7 Cranial Cruciate Ligament Injury/Disease I
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Cruciate Meniscal Syndrome
What condition of the stifle is one of the most important contributors to arthritis in animals?
Cranial cruciate ligament injuries
What is the MOST COMMON canine orthopedic condition?
Cruciate instability
What is the MAJOR cause of DJD (degenerative joint disease) in the canine stifle?
Human ACL: TRAUMA is the most common cause
CCLD dogs: SLOW DEGENERATIVE process, not a result of sudden trauma to a healthy ligament
What is the difference in pathophysiology between human ACL rupture and canine CCLD (cranial cruciate ligament disease)?
Female and neutered dogs at greater risk (because sex hormones are important for development, and if neutered before 2 y.o. may increase incidence). Can affect dogs of all sizes/ages/breeds. UNCOMMON in cats.
List the factors that influence CCLD (cranial cruciate ligament disease) in animals:
1. Over 50% of dogs with cruciate ligament problems in one knee develop similar problems IN THE OTHER KNEE
2. Partial tearing of the CCL is common and typically progresses to a full tear
Name two important features of Canine CCLD:
1. Rottweilers
2. Newfoundland
3. Staffordshire Terrier
4. Mastiff
5. Akita
6. Saint Bernard
7. Chesapeake Bay Retriever
8. Labrador Retriever
All breeds of dogs can be affected by CCLD. What breeds have a HIGHER INCIDENCE?
1. Greyhound
2. Dachshund
3. Basset Hound
4. Old English Sheepdog
All breeds of dogs can be affected by CCLD. What breeds of dogs have a LOWER INCIDENCE?
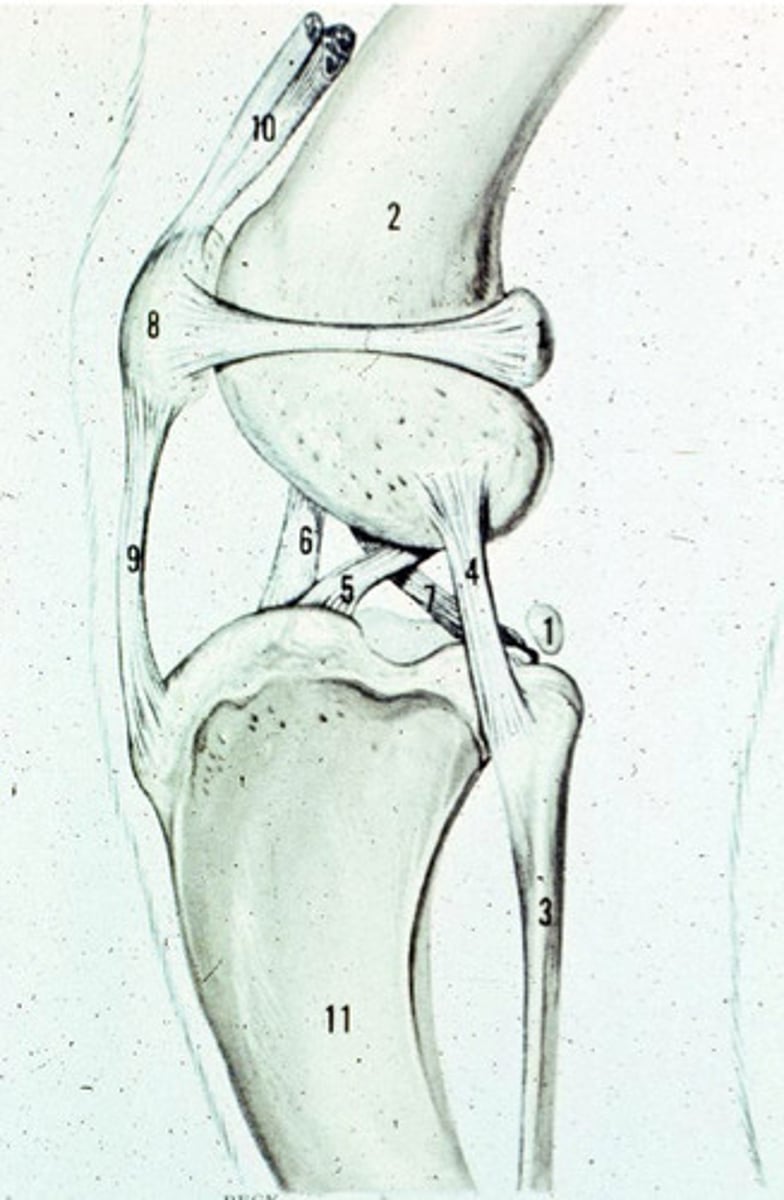
Cranial tibial ligament of the lateral meniscus
What is 1?
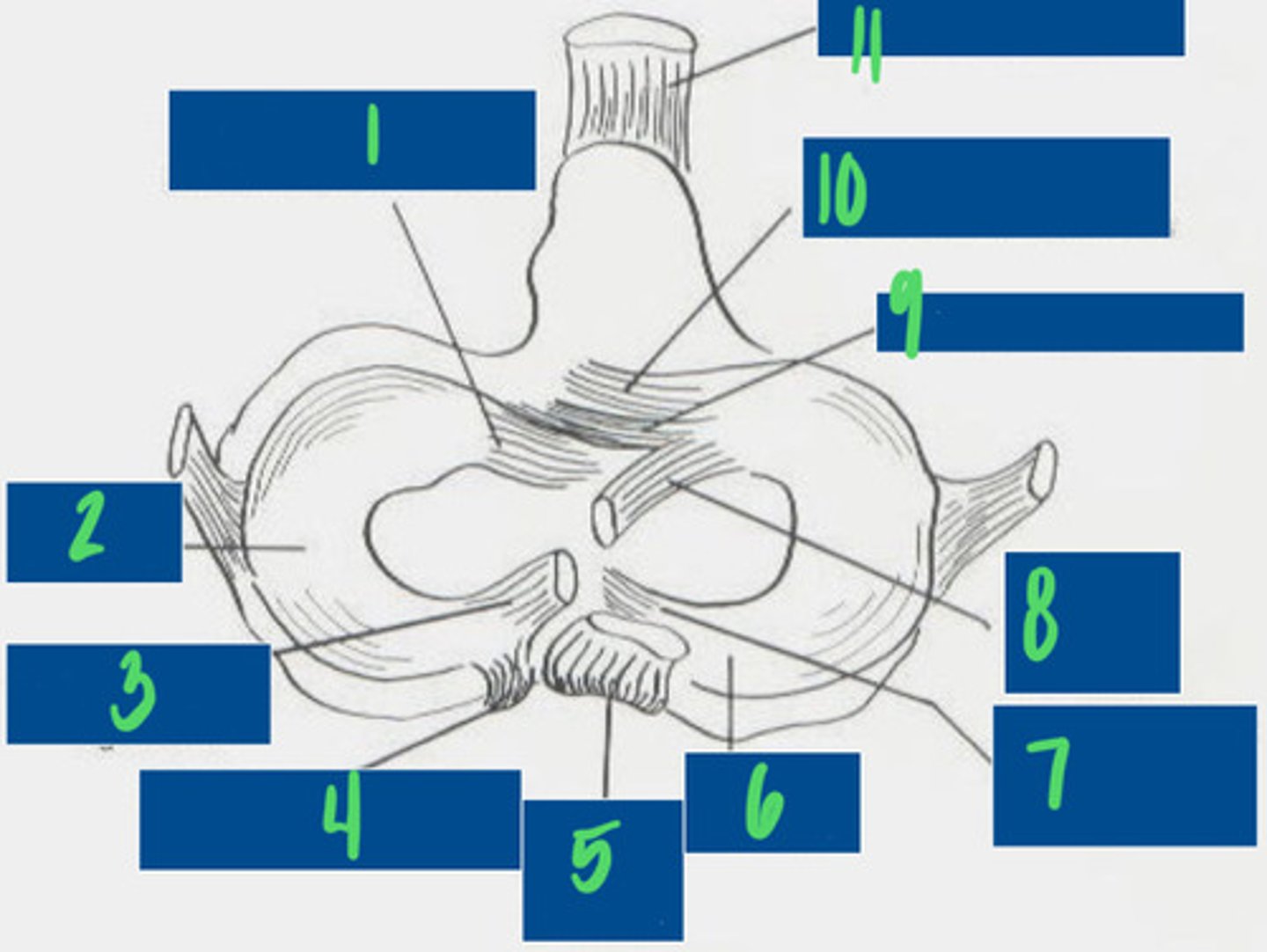
Lateral Meniscus
What is 2?
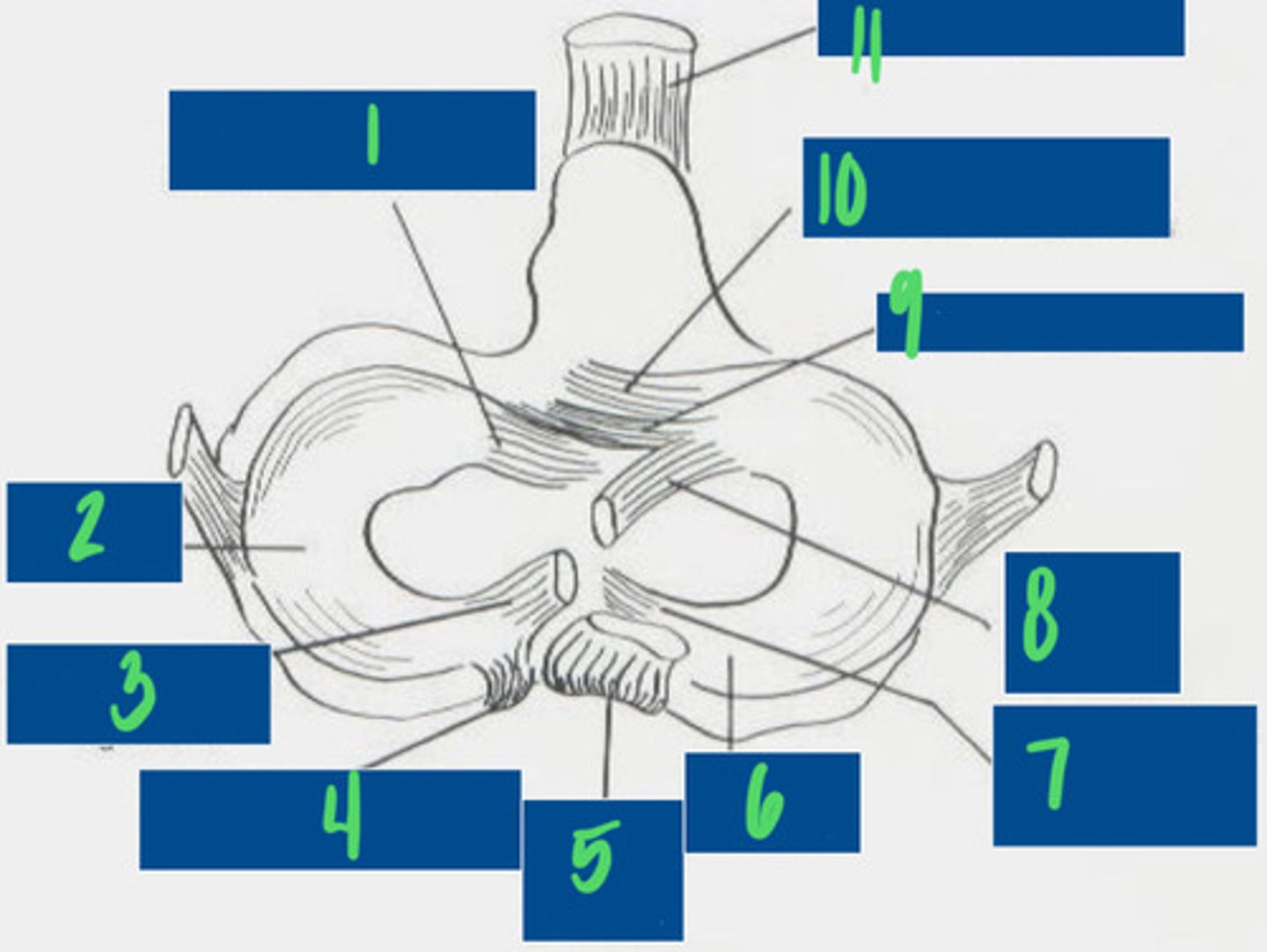
Meniscofemoral ligament
What is 3?
