Chapter 2: Economic Models: Trade-offs and Trade
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Model
any simplified representation of reality that is used to better understand real-life situations
their simplicity allows economists to focus on the effects of only one change at a time- allows us to hold everything else constant and study how one change affects the overall economic outcome.
other things equal assumption
in the development of a model, the assumption that all other relevant factors remain unchanged.
The most effective form of economic modelling is…
the construction of “thought experiments” - simplified, hypothetical versions of real-life situations.
Three simple but important economic models
Production possibility frontier
Comparative advantage
Circular-flow diagram
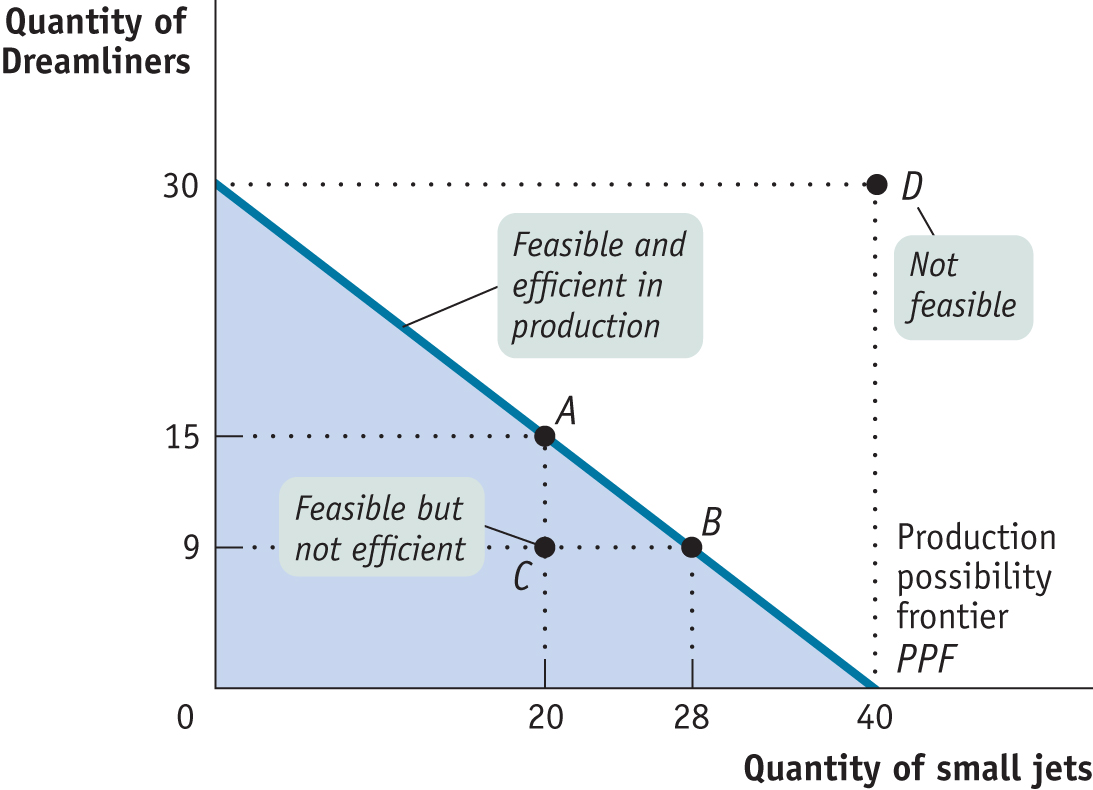
Production possibility frontier
a model that helps economists think about the trade-offs every economy faces
considers a simplified economy that produces only two goods
Comparative advantage
a model that clarifies the principle of gains from trade — trade between both individuals and between countries
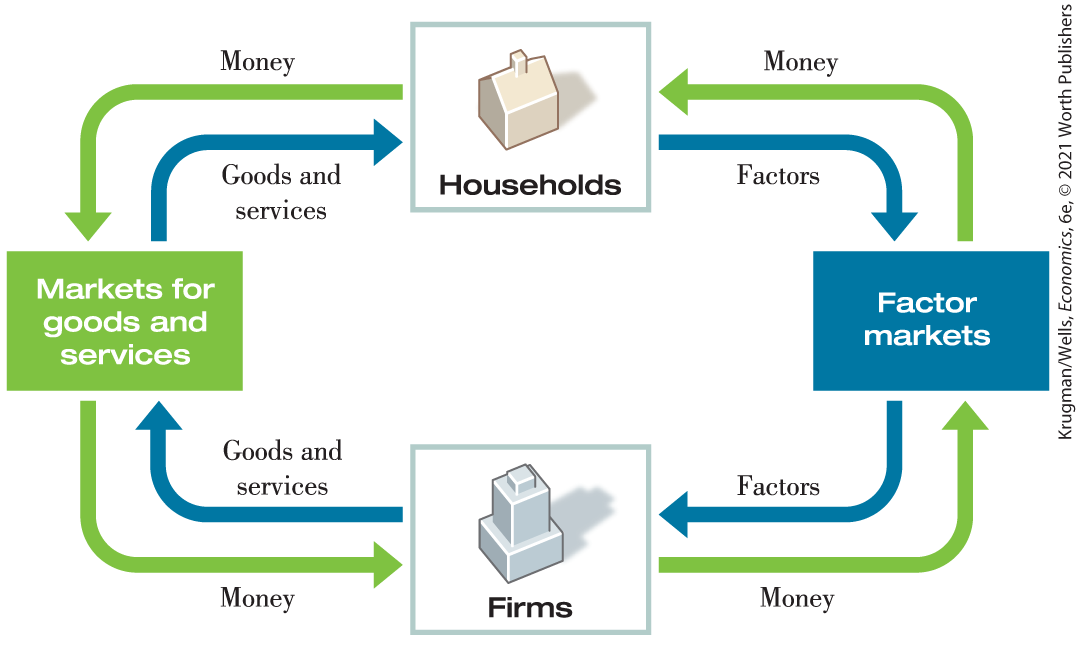
Circular-flow diagram
a schematic representation that helps us understand how flows of money, goods, and services are channeled through the economy.
