zoology ch.3 phyla of uncertain affinity
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Placozoa, Ctenophora, Rhombozoa, and Orthonectida are considered phyla of uncertain affinity because
their phylogenetic positions within the animal kingdom are debated, with molecular and morphological data sometimes conflicting on their evolutionary relationships to other groups
placazoa moving mechanisms
ciliary gliding
Trichoplax adherens
discovered in a saltwater aquarium in 1883
placozoa are thousands of cells organized in
a double layer, an upper epithelium and a lower epithelium
what orientation do placozoas have
Dorsal-ventral orientation
in placozoa, dorsal cells are
flattened, monociliate with lipid droplets
in placozoa, ventral cells are
columnar with NO lipid droplet
in placozoa, ventral cells can
invaginate (feeding?)
placozoa have mesenchymal middle layer
with amoeboid cells in gel matrix
placazoa perform asexual reproduction via
binary fission
placazoa are assume to have sexual reproduction because
eggs have been seen
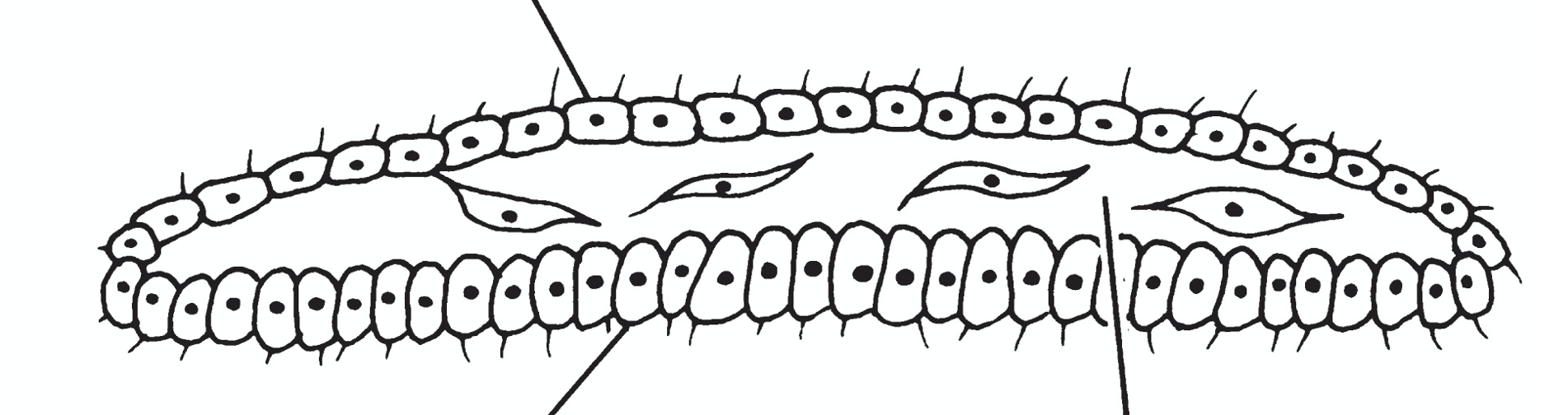
what is depicted here
a placozoa
phylum Ctenophora are coomonly called
comb jellies
