Muscle Anatomy (Muscle cell)
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
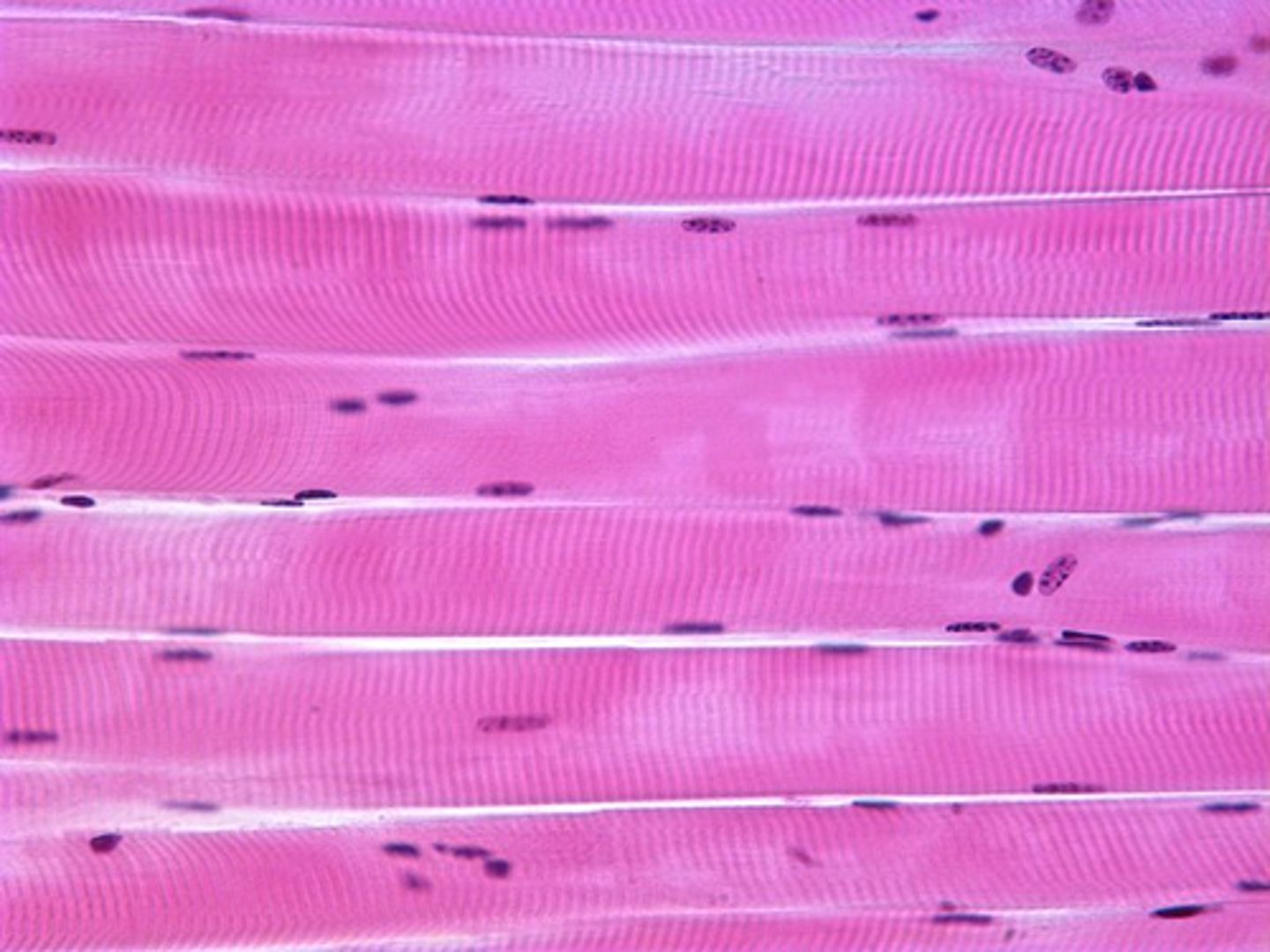
Skeletal muscle
Shape: elongated, striated cylindrical cells
Nucleus: Multinucleated
Control: voluntary
Found: attached to skeletal bones
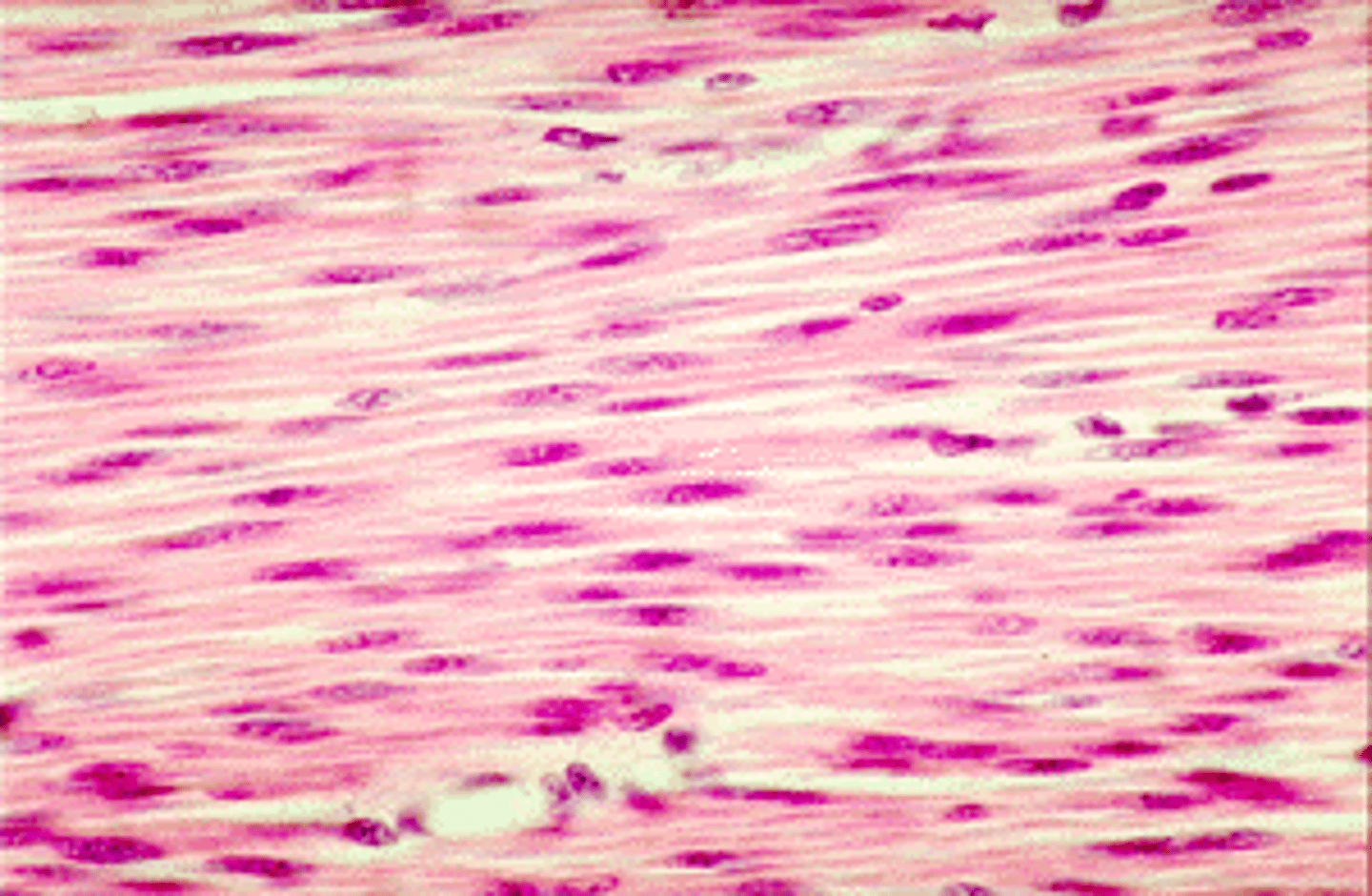
Smooth Muscle
Shape: spindle