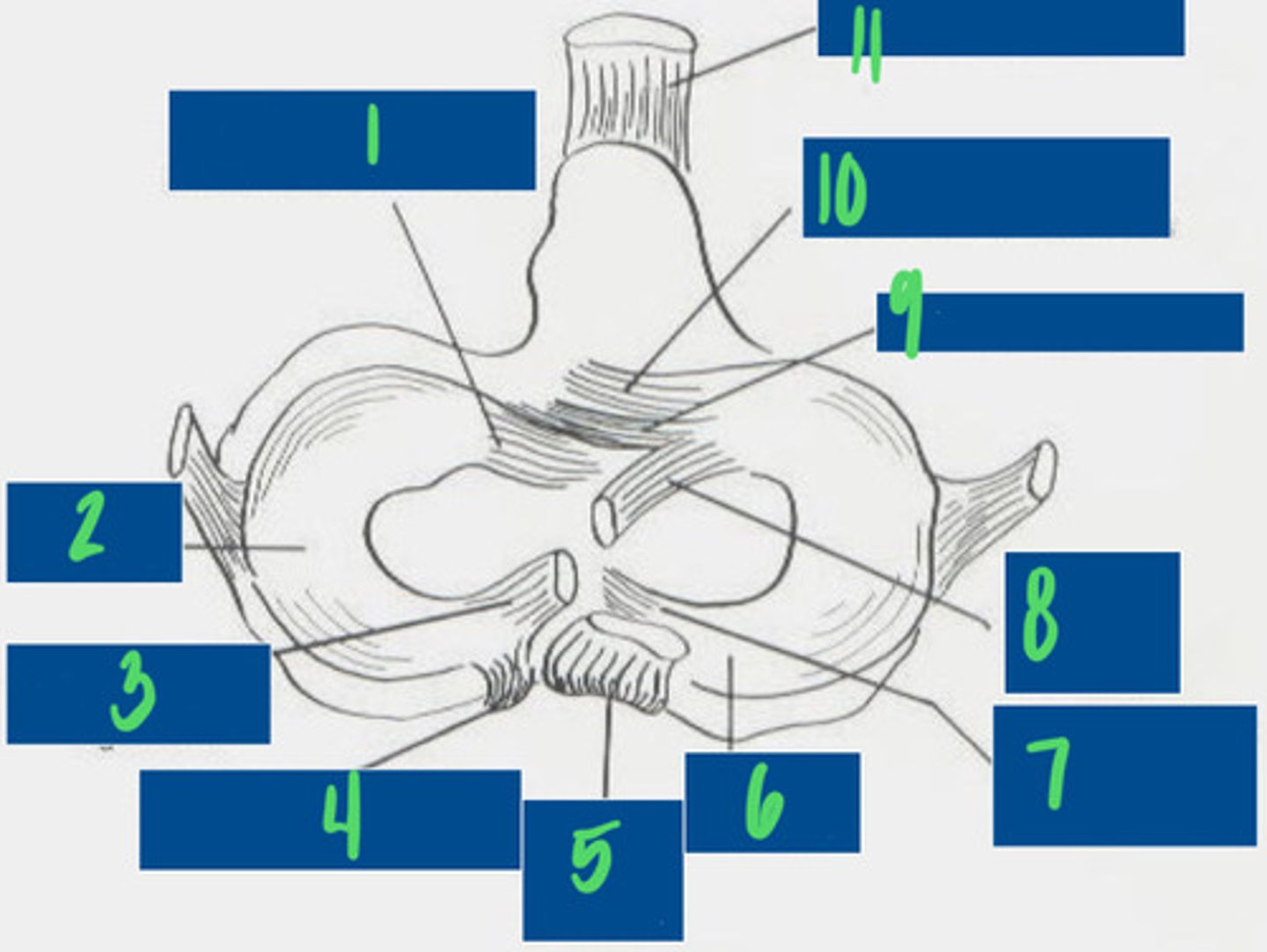
Caudal ligament of the lateral meniscus
What is 4?
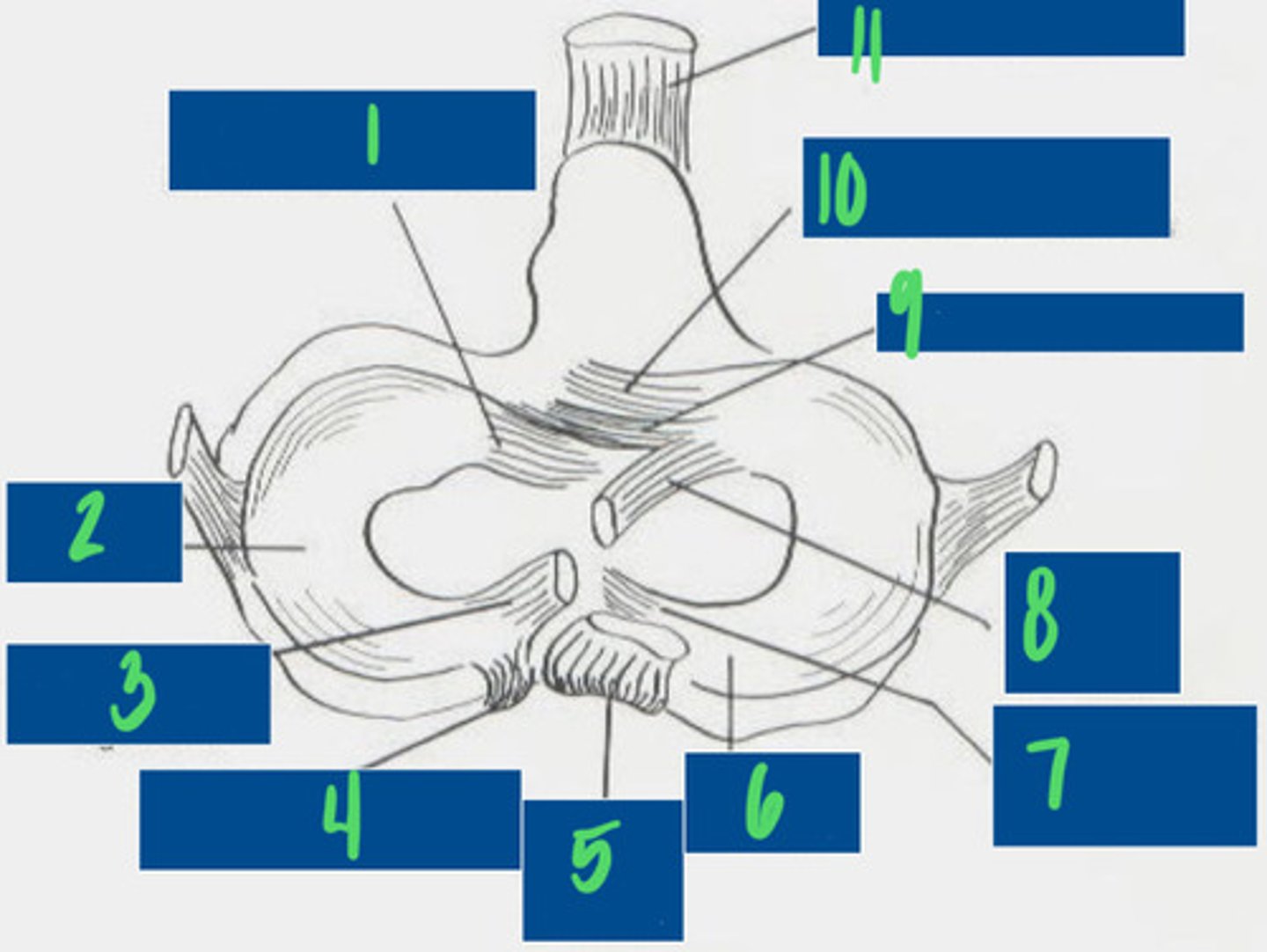
Caudal cruciate ligament
What is 5?
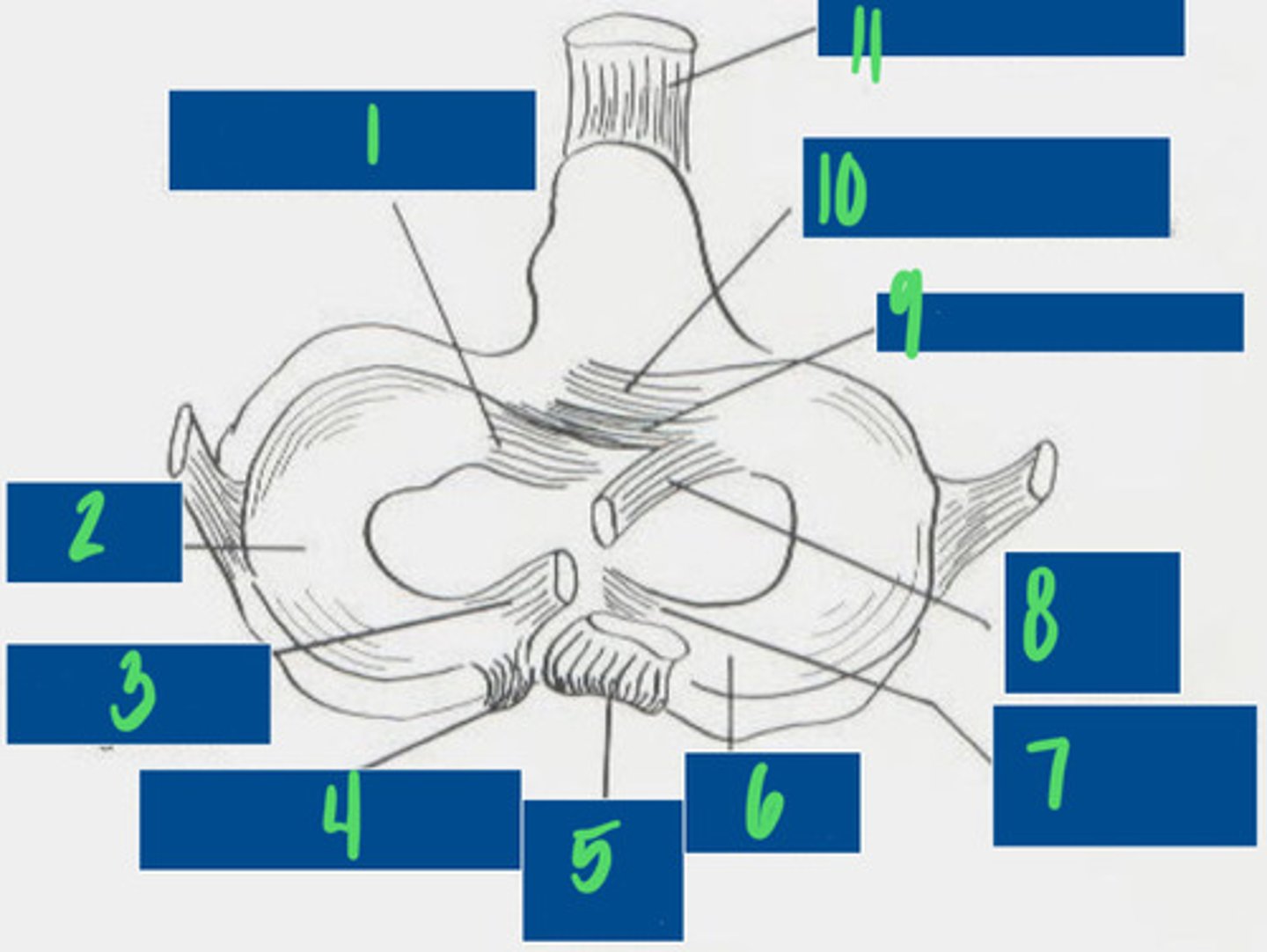
Medial meniscus
What is 6?
