week 9: Lipids and lipoproteins
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Roles of lipids (fats)
rich source of energy and efficient way for body to store calories
integral part of cell membranes and structure
Fatty acids
linear chains of carbon-hydrogen bonds terminating in carboxyl group
triglycerides
3 fatty acid molecules attached to 1 molecule of glycerol by ester bonds
Phospholipids
similar to triglycerides, except with only 2 esterified fatty acids
third position on glycerol backbone contains phospholipid head group
types of head groups: choline, inositol, serine, ethanolamine, all of which are hydrophilic in nature
Cholesterol
unsaturated steroid alcohol containing 4 rings and single side chain tail
synthesized almost exclusively by animals; not readily catabolized by most cells, not a source of fuel
All lipoproteins
typically spherical; diameters of 10-1,200 nm
composed of lipids and proteins; deliver fuel to peripheral cells
Chylomicrons
largest and least dense; diameters as large as 1,200nm
produced by intestine; deliver dietary lipids to hepatic and peripheral cells
transport exogenous triglycerides
normally not in fasting serum
plasma appearance
Very-low density lipoproteins (VLDL)
produced by liver
major carriers of endogenous triglycerides
Apo B
Low-density lipoproteins (LDL)
form as a result of lipolysis of VLDL
readily taken up by cells via LDL receptors in liver and peripheral cells
significantly smaller than VLDLs; can infiltrate extracellular space
Lipoprotein a (lpa)
LDL-like particles; heterogeneous in size and density
plasma levels of Lp(a) vary widely among individuals in population but remain relatively constant within a person
