C2.2.8 - C2.2.16 : HL (Neural Signalling)
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Depolarization
Voltage-gated sodium channels open, and the influx makes membrane potential more positive
The area causes next area to depolarize → propagation of action potential through axon
“self propagation”: impulse in one dendrite → action potential through axon → synaptic terminal
Threshold potential
Minimum change and membrane polarity for an action potential to occur
Usually starts when first receptor neuron (converts physical stimulus into first action potential; e.g: Retina = minimum light) begins chain of events
All-or-nothing action of depolarization
Refers to principle that if minimum threshold potential is reached (-55mV), then full action potential reached; if not, nothing happens
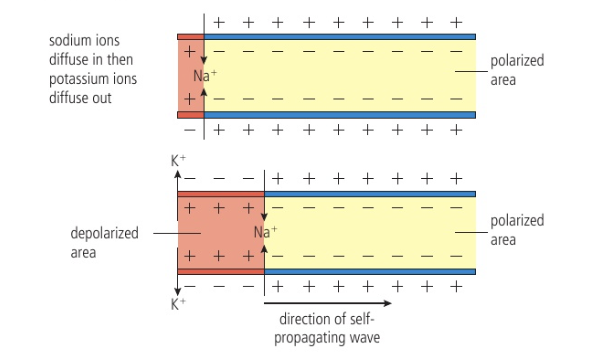
Repolarization
voltage-gated K+ channels open and K+ diffuse out of axon (creates negative value)
Sodium-potassium pump actively transports Na+ and K+ across membrane
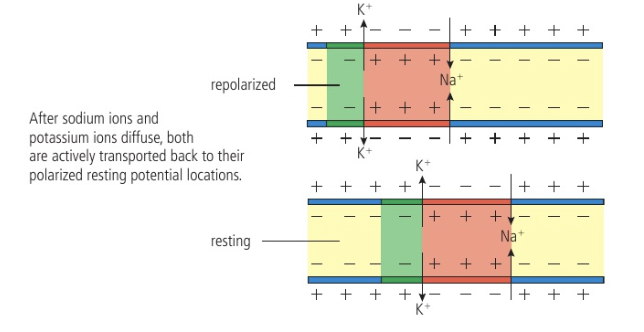
Refractory period
Period of recovery after depolarization during which neuron is unable to respond to additional stimulation
Oscilloscope
An electronic test instrument to measure membrane potential across neural membrane
Data is displayed as a graph with time (in milliseconds) on x-axis and membrane potential (millivolts, mV) on y-axis
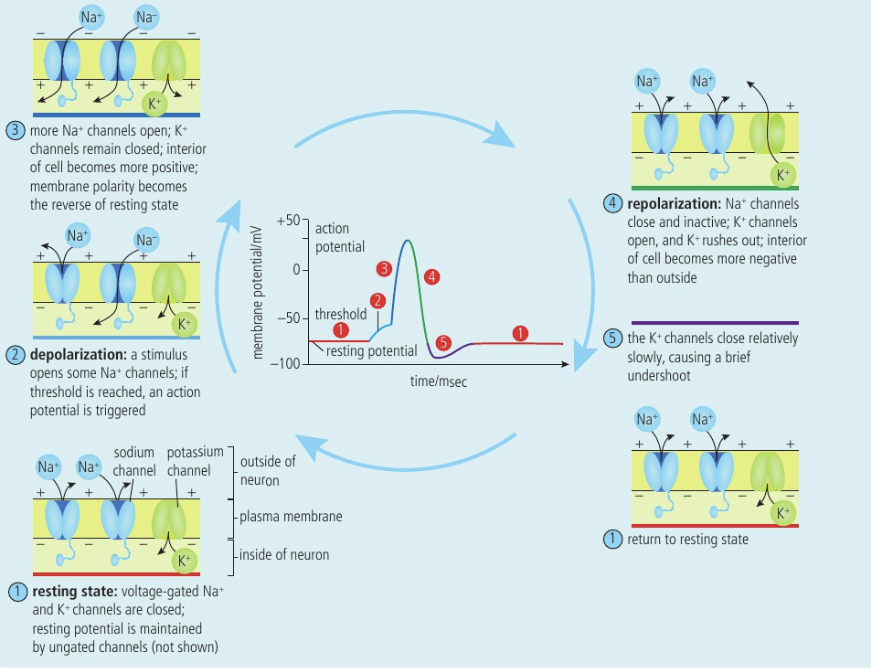
Main oscilloscope stages
Resting state: voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels are closed; resting potential is maintained by ungated channels
