Infection of urinary system
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
What is the definition of a Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)?
A UTI is an infection that can occur in any area of the urinary tract, including the ureters, bladder, kidneys, or urethra.
Where do Urinary Tract Infections usually develop first?
Urinary tract infections usually develop first in the lower urinary tract (urethra, bladder).
What can happen if lower urinary tract infections are not treated?
If these infections are not treated, they may progress to the upper urinary tract (ureters, kidneys).
What is considered the most common type of UTI?
Bladder infection (cystitis) is the most common UTI.
What are the names for infections of the urethra and the kidneys, respectively?
Infection of the urethra is called Urethritis. Infection of the kidneys is called Pyelonephritis.
How serious is Pyelonephritis?
Pyelonephritis is a serious condition that requires urgent treatment and can lead to reduced kidney function and possibly even death in untreated, severe cases.
What are the signs and symptoms listed for Cystitis?
The signs and symptoms for Cystitis are Dysuria, urgency, and frequency.
What are the signs and symptoms listed for Pyelonephritis?
The signs and symptoms for Pyelonephritis are Flank pain with tenderness, and dysuria, urgency.
List the causative pathogens of UTIs mentioned in the source.
The causative pathogens listed include E. coli, Klebsiella, Proteus, Pseudomonas, Streptococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus aureus, S. epidermidis, S. saprophyticus, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Ureaplasma urealyticum, and Chlamydia.
Which of the listed pathogens are the most common causes of UTIs?
The most common pathogens are E. coli, Klebsiella, Proteus and Pseudomonas.
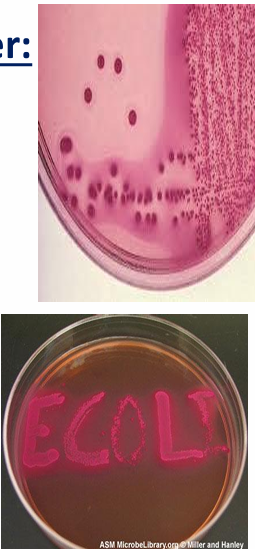
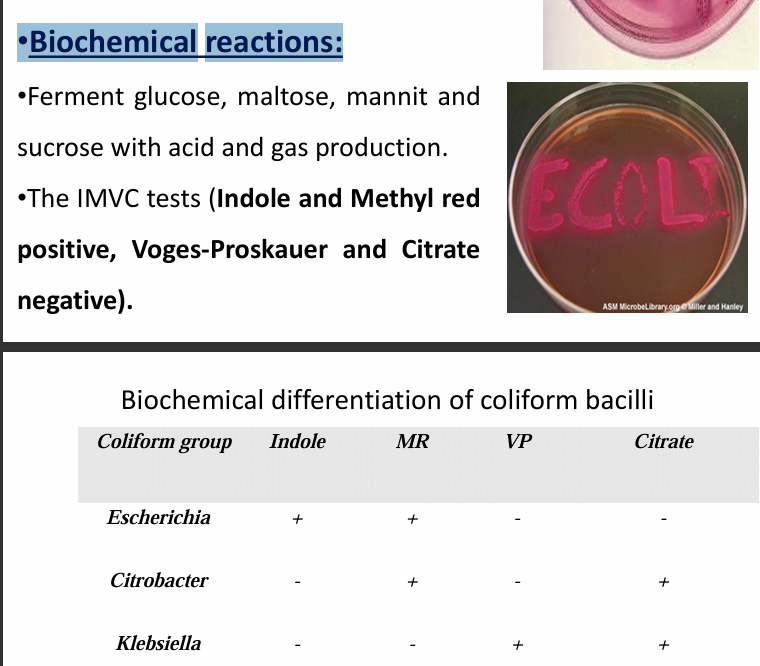
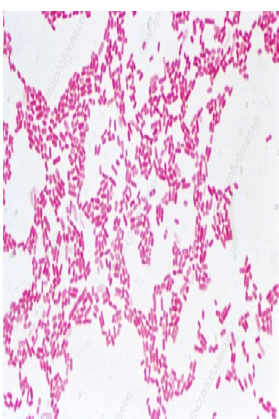
What are some general characteristics of E. coli?
E. coli inhabits the normal intestinal flora. They are Gram negative bacilli, motile, and non sporulated. They are facultative anaerobes and produce rose pink colonies on MacConkey’s agar.
How often is E. coli responsible for Urinary Tract Infections?
E. coli is responsible for 80% of Urinary Tract Infection cases.