High-density lipoproteins
smallest and most dense; synthesized by liver and intestine
can exist either as disk-shaped or spherical particles
capable of removing excess cholesterol from peripheral cells
highly heterogeneous; can be separated into 13 or 14 subfractions
lipids and lipoproteins
insoluble in water
primary lipids
cholesterol
triglycerides
lipoproteins (Chylomicrons, LDL, HDL)
phospholipids
fatty acids
Exogenous lipid metabolism (digestion)

Endogenous triglycerides
liver biosynthesis from glycerol and fatty acids
transported as VLDL
hydrolyzed by lipoprotein lipase (LPL)
VLDL → LDL (cholesterol rich)
Endogenous cholesterol
free cholesterol synthesized from acetyl CoA
bile acid (breaks down cholesterol)
steroid hormone precursor
synthesis = 90%, dietary = 10% of T. cholesterol
insoluble
Free cholesterol esterification (fatty acid addition)
LCAT (Lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase)
blood
ACAT (Acyl-cholesterol acyltransferase)
intracellular
1/3 free, 2/3 esterified
Synthesis modulation by [free cholesterol]
↑ free cholesterol inhibits HMG-CoA reductase
rate limiting step
cholesterol-lowering drug (blocks chol syn by inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase)
Transport by lipoproteins
LDL transports to the cells
HDl transports excess from cells to liver
excreted in bile, steroid hormone synthesis
Apolipoproteins
proteins that binds lipids
forms lipoproteins to help transport lipids
5 types A→E
protein on a lipid-protein molecule
ex. Apolipoprotein a: major protein on HDL
LDL “bad” cholesterol
Apo B
transports cholesterol to peripheral cells
binds to LDL receptors
↑↑ LDL → ↑ Atherosclerosis
