Chapter 4: Angiosperm Reproduction and Biotechnology
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
how does a pollinator know when an angiosperms flower is ready?
pollinator know by visual cues and volatile chemical
how do angiosperms reproduce?
sexually and asexually
Plants have what type of relationship with other species?
symbiotic relationship
What do plants breads do to get the trait they want in angiosperms species?
artificial selection
Diploid
sporophytes produce spores by meiosis
fertilization
Gametophytes produce haploid (n) gametes by; of gametes produces a
sporophytemitosis
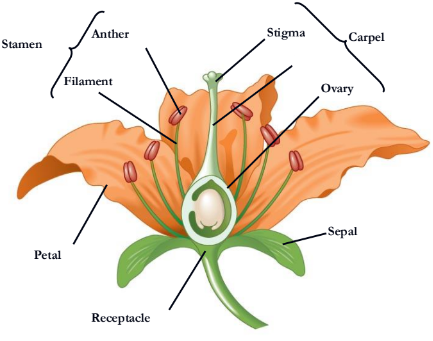
Flowers are the reproductive shoots of the angiosperm sporophyte; they attach to a part of the stem
receptacle
Flowers consist of four floral organs:
sepals, petals, stamens, and carpels
What stamen consists of?
a filament topped by an anther with pollen sacs that produce pollen
Where does pollen land on?
A carpel has a long style with a stigma
At the base of the style is an
ovary
ovary containing one or more is called
ovules
A single carpel or group of fused carpels
pistil
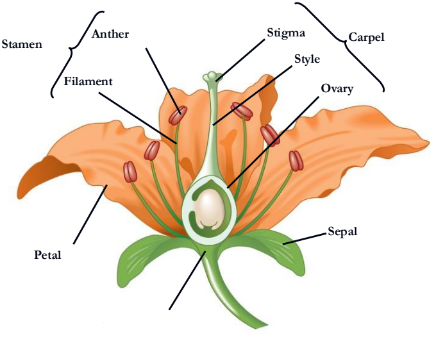
what is missing
receptacle
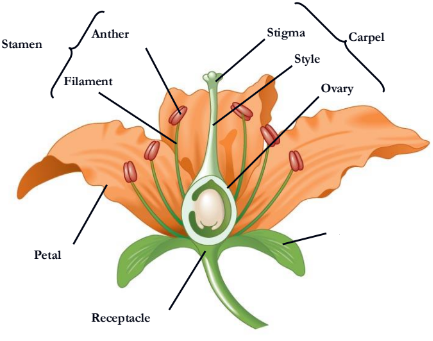
what is missing
sepal
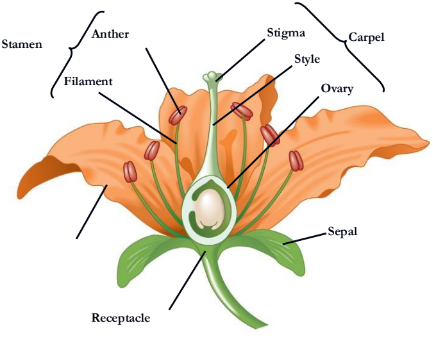
what is missing
petal
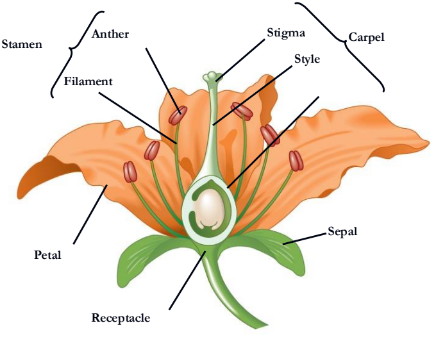
what is missing
ovary
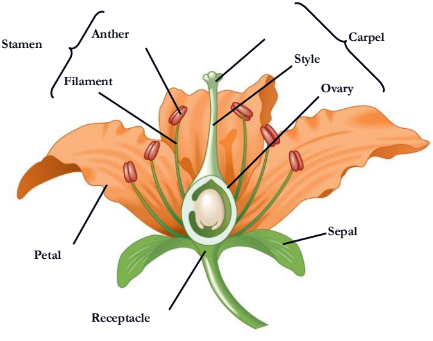
What is missing
style
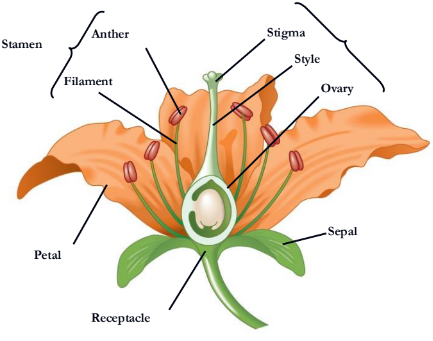
What is missing?