Nucleus: Uni-nucleated
Control: Involuntary
Found: in the walls of soft organs or blood vessels
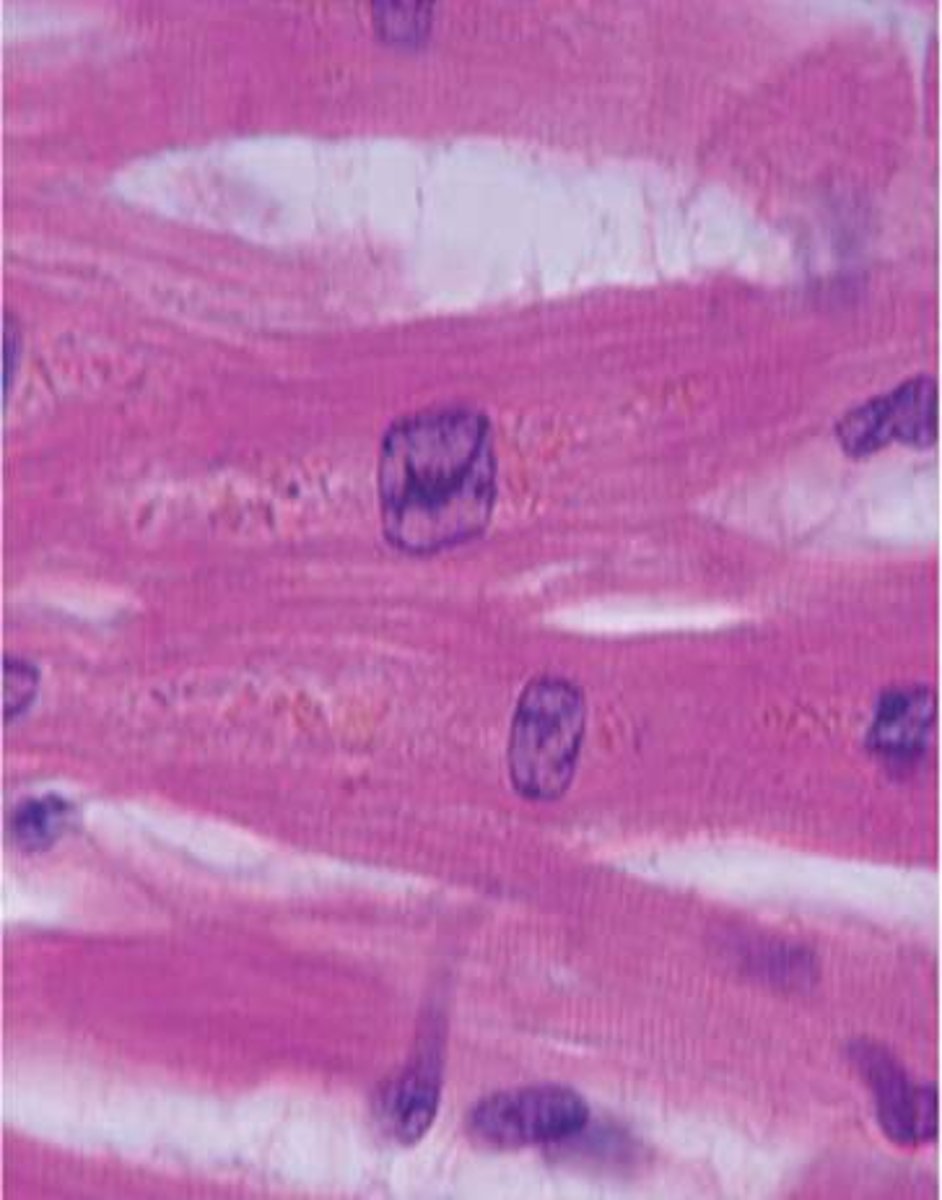
Cardiac Muscle
Shape: Branched, striated cells with intercalated discs to separate one cell from another
Nucleus: Uni-nucleated
Control: Involuntary
Found: in the walls of heart muscle