Depolarization: a stimulus opens some Na+ channels; if threshold reached (-55mV), an action potentially triggered
More Na+ channels open; K+ channels remain closed; interior of cell becomes more positive; membrane polarity becomes the reverse of resting state
Repolarization: Na+ channels close and inactive; K+ channels open, and K+ rushes out; interior of cell becomes more negative than outside
K+ channels close relatively slowly, causing brief under shoot
Return to resting state
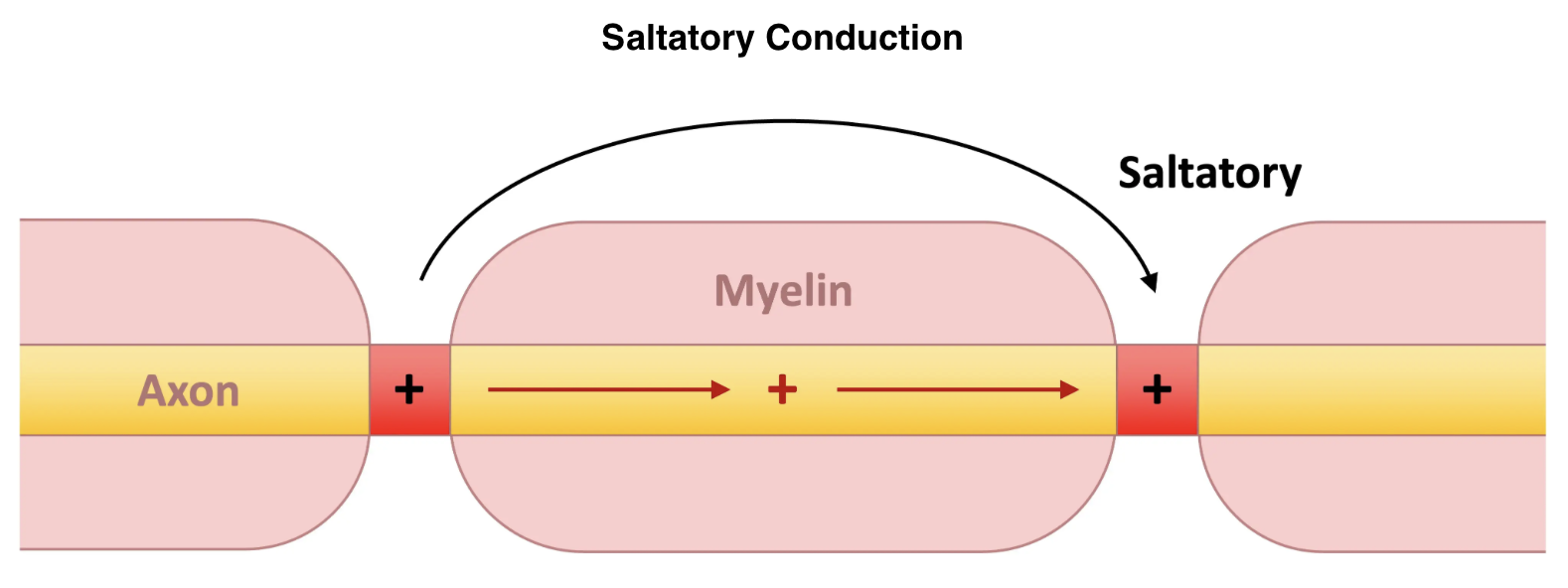
Salatory conduction
Name given to phenomenon where an action potential jumps from one node of Ranvier to the next as an impulse progresses along a myelinated axon
Allows much faster, transmission, velocity because ion movements happen only at the notes → depolarization, and repolarization only happen at nodes
Exogenous chemicals
Chemicals produced outside the body
Endogenous chemicals
Chemicals produced inside the body
2 Examples of exogenous chemicals
Neonicotinoid insecticides
Cocaine
Neonicotinoid insecticides (as an example of exogenous chemicals)
Class of insecticides chemically similar to nicotine and structurally similar to acetylcholine
Binds to the postsynaptic receptor of acetylcholine irreversibly and cannot be decomposed by acetylcholinesterase
Ion channels stay open, causing over stimulation of neurons → continue depolarization, leads to convulsions and death
Insects have higher proportion of acetylcholine receptors than mammals → effective pesticide
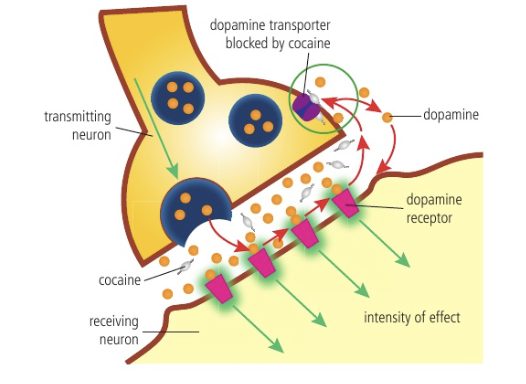
Cocaine
Drug that prevents the removal of docking from synapse and stimulates dopamine-releasing neurons to release more dopamine