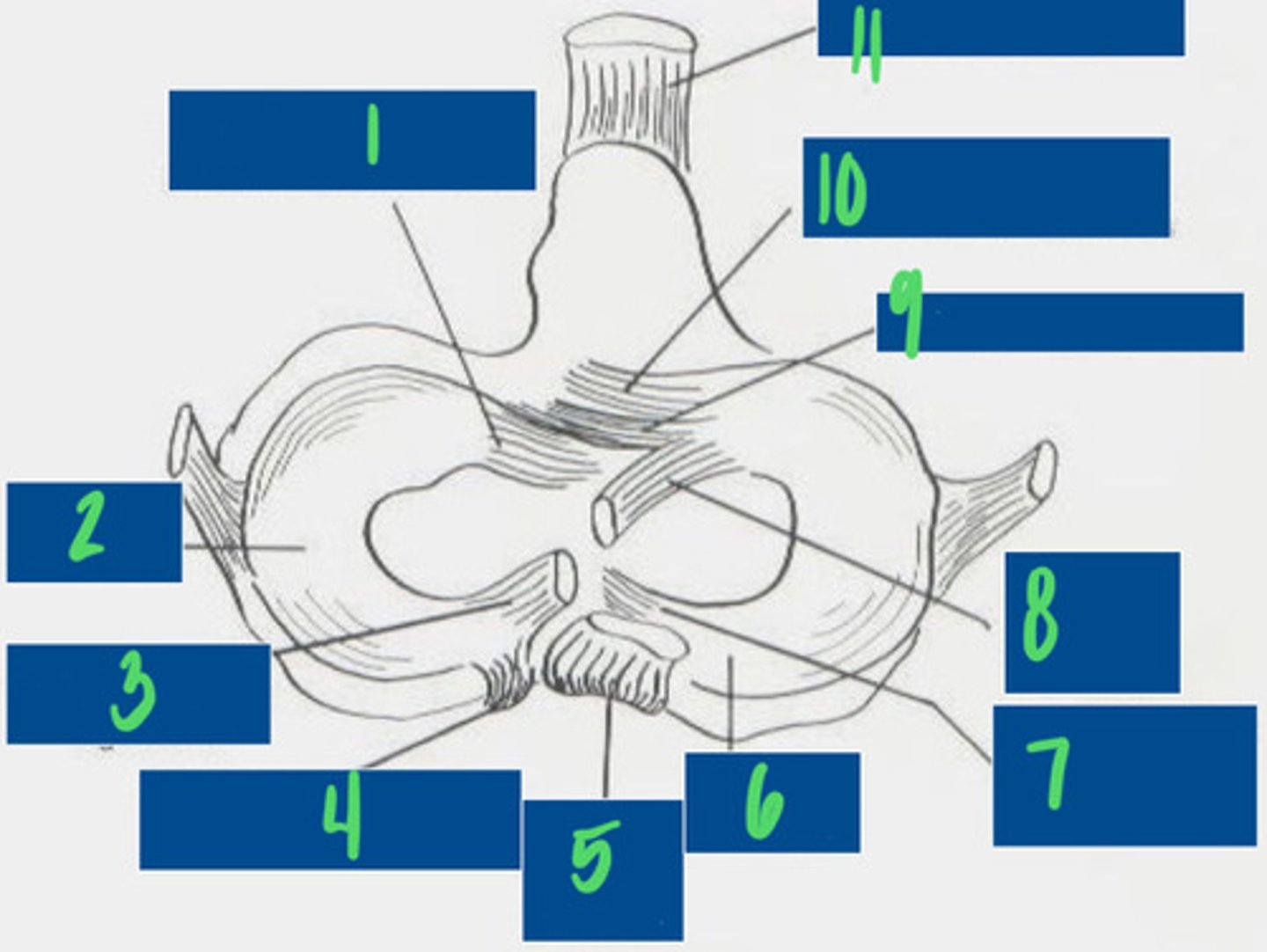
Caudal ligament of the medial meniscus
What is 7?
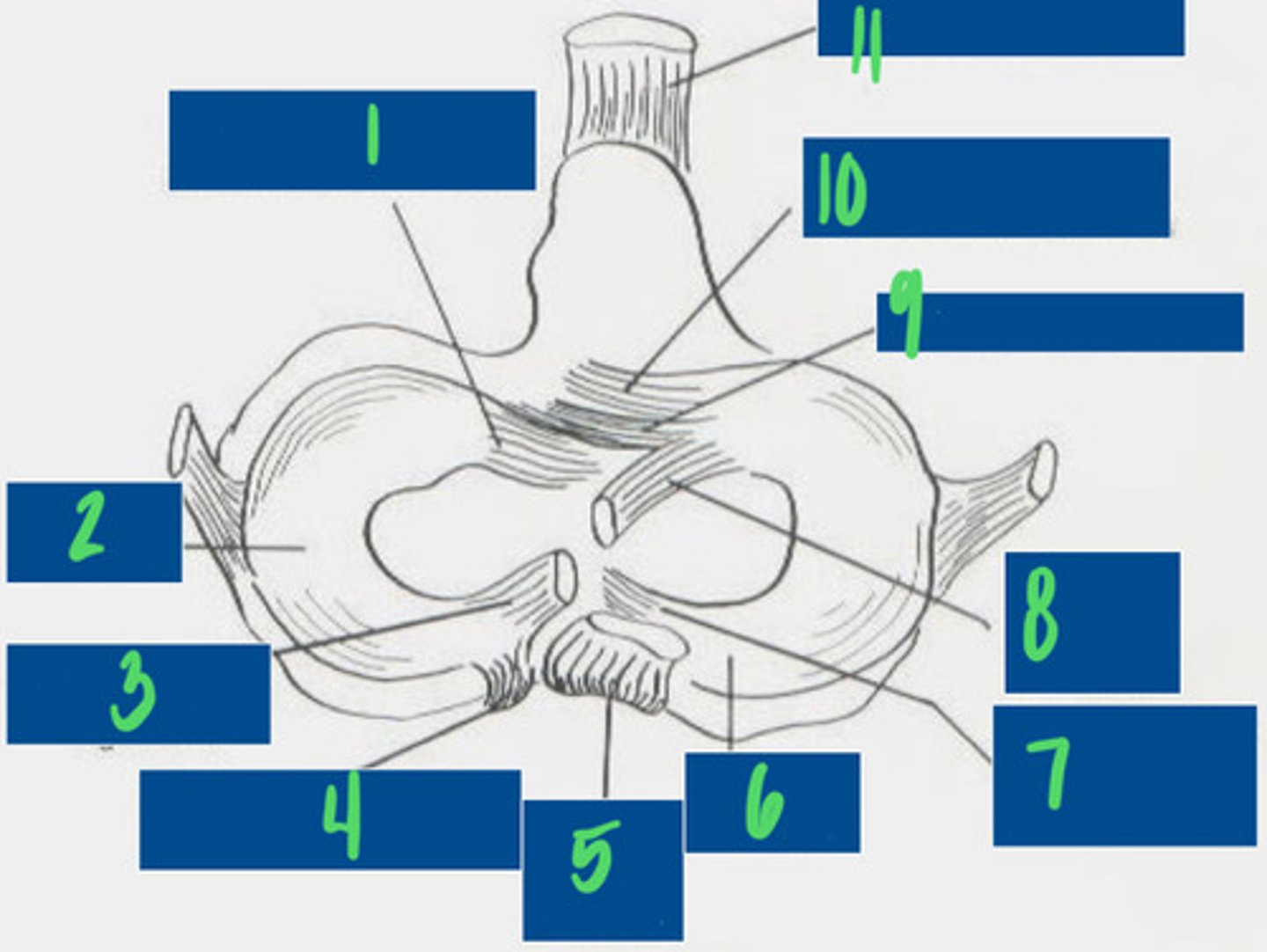
Cranial cruciate ligament
What is 8?
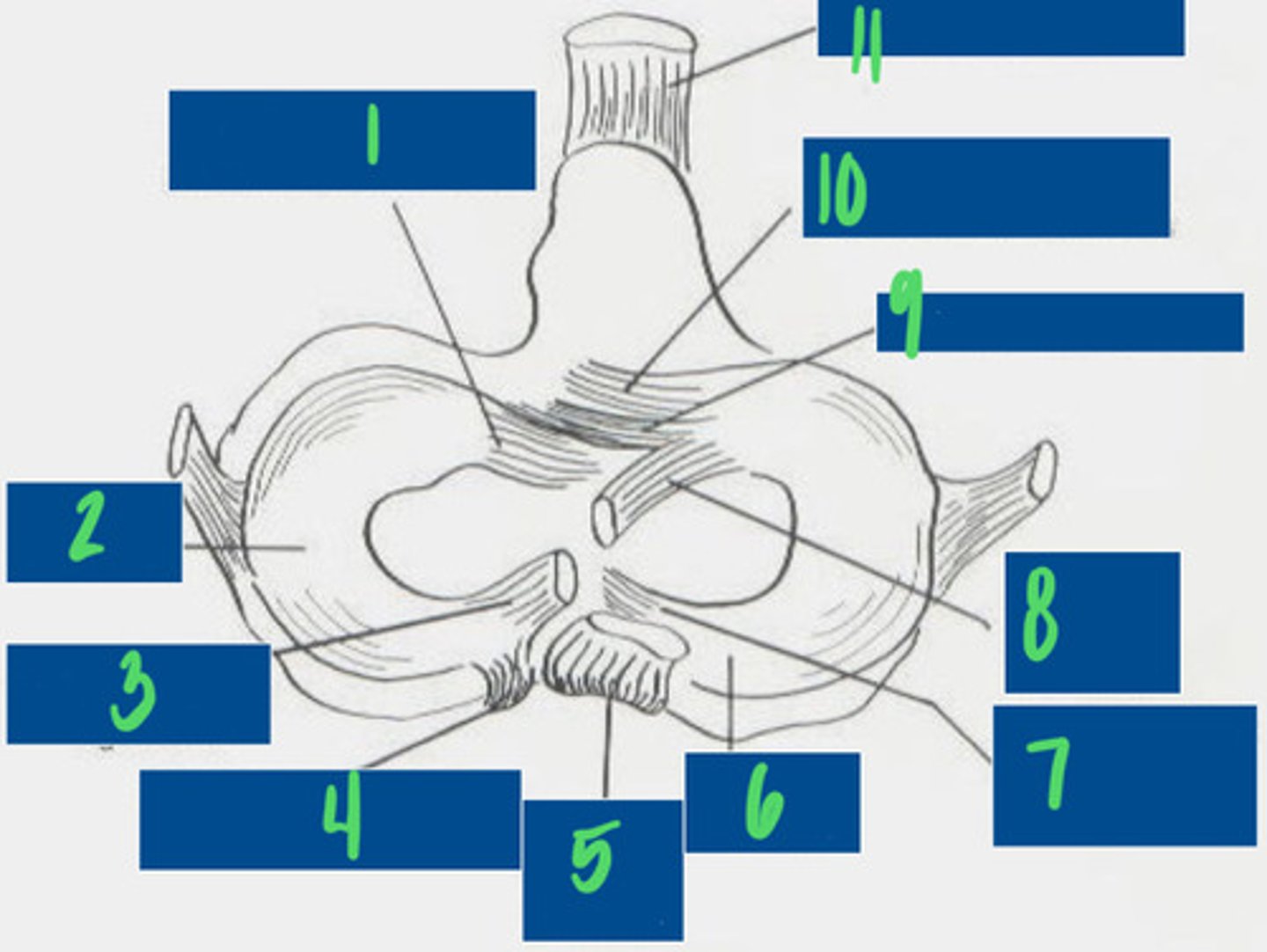
Transverse ligament
What is 9?