efficient in production
if the economy as a whole could not produce more of any one good without producing less of something else (production possibility frontier)
Innefficient in production
the economy could not produce more of some things without producing less of others — could produce more of everything
Efficient in allocation
requires the economy to allocate its resources so that consumers are as well off as possible
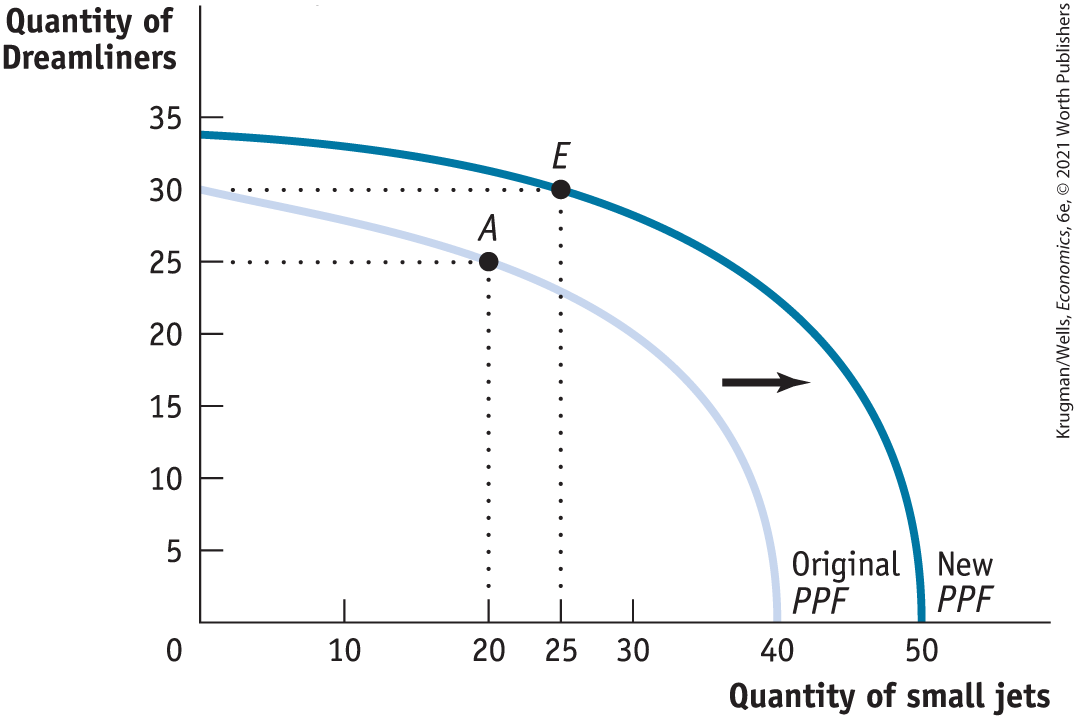
Graphically, economic growth means…
an expansion of the economy’s production possibilities — the economy can produce more of everything
results in an outward shift of the PPF because production possibilities are expanded
What can lead the PPF to shift outward i.e economic growth?
Increase in the economy’s factors of production— the resources used to produce goods and services.
progress in technology— the technical means for the production of goods and services
The main factors of production are:
the resources (land, labor, physical capital, and human capital)
gains from trade
the mutual gains that inidividuals can achieve by specializing in doing different things and trading with one another.
comparative advantage
the advantage an individual or country has in producing a good or service if its opportunity cosy of producing the good or service is lower than other countries’ or individual’s cost.
absolute advantage
the advantage a country has in producing a good or service if the country can produce more output per worker than other countries. Likewise, an individual has an absolute advantage in producing a good or service if they are better at producing it than other people..
barter
trade in the form of the direct exchange of goods or services that people for other goods or services that people want.
The simplest circular-flow diagram illustrates an economy that contains only two kinds of inhabitants:
households and firms
Household
an individual or a group of people (usually, but not neecessarily, a family) that share their income
Firm
an organization that produces goods and services for sale — and that employs members of households.
Two kinds of markets
markets for goods and services
factor markets
Markets for goods and services
households buy the goods and services they want from firms
factor markets
firms buy the resources they need to produce goods and services
capital market
market in which capital is bought and sold
factor markets determin an economy’s…
income distribution
income distribution
how the total income created in an economy is allocated between less skilled workers, highly skilled workers, and the owners of capital and land.
Two roles of economic analysis:
positive economics
normative economics
Positive economics
analysis that tries to answer questions about the way the world works, which have definite right and wrong answers (description) — models play a huge role - often makes forecats
Normative economics
analysis thaat involves saying how the world should work (prescription)
forecast
a simple prediction of the future
Why do economists disagree?
they may disagree about which simplifications to make in a model
economists may disagree about values