movement of molecules across membranes
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
what is diffusion
the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration down a concentration gradient occuring at random
is diffusion a passive or active process
passive - doesnt require energy
what is the importance of diffusion
all living creatures rely on diffusion to some extent
diffusion is important for extracting oxygen from blood vessels
is vital for respiration
important for removing carbon dioxide from the stomata of the plants
is vital for photosynthesis
the more concentrated a solution is, the more dissolved in it
dissolved solids are known as solutes
how is a solution formed
during diffusion, the solute distributes itself throughout the solvent, creating a solution
what is osmosis
the net movement of particles from an area of high water potential to an area of low water potential across a partially permeable membrane
is osmosis an active or passive process
passive - it doesnt require energy
do solutions with a high water potential contain a high or low concentration of water
high
do solutions with a lower water potential contain a high or low concentration of water
lower
do dilute solutions contain a high or low concentration of water
high
do concentrated solutions contain a high or low concentration of water
low
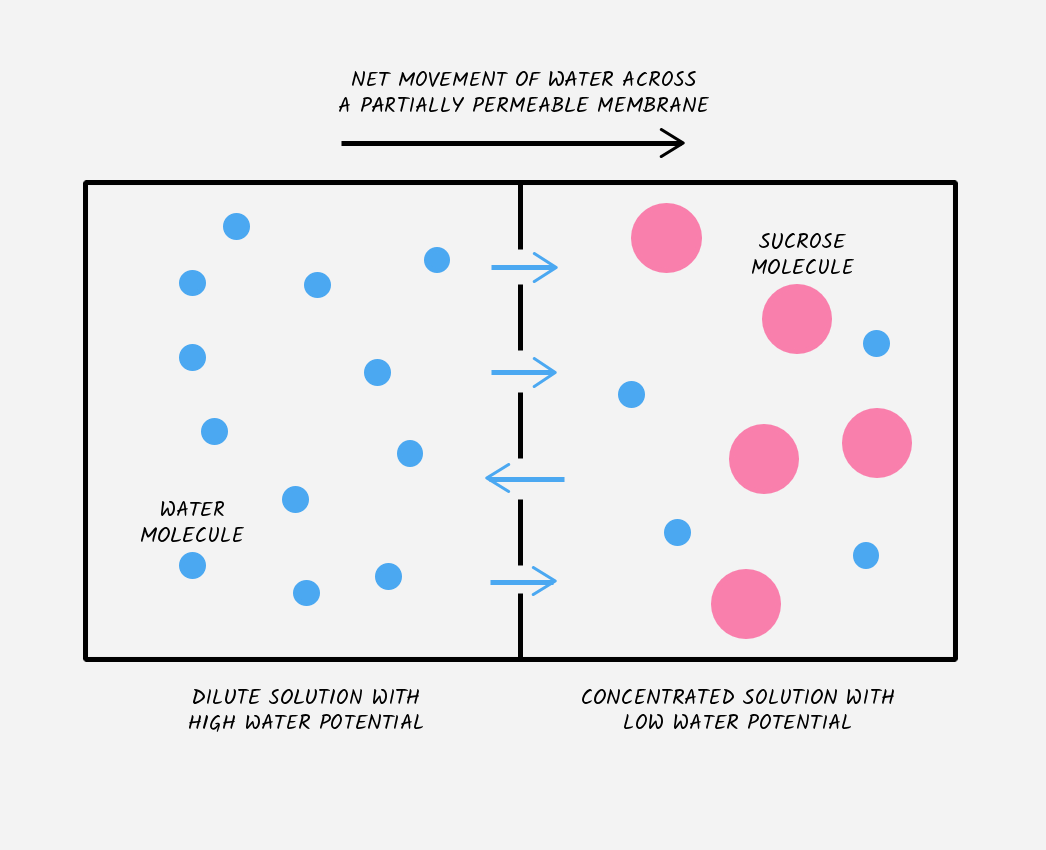
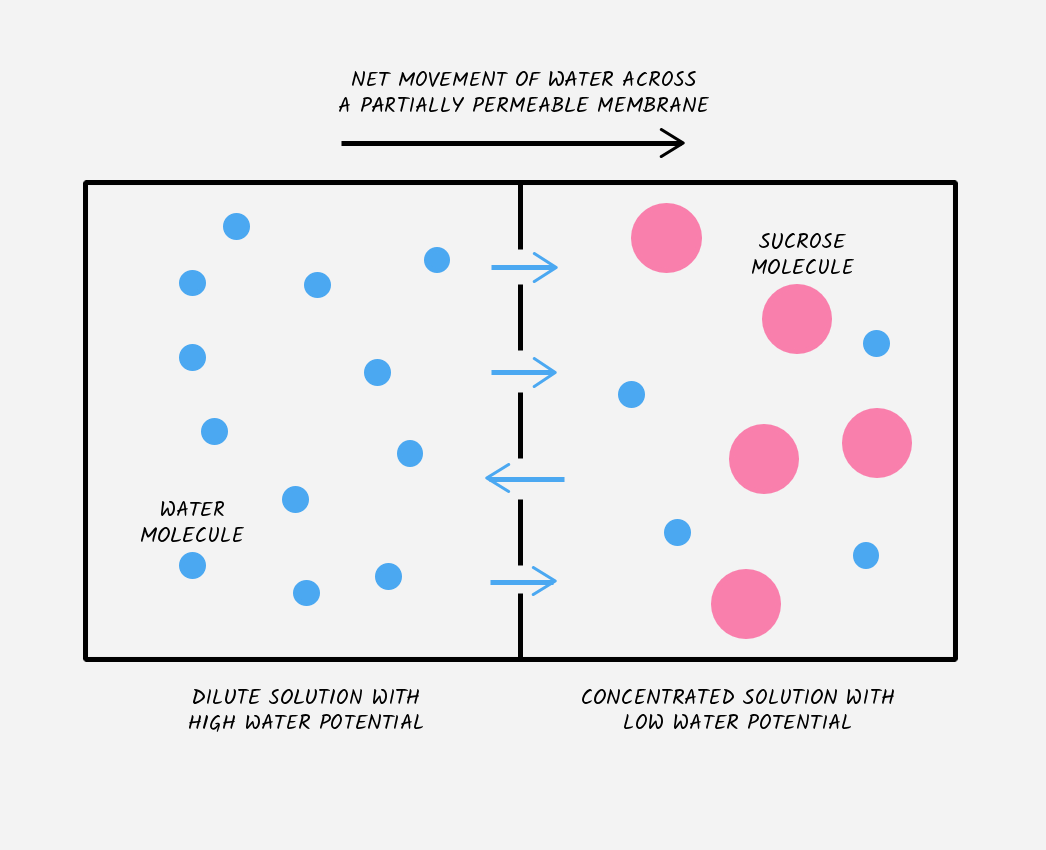
describe the occurence of osmosis in this diagram
during osmosis, water will move from an area of high water potential (left side) to an area of low water potential (right side) across a partially permeable membrane
what is the importance of osmosis
if the cell loses too much water, the cell wall can no longer support the cell leading it to becoming flaccid
plants with a higher water potential than it’s surroundings will lose water to the environment
this is because water moves from high to low concentrations, down the concentration gradient
what is plasymosis
when the cell wall detaches from the cell membrane likely leading to the death of the cell