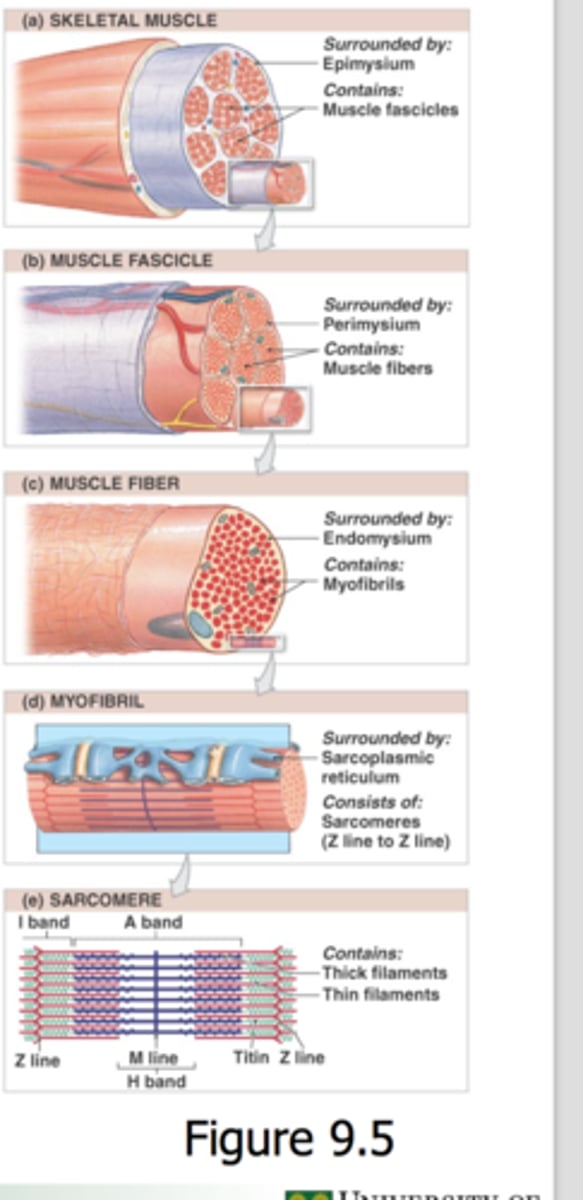
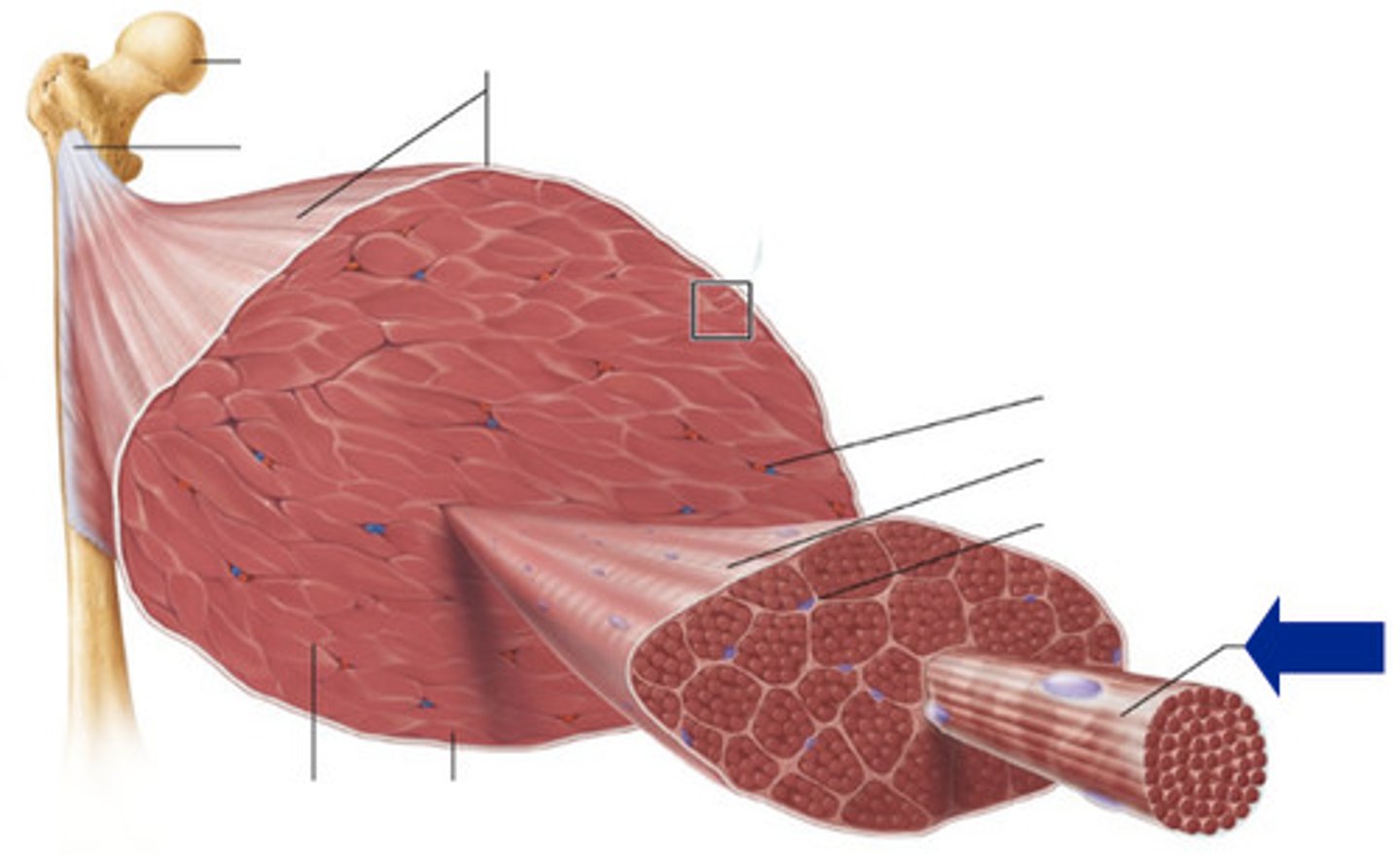
Entire Skeletal Muscle
Highest order of muscle anatomy hierarchy
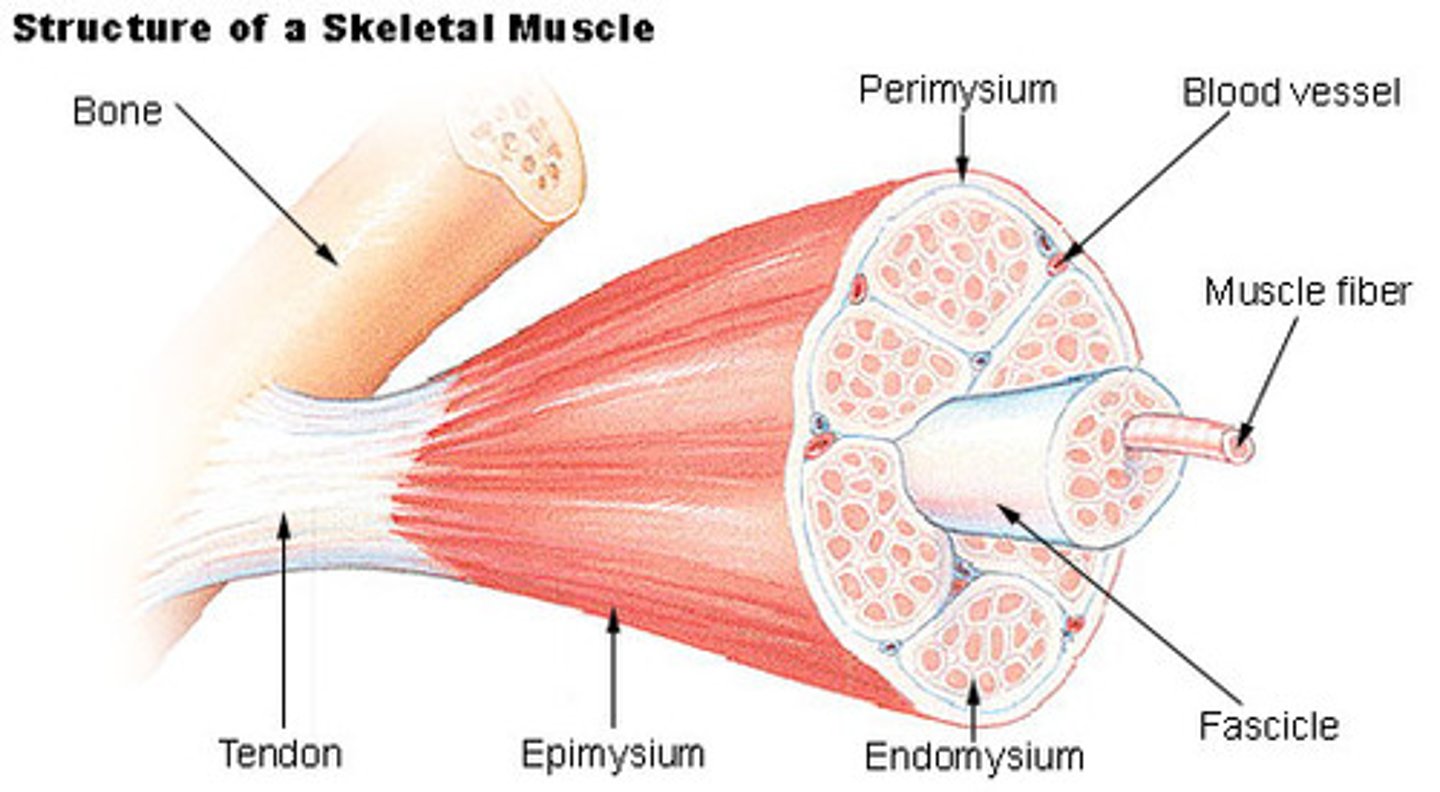
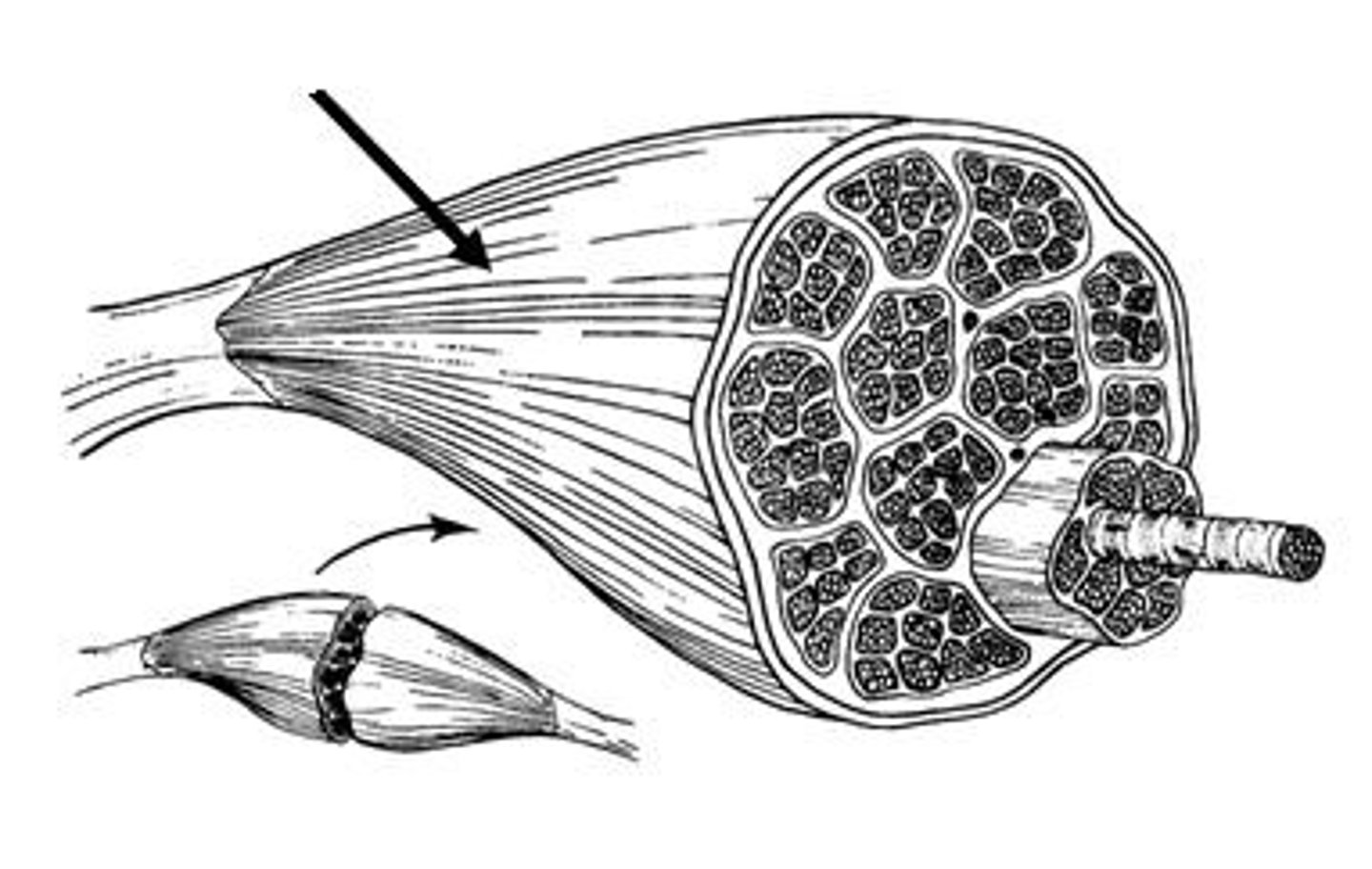
Epimysium
Membrane that wraps around the entire skeletal muscle
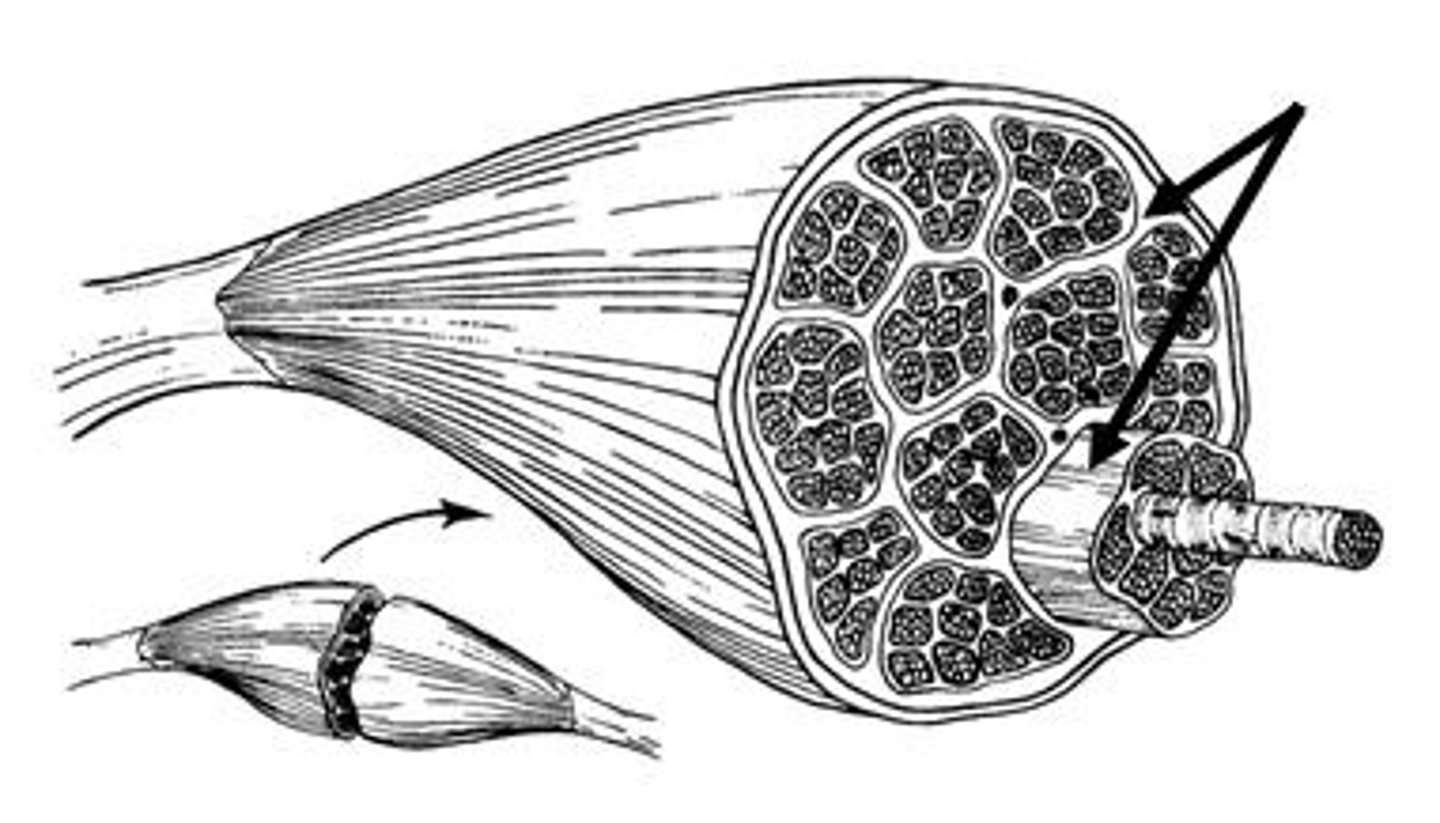