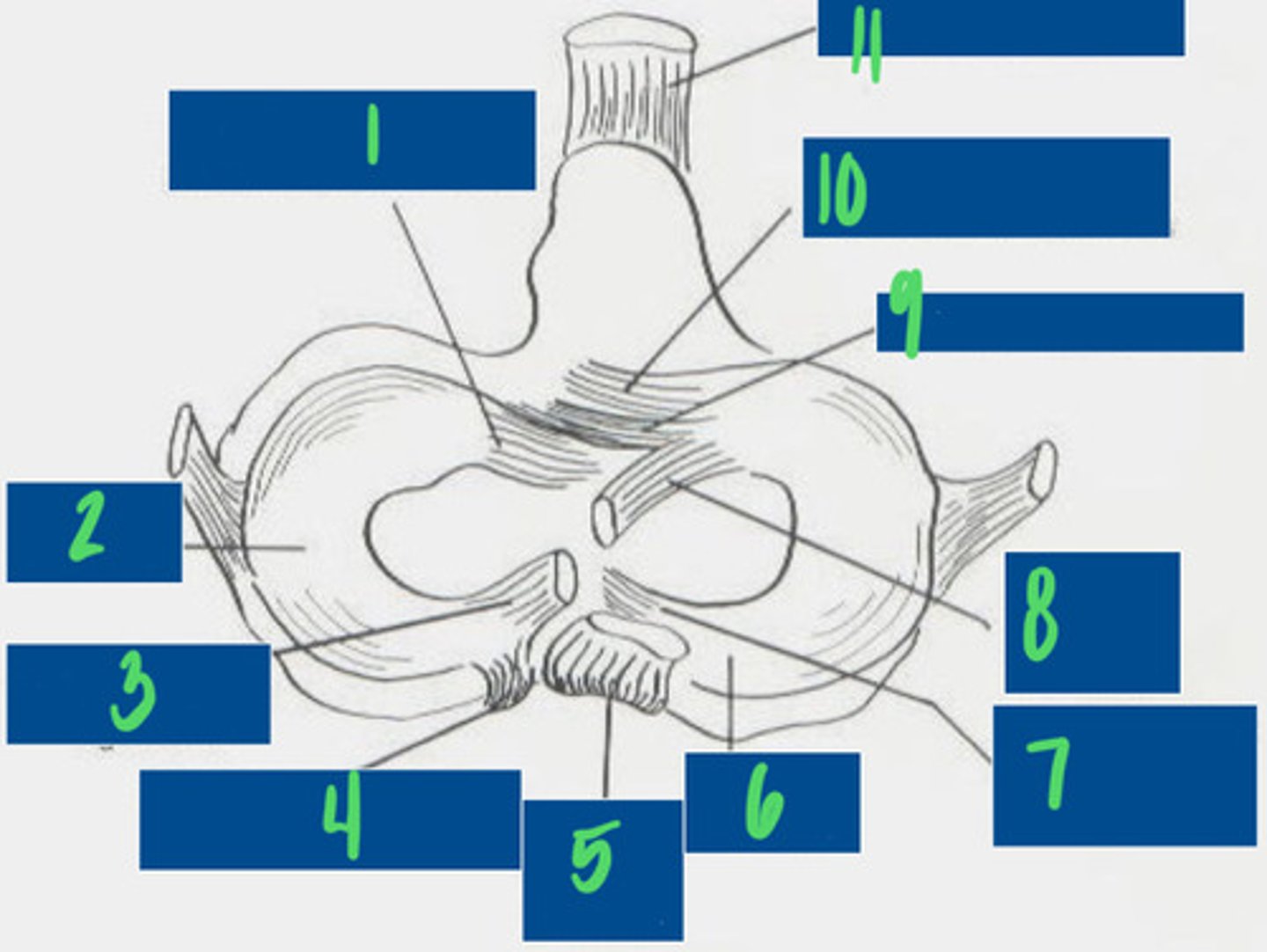
Cranial tibial ligament of the medial meniscus
What is 10?
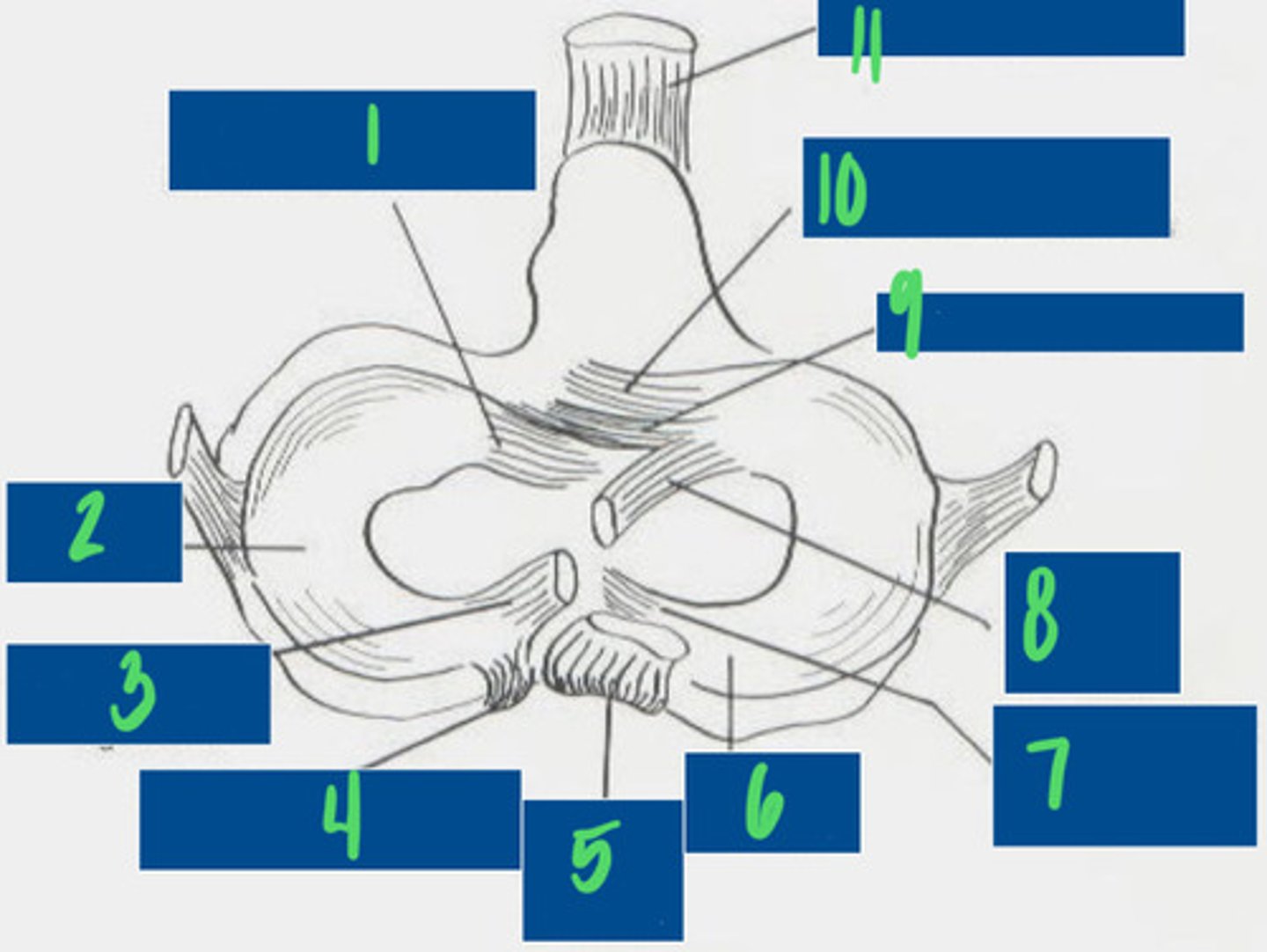
Patellar ligament
What is 11?
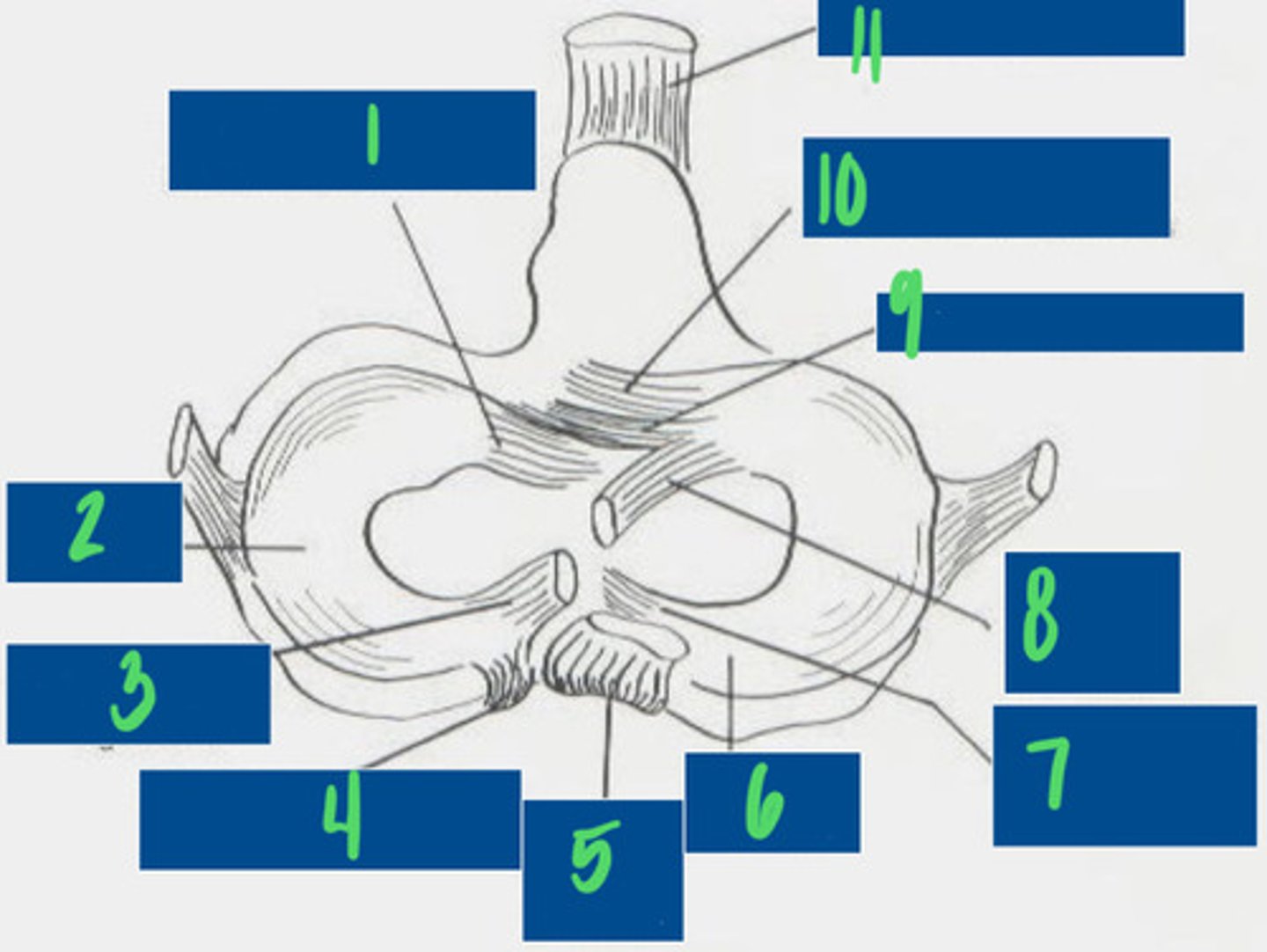
Cranial Cruciate ligament
What is 5?
Caudal Cruciate ligament
What is 7?