how is diffusion affected by temperature
as temperature increases, the rate of diffusion and osmosis will be faster as kinetic energy increases
how is diffusion affected by diffusion distance
as diffusion distance decreases, the rate of diffusion and osmosis increases as there is less distance to travel
how is diffusion affected by the steepness of the concentration gradient
as the steepness of the concentration gradient increases, the rate of diffusion and osmosis increases
what is the concentration gradient
the difference in the concentrations of a solute in two different locations
how is diffusion affected by the SA:V ratio
as the SA:V ratio increases the rate of diffusion and osmosis increases because they have more SA than V for diffusion to take place
what is the SA:V ratio of an object
the amount of SA compared to the V of an object
will diffusion and osmosis increase with a thinner or thicker membrane
thin membranes - cause shorter diffusion pathways
what is active transport
the movement of particles against a concentration gradient - occurs when particles are moved from a region of low concentration to a region of higher concentration
is active transport an active or passive process
active - requires energy to pump molecules through protein channels which is derived by respiration in the form of ATP
what is the diffusion practical
a coloured crystal (usually KMnO4) is added to a solvent (water)
the crystal particles will dissolve and spread out throughout the solvent
what is the osmosis practical
semi-permeable visking tube is filled with sugar solution and placed in a beaker of water
because the concentration of water is higher in the beaker than in the tubing
water molecules will move into the tubing by osmosis
potatoes are cut into tubes and submerged into sucrose solutions of various concentrations
those that are submerged into more concentrated solutions will decrease in mass, those that are more dilute will increase in mass
how do you calculate percentage change
percentage change = change in value/original value