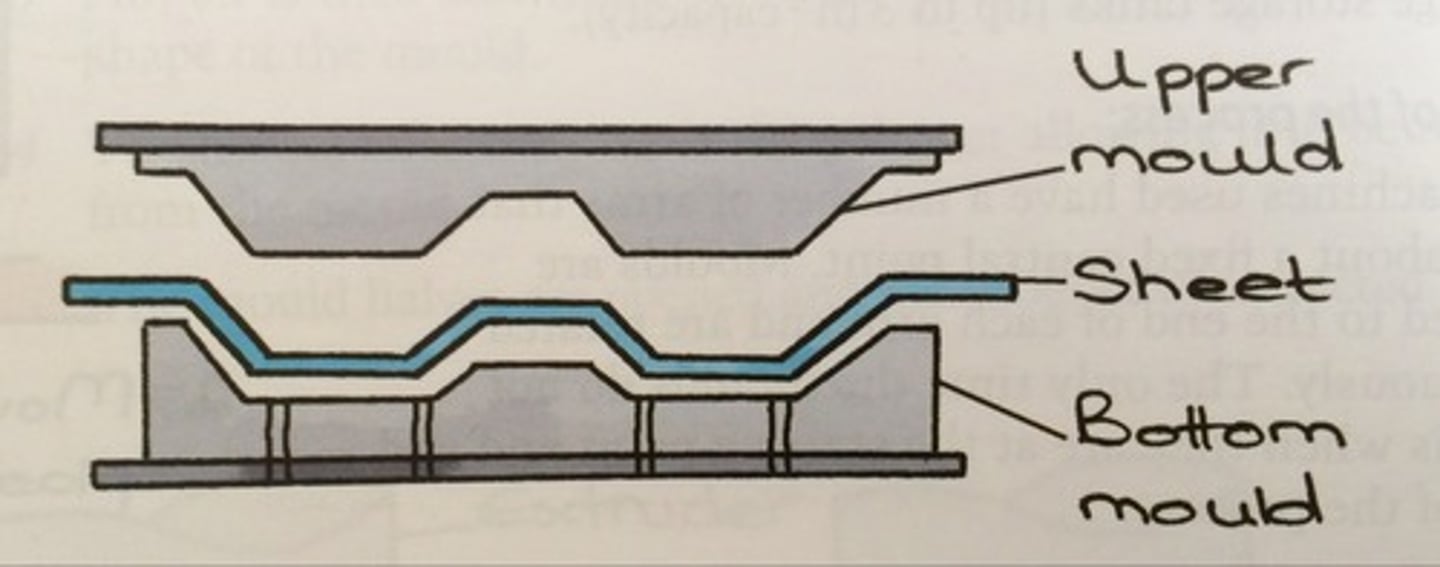
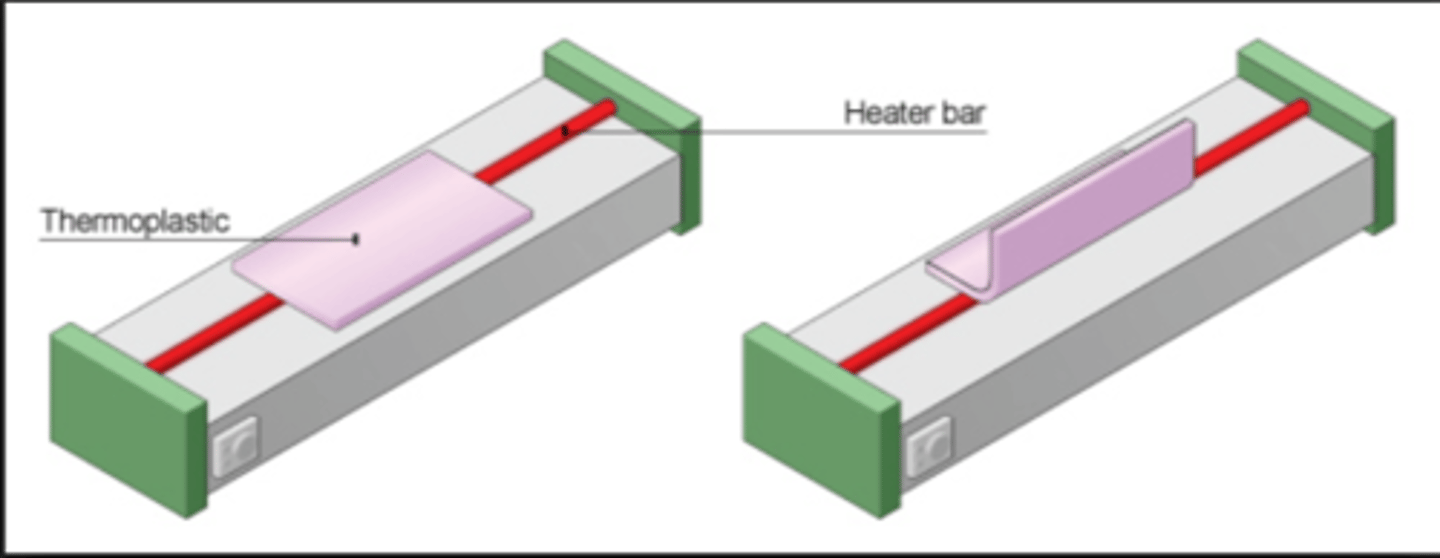
line bending
A polymer process used to product bends in sheet thermoplastic
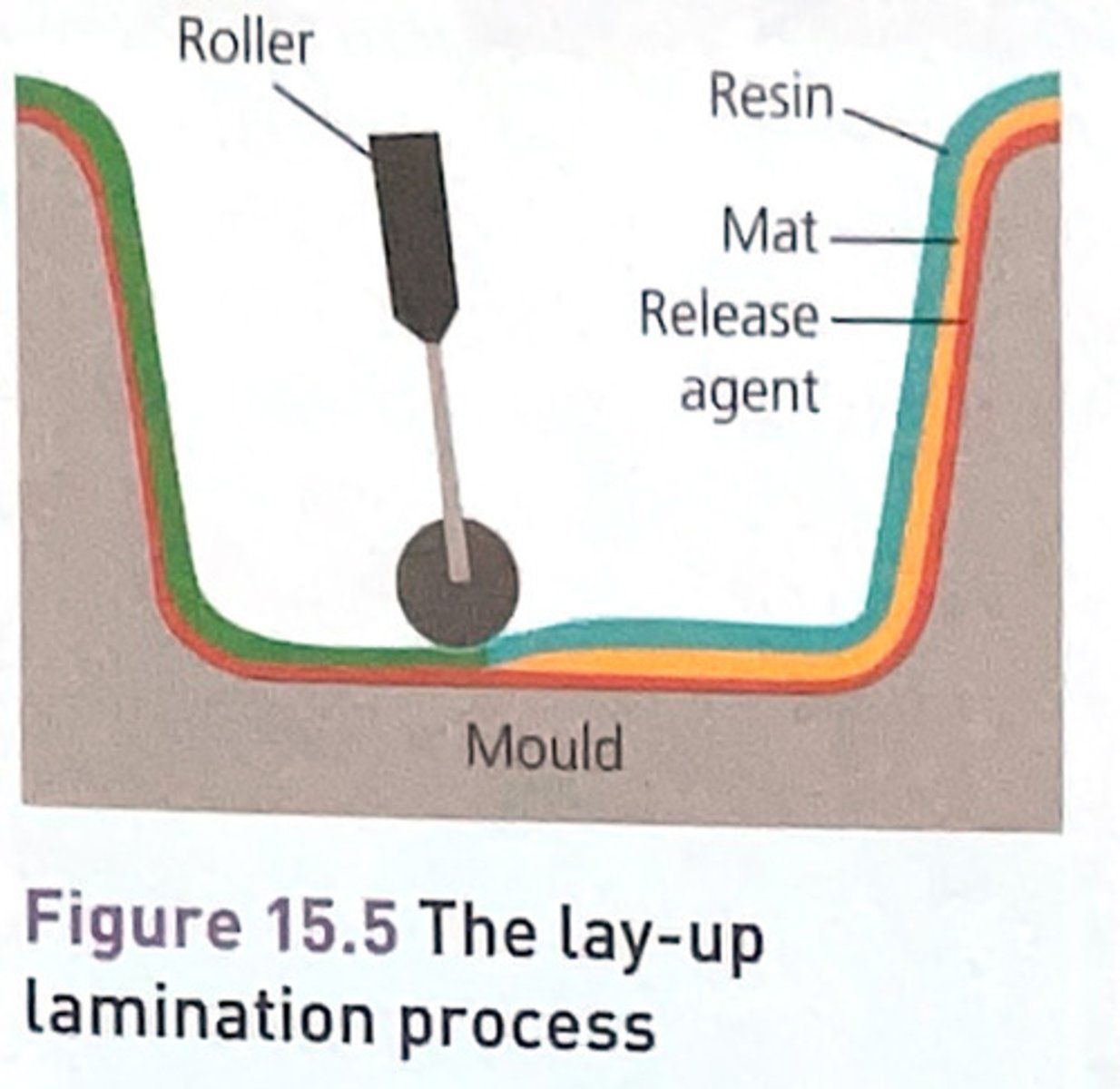
Laminating (lay-up)
1.A mould or former in the shape of the product is prepared. It can be made of timber, mdf or high density foam
2.The mould is coated with a release agent such as wax or is covered in parcel tape
3.a top layer of gel coat ( polyester resin + pigment ) is applied.The resin might have an additive to prevent degradation from UV and hydrolysis. If using CFRP then curing takes place if a specialist over known as autoclave
4.fiberglass matting is cut to size and laid over the former.Polyester resin is brushed onto the matting and a small roller is used to push out any air bubbles .
