Canadian Interrogation Rights, Techniques, and False Confessions
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
What is the primary goal of police interrogation?
To obtain a confession or gather information.
What are the two types of interrogation in Canada?
Custodial and Non-custodial.
What defines a custodial interrogation?
An interrogation where the suspect is arrested or detained, depriving them of freedom.
What must be communicated to suspects during custodial interrogations?
Their legal rights.
What does the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms guarantee regarding legal rights?
The right to remain silent and the right to get legal advice.
What percentage of people understood their right to silence according to Moore & Gagnier (2008)?
50% understood the right to silence caution.
What is a common reason why people fail to understand their rights during interrogation?
Police often read rights too quickly and in complex language.
What is the implication of the 'caution card' in interrogations?
It is meant to inform suspects of their rights, but many do not understand it.
What does the term 'false confessions' refer to?
Confessions that are obtained under coercive circumstances or false pretenses.
What is the significance of the case R. v. Oickle (2000)?
It established guidelines for the admissibility of confessions in court.
What are the conditions under which a confession is considered admissible?
It must be voluntary and given with an operating mind, without oppression or coercion.
What does the Reid Technique emphasize in interrogations?
Psychological persuasion and a guilt-presumptive approach.
What is the fundamental issue with the Reid Technique?
It assumes that police only interrogate guilty individuals, which is not always true.
What are some tactics used in the Third-Degree Approach?
Physical abuse, isolation, and deprivation of basic needs.
What does the term 'accusatorial approach' refer to?
An interrogation philosophy that presumes guilt and employs psychological pressure.
What is meant by 'information overload' in the context of legal rights?
Providing too much information at once, making it hard for suspects to understand their rights.
What is a common misconception among laypeople regarding interrogation rights?
That suspects have the right to have a lawyer present during police questioning.
What is the role of judges in relation to interrogation tactics?
Judges decide whether interrogation tactics are acceptable and if confessions are admissible.
What is the impact of complex language on understanding legal rights?
Complex language can hinder comprehension, especially for those with lower education levels.
What is the purpose of the 'caution card'?
To inform suspects of their rights in a clear and concise manner.
What does the term 'voluntary confession' mean?
A confession given freely and without coercion.
What is the significance of the 'polygraph ploy' in interrogations?
It is a tactic used to create pressure or imply leniency to elicit confessions.
What is the effect of sleep deprivation during interrogations?
It can lead to increased compliance and potential false confessions.
What is 'quid pro quo' in the context of police interrogations?
An implied exchange where suspects may be promised leniency in return for a confession.
What are 'implicit interrogation tactics'?
Tactics that are not overtly coercive but can still lead to false confessions.
What is the main criticism of the interrogation tactics used in R. v. Oickle?
They pose a risk of false confessions due to their vague nature.
What is the primary assumption of police during an interrogation?
The suspect is guilty, using either fabricated or real evidence.
What is the purpose of stating that the interview is not about determining guilt?
To focus on understanding the suspect's motivations or reasons.
What are the two emotional themes that can be developed for suspects?
Distress/remorse and nothing.
What approach should be taken with emotional suspects?
Use sympathetic appeals and factual analysis.
What techniques can be used for non-emotional suspects?
Catch them in a lie, associate them with the crime scene, and suggest non-criminal intent.
What should an interrogator do when a suspect attempts to deny involvement?
Interrupt any attempted denials to maintain control of the conversation.
How do denials differ between innocent and guilty suspects?
Innocent suspects tend to be spontaneous, while guilty suspects are often hesitant and defensive.
What is the goal when handling objections from suspects?
To allow the objection and return to the main theme of the interrogation.
What is the purpose of the alternative question technique?
To present suspects with two explanations for the crime, both leading to a confession.
What is the significance of a written confession?
It is more incriminating, although less important now with videotaped interrogations.
What is the psychological strategy behind the Reid technique?
To make the anxiety of not confessing greater than the anxiety of the consequences of confessing.
What is the initial step in detecting deception according to the Behavioral Analysis Interview (BAI)?
To determine if the suspect is guilty.
What is a major problem with investigator bias during interrogations?
It leads to more coercive and guilt-presumptive questioning.
What are the two coercive tactics used in interrogations?
Minimization (soft sell) and maximization (scare tactics).
What factors can make a suspect vulnerable during an interrogation?
Current mental state, low IQ, drug intoxication, sleep deprivation, and anxiety.
What is the difference between the information gathering approach and the accusatorial approach?
The information gathering approach promotes dialogue and truth-seeking, while the accusatorial approach aims to obtain a confession.
What does the PEACE model stand for?
Planning and Preparation, Engage and Explain, Account, Challenge, and Evaluate.