Stigma
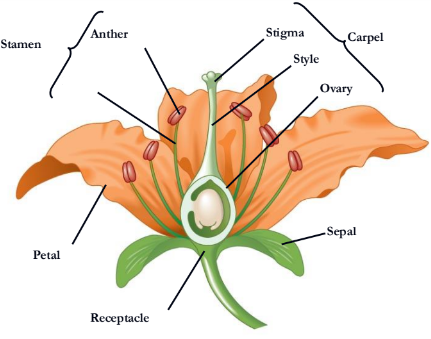
what is missing?
Carpel
What is missing
Filament
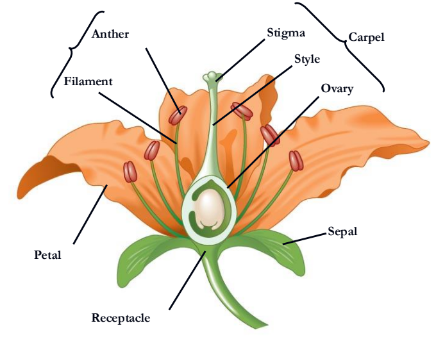
What is missing?
Stamen
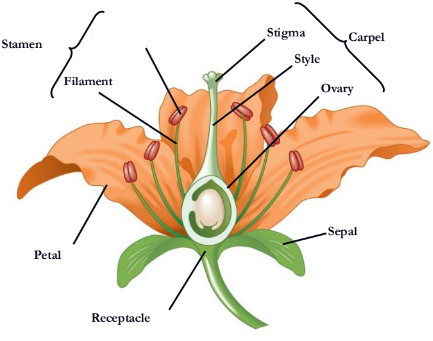
What is missing?
Anther
Complete flowers
contain all four floral organs
Incomplete flowers
lack one or more floral organs, for example stamens or carpels
inflorescences
Clusters of flowers are
Pollen develops from microspores from where?
within the microsporangia, or pollen sacs, of anthers
pollen grain produces a pollen tube
that grows down into the ovary and discharges sperm near the embryo sac
What does a pollen grain consist of?
two-celled male gametophyte and the spore wall
embryo sacs
megaspores are produced by meiosis and develop into; this is the female gametophytes
pollination
is the transfer of pollen from an anther to a stigma
give examples of pollinator/thing that happen naturally
wind, bee, moth and butterfly, fly, bird, bat, or water
Double fertilization
results from the discharge of two sperm from the pollen tube into the embryo sac
endosperm
giving rise to the triploid (3n) food-storing
In angiosperms, the sporophyte is the _______ generation, the large plant that we see
dominant
The gametophytes are _____ in size and depend on the sporophyte for nutrients
reduced
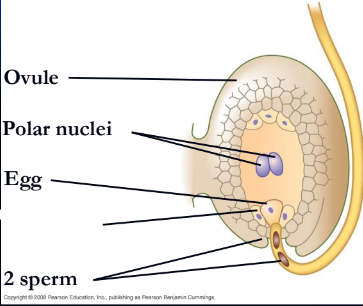
What is missing?
