supernovae, neutron stars, and black holes
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:29 AM on 4/25/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
1
New cards
what is a supernova?
a star whose luminosity rapidly increases due to it exploding
2
New cards
what are the features of a supernova?
* a rapid increase in brightness
* the emission of gamma ray bursts
* an extremely high maximum brightness
* the emission of gamma ray bursts
* an extremely high maximum brightness
3
New cards
explain why a supernova is not displayed on a typical HR diagram
it is too bright to be displayed on the absolute magnitude scale
4
New cards
why might astronomers be worried about a supernova occurring near Earth?
because supernova emit gamma-ray bursts which:
* transfer a similar amount of energy as the total energy output of the Sun in just a few seconds
* are concentrated along the star’s axis of rotation (highly collimated)
so if the axis was pointing towards Earth, the burst could cause a mass extinction event due to the ionising nature of gamma
* transfer a similar amount of energy as the total energy output of the Sun in just a few seconds
* are concentrated along the star’s axis of rotation (highly collimated)
so if the axis was pointing towards Earth, the burst could cause a mass extinction event due to the ionising nature of gamma
5
New cards
what is a type 1a supernova?
a specific type of supernova created from a white dwarf in a binary star system increasing in mass then exploding
it has an absolute magnitude of -19.3
it has an absolute magnitude of -19.3
6
New cards
explain why a type 1a supernova would not appear on a typical HR diagram
it is too bright to fit on the scale
* a type 1a supernova has an absolute magnitude of -19.5
* the brightest absolute magnitude on a typical HR diagram is -10
* a type 1a supernova has an absolute magnitude of -19.5
* the brightest absolute magnitude on a typical HR diagram is -10
7
New cards
sketch the light curve of a type 1a supernova
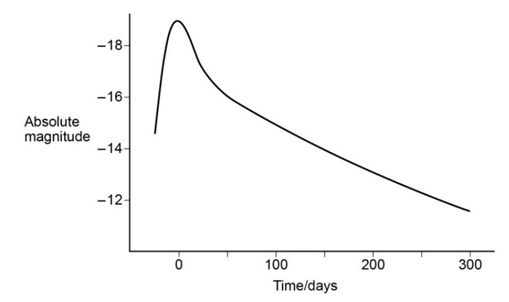
8
New cards
Define the term “standard candle” and give one example of a standard candle used in astronomy.
* an object whose absolute magnitude is known
* type 1a supernovae
* type 1a supernovae
9
New cards
how can type 1a supernovae be used as standard candles?
* if observing two galaxies that both contain type 1a supernovae
* the galaxy in which the supernova appears **brightest** is the **closest**
* as they have the same absolute magnitude
* the galaxy in which the supernova appears **brightest** is the **closest**
* as they have the same absolute magnitude
10
New cards
how can type 1a supernovae be used to calculate distances?
* using m-M=5log(d/10)
* M = -19.3
* M = -19.3
11
New cards
explain how are type 1a supernovae and dark energy related
the surprisingly high speeds at which type 1a supernovae are moving away from us provide evidence for the existence of dark energy
* measurements of type 1a supernovae found that they were travelling much faster than predicted
* so the Universe is expanding at an accelerating rate
* astrophysicists had no way of explaining this so they proposed an invisible dark energy
* measurements of type 1a supernovae found that they were travelling much faster than predicted
* so the Universe is expanding at an accelerating rate
* astrophysicists had no way of explaining this so they proposed an invisible dark energy
12
New cards
what are the two things that can happen after a supernova?
the star becomes either a **neutron star** or a **black hole**
13
New cards
state three key properties of a neutron star
* mass of around 2 solar masses
* extremely high density
* made up of neutrons (as protons and electrons combine)
* extremely high density
* made up of neutrons (as protons and electrons combine)
14
New cards
what is a black hole?
an object whose escape velocity is greater than the speed of light
15
New cards
why can’t black holes be plotted on HR diagrams?
* too dim as no light escapes a black hole
* too low in temperature as it’s only just over 0 K
* too low in temperature as it’s only just over 0 K
16
New cards
where are supermassive black holes found?
at the centre of galaxies
17
New cards
define Swartzchild radius
the distance from the centre of a black hole to its event horizon
18
New cards
what is an event horizon?
the boundary of a black hole - the point at which the escape velocity is equal to the speed of light
19
New cards
what is the escape velocity like **inside** the Swartzchild radius?
greater than the speed of light (hence why light cannot escape from a black hole)