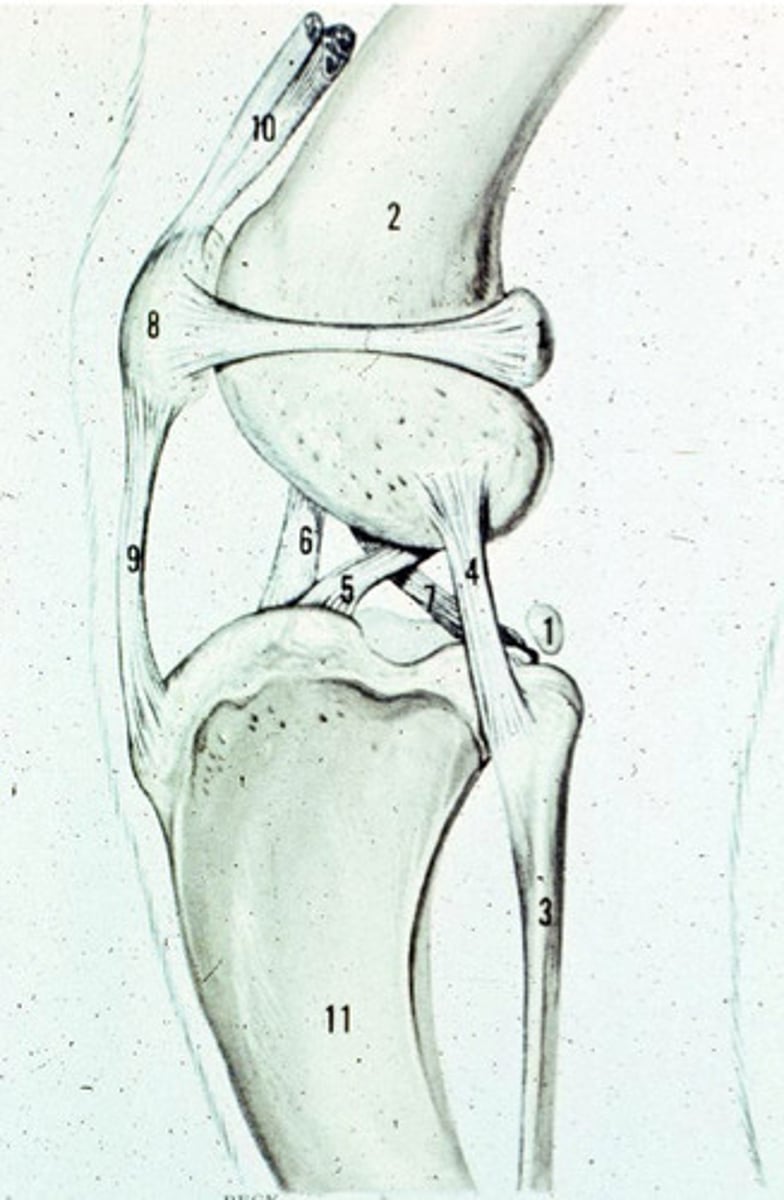
For where they attach to the tibia
How do you name the cranial and caudal cruciate ligaments?
Limit medial and lateral movements of the tibia
What is the purpose of the medial and lateral collateral ligaments of the stifle?
1. restrains CRANIAL translation of tibia on femur
2. retrains HYPEREXTENSION of stifle
3. limits INTERNAL ROTATION of tibia on femur
4. limits valgus and varus motion in flexed joint
What are the functions of the cranial cruciate ligament?
1. restrains CAUDAL translation of tibia on femur
2. restrains HYPEREXTENSION of stifle joint
3. limits INTERNAL ROTATION of tibia on femur
4. limits varus and valgus motion in flexed joint
What are the functions of the caudal cruciate ligament?
Limits excessive internal rotation
During flexion, cruciate ligaments twist on each other and limit what kind of excessive movement?
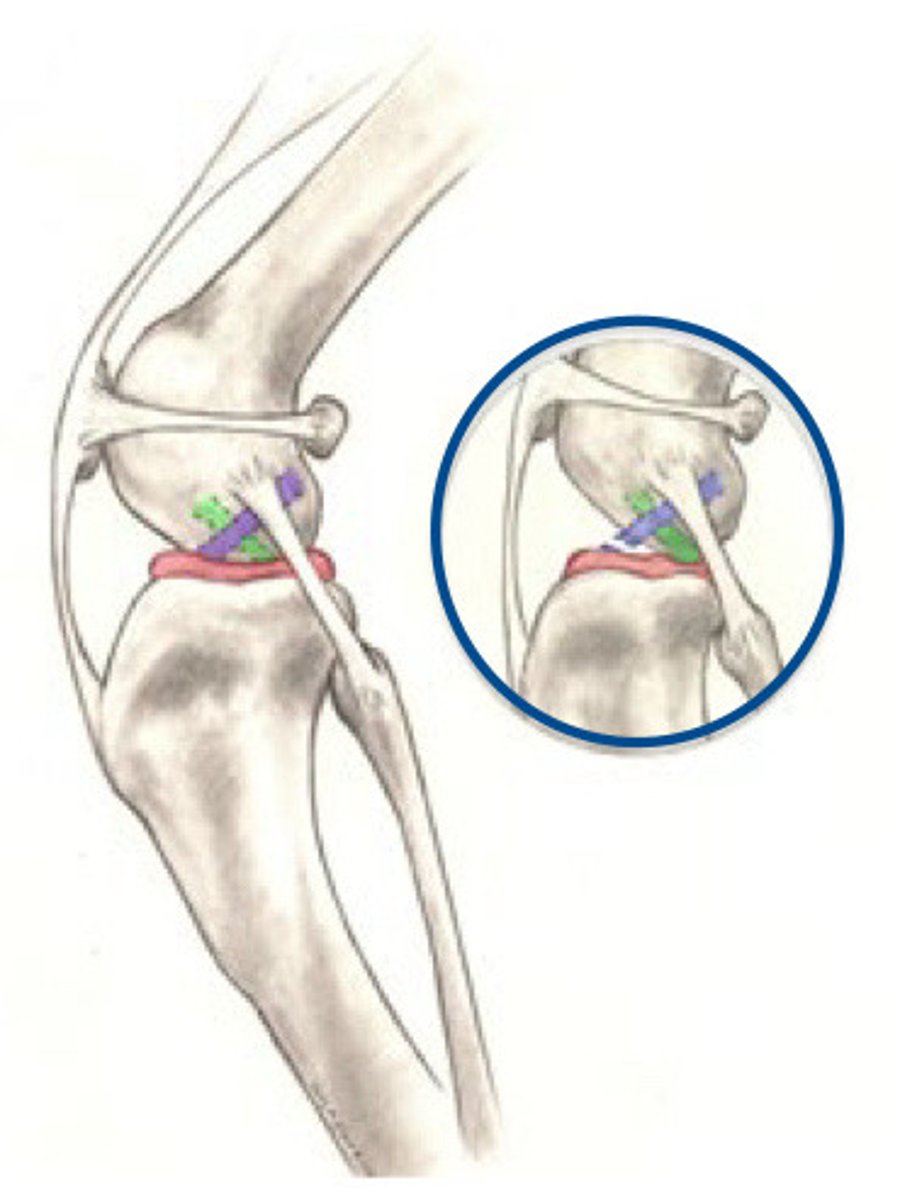
Cranial Cruciate Ligament
What is purple?
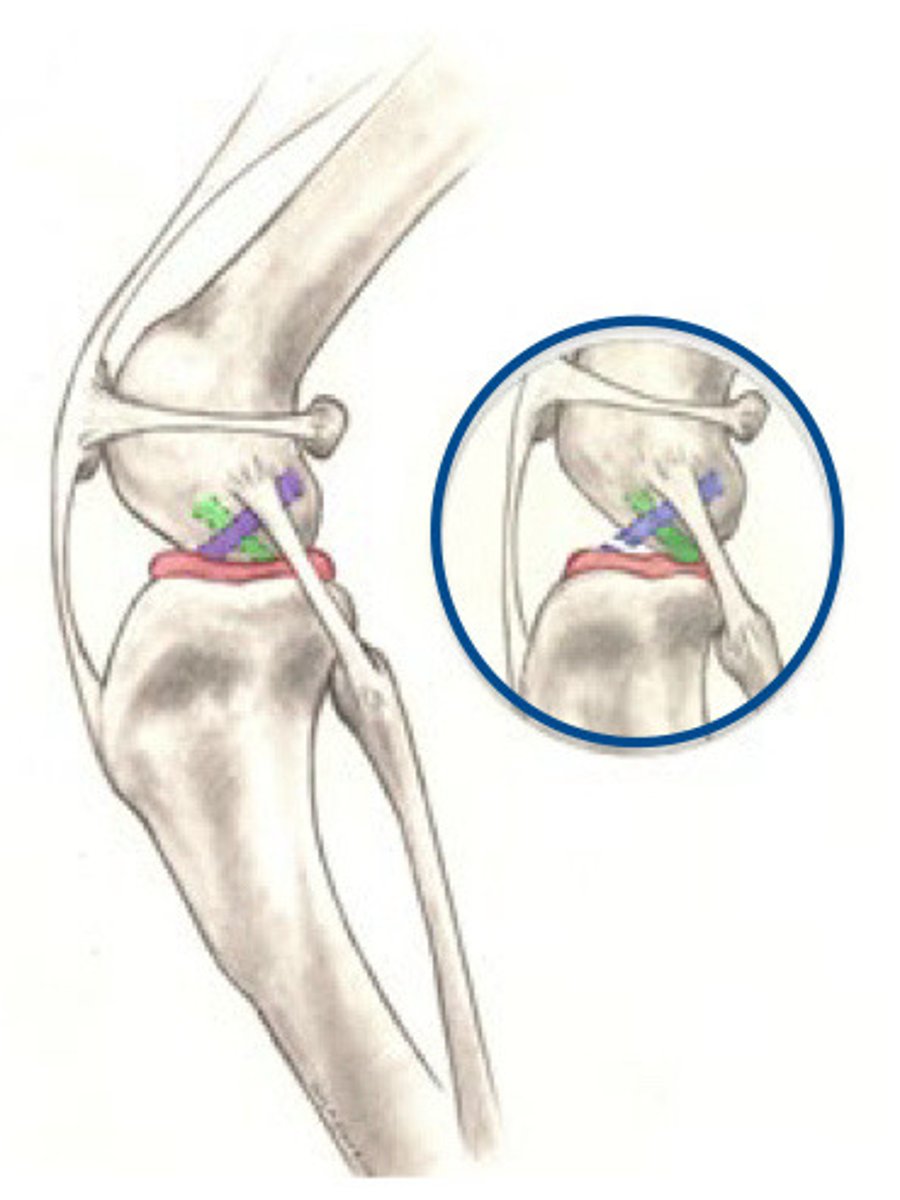
Meniscus
What is pink?
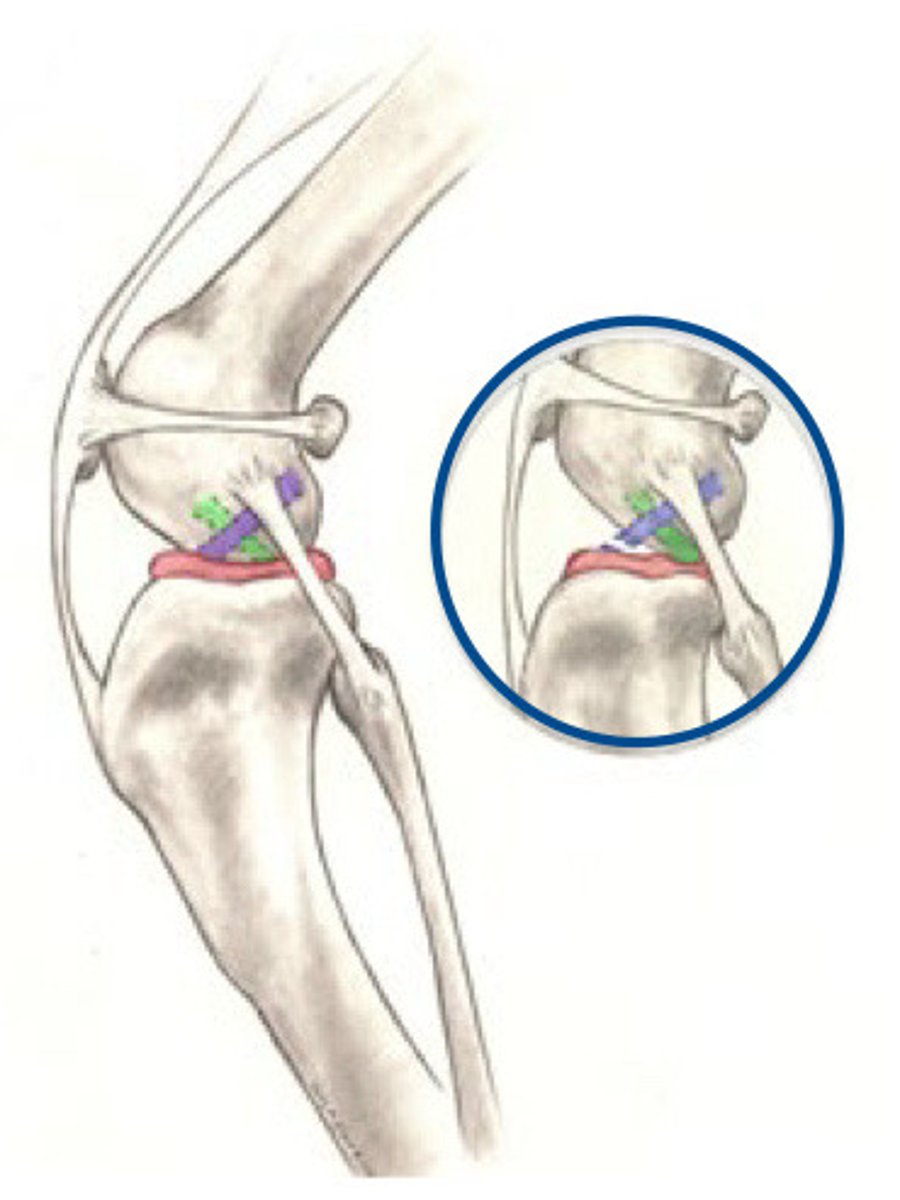
Caudal cruciate
What is Green?