HDL “good” cholesterol (helpful)
Apo A
transports excess cholesterol from peripheral cells to liver
↑↑HDL → ↓ Risk of atherosclerosis
Lipoprotein (a) significance
LDL-like molecules containing an extra apolipoprotein - apo (a) [usually on HDL]
elevations thought to be independent factor for increased CHD risk
genetic based, not dietary
most LDL lowering drugs don’t lower Lp(a)
Dyslipidemias (abnormal serum lipids)
family history, physical exam, nutritional/social habits
assess risk, diagnose, monitor: atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease (CAD)
genetic or acquired
altered lipoprotein synthesis, transport catabolism
hyperlipoproteinemias/hypolipoproteinemias
Hyperlipoproteinemias
hypertriglyceridemia
hypercholesterolemia
combined hyperlipidemia
hyperlipoproteinemia diagnosis
intital ↑↑ triglyceride and/or cholesterol
repeat with 12hr fasting specimen
Xanthomas (fat nodules underneath skin)
primary or secondary disorder
1° Hypertriglyceridemia
inherited chylomicron with VLDL clearance defect
↓ lipoprotein lipase activity
2° Hypertriglyceridemia
Dietary
hypothyroidism
DM
nephrotic syndrome
obstructive liver disease
Hypertriglyceridemias
↑↑ chylomicrons
↑↑ VLDL
↑↑ chylomicrons and VLDL
LDL-cholesterol
familial hypercholesterolemia
↓ LDL receptor #/activity
↑atherosclerosis and CAD
marked ↑↑T. chol., LDL
many 2° conditions
↑↑LDL, TG, VLDL
↑HDL-Cholesterol
familial hyper-alphalipoproteinemia
↑↑HDL , sl ↑ T. chol
↓CAD risk
Combined hyperlidpidemia
Primary ↑↑ TG and T. Chol
dysbetalipoproteinemia
impaired VLDL → LDL
↓ LDL
asymptomatic, possible xanthomas
Combined hyperlipidemia conditions
familial high cholesterol
coronary heart disease