Synergid
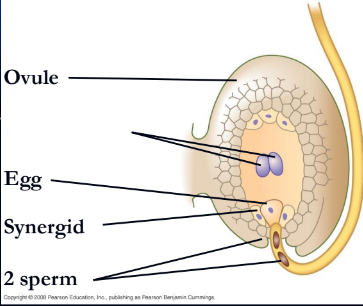
What is missing?
Polar nuclei
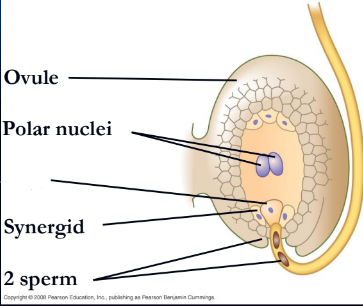
What is missing
Egg
What happen double fertilization?
each ovule develops into a seed
What happens to the ovary after fertilization?
The ovary develops into a fruit enclosing the seed(s)
In most monocots and some eudicots, endosperm stores nutrients that can be used by
the seedling
seed coat
The embryo and its food supply are enclosed by a hard, protective
During the seed of maturity seed enters a state of what?
dormancy
radicle
Below the cotyledons the embryonic axis terminates in the
In some eudicots, such as the common garden bean,
the embryo consists of the embryonic axis attached
to two thick cotyledons
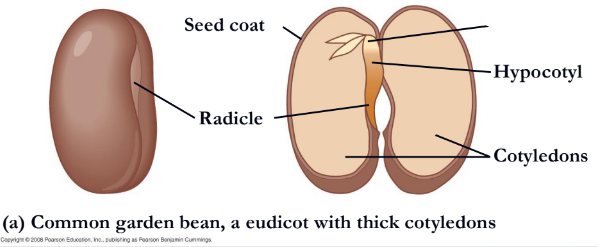
What is a eudicot or monocot?
eudicot bean
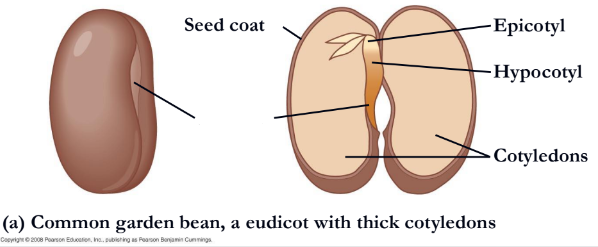
What is missing?
radical
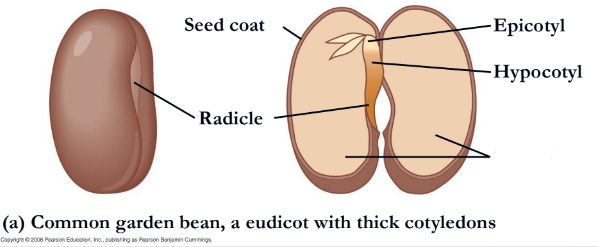
What is missing?
Cotyledons
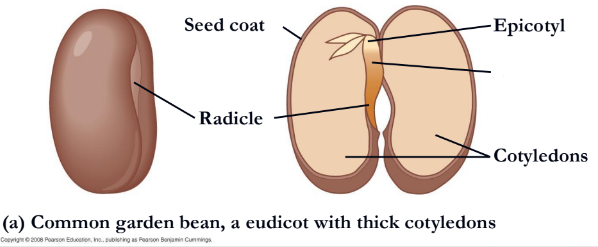
What is missing?