ctenophores have Ctetnes, meaning they have
comb rows
ctenophora germ layers
Diploblastic, but maybe triploblastic
in ctenophores musculature is formed by
mesenchymal tissue
some ctenophores have
colloblasts
ctenophores are the first phylum to have
anuses
ctenophores have how many anal pores
2 anal pores
ctenophores have a nervous system that is compromised of a
nerve net
ctenaphores are more complex than
cnidaria
ctenophores do not have which of the following systems
respiratory, excretory or circulatory
ctenophores have no alternation of generations, meaning they are
monomorphic
monomorphic
existing in one form (little to no morphology)
ctenophores are monoecious meaning they are
hermaphrodites (having both the male and female reproductive organs in the same individual)
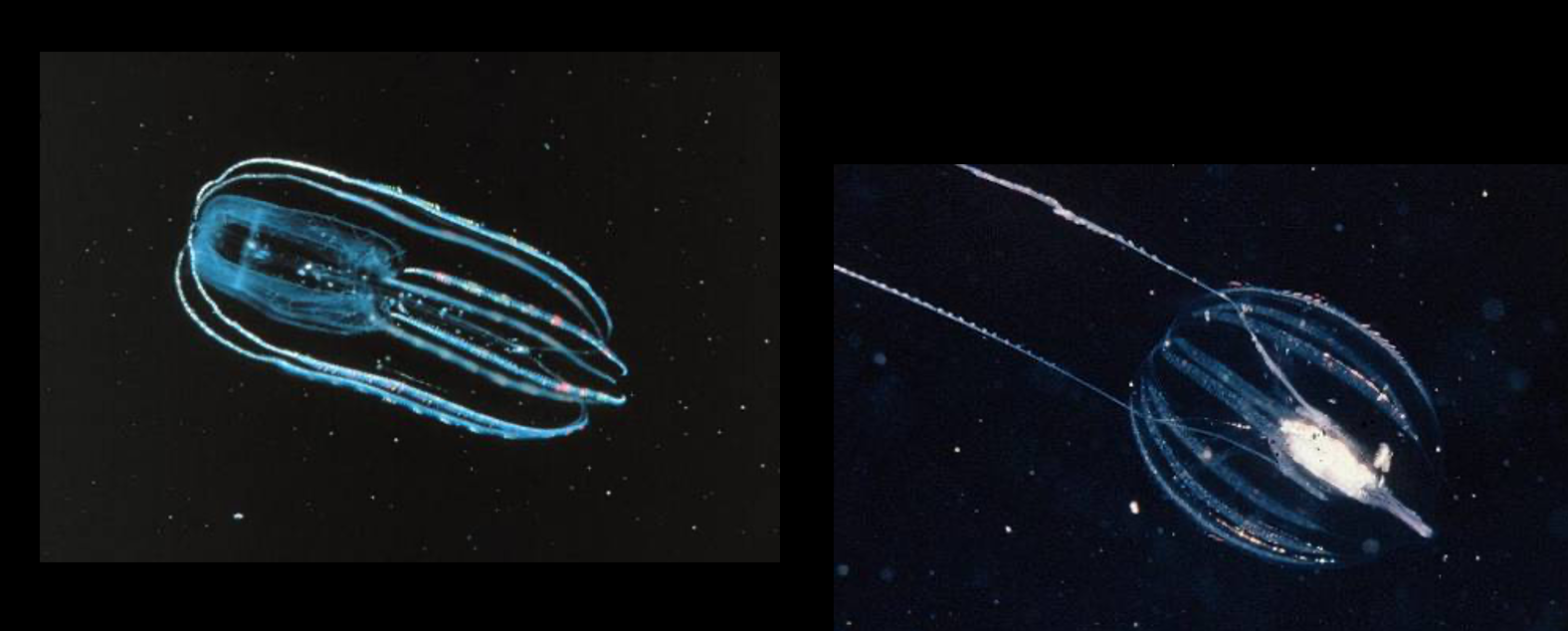
what is depicted here
phylum ctenophora (comb jellies)
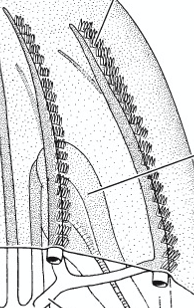
what is depicted here
ctenophores comb rows
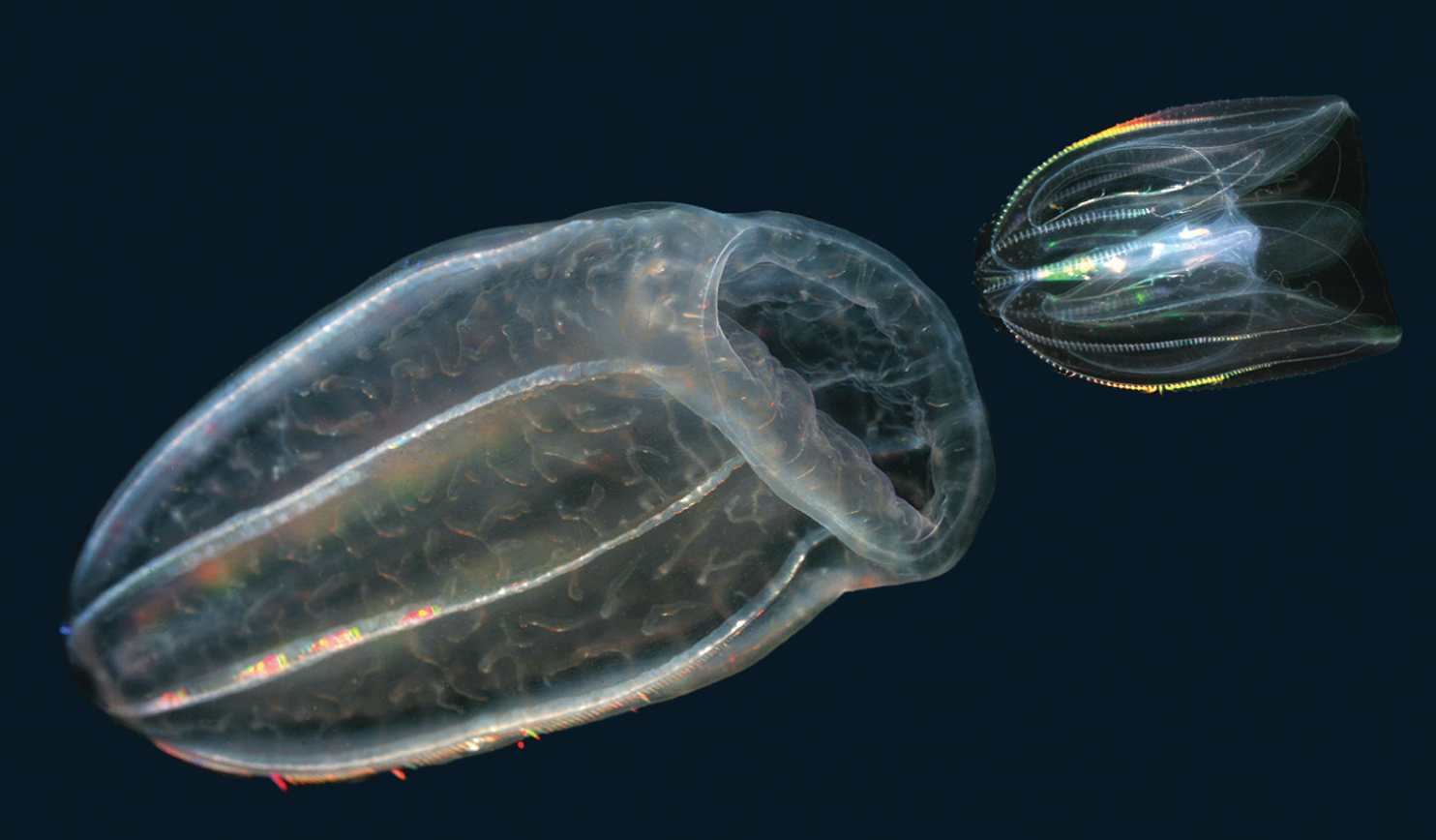

ctenophores are various carnivores, meaning
they would eat each other
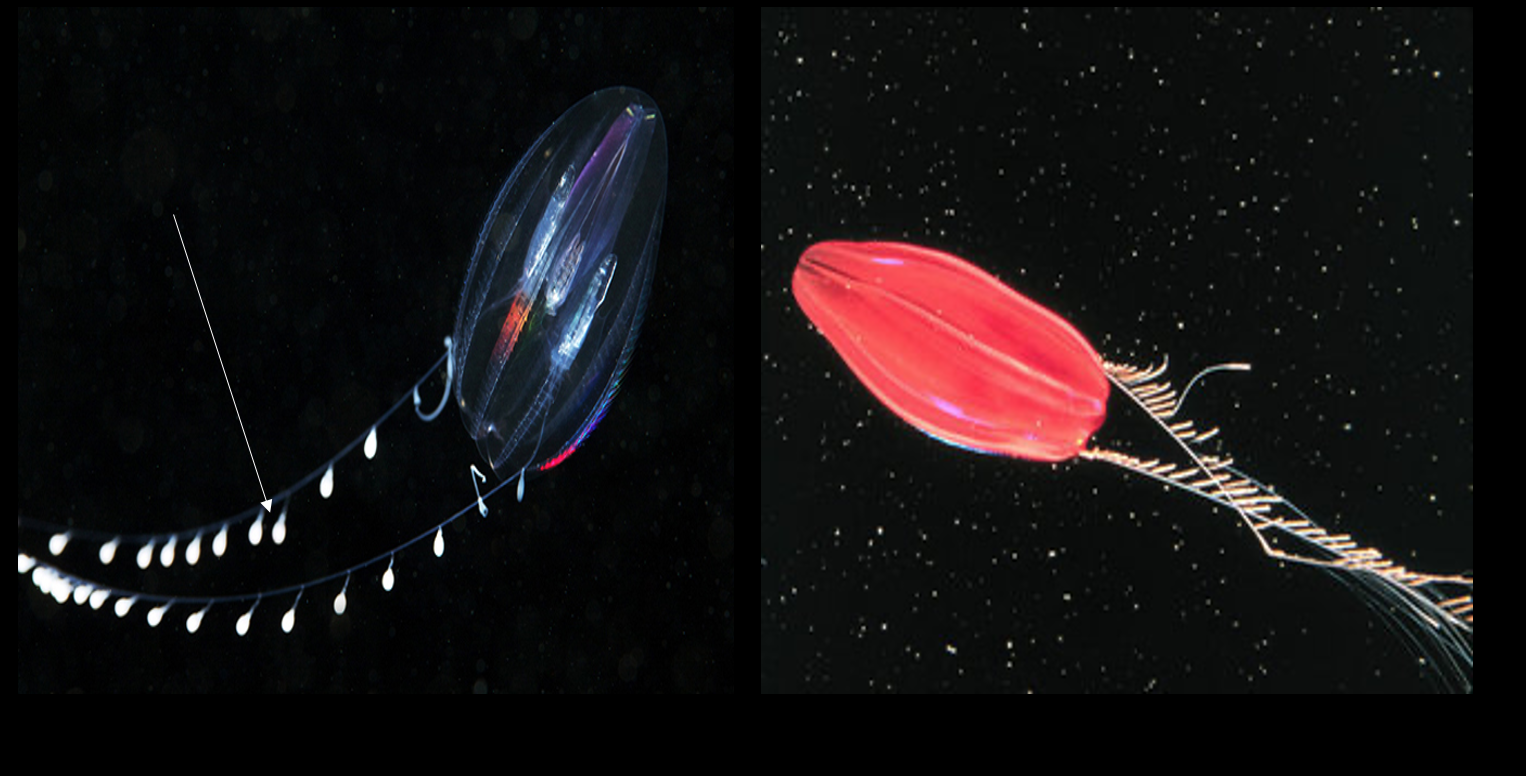

what is the arrow signaling to
Ctenophora colloblasts