Perimysium
Membrane that wraps around a fascicle
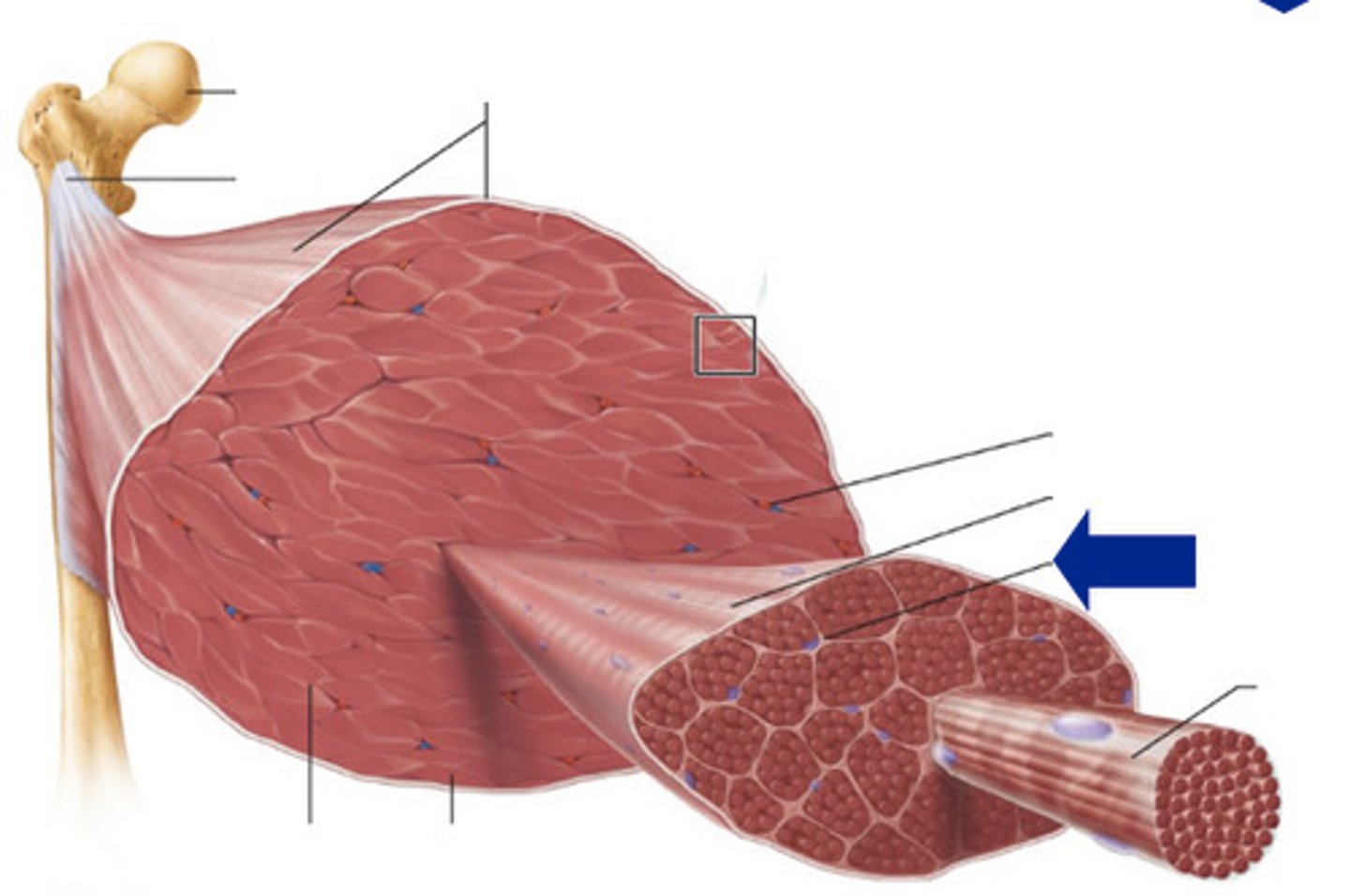
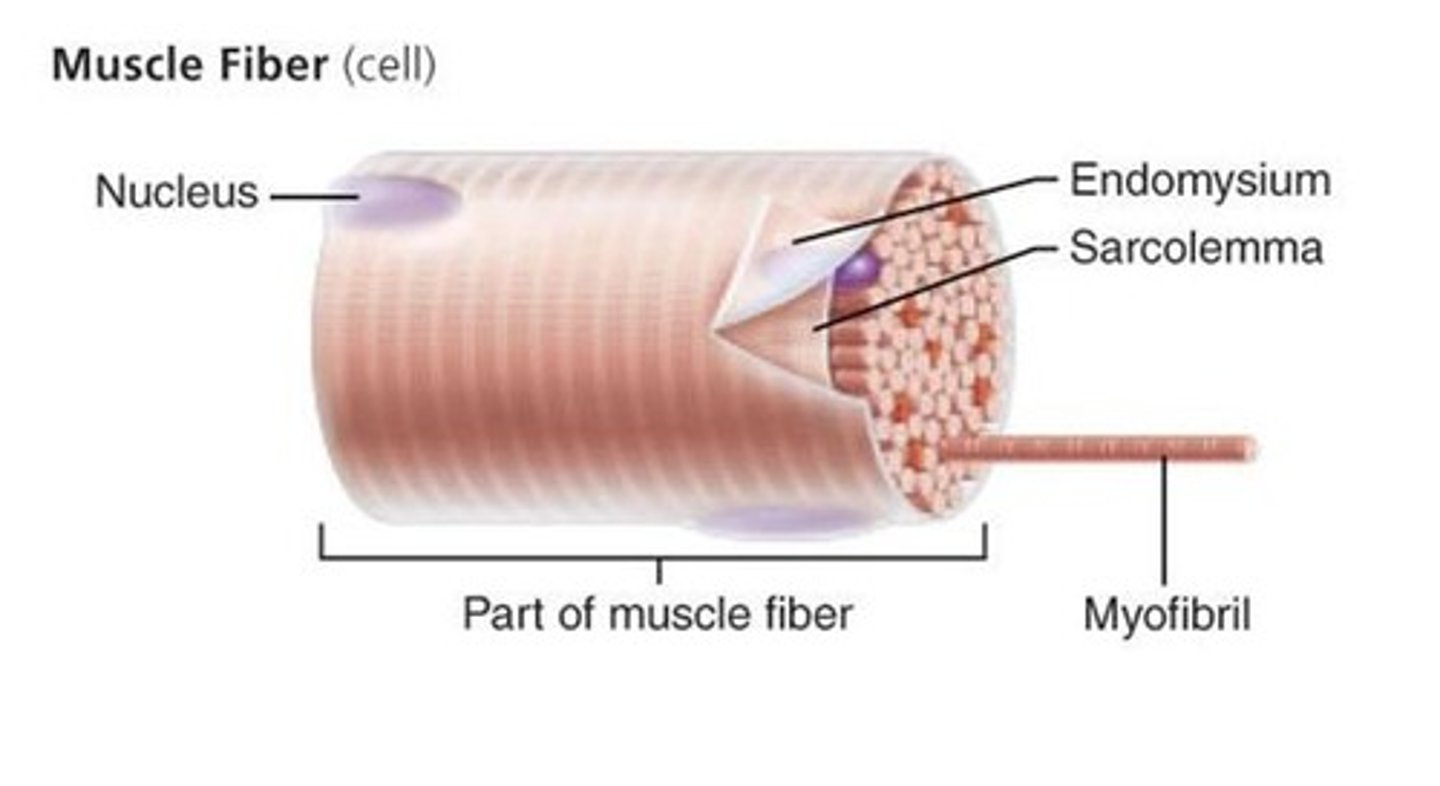
Endomysium
Membrane that is found within a fascicle and around muscle fibers
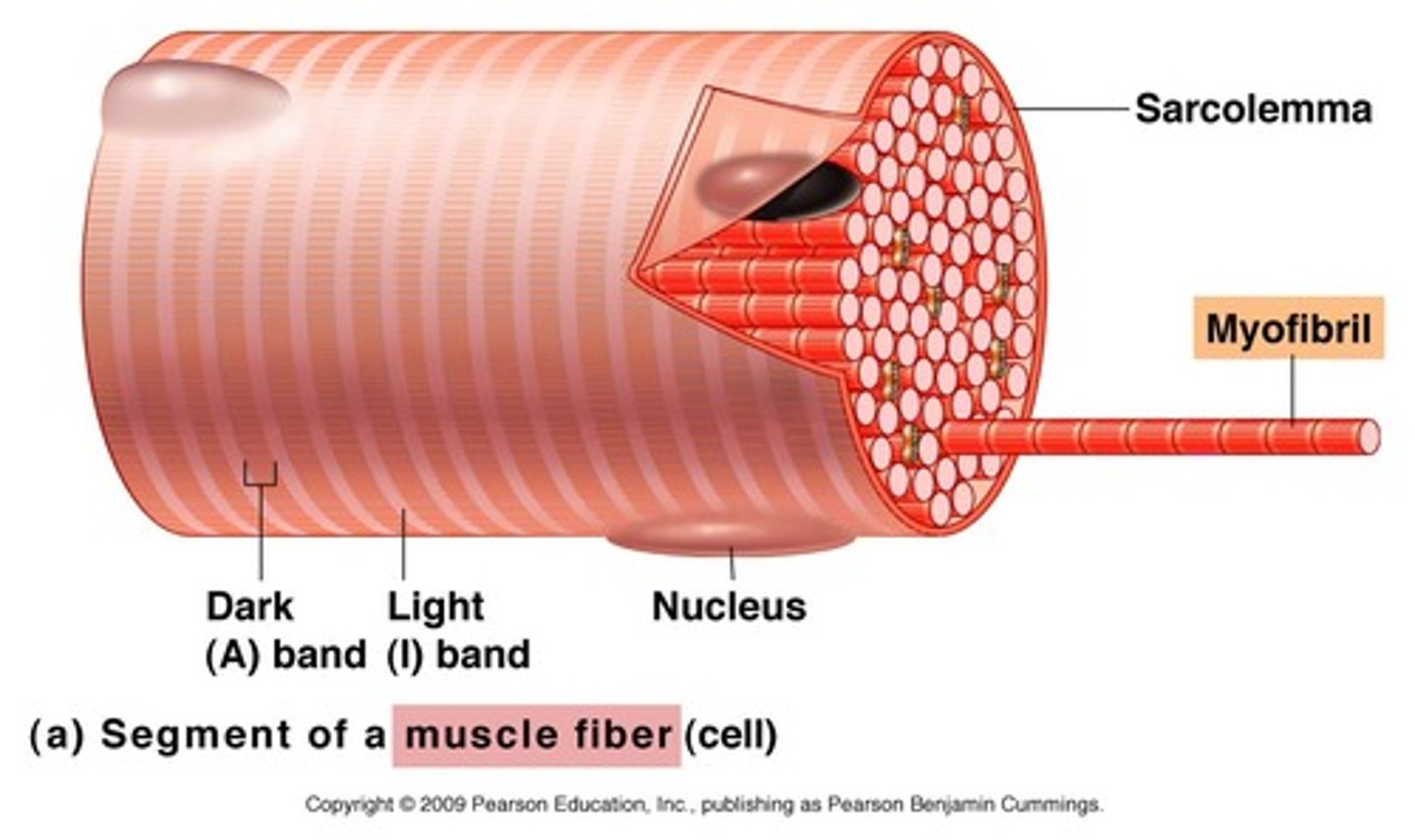
Sarcolemma
The plasma membrane of a muscle cell
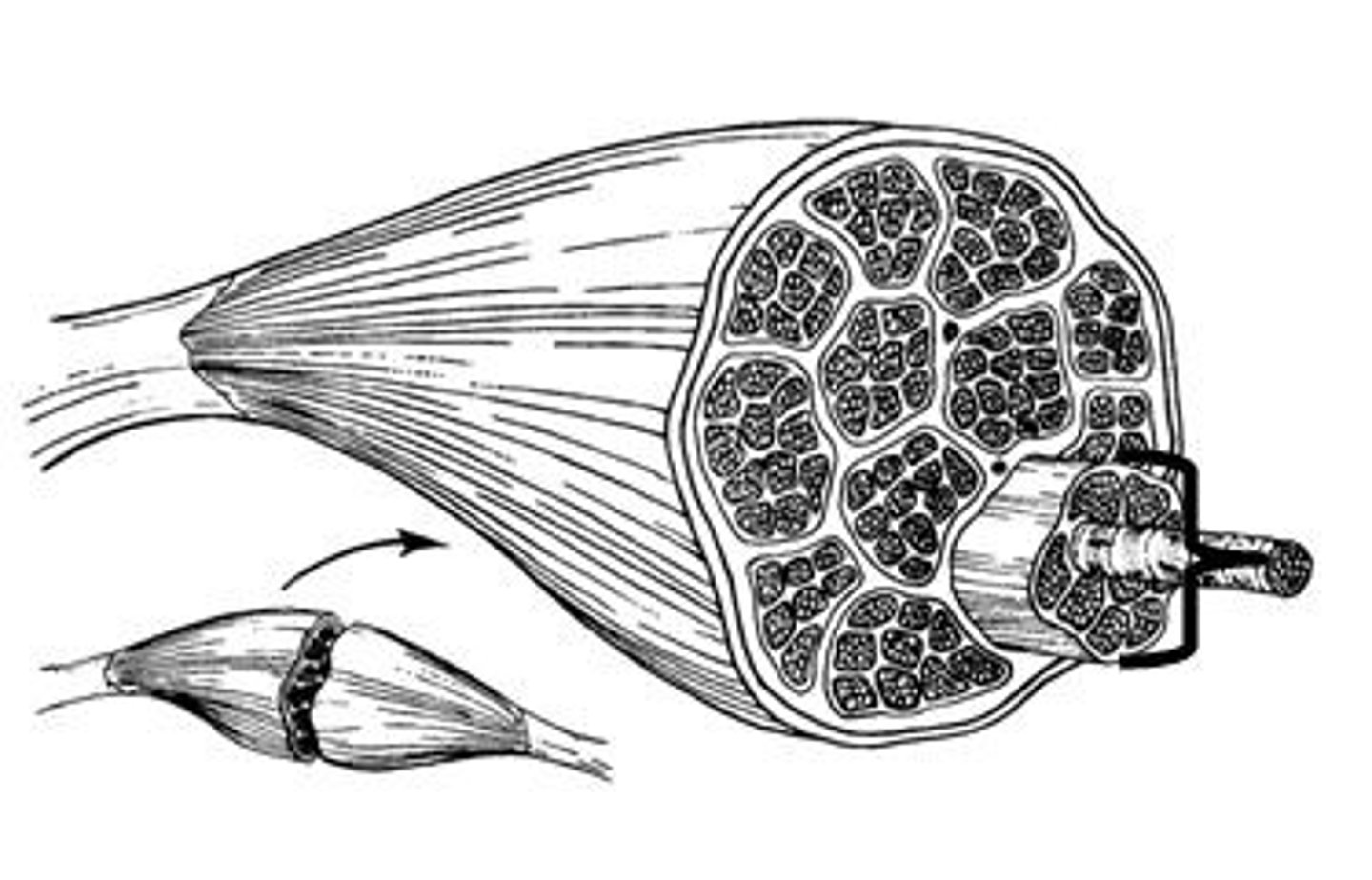
Fascicle
Consists of bundles of muscle fibers
Muscle Fiber
Consists of bundles of myofibrils; also called a muscle cell
Myofibril
Consists of bundles of myofilaments
Myofilaments
The smallest unit of hierarchy of skeletal muscle tissue; examples includes myosin and actin. Bundles of myofilaments make up myofibrils.