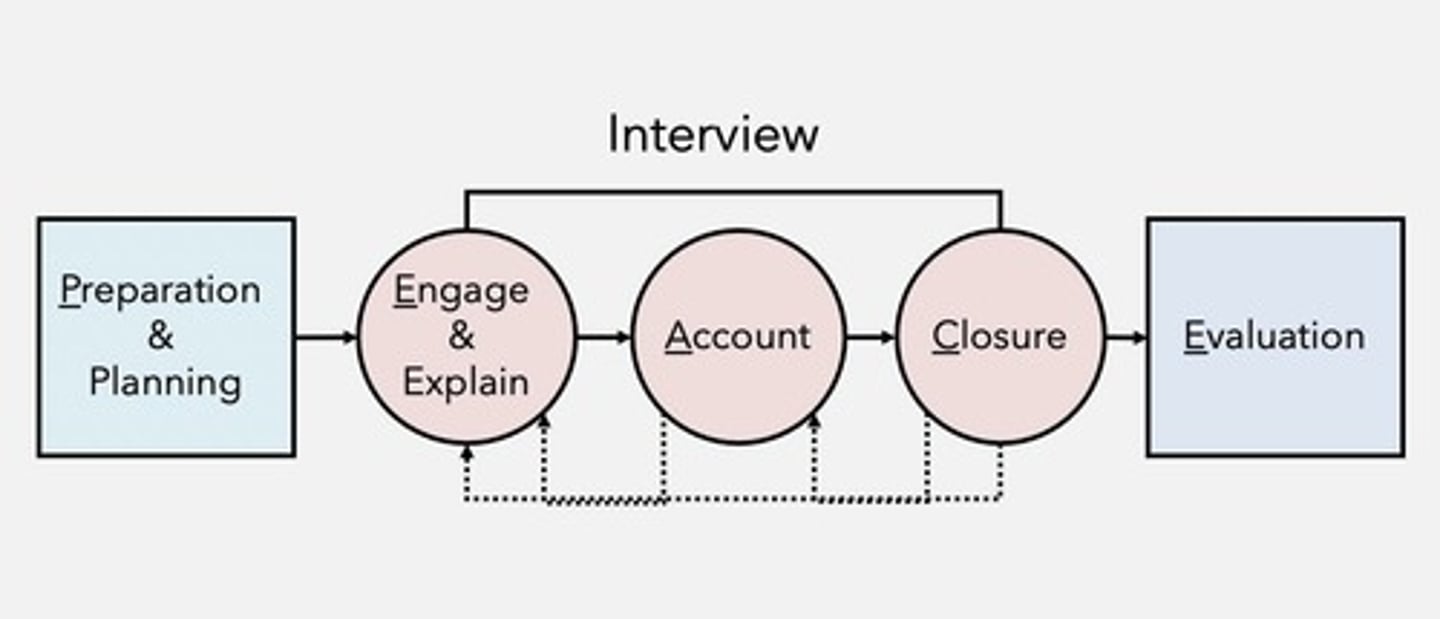
What is the most important phase of the PEACE model?
The Account phase, where complete and accurate information is gathered.
What is the role of the interviewer in the PEACE model?
To be an objective fact finder and promote dialogue.
What is a trailer question in the context of an interrogation?
A question that encourages the interviewee to provide a free narrative without interruption.
What is the purpose of probing questions during an interrogation?
To clarify and seek detailed information from the interviewee.
What is the challenge phase in the account process?
A clarification-seeking task where the interviewee can explain discrepancies.
What is the final phase of an interrogation process?
Evaluation, which includes self-evaluation and considering the effect of new information.
What are the key components to summarize after an interview?
Main points, allowing the interviewee to add information or ask questions.
What are the characteristics of evidence for PEACE?
It doesn't contain unethical practices, is scientifically supported, and includes the offender's perspective.
What does the term 'Convergence of Evidence' refer to?
The integration of findings from experimental research and meta-analysis.
What did Meissner et al. (2014) conclude about information-gathering approaches?
They found that information-gathering approaches are superior for true confessions but less effective for false confessions.
What is the difference between custodial and non-custodial interrogation?
Custodial interrogation occurs inside a police facility, while non-custodial interrogation takes place outside, such as in the 'Mr. Big' technique.
What is the 'Mr. Big' technique?
A controversial non-custodial interrogation method where undercover police create a fabricated criminal organization to elicit confessions.
What are the stages of the 'Mr. Big' technique?
1. Intelligence probe, 2. Introduction, 3. Scenario development, 4. Evidentiary scenario.
What are the risks associated with the 'Mr. Big' technique?
It can lead to false confessions, lacks legal safeguards, and only the final meeting is recorded.
What are the three types of false confessions?
Voluntary, compliant, and internalized false confessions.
What is a voluntary false confession?
A confession made without prompting, often to protect someone else or due to a desire for notoriety.
What is a compliant false confession?
A confession made under pressure from police, often to escape a situation or avoid punishment.
What is an internalized false confession?
A confession where the individual believes they committed the crime due to suggestive questioning.
What are some risk factors for false confessions?
Situational factors like pressure during interrogation and dispositional factors like low self-esteem.
What is the 'Cheating Paradigm' study by Russano et al. (2005) about?
It examines how different interrogation tactics affect the rate of false confessions.
What was the rate of false confessions in the 'Cheating Paradigm' with no tactics?
6%.
What was the highest rate of false confessions observed in the 'Cheating Paradigm'?
43% when both minimization tactics and a deal were offered.
What are the consequences of false confessions?
They can bias subsequent decisions, interpretation of evidence, and lead to harsher punishments.
What stigma do wrongfully convicted individuals face after exoneration?
They often deal with social stigma, lack of reintegration support, and financial and psychological struggles.
What is the significance of the US National Registry of Exonerations?
It tracks wrongful convictions and the frequency of false confessions in the US.
What percentage of false confessions were found in the US National Registry of Exonerations?
Approximately 16%.
What is the role of suggestibility in false confessions?
Suggestibility refers to how individuals accept information communicated during questioning, which can lead to false confessions.
What factors increase suggestibility in individuals?
Low verbal ability, low self-esteem, adverse life events, and trait anxiety.