Reproduction in Humans
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Female Gamete
Ovum (ova pl)
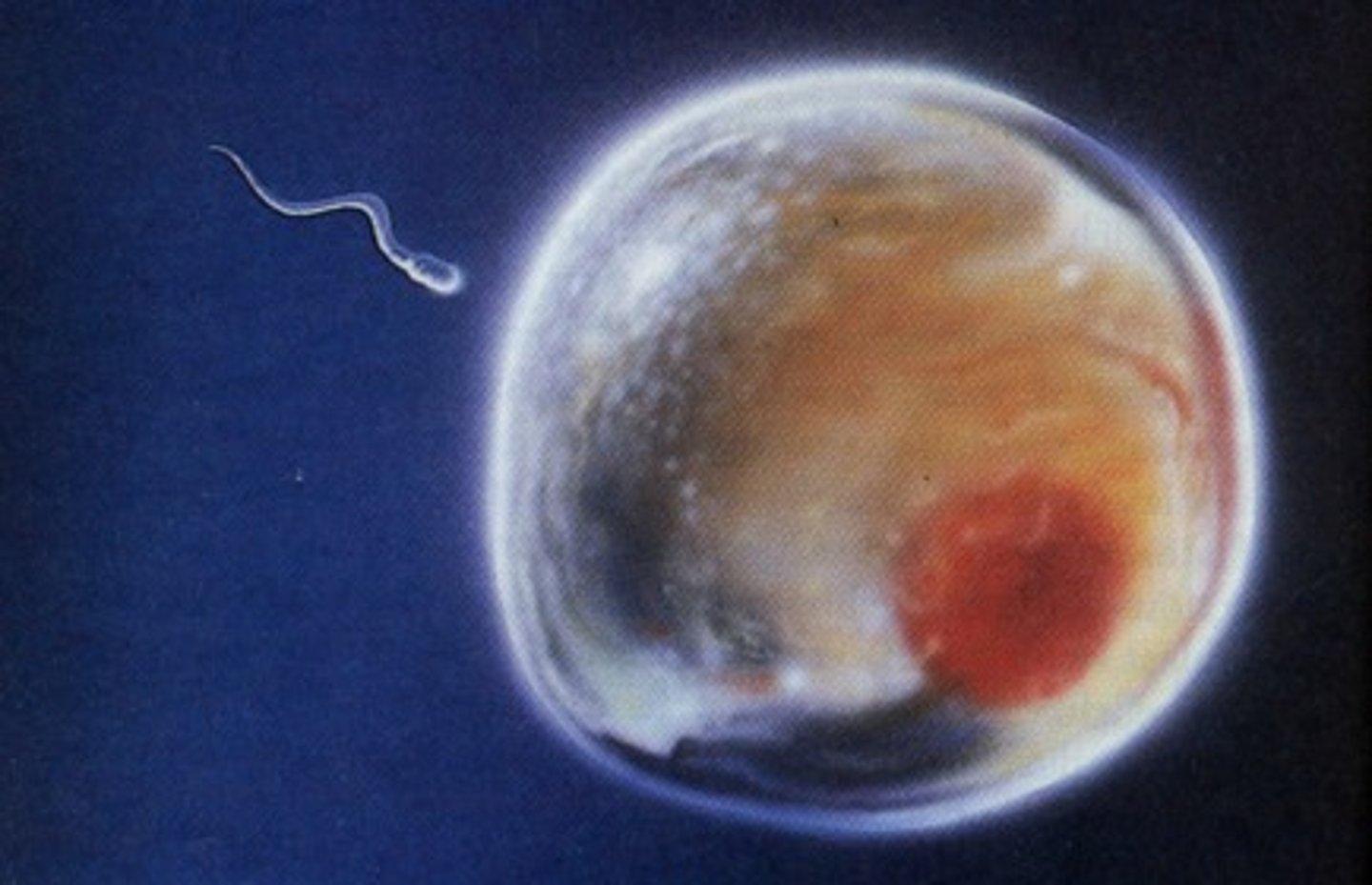
Vagina
A canal that joins the cervix (the lower part of uterus) to
the outside of the body
It is also known as the birth canal
Uterus
A hollow, pear-shaped organ that is the home to a developing foetus
The fertilised egg then moves here to implant in the uterine lining
Site of implantation
Corpus
The main body of the uterus
Can easily expand to hold a developing baby
Ovaries
Small, oval-shaped glands that are located on either
side of the uterus
Produce eggs and hormones
Fallopian Tubes (Oviduct)
Narrow tubes that are attached to the upper part of the uterus and serve as pathways for the ova to travel from the
ovaries to the uterus
Fertilisation of an egg by a sperm normally occurs here
Urethra (Female)
Tube leading from the urinary bladder to the outside of the body
Shorter than the male's
Mucus Plug (Operculum)
Forms inside the cervical canal to create a barrier against pathogens
Functions of the Female Reproductive System
It creates ova that are essential for reproduction
Organised to deliver the ovum to the region of fertilisation
Fertilisation of ovum
Implantation of the fertilised egg in the walls of the uterus and starting the stages of pregnancy are the next steps for fertilised eggs.