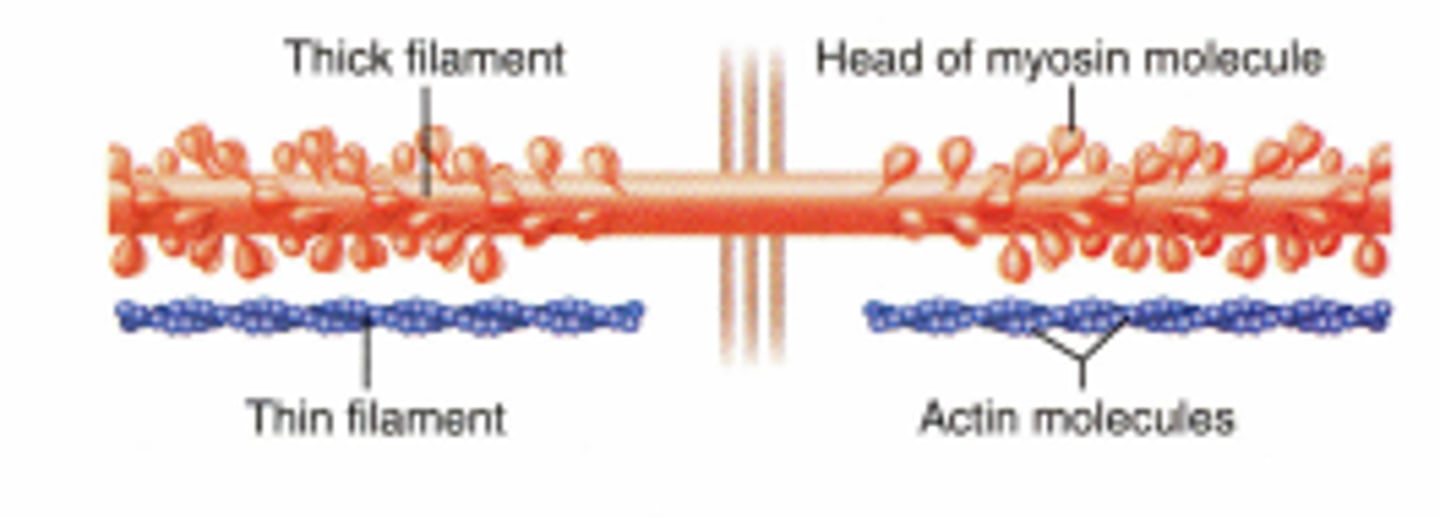
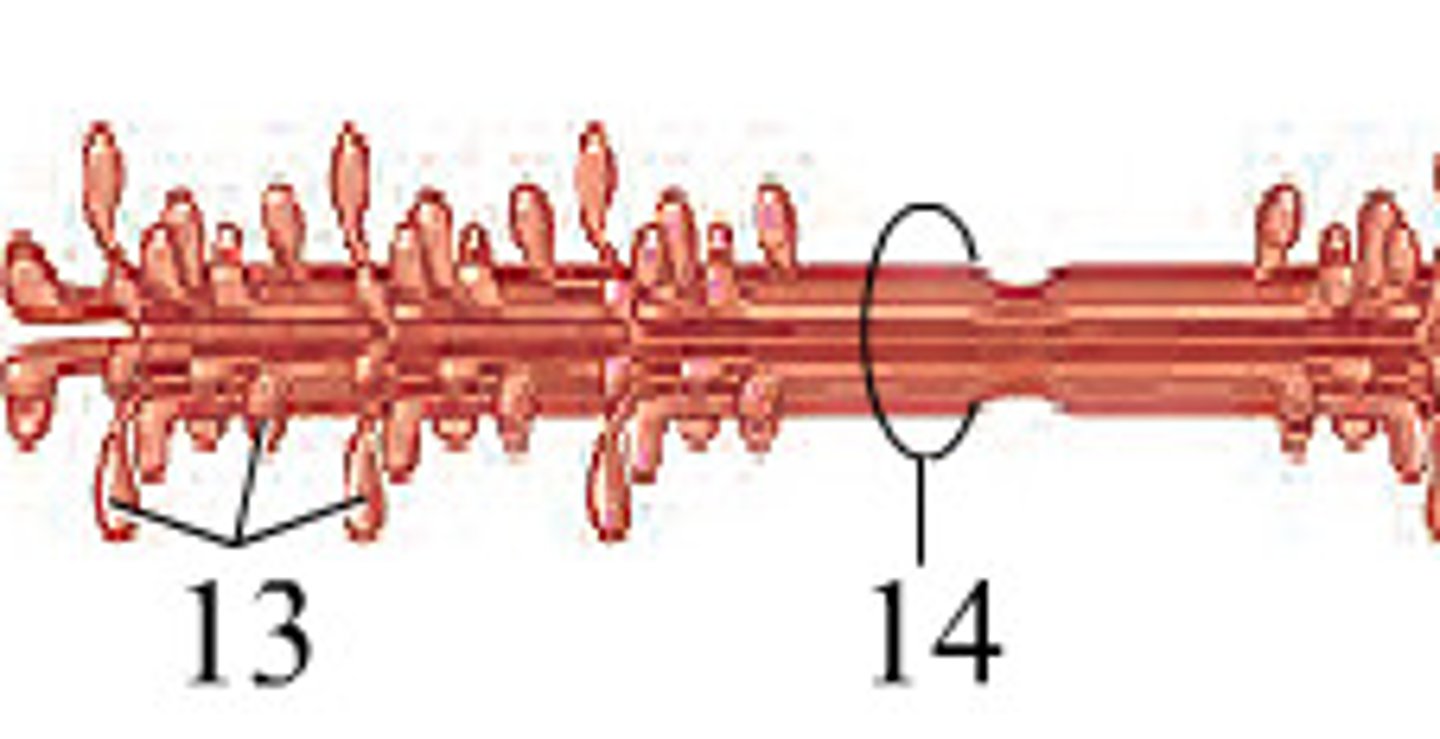
Myosin
Thick myofilament; consists of golf club-like heads that bind to actin
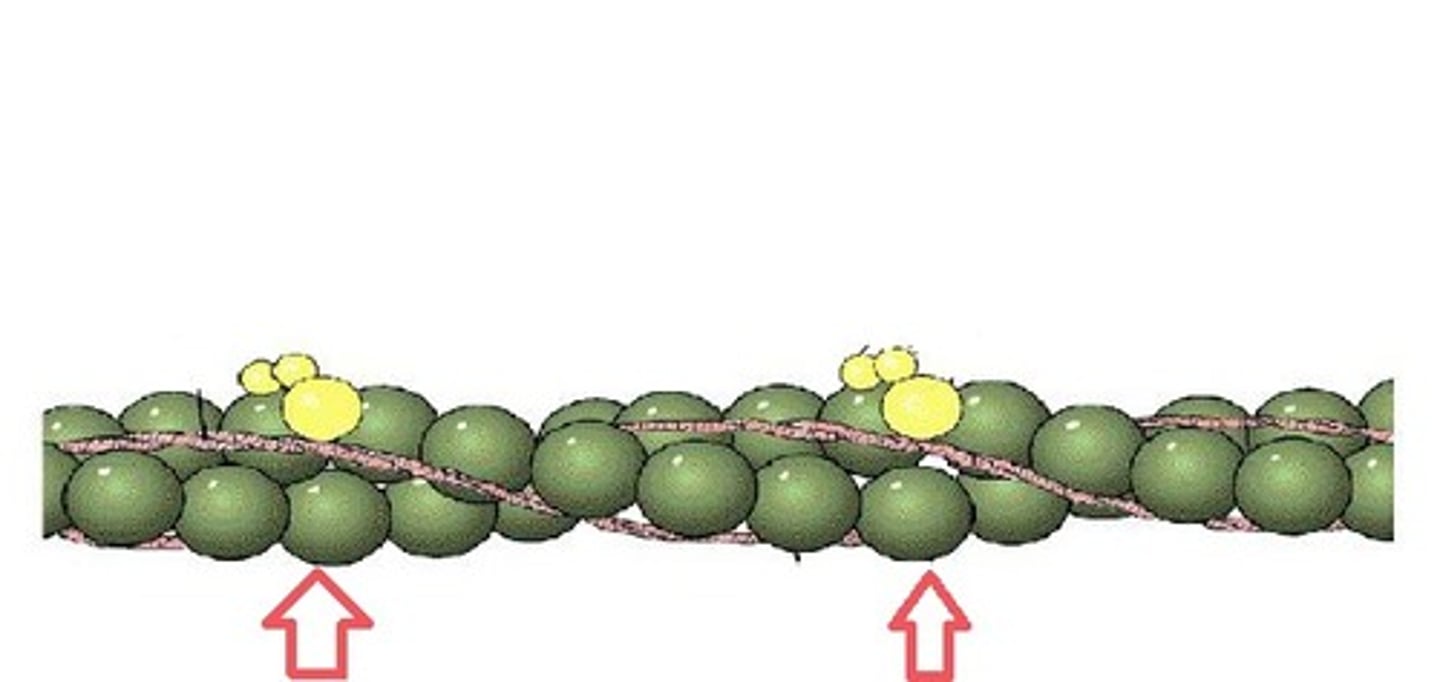
Actin
Thin myofilament; contains two compounds (troponin and tropomyosin)
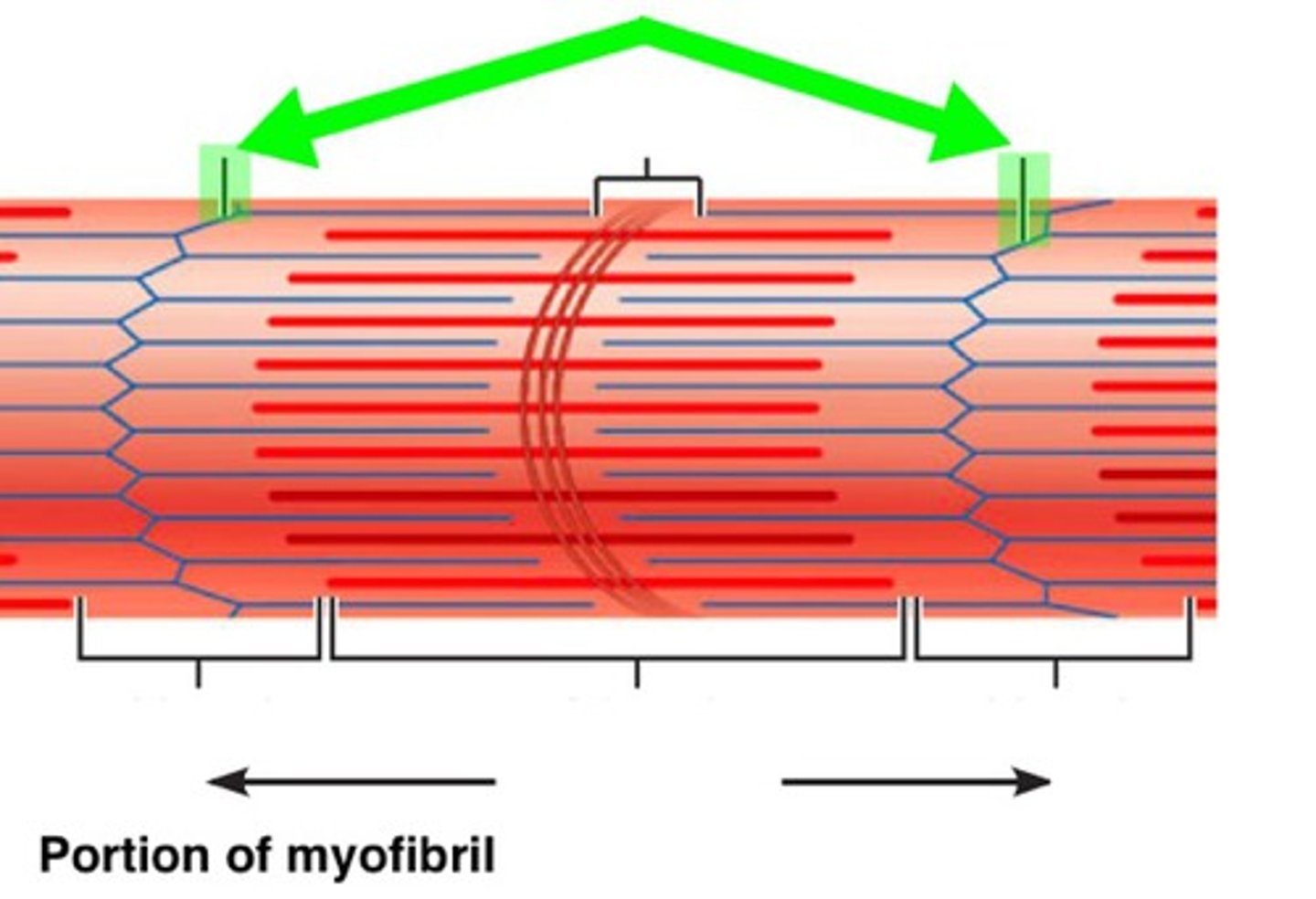
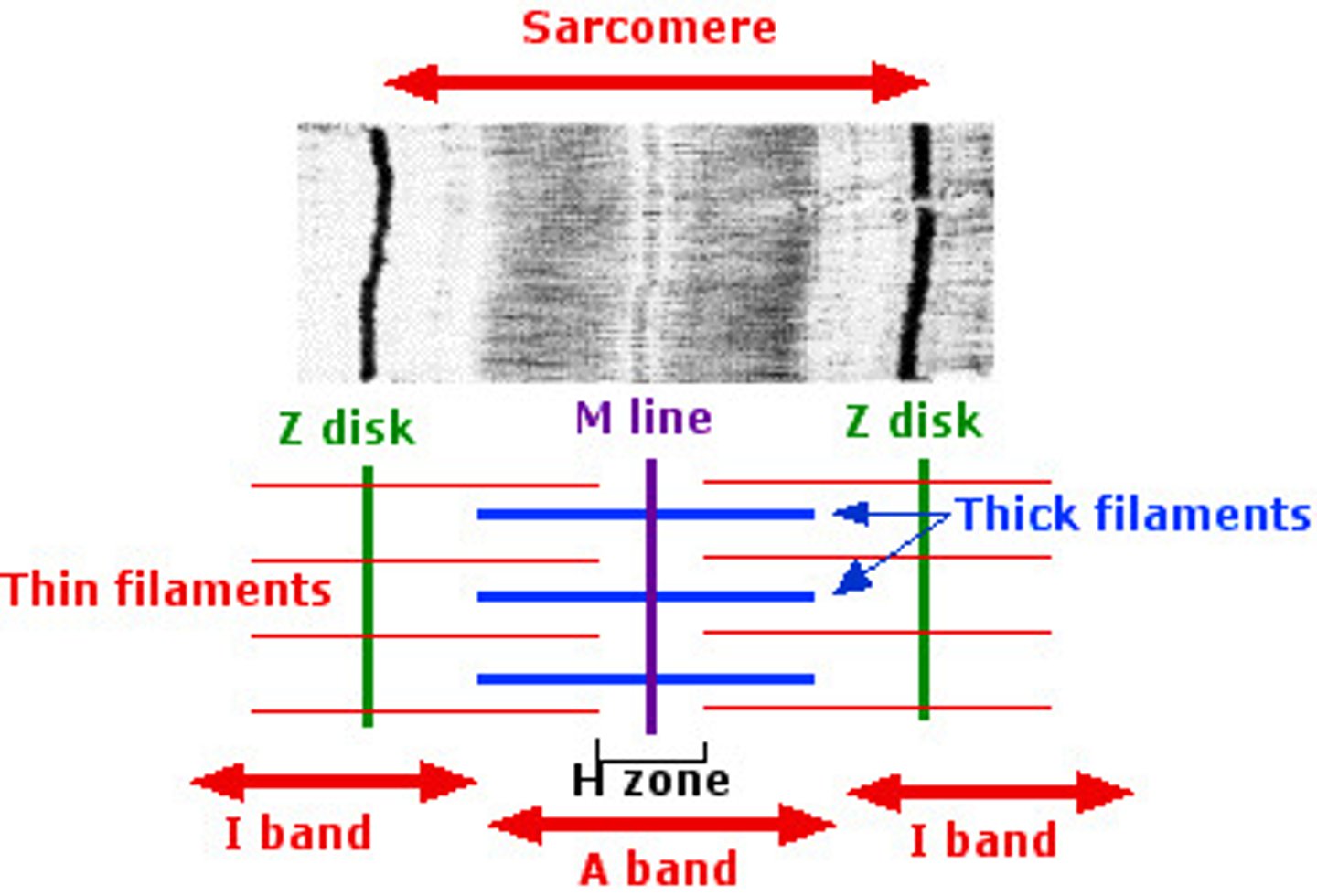
Sarcomere