Usually dopamine is removed by dopamine transporter (a protein)
Cocaine binds to dopamine, transporter, and blocks removal → dopamine floods brain
Repeated use can cause reward pathways to alter, reinforcing addiction
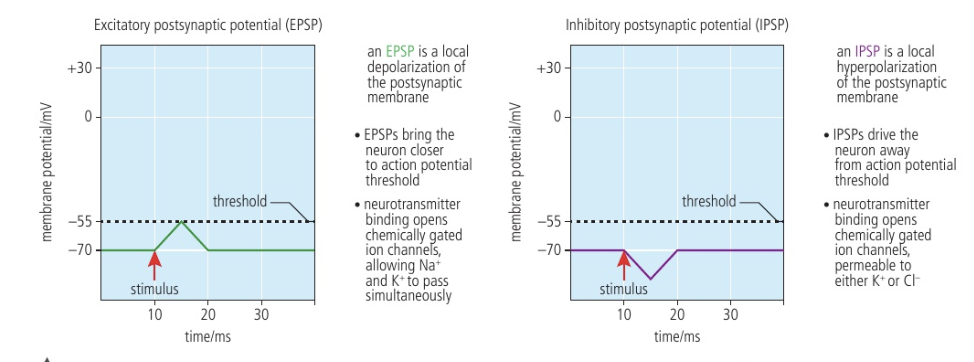
Excitatory neurotransmitters
Generate action potential by increasing membrane, permeability of postsynaptic neuron to positive ions (e.g: acetylcholine)
Increase permeability to Na+ causes more Na+ to diffuse in postsynaptic neuron
Neuron depolarizes due to positive charge inside axon → impulse carried forward
Inhibitory neurotransmitters
Inhibit action potential by hyperpolarization
Makes the inside of neuron more negative because Cl- moving in or K+ moving out
Results in neuron, being hyperpolarized, allowing inhibition of impulse
→ Binds to a specific receptor
(e.g: GABA)
Summation of inhibitor
If the sum of signals is inhibitory, then impulse is not carried forward
If some of signals is excitatory, the signal is carried forward
Class of sensory receptors
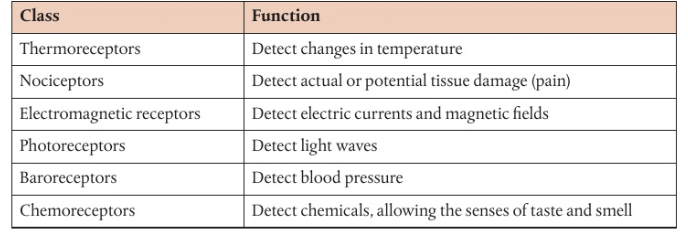
Nociceptors
Sensory receptors of pain
Have chemical chemicals for positive ions that open in response to stimuli like temperature, chemicals…
If threshold potential is reached → action potential generated and conducted to CNS for interpretation
Hot chili have Capsaicin → combined to nociceptors opening Ca2+ channels, causing impulse
Reductionism
Approach that reduces the complex phenomenon of organisms to the interactions of their parts → some of parts makes organism
Emergence
Believes that the hole is greater than the sum of parts