Chemistry- tests p3
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Test for the presence of NH4+ ions in a solution of NH4CL
1- Add sodium hydroxide and WARM.
2- A gas would be released, test the gas using a DAMP red litmus paper, it will turn blue.
Test to indicate the presence of OH- group
1- Add phosphorous (V) chloride (PCL5)
2- Steamy white fumes released/seen.
Chemical test and the expected observation for a carbon carbon double bond.
1- Add aqueous bromine.
2- Aqueous bromine decolorises from orange to colorless.
Describe a test and the expected result to confirm the presence of chloride ion in a compound.
1- Dissolve compound in dilute nitric acid.
2- Add silver nitrate solution.
3- White precipitate forms.
Chemical test to distinguish between oxidation products of aldehyde(C=O H) and ketone (C=O)
1- Fehling’s solution and warm
With aldehyde- brick red precipitate.
With ketone- no brick red precipitate.
2- Tollen’s reagent and warm
With aldehyde- silver mirror.
With ketone- no silver mirror.
Test to distinguish between primary, secondary with tertiary alcohol.
Add potassium dichromate (VI) in dilute sulfuric acid.
If primary or secondary alcohol is present, the colour would change from orange to green.
When organic compound like cyclohexane/hexene added to Iodine, what are the colors of the layers formed?
Two layers formed:
Organic layer (upper layer)- purple
Aqueous layer (lower layer)- yellow
#6 sample question: Describe the steps needed to make a standard solution.
1- Use a volumetric flask.
2- Dissolve solid in conical flask in distilled water.
3- Pour solution into volumetric flask using a funnel with washings.
4- Make 250cm3 and shake.
Different test other than use of silver nitrate for iodide (any halide) ion.