The single contractile unit of muscle tissue; the distance from one Z line to another Z line
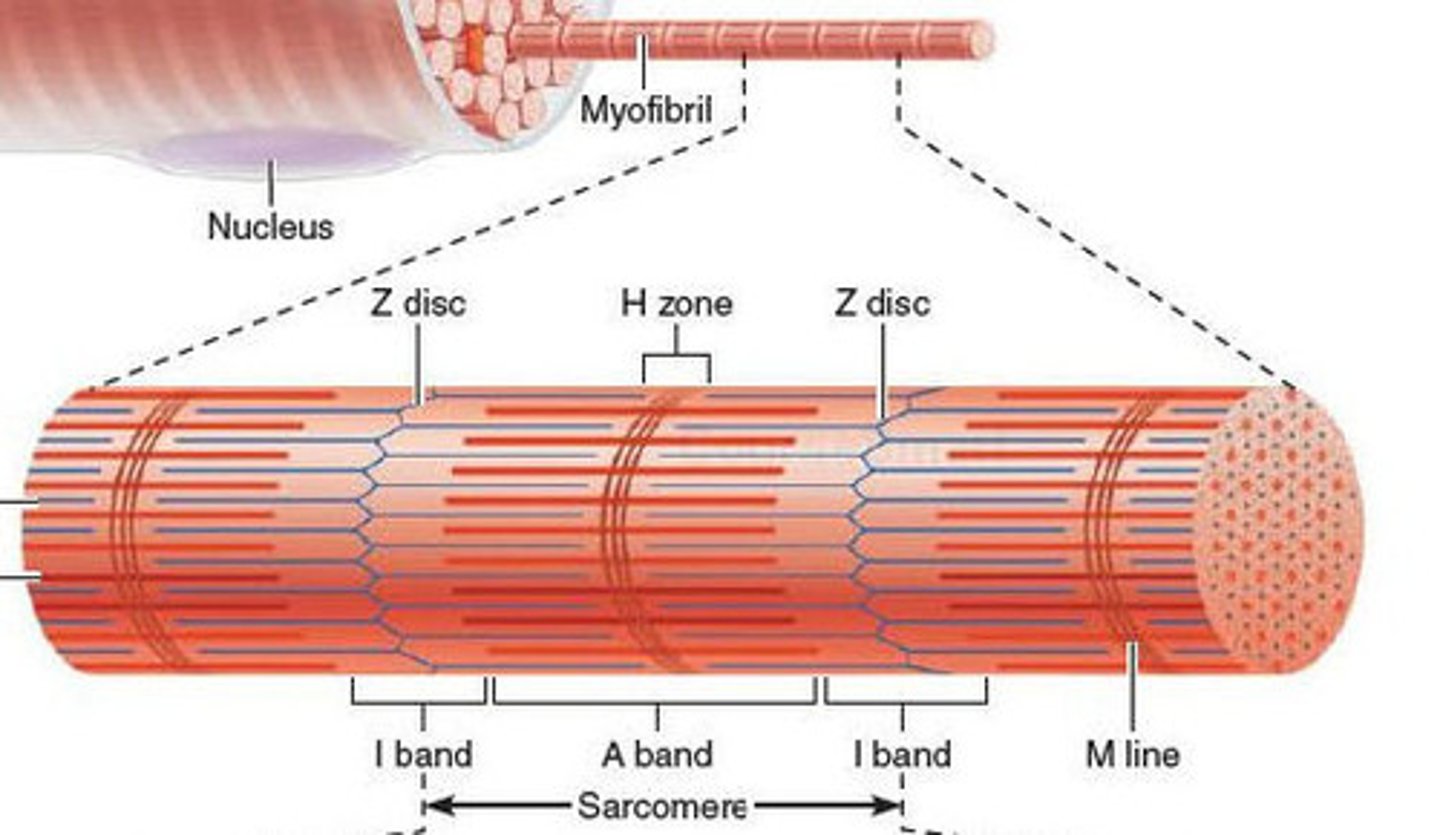
I band
Area that only contains actin filament; also called the Light Bands
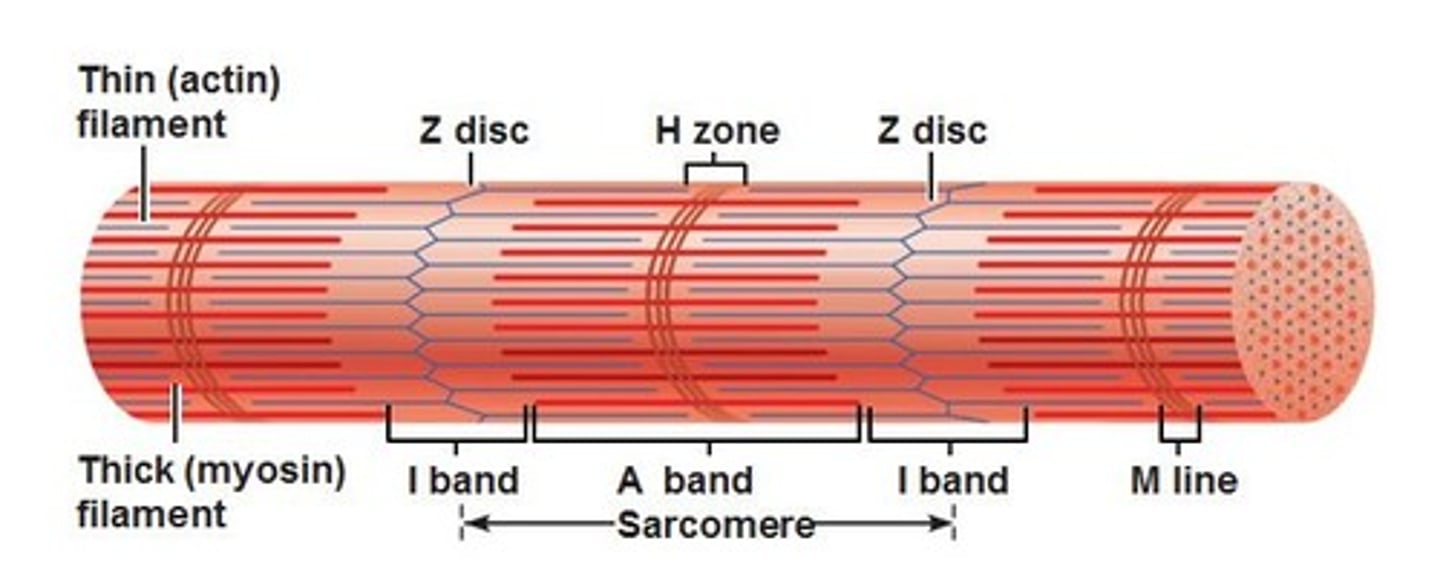
A band
Area that contains actin and myosin filaments that overlap; also called Dark Bands
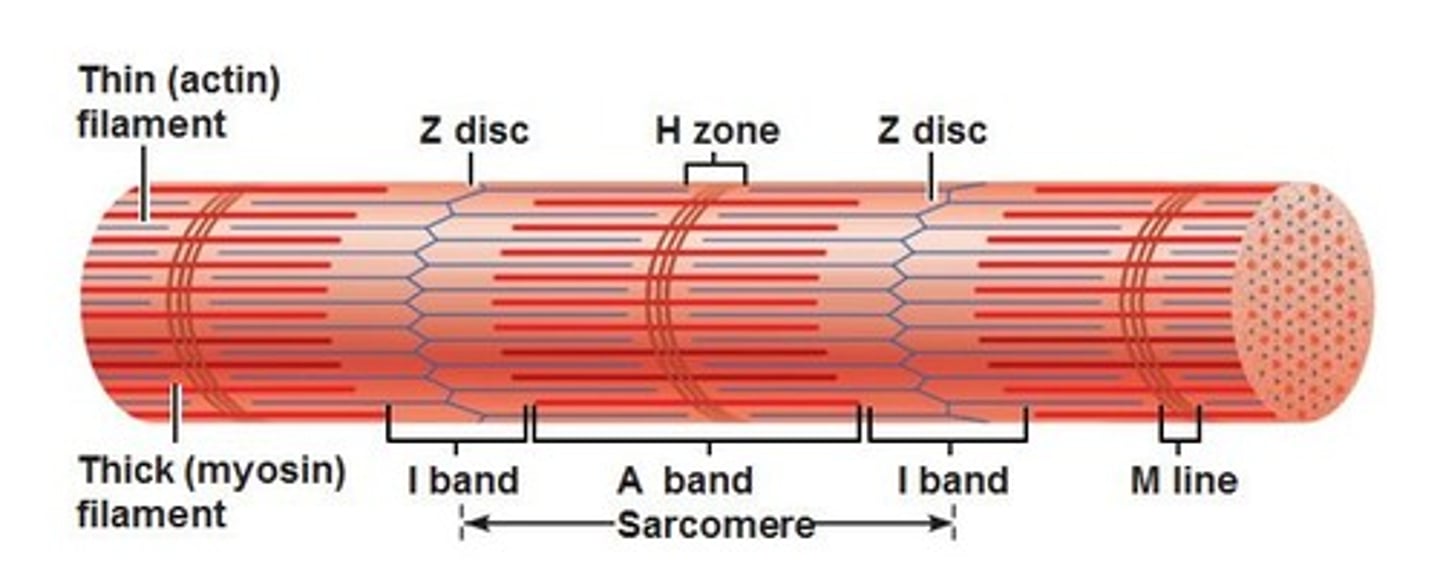
H zone