Hypocotyl
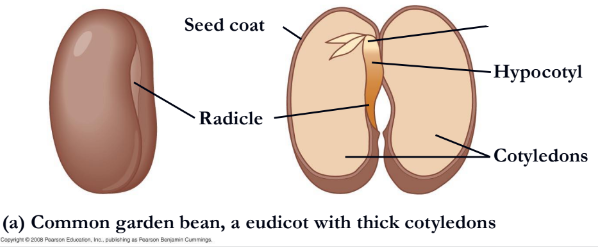
What is missing
Epicotyl
A monocot embryo has ___ many of cotyledon
one
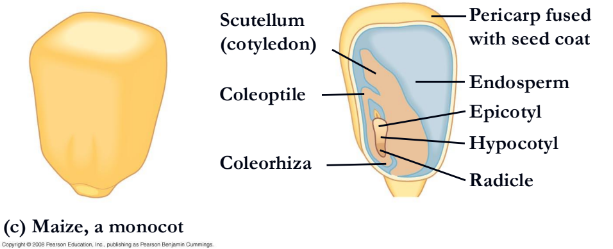
What is it a(n) eudicot or monocot?
Monocot, corn
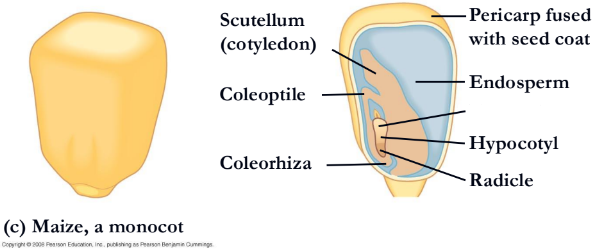
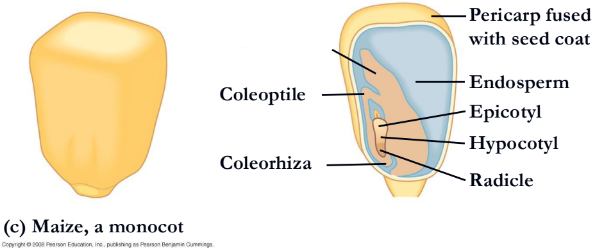
What is missing?
Epicotyl(corn)
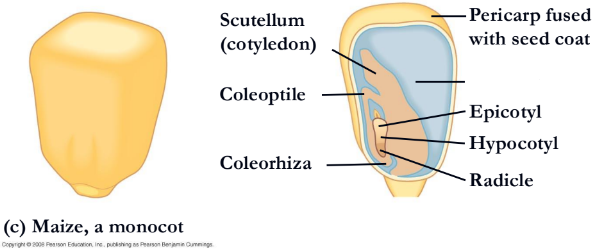
what is missing?
endosperm
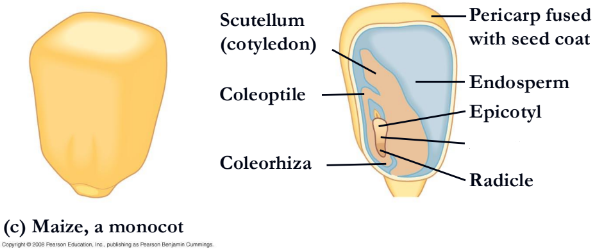
what is missing?
hypocotyl(corn)
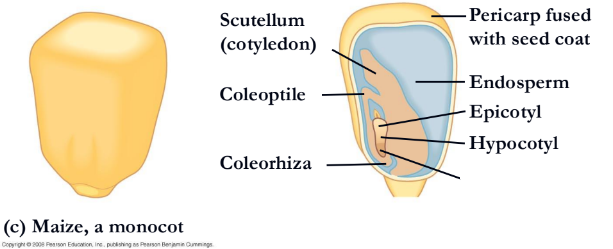
what is missing?
radicle(corn)
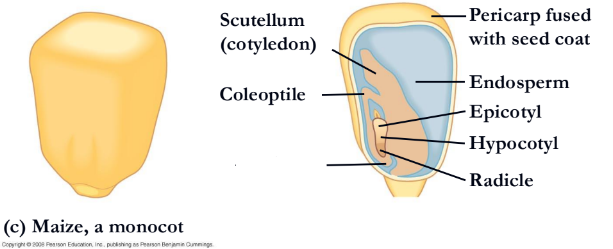
What is missing?