5. step 3 is repeated until the desired thikness is achieved and fine tissue matting is used on top layers. A vacuum bag may be used to compress the layers of GRP before it sets
6. The GRP is allowed to set
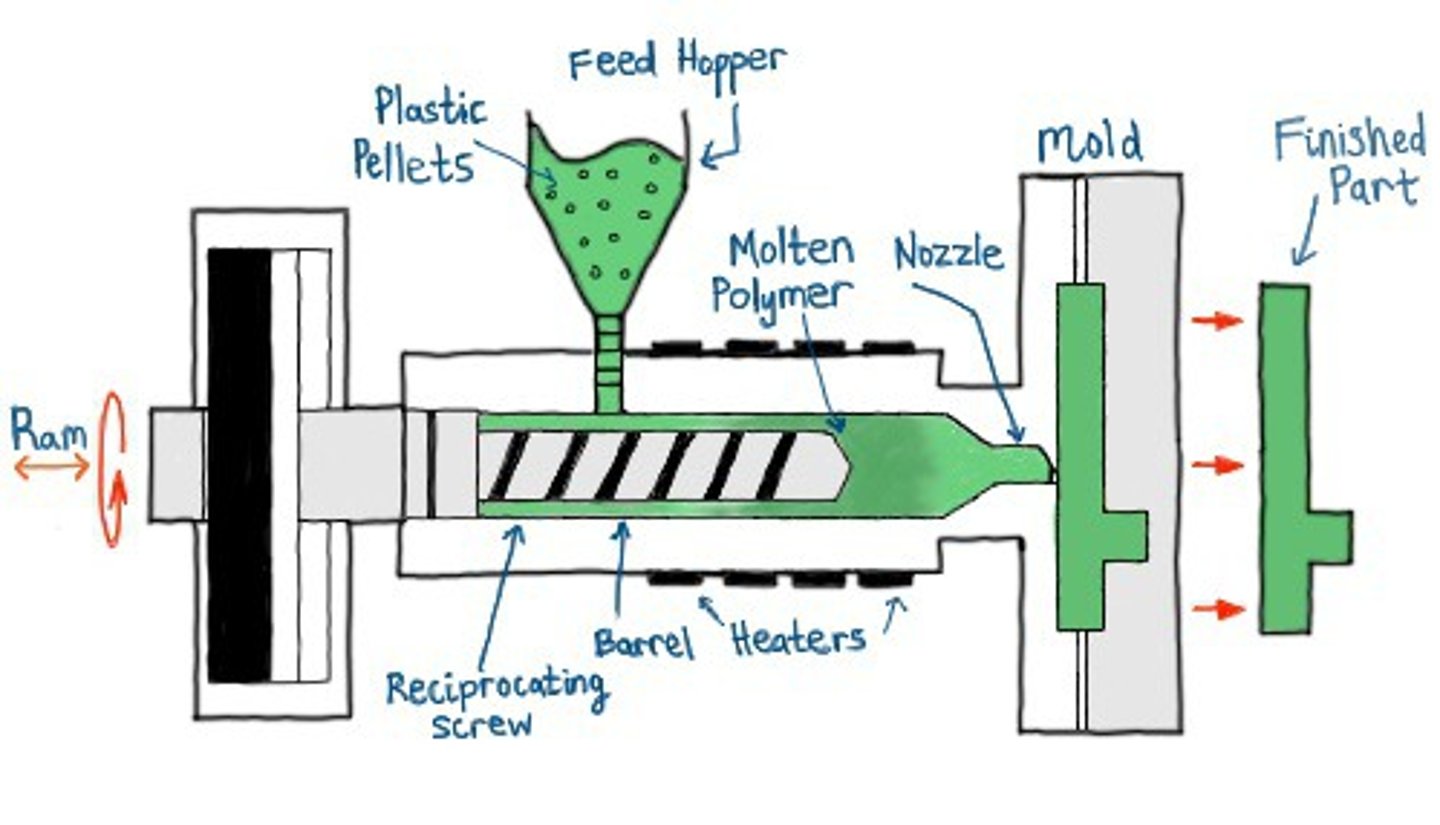
injection molding
1. Thermoplastic granules are poured into a hopper
2. A screw thread is rotated by a motor. this pulls the granules through the chamber and past electric heaters
3. The heaters melt the polymer
4. When a sufficient charge of polymer has melted and formed at the end of the screw, a hydraulic ram forces the screw thread forward. This injects the polymer into the mould
5. The mould is water cooled, which enables the molten polymer to harden quickly