What are some general characteristics of Klebsiella?
Klebsiella are non motile and capsulated Gram negative bacilli. They are facultative anaerobes and give pink, large, and mucoid colonies on MacConkey's agar.

What are some general characteristics of Proteus?
Proteus are pleomorphic Gram negative bacilli, motile by peritrichious flagella, and non lactose fermenters.

What are some general characteristics of Pseudomonas?
P. aeruginosa is a Gram negative rod, motile by a single polar flagellum, and has a specific fruity odor.
What are some virulence factors of E. coli that contribute to UTIs?
Virulence factors include adherence to mucosal surfaces, motility by flagella, biofilm formation, LPS, siderophores, and toxins.
What are some virulence factors of Klebsiella?
Virulence factors include capsule, adhesions or colonization factors, and siderophore production.
What are some virulence factors of Proteus?
Virulence factors include adhesins, motility, toxins, enzymes such as urease, and immune evasion.
What are some virulence factors of Pseudomonas?
Virulence factors include siderophores, toxins, biofilm formation, other secreted enzymes, and motility.
What is the recommended method for collecting a urine sample for UTI diagnosis?
Mid-stream urine samples collected aseptically in universal containers are recommended.
How should a urine sample be collected from a catheterized patient?
If a urine sample must be taken from a catheterized patient, it must be taken from the catheter itself, not from the urine bag.
How should urine samples be transported or stored?
Rapid transport of urine samples is important. Samples can be stored for 4 hours at 4°C or with the addition of boric acid.
How can microscopic examination help in UTI diagnosis?
Direct wet film examination is used for pus cells count.
What is a common culture medium used for bacteriological examination of urine?
Culture is often done on CLED medium.
How is significant bacteriuria typically defined in a urine sample?
More than 100,000 colonies per ml is generally considered significant bacteriuria.
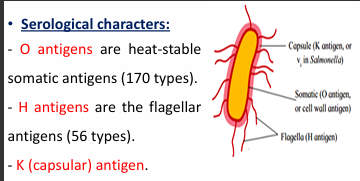
Discuss the serological classification of Escherichia coli and explain the significance of O, H, and K antigens.
Describe the Extra intestinal diseases that caused by E. coli

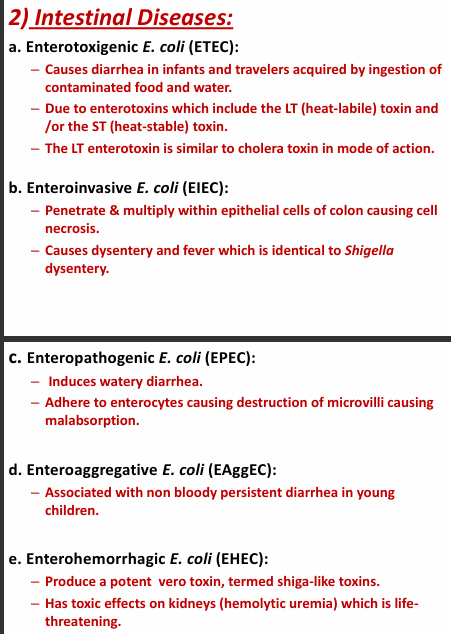
Describe the intestinal diseases that caused by E. coli
The biochemical reactions of E. coli culture