Area that only includes myosin filament (#7)
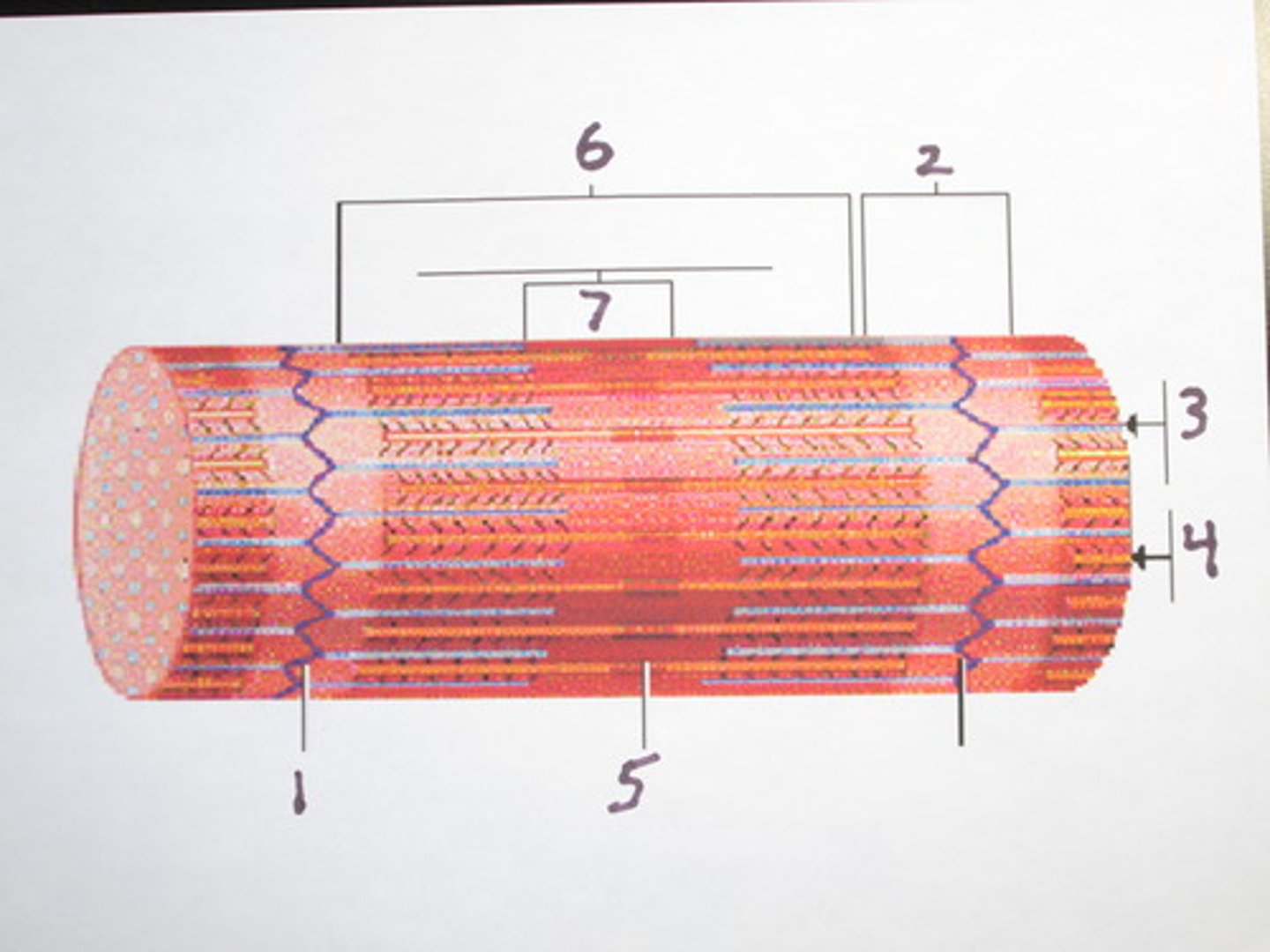
Z line
Attachment site that serves to anchor actin filaments in place
M line
Attachment site that serves to anchor myosin filaments in place
List the hierarchy of skeletal muscle tissue from smallest to largest
Myofilament, sarcomere, myofibrils, muscle fibers, fascicles, the entire skeletal muscle