6. The mould opens and ejector pins push the moulding out
7. Any excess polymer is trimmed off the moulding. Formers or jigs may be used to maintain the dimensional accuracy of the moulding while it cools and hardens completely
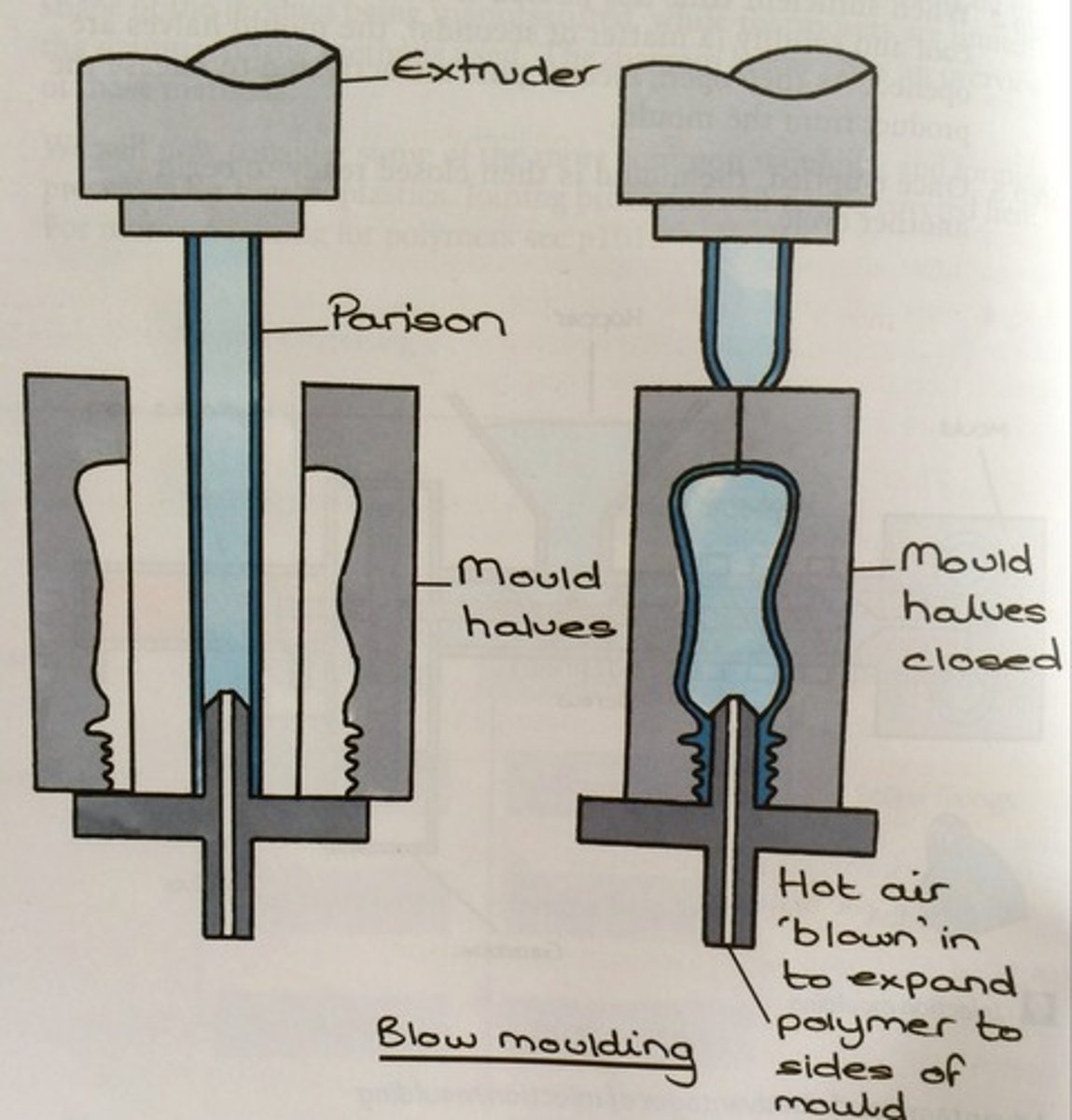
blow moulding
1. The polymer is fed into the hopper
2. An Archimedean screw pulls the polymer through a heated section, melting the polymer
3. The melted polymer is extruded as a tube which is called a 'parison
4. The mould sides close around the parison and air is injected into the mould, forcing the polymer to the sides
5. The polymer is allowed to cool for a few seconds, the mould opens and the finished bottle is ejected
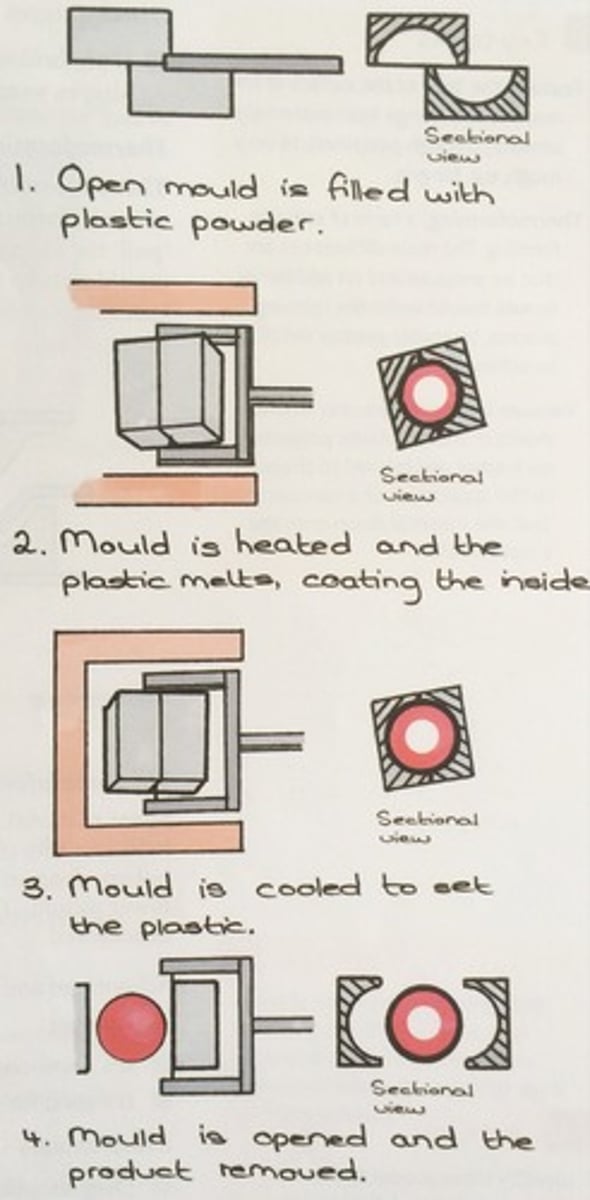
rotational moulding