A large angle puts greater cranial force on tibia at weight bearing, predisposing the animal for cranial cruciate rupture since the cranial cruciate ligament prevents cranial translation of the tibia
How is a larger tibial plateau angle a problem?
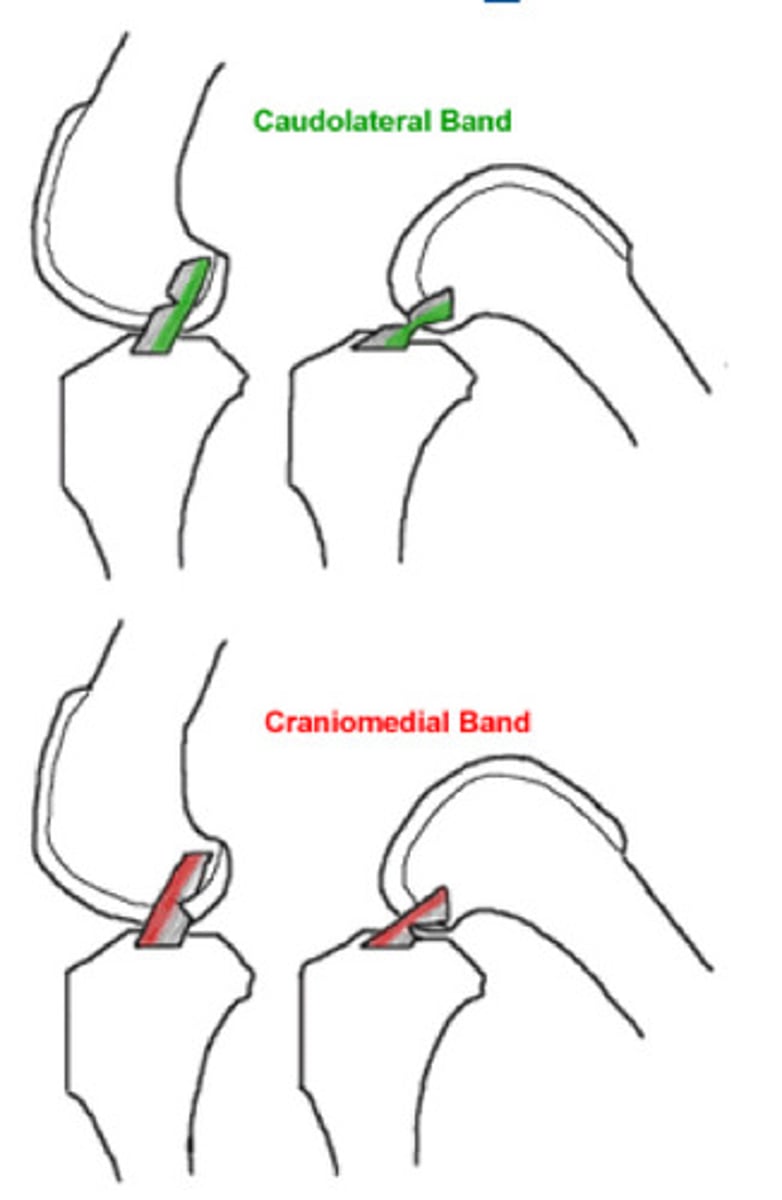
1. large CAUDAOLATERAL band
2. small CRANIAOMEDIAL band
What are the two components of the cranial cruciate ligament?
Caudolateral bundle of cranial cruciate ligament
What is 1a?
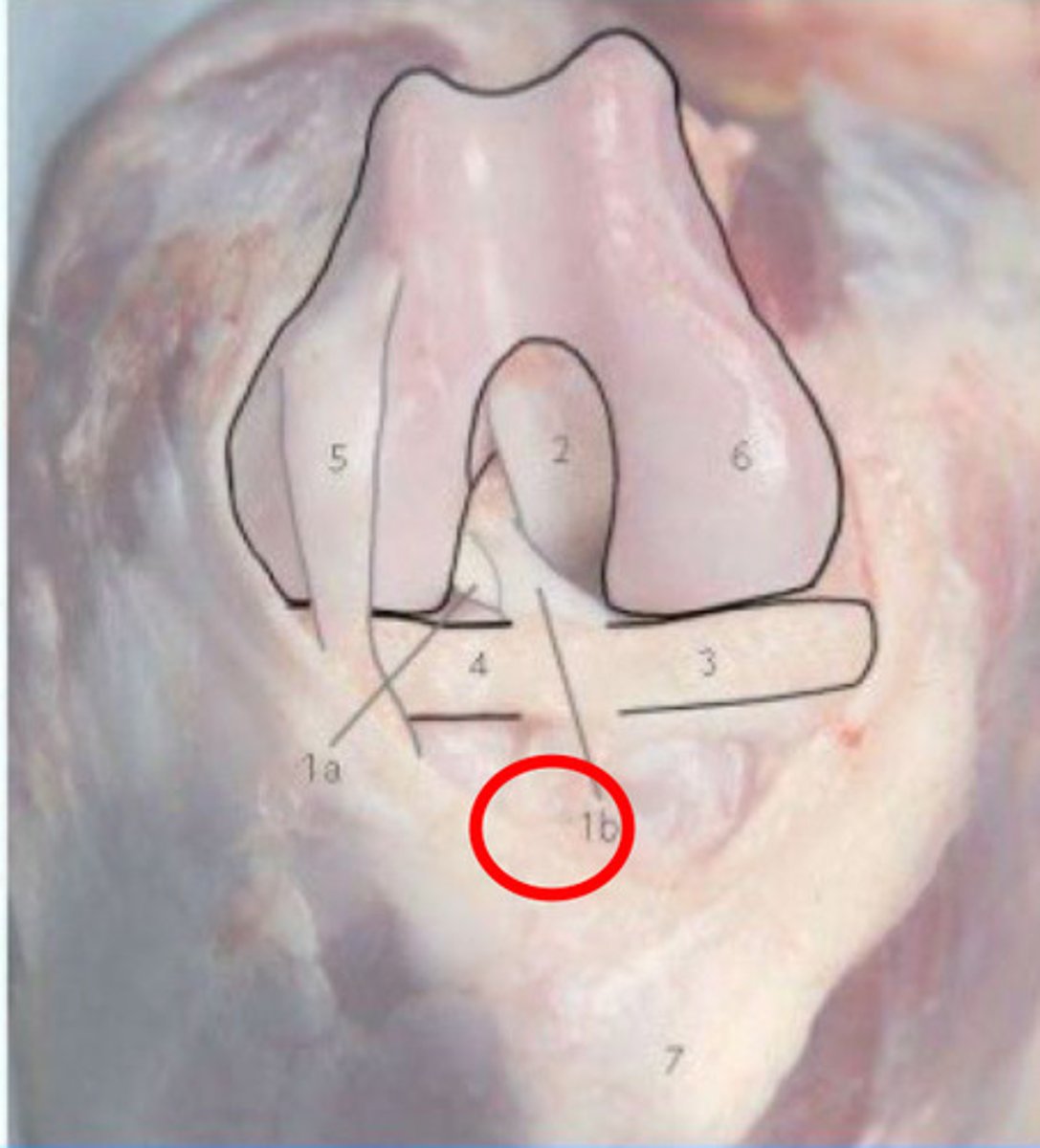
Craniomedial band of cranial cruciate ligament
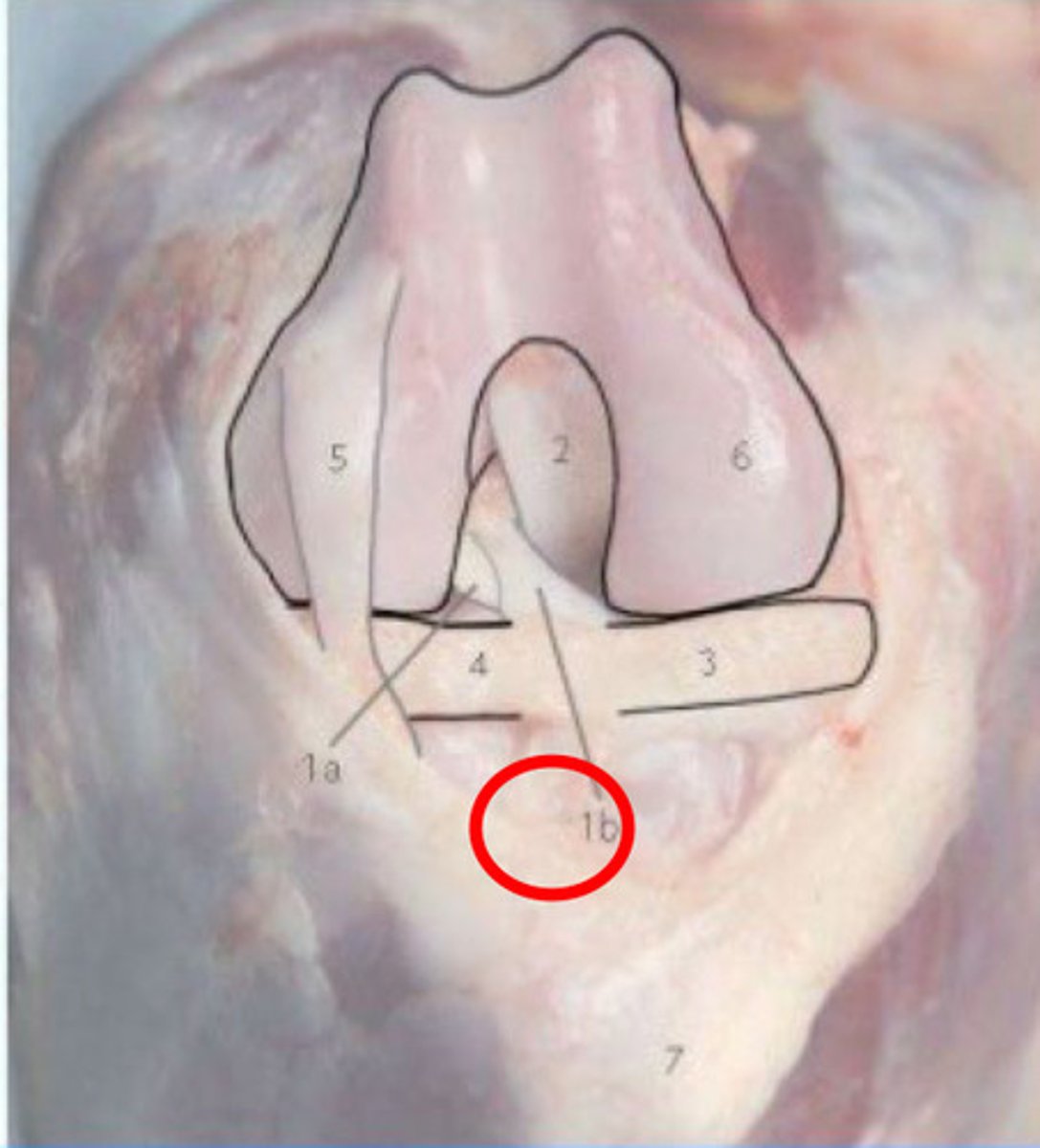
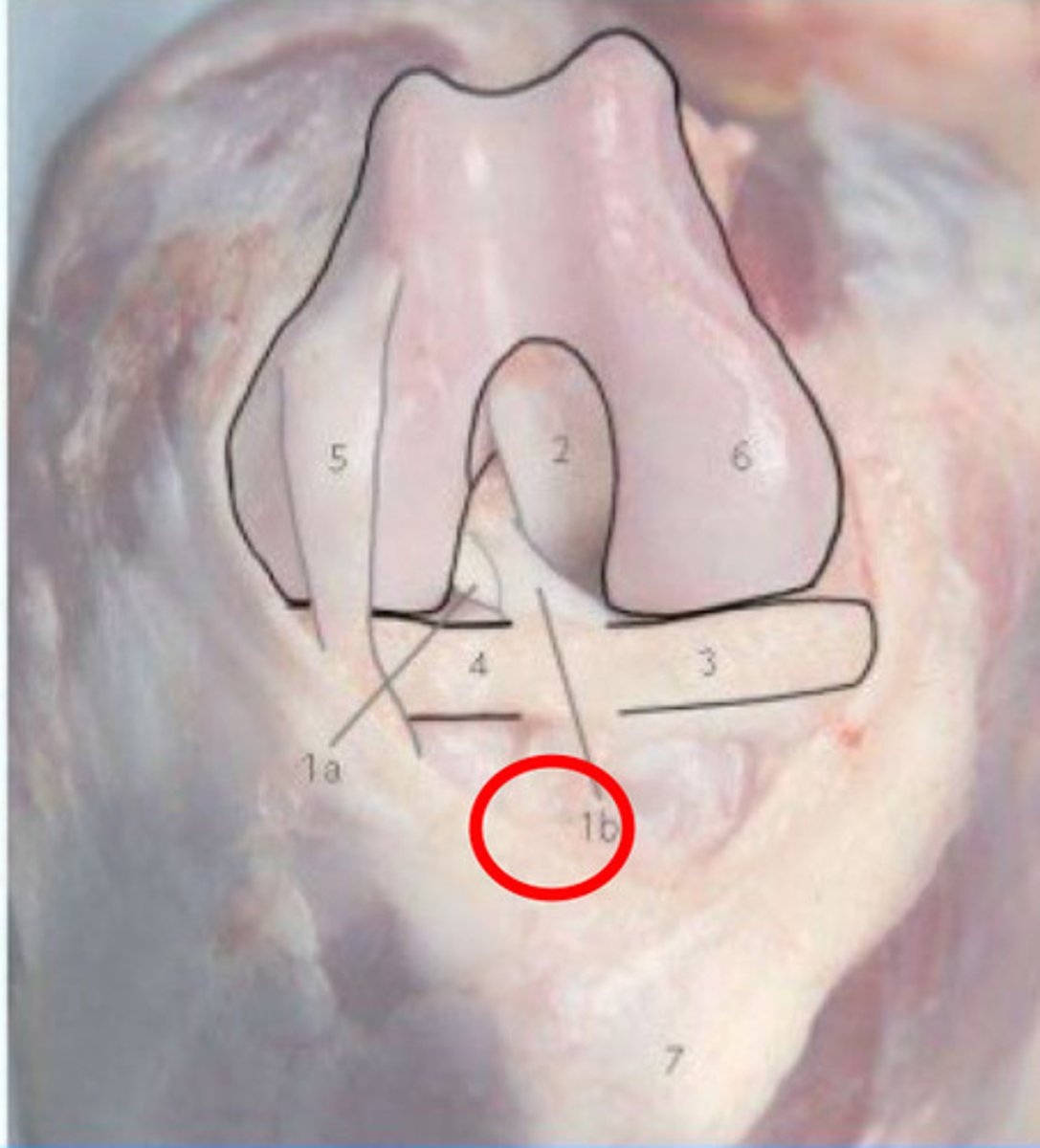
What is 1b?