Involved in the production of female sex hormones to maintain the reproductive cycle
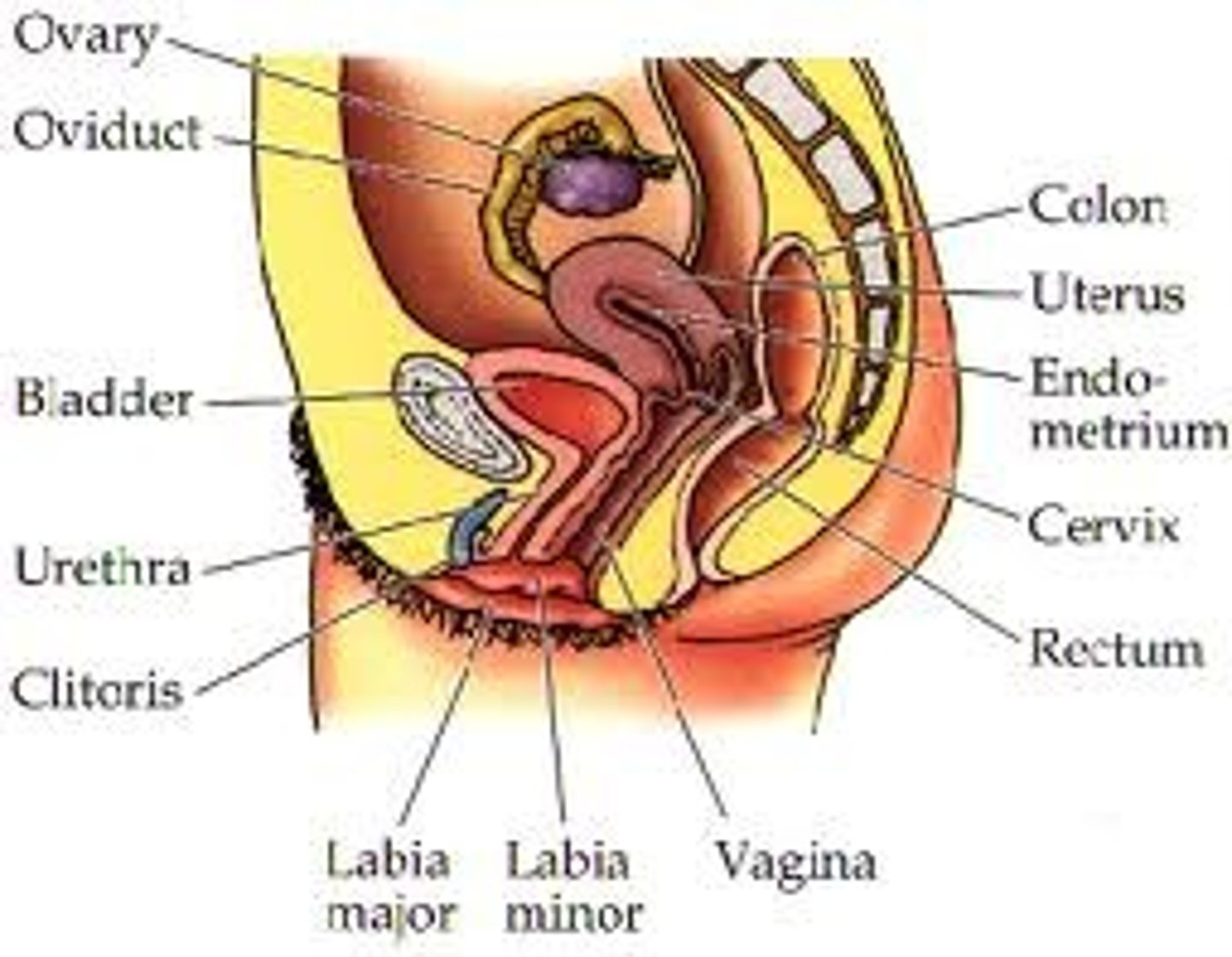
Male Gamete
Sperm
Epididymis
A long, coiled duct on the outside of the testis in which sperm mature and are stored
Testes
Produce sperm
Must be at a temperature slightly cooler than the body temperature for normal sperm development
Scrotum
External sac that contains the testes
Special muscles in the walls allow it to contract and relax, moving the testes closer to the body for warmth and protection or farther away from the body to cool the temperature
Semen
The combination of sperm, nutrients (carbs) and seminal fluid
Seminal vesticle + prostate + cowper's gland + sperm
Urethra (Male)
Serves as the passageway for sperm and fluids from the reproductive system and urine from the urinary system