what is the function of colloblast in ctenophora
prey capture
grade mesozoa was formally
a phylum
grade mesozoa is now divided into which two phylums
Orthonectida, Rhombozoa
grade mesozoa was considered the “missing link”
between the protozoans and metazoans
the organization of the grade mesozoa is very
simple
why is the organization of grade mesozoa simple
it includes ciliated, minute, worm-like organisms
grade mesozoa is encompassed with how many cells
20-30 cells only in 2 layers
grade mesozoa is compromised of all _ of marine organisms
endoparasites (live inside a host's body and can cause symptoms including diarrhea, malnutrition, and organ damage)
Phylum Orthonectida are poorly
understood
Phylum Orthonectida have how many families
2 with around 20 species
Phylum Orthonectida body structure
single layer of ciliated outer cells surrounding a mass of sex cells
Phylum Orthonectida are dioecious, meaning they are
gonochoristic
gonochoristic
species with separate sexes, where each individual is either male or female and remains that sex throughout its life
Phylum Orthonectida have hosts meaning that they are
parasites
Phylum Orthonectida that swim freely in hosts
Echinoderms, Annelids, Platyhelminthes (flat worms), Bivalves
Phylum Orthonectida and Phylum Rhombozoa reproduction strategy
sexually and asexually
Phylum Orthonectida reproduction starts with
internal fertilization
Adults leave host and sperm leaves male and penetrates female
in Phylum Orthonectida, after internal fertilization
Zygote is ciliated larva and leaves female to find new host
in Phylum Orthonectida, after larva found a new host
Larva loses cilia when enters host and becomes a syncytial plasmodium
in Phylum Orthonectida, after larva becomes a syncytial plasmodium
Plasmodium breaks up into new adults
Phylum Rhombozoa is also called
Dicyemida
in Phylum Rhombozoa asexual found in
immature/juvenile hosts (Cephalopods)
in Phylum Rhombozoa, asexual forms are
nematogens
in Phylum Rhombozoa, asexual organisms produce
vermiform larva
in Phylum Rhombozoa, organisms produced by asexual organisms undergo
direct development and form more nematogens
in Phylum Rhombozoa, sexual organisms produce
infusiform larva
in Phylum Rhombozoa, larva released in
urine of host
in Phylum Rhombozoa, products of sexual organisms parasitize
very few species of Cephalopods