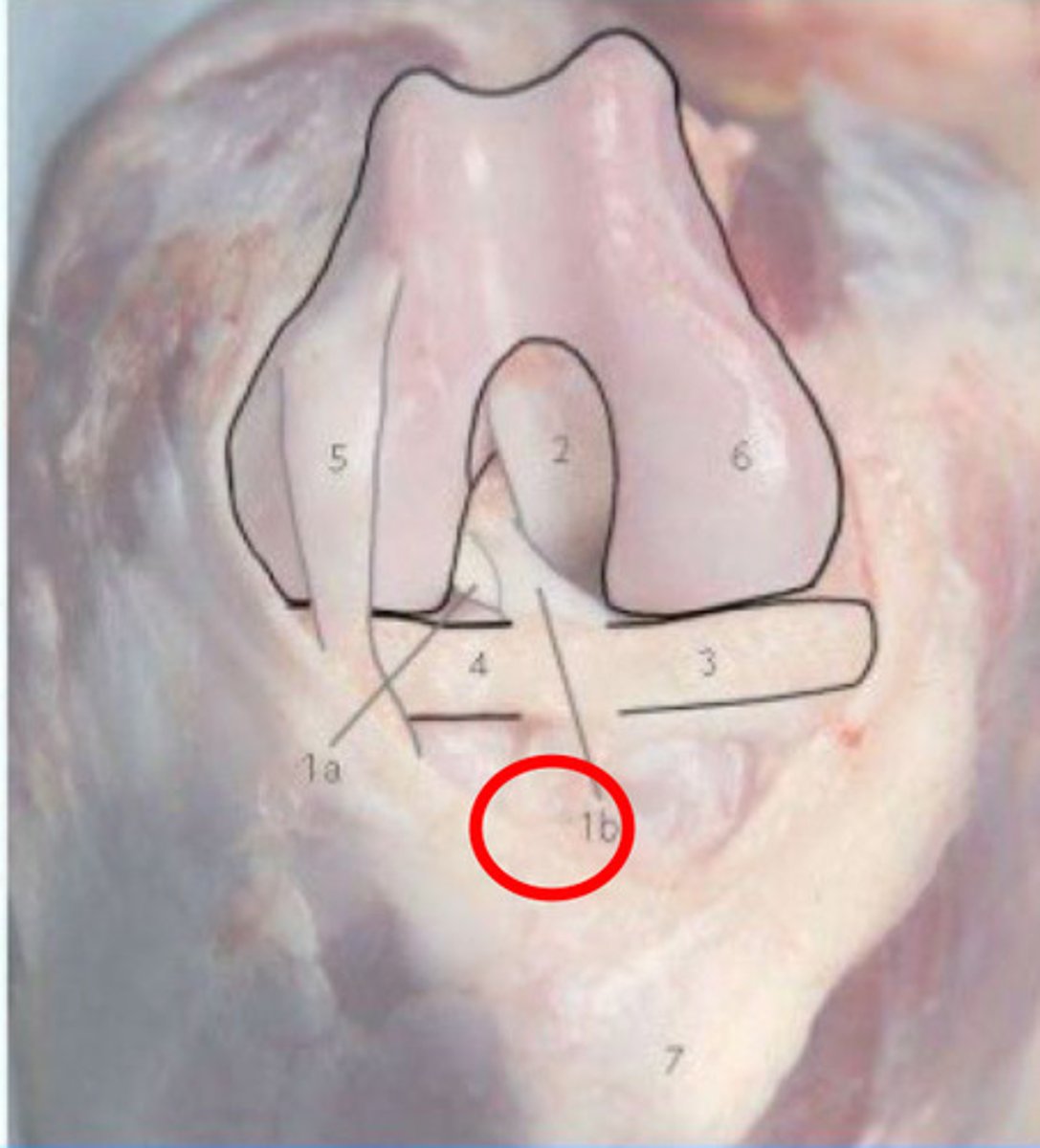
Caudal Cruciate Ligament
What is 2?
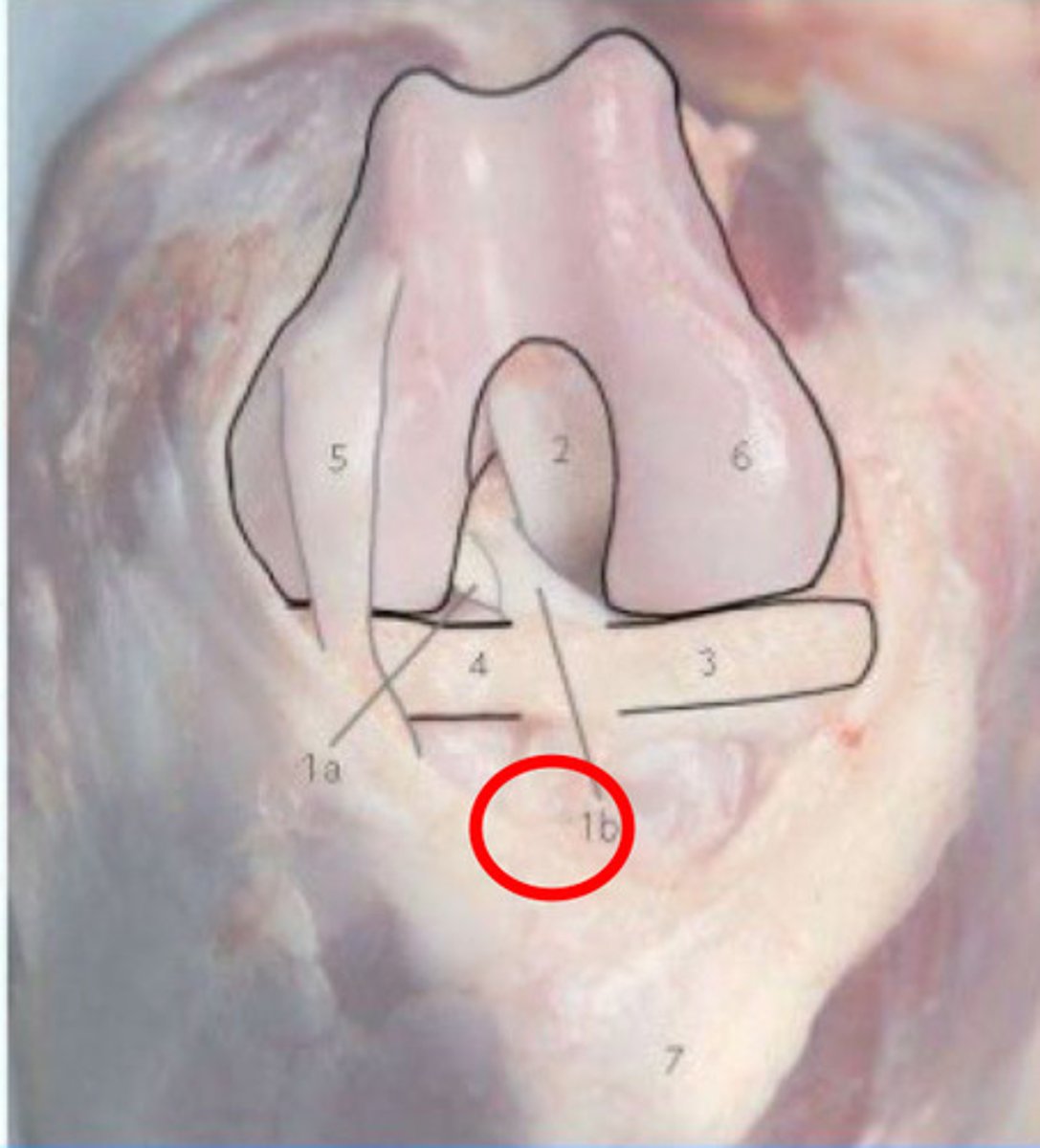
Medial Meniscus
What is 3?
Lateral meniscus
What is 4?
Long digital extensor tendon
What is 5?