coleorhiza
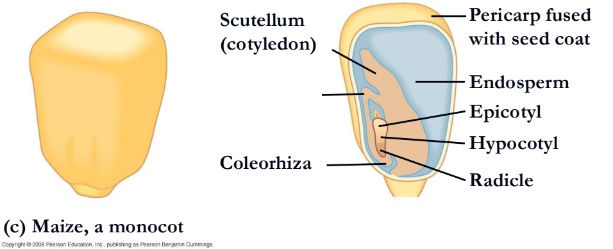
What is missing?
coleptile
what is missing?
scutellum(cotyledon)
what will increase chances of seed dormancy?
the chances that germination will occur at a time and place most advantageous to the seedling
What makes the seed come out out of it’s dormancy?
often requires environmental cues, such as temperature, lighting changes, fire, rain, chemical digestion, etc.
What does germination depend on?
imbibition
What is imbibiton?
the uptake of water due to low water potential of the dry seed
What grows first from seed development?
The radicle (embryonic root) emerges first
What grows second from seed development?
the shoot tip breaks through the soil surface
fruit
develops from the ovary
What is the function of the fruit?
It protects the enclosed seeds and aids in seed dispersal by wind or animals
How can a fruit be classified as dry?
if the ovary dries out at maturity
How can a fruit be classified as fleshy?
if the ovary becomes thick, soft, and sweet at maturity
Fruits are classified depending on their developmental origin:
Simple Fruit, Aggregate Fruit, Multiple Fruit, accessory fruit
Name a good example of a simple fruit?
pea fruit
Name an example of aggregate fruit?
raspberry fruit
name an example of a multiple fruit
pineapple fruit
name an example of accessory fruit?
apple fruit
Fruit dispersal mechanisms include:
-Water
-Wind
-Animals
Many angiosperm species reproduce
both asexually and sexually
Sexual reproduction
results in offspring that are genetically different from their parents
Asexual reproduction
results in a clone of genetically identical organisms
Fragmentation
separation of a parent plant into parts that develop into whole plants, is a very common type of asexual reproduction
In some species, a parent plant’s root system gives rise to adventitious shoots that become
separate shoot systems
Apomixis
is the asexual production of seeds from a diploid cell
vegetative reproduction
Asexual reproduction is also called
how can asexual reproduction beneficial for a plant?
it’s only beneficial if it’s in a stable environment
How can asexual reproduction be bad for the plant?
a clone of plants is vulnerable to local extinction if there is an environmental change; only a fraction of seedlings survive
The benefit of sexual reproduction
generates genetic variation that makes evolutionary adaptation possible
Many angiosperms have mechanisms that make it difficult or impossible
for a flower to self-fertilize
Dioecious
species have staminate and carpellate flowers on separate plants
self-incompatibility
a plant’s ability to reject its own pollen
What is the gene that makes plants self-reject
S-gene
cuttings
Many kinds of plants are asexually reproduced from plant fragments
callus
is a mass of dividing undifferentiated cells that forms where a stem is cut and produces adventitious roots
How have humans devised methods for asexual propagation for plants?
Most methods are based on the ability of plants to form adventitious roots or shoots
How is grafting done?
Most methods are based on the ability of plants to form adventitious roots or shoots, the stock provides the root system and then scion is grafted onto the stock
Transgenic
plants are genetically modified (GM) to express a gene from another organism
Protoplast fusion
is used to create hybrid plants by fusing protoplasts, plant cells with their cell walls removed
Plant biologists have adopted ____ methods to create and clone novel plant varieties
in vitro
Maize
a product of artificial selection, is a staple in many developing countries
How do mutations arise?
mutations can happen randomly or can be induced by breeders
How are mutations beneficial?
Desirable traits can be introduced from different species or genera