1- Add concentrated sulfuric acid.
2- Rotten egg smell, yellow solid, black solid observed,
Presence of sulfate ions test.
1- Add barium chloride solution.
2- Add hydrochoric acid.
3- White precipitate forms.
Steamy fumes formed when PCL5 added, why?
HCl given off.
Butan-1-ol converted to but-1-ene, how?
Concentrated phosphoric acid (H3PO4)
How to IDENTIFY and CONFIRM the presence of chloride ions?
HOW TO IDENTIFY:
1- Add dilute nitric acid
2- Add silver nitrate solution
3- White precipitate forms.
HOW TO CONFIRM:
1- Precipitate would dissolve in dilute ammonia.
Describe a test and its result, other than flame test which could be used to confirm that the bottle contains traces of barium chloride.
1- Add dilute sulfuric acid.
2- White precipitate forms.
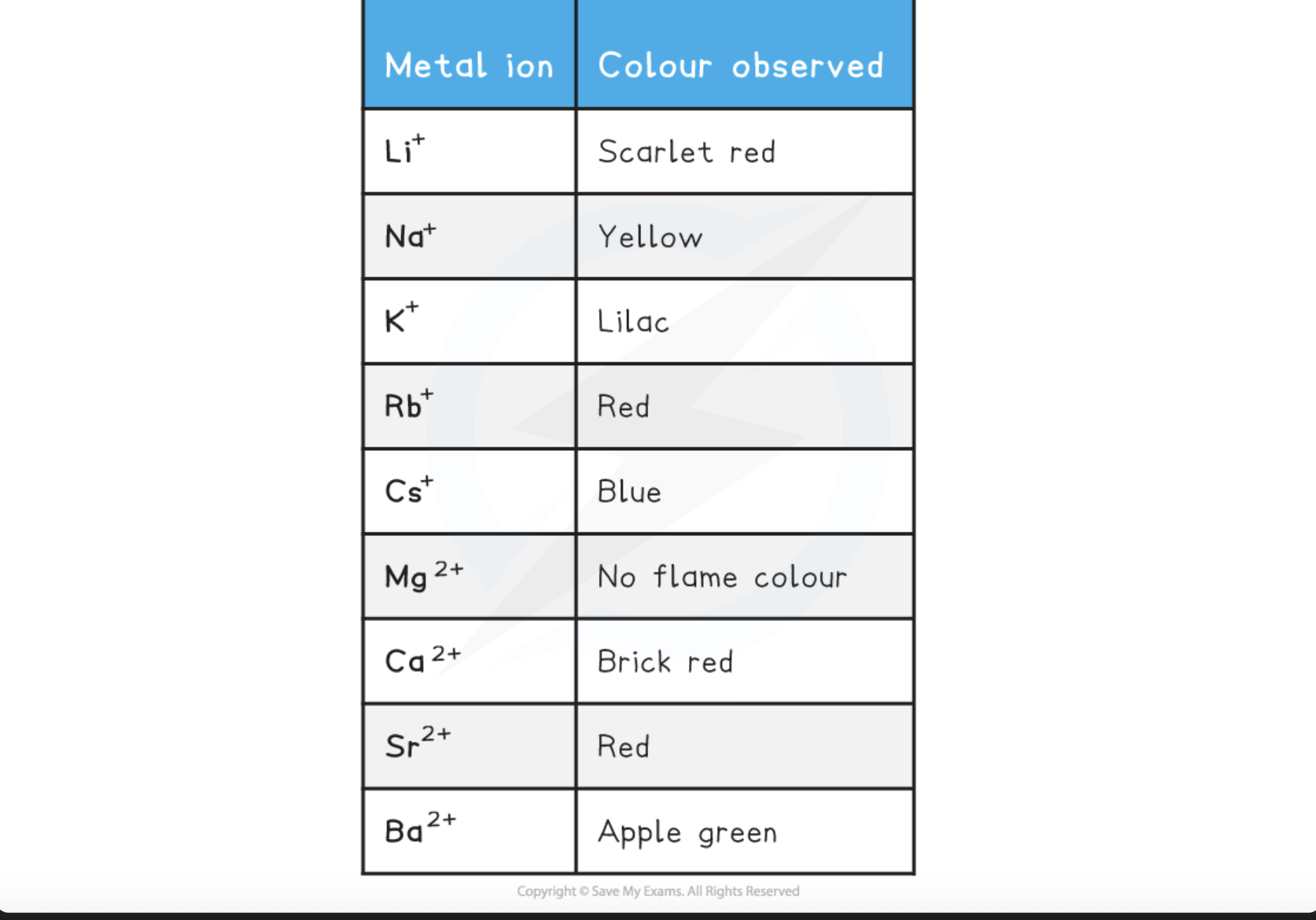
Flame tests
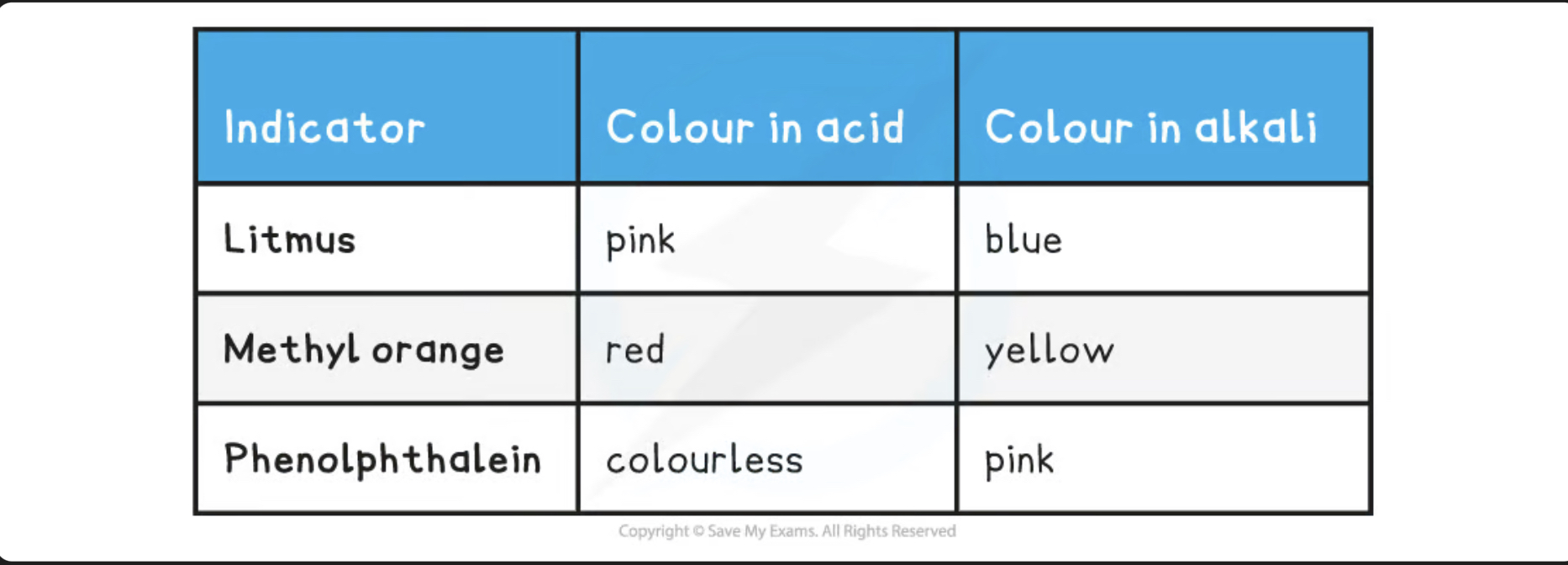