diabetes
alcohol
hypothyroidism adds to problem
Primary hypolipoproteinemias
↓T. Chol and HDL
Tangier disease
↓↓↓ Apo A synthesis
↑ Cholesterol esters → orange-yellow tonsils
↑↑CAD risk
Hypobetalipoproteinemia
↓ T. Chol and LDL
↓ Apo B synthesis
Secondary hypolipoproteinemias
hyperthyroidism
liver parenchymal disease-destruction and regeneration of liver cells leading to cirrhosis
Total cholesterol methods
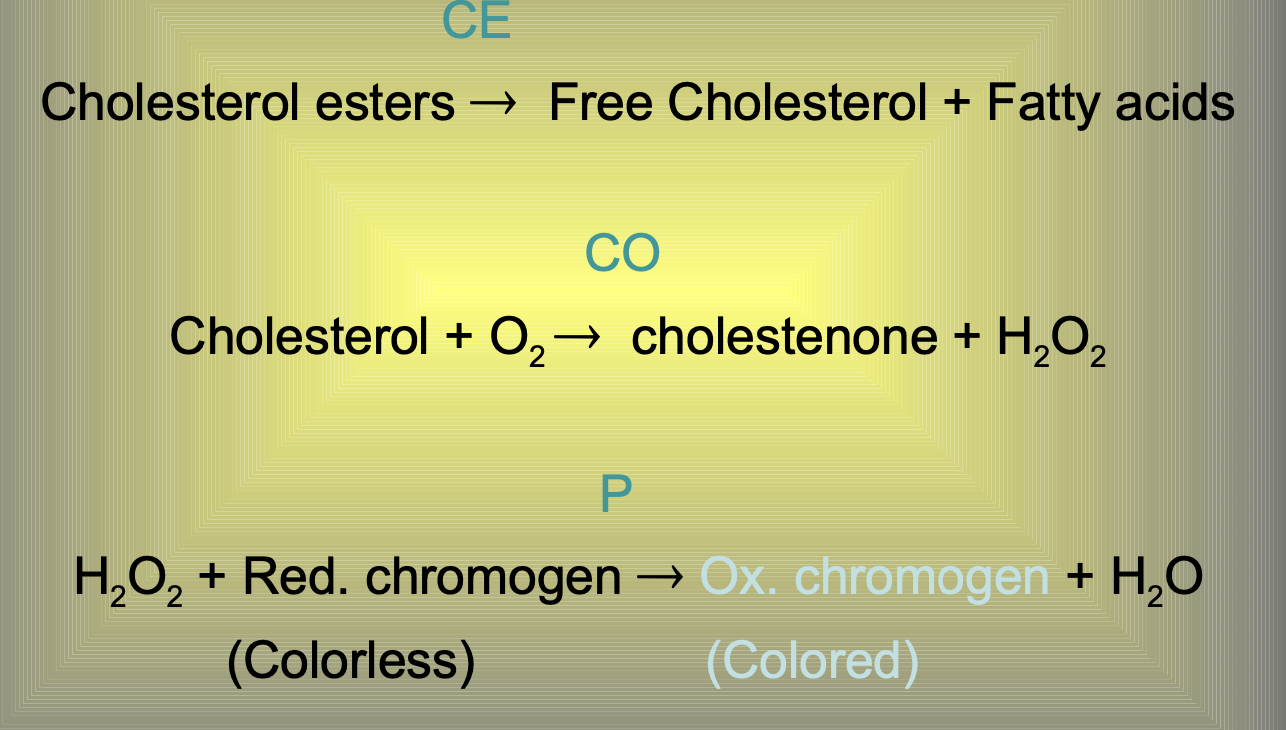
HDL-cholesterol methods
selective lipoprotein precipitation
reagent
divalent cations in buffer, heparin or dextran
Apo B-containing lipoproteins precipitate, leaving HDL in supernatant
centrifuge
measure HDL in supernatant
↑ TG interferes → dilute and repeat PPT step
Homogenous (direct) HDL
no manual separation step
selective inhibition of non-HDL lipoproteins with T. Chol reagent
↑TG does not interfere with most methods
Friedewald calculation
LDL-C = (total cholesterol) - (HDL-C) - (TG/5)
Valid only when TG < 400mg/dL
↑↑LDL/HDL ratio = ↑↑CAD risk
LDL-cholesterol methods
analytical methods
selective lipoprotein preciptation
immunoseparation
4°C overnight EDTA plasma appearance
creamy top layer = ↑ chylomicrons
turbidity = ↑↑VLDL
yellow-orange color = ↑↑LDL??
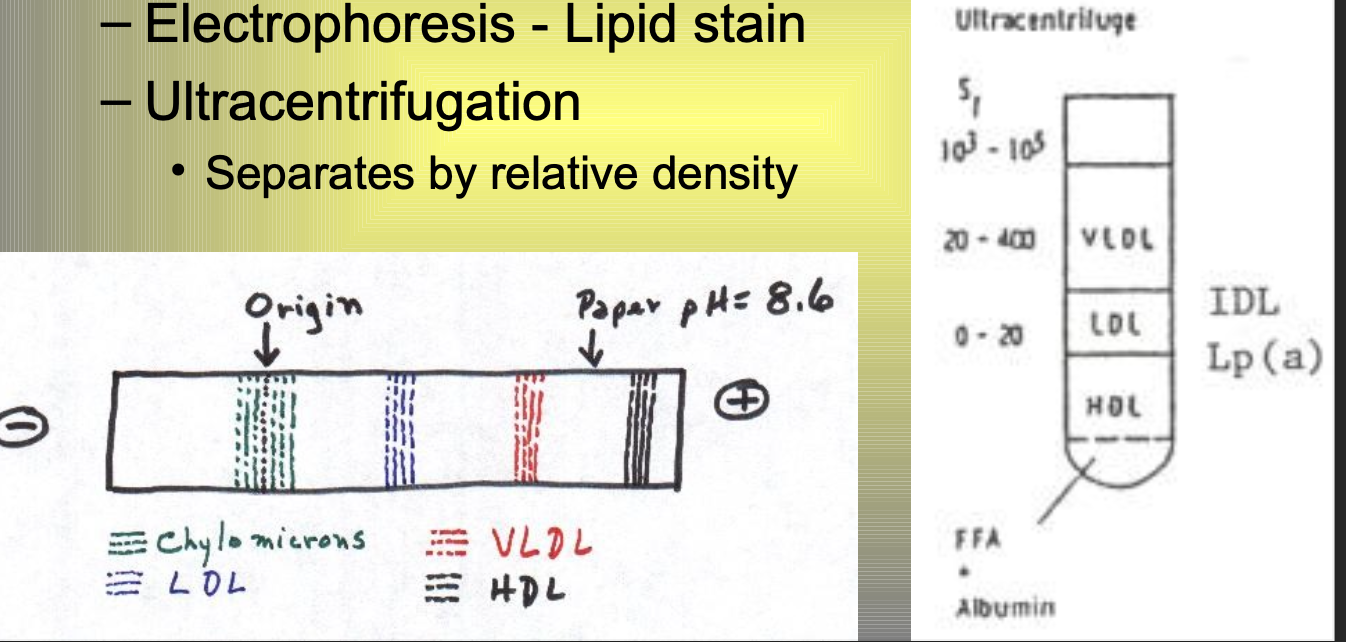
Lipoprotein separation
TG>400 mg/dL OR suspect abnormal lipoproteins: B-VLDL (floating B-lipoprotein)
electrophoresis - lipid stain
ultracentrifugation
separates by relative density
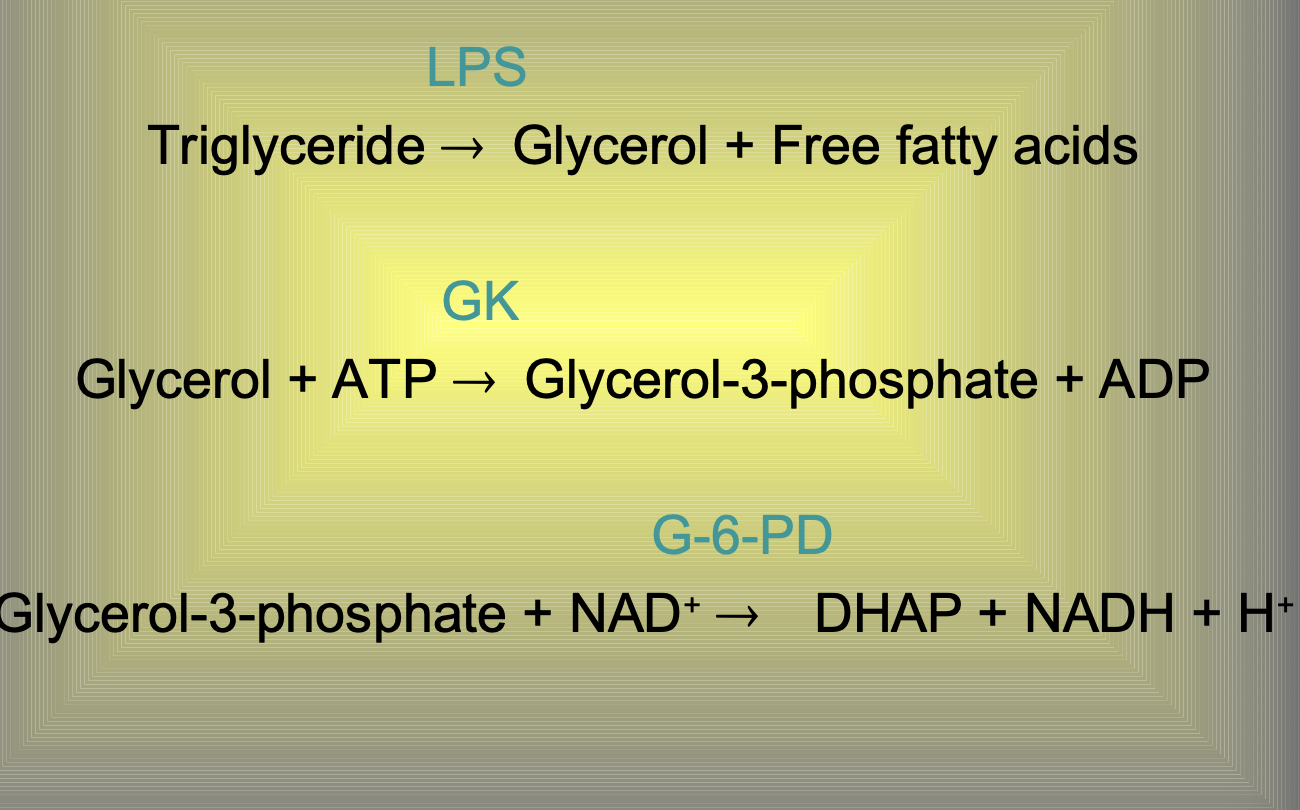
Triglyceride method
Desirable lipid ranges
Total cholesterol = <200mg/dL
HDL-cholesterol = >37 mg/dL (male) >40 mg/dL (female)
LDL-cholesterol = <130 mg/dL
triglyceride = <250 mg/dL