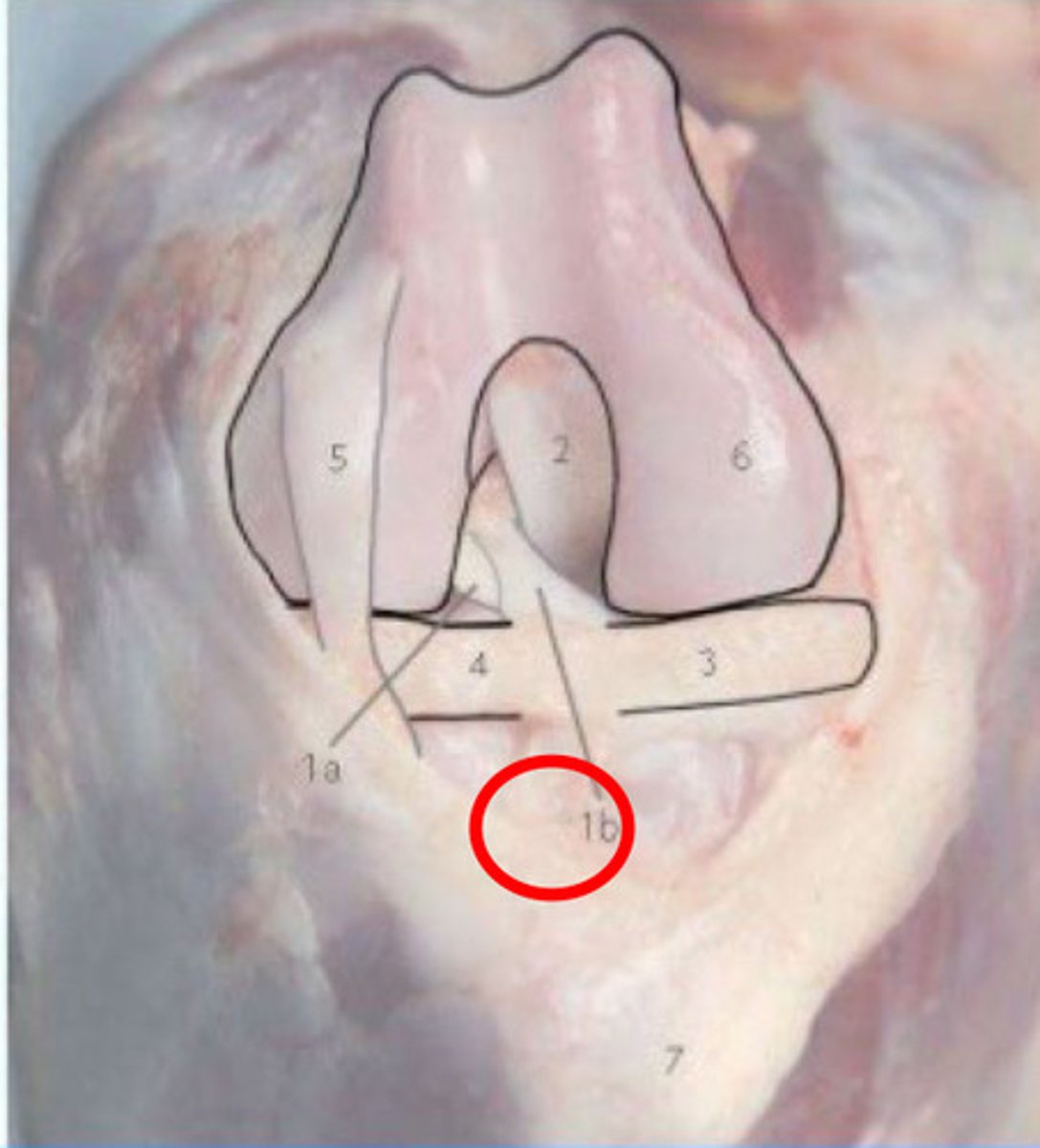
1. the caudolateral band is taut in extension and has laxity in flexion = alone, if ruptured = no drawer sign
2. the craniomedial band is taut in all phases of flexion and extension, and thus is more likely to rupture = will show drawer in flexion, but no drawer in extension
What is this telling you about cranial cruciate partial ruptures?
Arthroscopy
What is the most common thing to diagnose cranial cruciate partial ruptures?
Progressive DJD, loss of muscle mass, decreased limb use, and decreased performance
What is the result of stifle instability secondary to loss of integrity of the cranial cruciate ligament?
1. long term impairment due to osteoarthritis
2. tearing of meniscus
List the common complications of CCLD :
1. feel for medial buttress
2. drawer test
3. radiographs (MANDATORY) even though they do not show status of CCL or meniscus
4. tibial compression test (tibial thrust)
Name some things you can do to diagnose CCLD:
1. sit with legs to outside (not square)
2. popping "meniscal click" and pain on extension of stifle
3. medial buttress (palpable thickening of medial aspect of stifle)
4. non-weight bearing lame (when partially damaged ligament ruptures completely)
List some clinical signs associated with CCLD:

Medial
When there is CCLD, there is commonly tearing of the meniscus. Which one?
Partial meniscectomy
If there is meniscal damage in dogs as a complication of CCLD, you often have to excise damaged parts of the meniscus. What is this called?
Cranial drawer test. A negative doesn't rule out CCL tear due to periarticular fibrosis or meniscal entrapment stopping the "drawer" even if the tear is present
What is this? What can be the problem with a negative test?
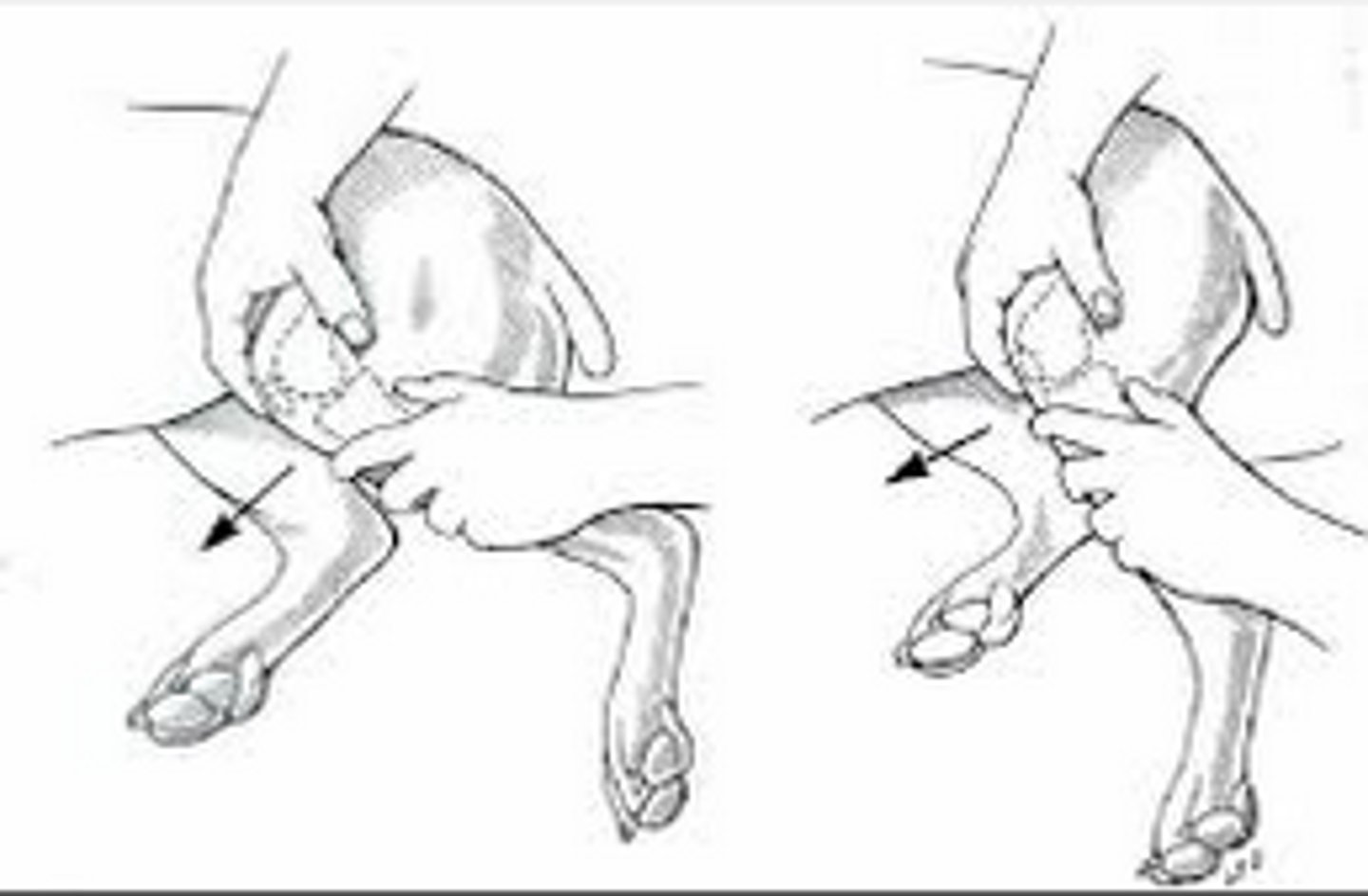
Index finger over patella
Indexfinger TIP on tibial tubercle
Other hand on manus pushing up
Name the landmarks for a tibial compression test
1. patella
2. lateral fabella
3. tibial tuberosity (tubercle)
4. fibular head
Name the landmarks for a cranial drawer test:
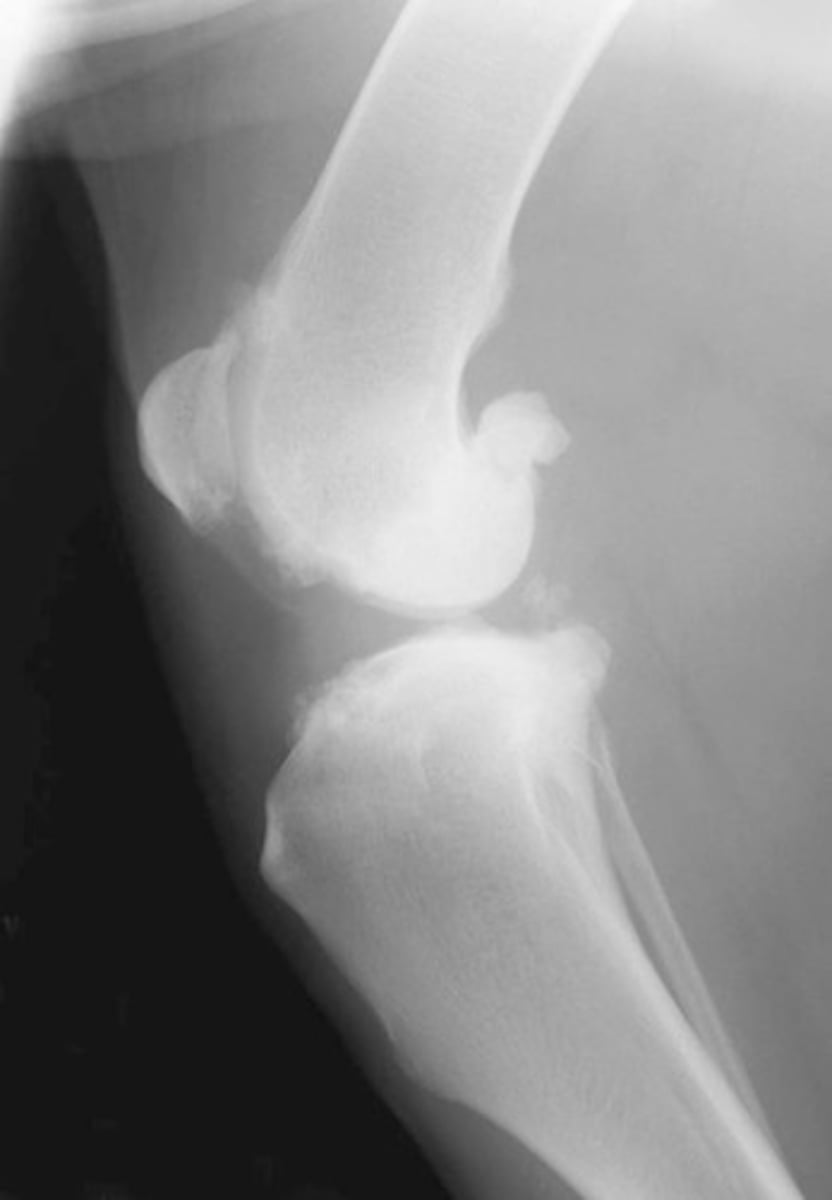
Remember you cannot see actual ligament rupture itself: look for loss of fat pad definition, distention of caudal joint capsule, osteophyte formation alone trochlear ridge, and subchondral bone sclerosis of tibia plateau
What would a cranial cruciate rupture x-ray look like?