Titration indicators colours in acid and alkali
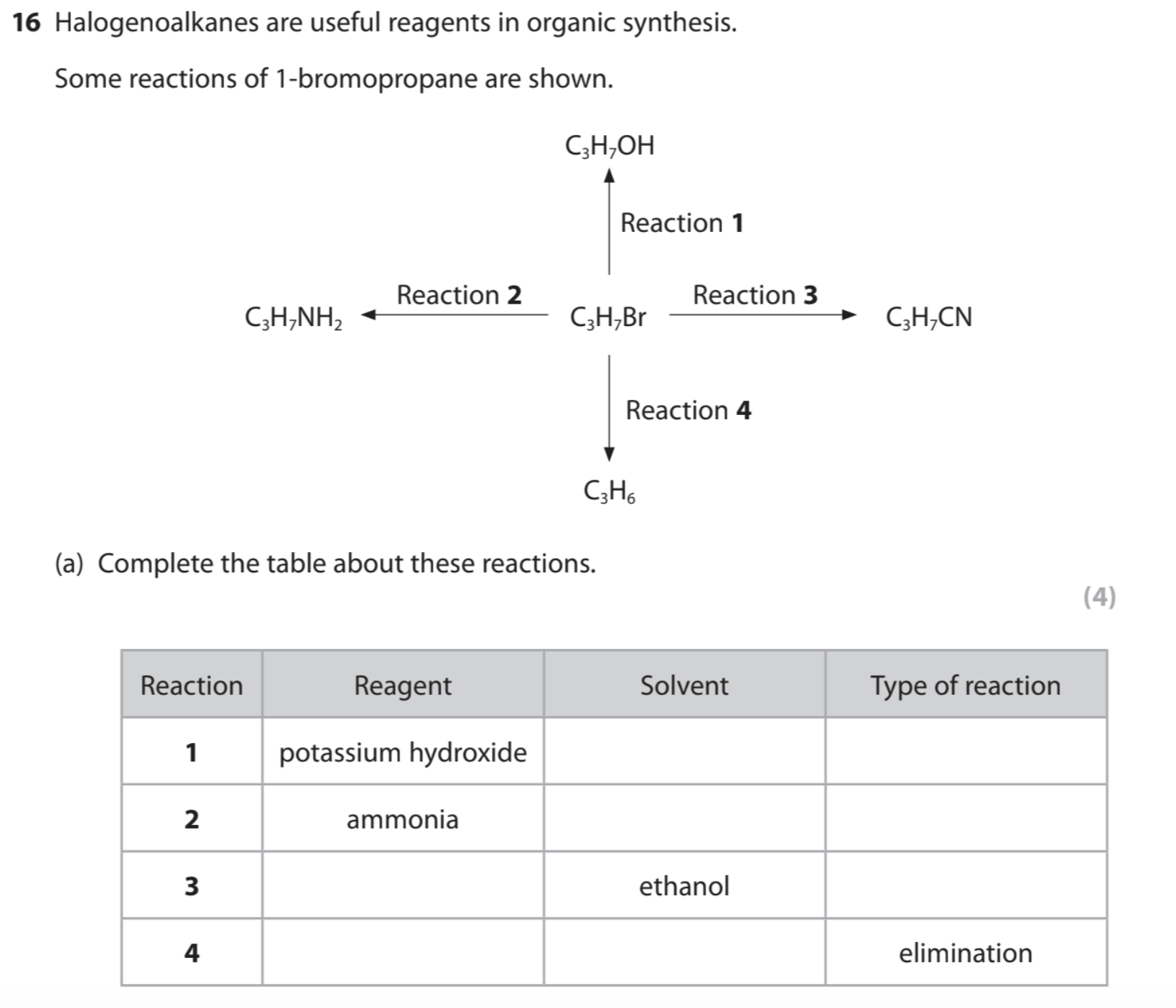
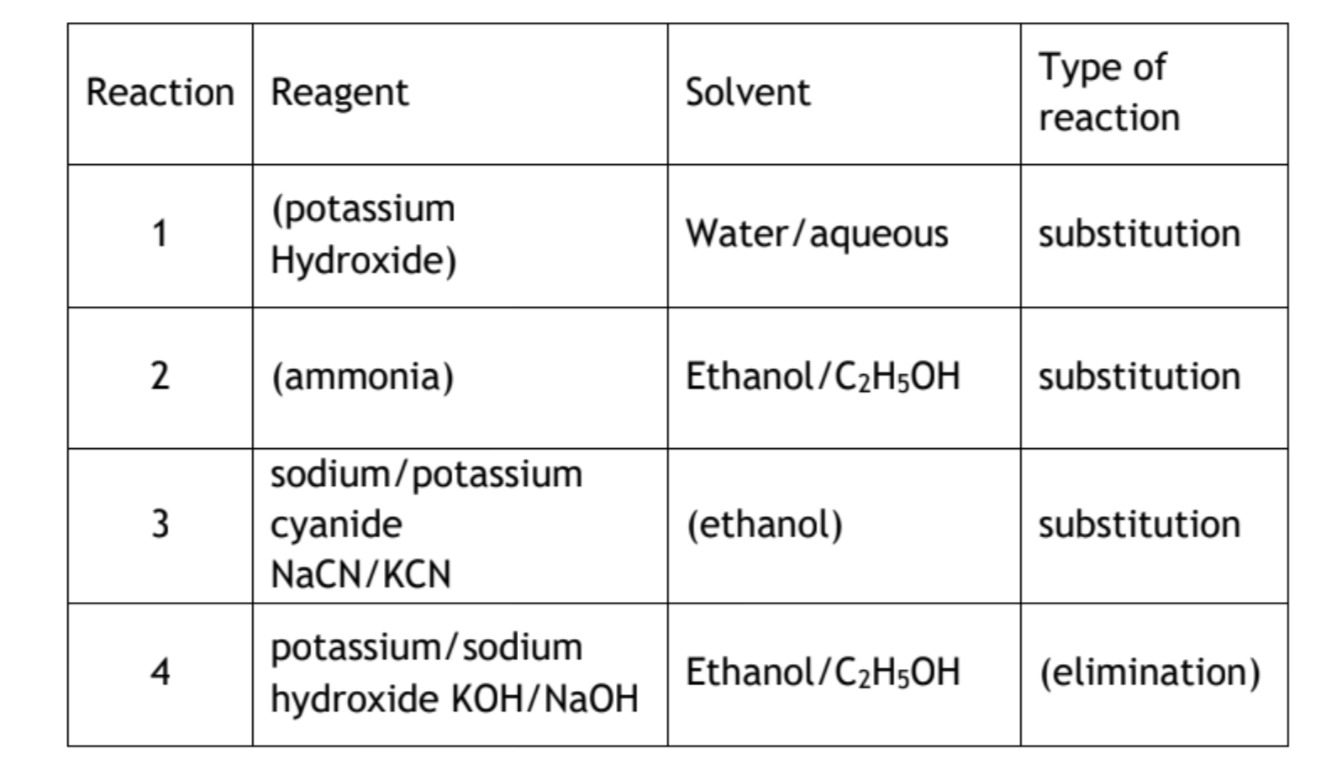
Organic conditions
Test to identify an aqueous solution containing hydrogencarbonate ions, HCO3-
Nitric acid.
What are the reagents that could be used to produce a chloroalkane from a tertiary alcohol?
PCL5, concentrated HCL, concentrated H2SO4 and KCL.
Reagents for testing for carboxylic acid
Add aqueous sodium carbonate.
Effeservence shows the presence of CO2 gas.
Reagents and conditions for alkene to alcohol
Reagents and conditions for alkene to diol
ALKENE TO ALCOHOL
1- Concentrated phosphoric acid
ALKENE TO DIOL
1- Potassium permanganate in dilute sulfuric acid.

#1 example question: organic
Oxidation
Sulfuric acid, potassium dichromate (VI)
distilled
orange—> green

Hazard symbols
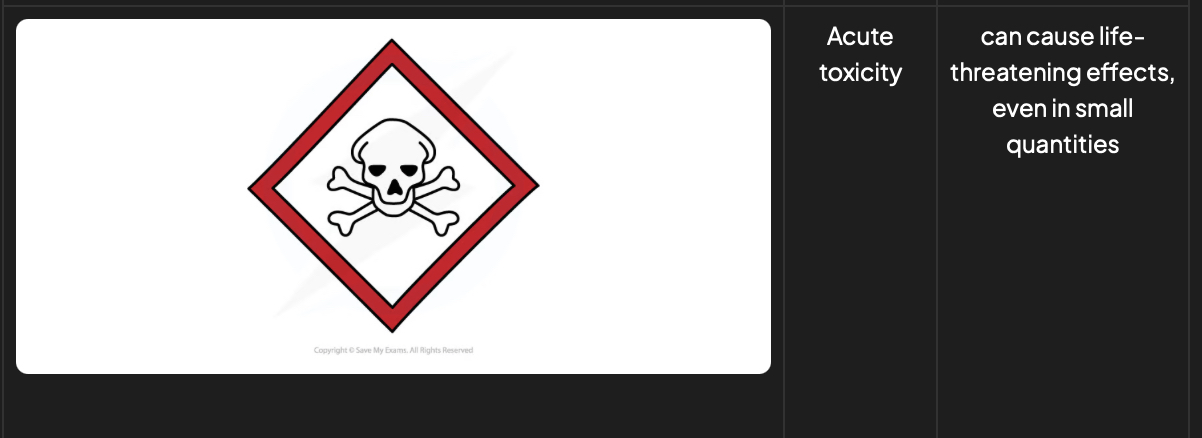

Hazard symbols
