Psychology Key Terms Learning
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam Revision and Glossary
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Conditioned response (CR)
The learnt response to a conditioned stimulus.
Conditioned stimulus (CS)

Formerly neutral stimulus that after association with an unconditioned stimulus, produces a conditioned response.

Unconditioned response (UCR)

A response evoked by an unconditioned stimulus without going through any prior learning.

Unconditioned stimulus (UCS)

Any stimulus that can evoke a response without going through any previous learning.
Neutral stimulus (NS)
A stimulus that does not evoke a response at first, however becomes a conditioned stimulus through association with the unconditioned stimulus.

Classical Conditioning

learning via association, a process of behaviour modification by which a subject comes to respond to a previously neutral stimulus that has been repeatedly presented along with an unconditioned stimulus that produces a response.
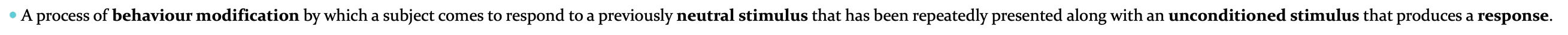
Operant Conditioning

learning via reward and punishment, Learning that occurs in the context of experiencing rewards or punishments as a result of specific behaviour.
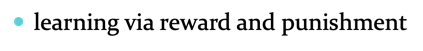

Observational Learning

(learning via observing others)
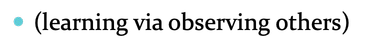
CONTINGENCY

Predictability of occurrence of one stimulus from the presence of another.

CONTIGUITY

The time interval in the UCS-CS pairing.
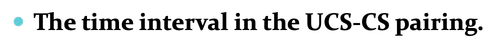
STIMULUS GENERALISATION

The transfer of a response learned to one stimulus to another similar stimulus.

STIMULUS DISCRIMINATION

The process of learning to distinguish a particular stimulus from another stimuli.
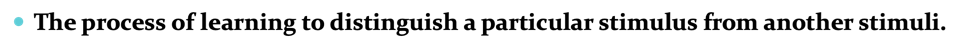
EXTINCTION

A reduction in the strength or rate of a conditioned response to the CS when the UCS is withheld.

SPONTANEOUS RECOVERY

Reappearance, after a rest period, of an extinguished conditioned response.
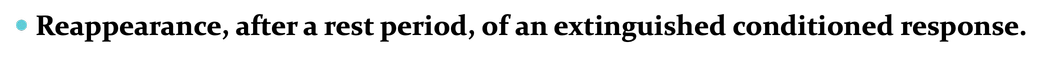
Biological Preparedness

A natural tendency to form specific associations between stimuli and responses rooted in evolutionary survival mechanisms, Helps organisms learn quickly about potential threats or dangers
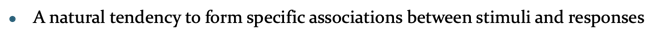
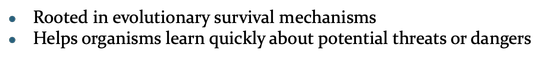
Flooding

involves repeated exposure to the highly distressing stimulus (CS) until the lack of reinforcement (UCS) results in extinction of the phobia (CR)

Systematic Desensitisation

is a treatment for phobias in which the individual is trained to relax while being exposed to progressively more anxiety -provoking stimuli. It combines the extinction of the original conditioned response, and the
counter-conditioning
of a relaxation
response.

Acquisition Phase

Repetition of pairing UCS & NS

Performance Phase

Classical conditioning achieved

REINFORCEMENT

is any process that increases the frequency of a targeted behaviour.

Positive Reinforcement

Pleasant stimulus added after a behaviour

Negative Reinforcement
Unpleasant stimulus removed by a behaviour
Shaping

In this case a process called shaping will be used:
1.To start with any behaviour at all similar to the target will be rewarded
2.Once this has been learned, only behaviours closer to the desired behaviour are rewarded.
3.Eventually, only the desired behaviour is rewarded.

Aversion Therapy
a type of behavioural therapy that involves repeat pairing an unwanted behaviour with discomfort
Psychoimmunology
Where classical conditioning can be applied to the immune system.
Systematic Desensitisation
Phase 1: The patient is taught relaxation techniques such as meditation and controlled breathing.
The therapy will attempt to use classical conditioning to associate this relaxation with the fearful stimulus.
Because relaxation is incompatible with anxiety, this counter-conditioning should help inhibit the previously conditioned anxiety response.
Phase 2: The patient creates a fear hierarchy starting with stimuli that produce the least fear or anxiety, and building up in stages to the most fearful stimuli.
This list will provide the structure for systematic
desensitisation.
Phase 3: The patient works through
their fear hierarchy, starting with
the least unpleasant stimulus.
They repeatedly imagine, or are
exposed to the fearful stimulus
while practicing their relaxation
techniques until there is no anxiety
at all.
They then work their way up to the most stressful stimulus, continuing until even that produces no fearful response.
Fixed Interval
When an organism will be reinforced for a response only after a fixed time interval.
Fixed Ratio
when an organism must make a certain number of responses in order to receive reinforcement.
Variable Interval
when the reinforcement is given to a response after a specific unpredictable amount of time has passed.
Variable Ratio
when the reinforcement is given after an unpredictable number of responses made by the organisms.
Observation Principles (ARRM)
Attention, Retention, Reproduction, Motivation
Attention