Respiratory System – Page 1 Vocabulary
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering key terms from Page 1 notes on respiratory structure, function, defense, and anatomy.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Respiratory membrane
The thin barrier across which gas exchange occurs between alveoli and pulmonary capillaries; driven by pressure gradients; oxygen diffuses into blood and carbon dioxide diffuses out.
Gas exchange
The diffusion of oxygen into the blood and carbon dioxide out of the blood across the respiratory membrane.
Oxygen diffusion
Movement of oxygen from alveolar air into the blood.
Carbon dioxide diffusion
Movement of carbon dioxide from the blood into the alveolar air to be exhaled.
Thermoregulation
Regulation of body temperature by the respiratory system, including warming/humidifying inhaled air and releasing heat via exhalation.
Nasal passages
Upper airway region where air is warmed, humidified, and filtered; part of the respiratory tract.
Trachea
The windpipe; a main airway that conducts air from the larynx to the bronchi.
Primary bronchus
The main airway that forks from the trachea into each lung.
Secondary bronchus
Branch of the primary bronchus that supplies a lobe of the lung.
Tertiary bronchus
Branch of the secondary bronchus that supplies a bronchopulmonary segment.
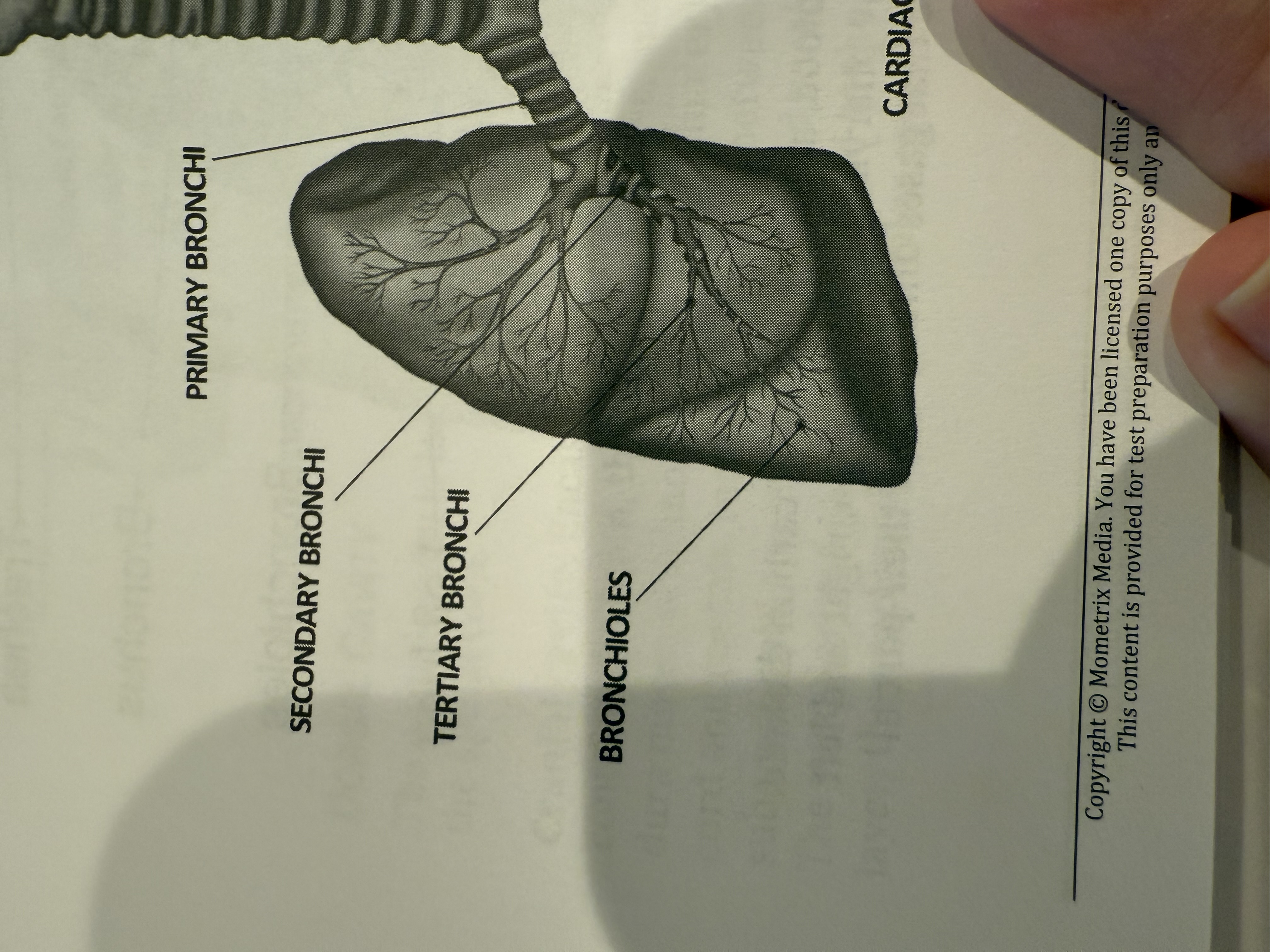
Bronchioles
Small airways following the bronchi leading toward the gas exchange regions.
Terminal bronchioles
The last conducting airways before the respiratory zone; lead to respiratory bronchioles.
Respiratory bronchioles
Small airways that contain some alveoli and mark the start of gas exchange.
Alveolar ducts
Ducts that lead to alveolar sacs and end in clusters of alveoli.
Alveolar sacs
Clusters of alveoli at the end of alveolar ducts where gas exchange occurs.
Alveoli
Tiny air sacs where gas exchange occurs between air and blood.
Pleura
A serous membrane surrounding the lungs and lining the thoracic cavity.
Parietal pleura
The portion of the pleura that lines the walls of the thoracic cavity.
Visceral pleura
The portion of the pleura that covers the surface of the lungs.
Mediastinum
The central thoracic cavity region that separates the two lungs and contains the heart and major vessels.
Hilum
The region where primary bronchi, blood vessels, and nerves enter/exit each lung.
Cardiac notch
A heart-shaped indentation on the left lung accommodating the heart.
Larynx
The voice box; part of the upper airway containing vocal cords.
Pulmonary artery
The vessel that carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs for oxygenation.
Pulmonary vein
The vessel that returns oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart.
Cilia
Hairlike projections lining the respiratory tract that move mucus and trapped debris out of the airways.
Mucus
A sticky secretion that traps particulate matter in the airways.
Lysozyme
An enzyme in mucus that helps break down bacteria.
Immunoglobulin A (IgA)
An antibody produced in mucosal linings that neutralizes pathogens.
Mast cell
An immune cell that releases inflammatory chemicals to increase blood flow during threats.
Macrophage
A large phagocytic cell that engulfs particulates and pathogens in lung tissue.
Particulate matter
Inhaled particles that can cause disease; filtered by mucus and cilia in the airways.