Sphincter
While the reproductive fluids pass through, it contracts tightly to keep urine from entering the urethra
Foreskin (Prepuce)
A retractable double-layered fold of skin that covers and protects the glans penis
Loose and elastic, allowing for changes in penis size during an erection
Erectile Tissue
Fills with blood to make the penis rigid and erect for penetration
Prostate
The gland in males that controls the release of urine and secretes a part of semen that enhances motility and fertility of sperm
Vas Deferens (Sperm Duct)
Long, muscular tube that transports mature sperm to the urethra in preparation for ejaculation
Cowper's Gland
Two pea-sized glands located on either side of the uretha that secretes a lubrication fluid
Flagellum
Sperm tail
Functions of the Male Reproductive System
Produce, maintain and transport sperm and semen
Discharge sperm into the female reproductive tract
They produce and secrete male sex hormones
Zygote
The fertilized egg
Enters a 2-week period of rapid cell division and develops into an embryo
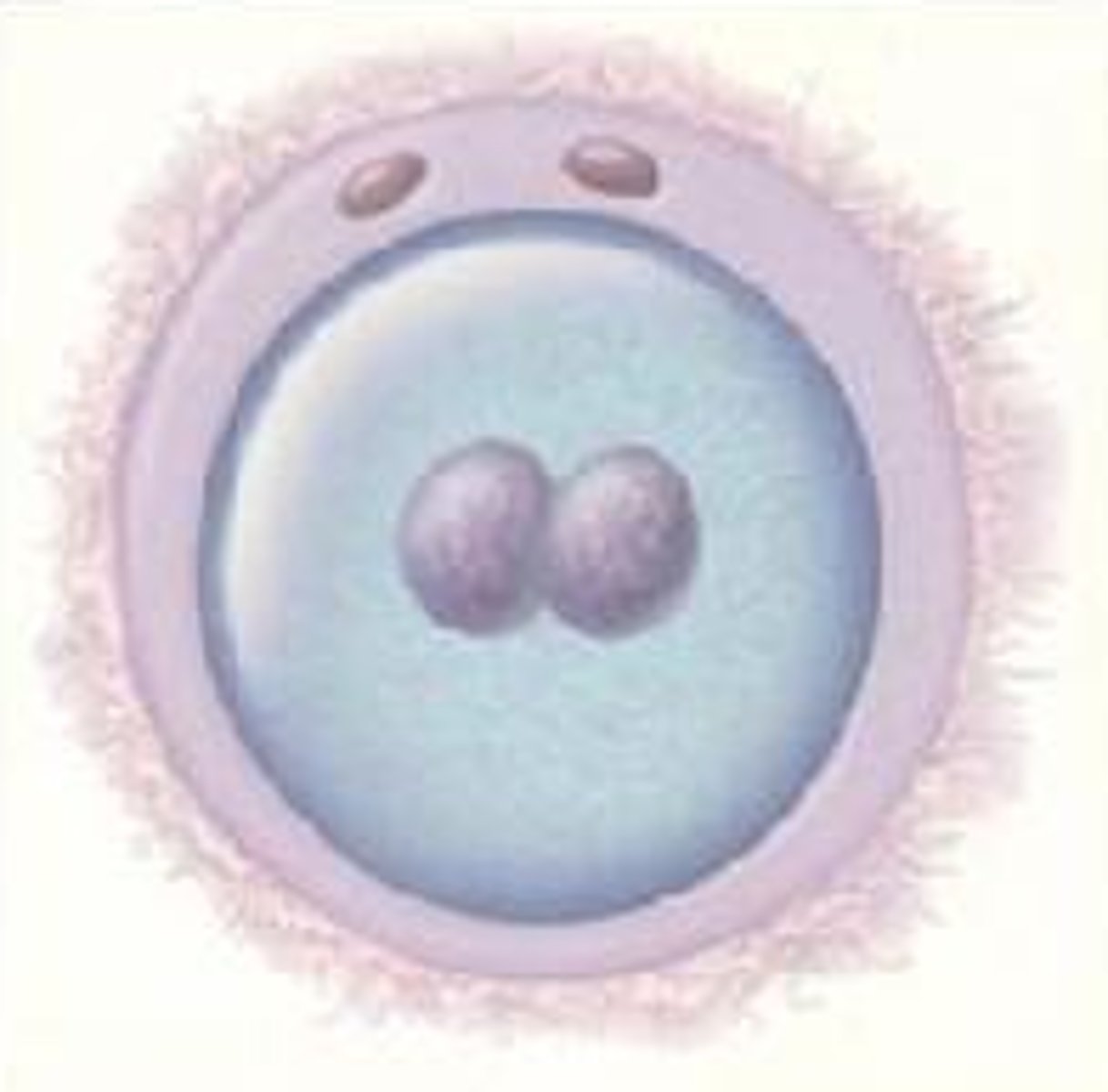
Embryo
the developing human organism from about 2 weeks after fertilization through the second month
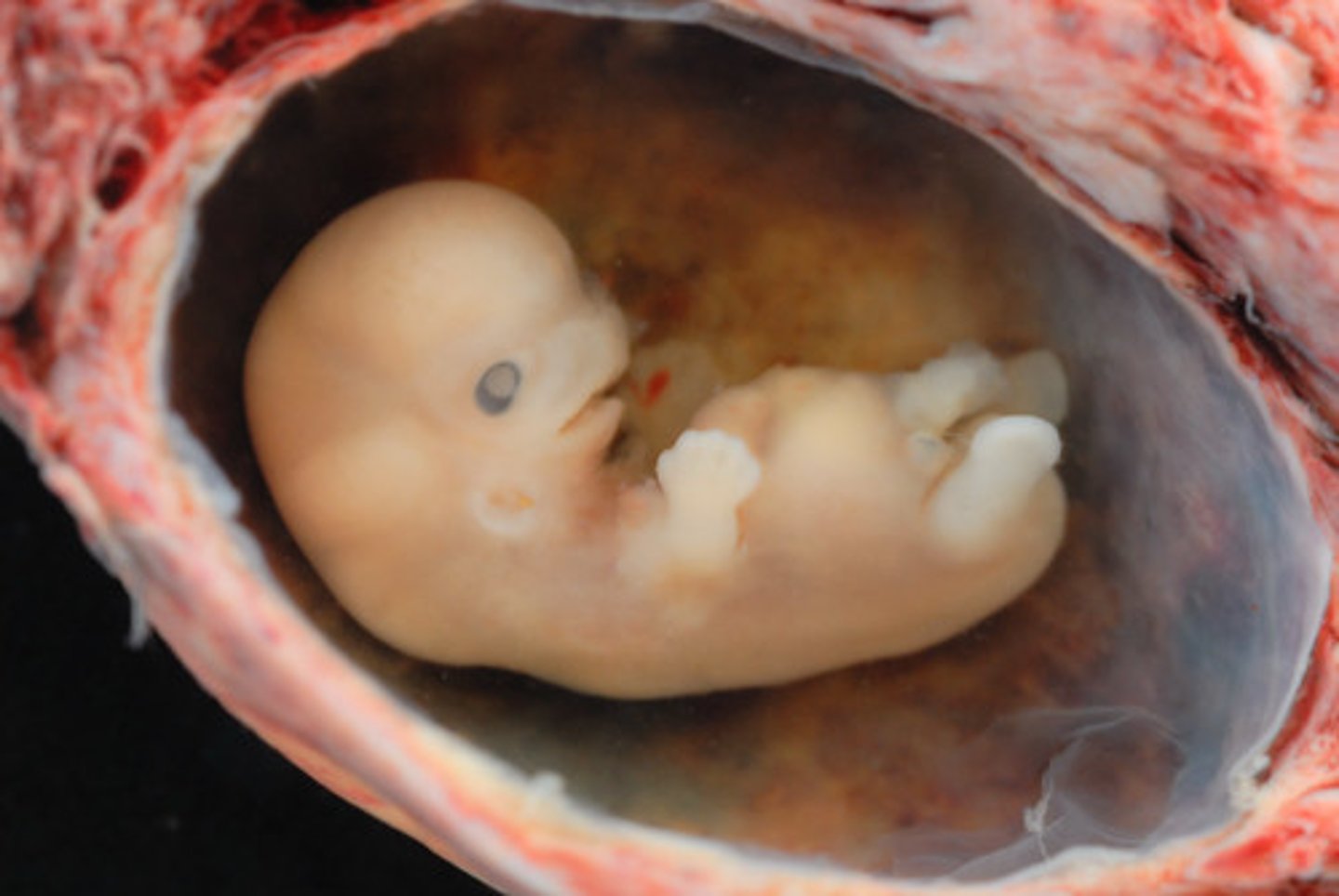
Foetus
Unborn baby
Usually around 8 weeks from conception
Cilia
The hairlike projections on the outside of cells that move in a wavelike manner
Helps move the ova
Cervix
The lower part of the uterus
Connects the vagina to the main body of the uterus
Seminal Vesicles
Sac-like pouches that attach to the vas deferens near the base of the bladder
It produces the fluid that sperm swims in