1. Polymer powder or granules are loaded into a mould, which is clamped and sealed
2. The mould is transferred to an oven where it is heated to 260 - 370 degrees depending upon the polymer used.The mould is rotated slowly around two axes and as the polymer is heated, it coats the inside of the mould
3.Once the polymer has achieved the correct thickness, the mould is cooled. usually a fan and water is used to cool the polymer
4. When the polymer has solidified, the part will shrink slightly, allowing it to be removed
extrusion
1. Polymer granules are loaded into a hopper
2. The Archimedean screw moves the polymer granules past heaters
3. The heater softens the polymer
4. When sufficient polymer has melted, the hydraulic ram pushes the Archimedean screw, forcing the polymer through a steel die. The shape of the die determines the size of the extrusion
5. The extrusion may be supported by rollers as it leaves the die and is cooled by water or air
6. The extrusion is then cut to the desired lengths
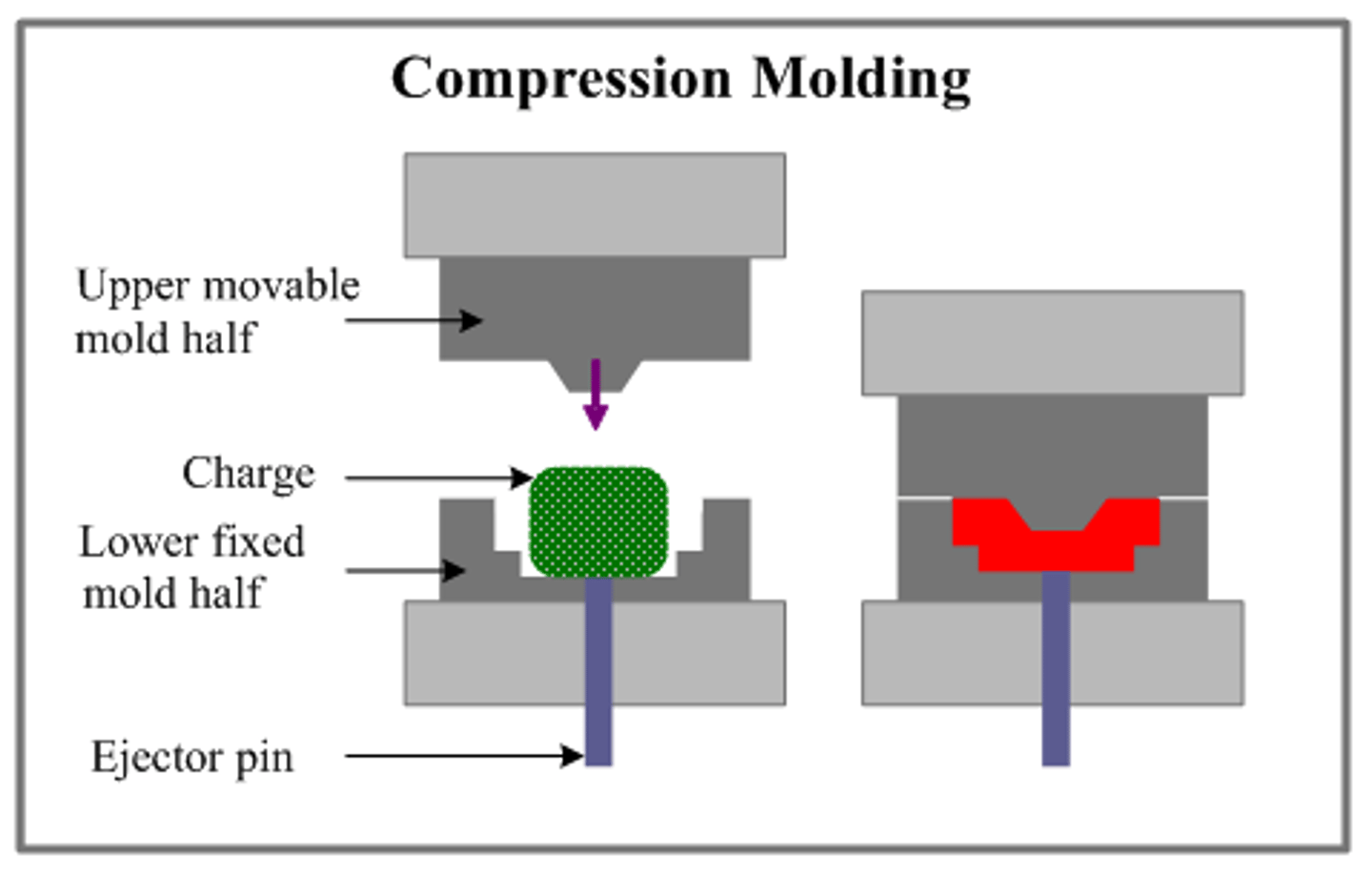
compression moulding
1. A slug of pre-weighed thermoset polymer is inserted into pre-heated moulds.
2. The moulds are closed and hydraulic pressure is applied. The pressure ensures that the polymer takes the shape of the mould
3. The mould remains closed while cross-linking takes place and the thermoset cures
4. When the moulding has cured, the machine opens and the product is removed
5. Excess polymer known as a flash is removed