Intercepted Solar Irradiance
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
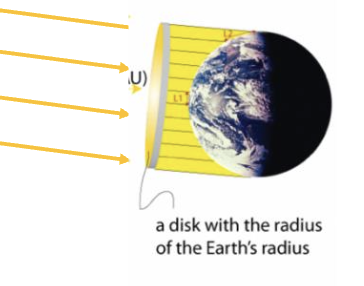
What happens to the sun’s rays that hit the Earth’s terrestrial disk?
Since the sun is at a very large distance away they are practically parallel to one another.
Therefore the projection from the sun’s rays are?
a circular disk of radius equal to the Earth’s radius.
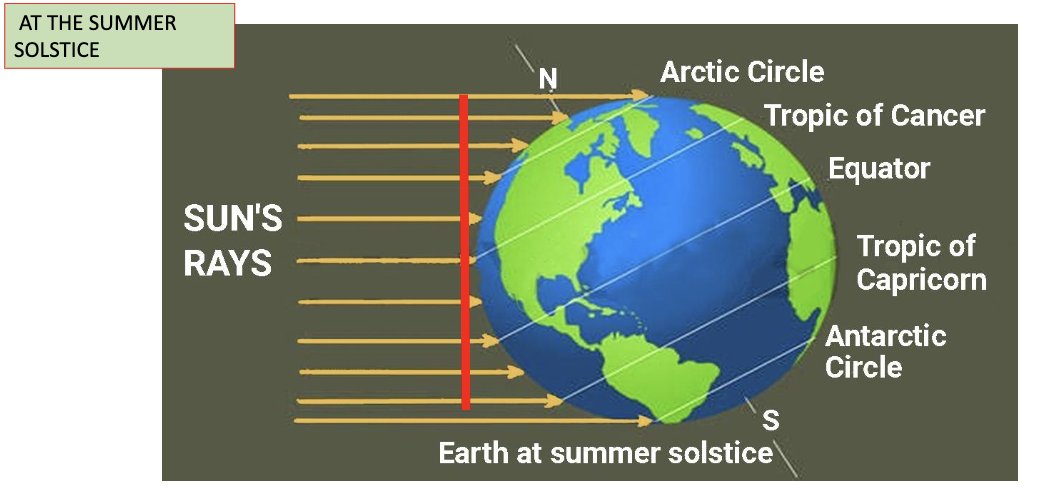
At the summer solstice that “disk” is:
tangent to the tropic of cancer
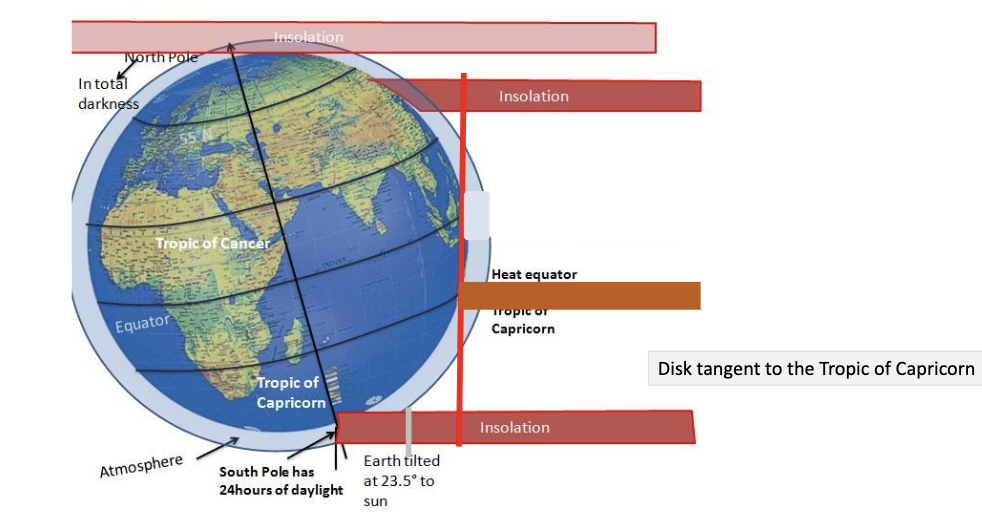
At the winter solstice that “disk” is:
tangent to the tropic of Capricorn.
Earth’s radiative equilibrium describes
that to maintain temperature constant there is no energy gain or loss due to radiation
What happens to solar radiation once it enter at the TOA of the atmosphere?
transmission, reflection, scattering and/or absorption
Outcome: Transmission
EM wave passes straight through medium
Outcome: scattering
deflection of light in all directions by air molecules, small particles, droplets etc.
Outcome: absorption
EM radiation absorbed by air molecules, aerosol particles or cloud droplets
Outcome: reflection
light sent backward by an interface between two media, such as air and water.
Detail of reflection
specular (mirror effect) or diffuse (reflection in many directions — scattering)
What happens to EM waves once they hit a terrestrial body?
they may be reflected back to space
Albedo:
represents reflectivity of a surface to shortwave radiation… gives a ratio alpha

What does this albedo value depend on?
Depends on type of surface and on angle of solar irradiance
What is the albedo of the planet earth at the top of the atmosphere?
About 30%
What is the solar irradiance budget?
balance between the amount of energy the earth receives from the sun and the amount it emits back into space
Solar irradiance budget distribution:
~30% reflected/scattered back to space, ~19% absorbed by air molecules and clouds, ~ 51% absorbed by surface
Radiative equilibrium requirement considering the terrestrial system’s mean albedo α where:
α x ETOA is reflected back to space and (1-α) x ETOA enters the terrestrial system
What does there no energy gain or loss due to radiation do to Earth’s temp?
It ensures that the average temperature of Earth does not change over time, this means that the outgoing and incoming amount of radiant flux must be equal.
Earth’s Radiative Equilibrium Temperature (Te)
temperature that the black body Earth acquires for equal amounts of incoming and outgoing radiation
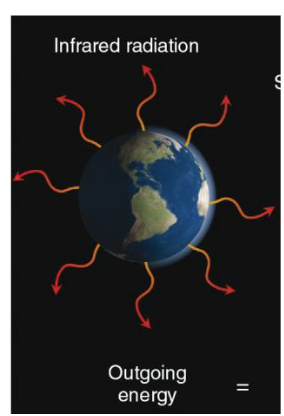
Emitted Infrared Radiation (earth)
Intercepted Solar (earth)
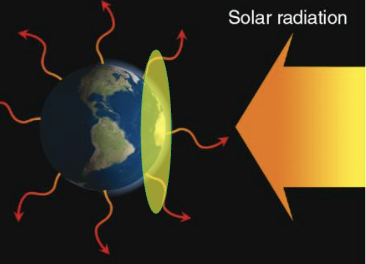
What is the total intercepted solar radiant flux by a “disk” of radius R at the TOA?
given by: S0 x (πR²)
The solar radiant flux (So) is absorbed by what?
absorbed per 1m² by the circular disk… which is the projection of the sunlit hemisphere on a plane perpendicular to the sun rays
A black body emits σTe4 W from every:
1m², meaning that a spherical surface of radius Re will emit as a black body a total radiant flux of σTe4 x (4π)W
Note*, that the emission to space
is from both hemispheres (sunlit and dark)
For radiative equilibrium we need:
mean absorbed radiant flux = mean emitted radiant flux
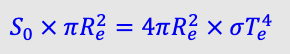
Does the atmosphere behave like a black body?
No, unlike the Earth’s surface which does. the atmosphere allows reflection, scattering, transmission (certain wavelengths) and absorption (certain wavelengths of EM waves
mirror effect
reflection back at a specific angle