Elderly
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Effects of aging on body
↓ ROM
Shrinking of vertebral discs/ ↓ height
Altered bone remodeling
↓ lean body mass and muscle atrophy
Joint degradation/ arthritic changes
↑ postural sway and ↓ balance
Foot problems
↓ ROM
seen body-wide but mostly in hips and shoulders
Shrinking of vertebral discs/ ↓ height
disc mass and vertebrate shrink/ atrophy causes a ↓ in height
Altered bone remodeling
bones don’t regenerate as quickly
explains why elderly take longer to heal
↓ lean body mass and muscle atrophy
muscle becomes fat (sarcopenia)
Joint degradation/ arthritic changes
joint pain and stiffness
osteoarthritis is most common
↑ postural sway and ↓ balance
↑ sway=↓ balance
base of support moves in front of COM=↓ balance
Foot problems
bunions, hammer toes, callouses, etc. contribute to gait problems and falls
loss of feeling in feet (neuropathy)
Older Adults
65+
Key manifestations:
Reduced physical functioning
Fragility
Deconditioning
Age-associated diseases
Result:
Loss of ability to perform ADL’s
Loss independence
Effects of Aging on Body System Functioning: Skeletal muscle
↓ musc mass by ~50% from youth to elderly
↓ muscle strength, velocity
↓ type II fibers
anaerobic fibers- allows us to move quickly (i.e. reflexes, sprinting)
Effects of Aging on Body System Functioning: Bone, cartilage, connective tissues
↓ BMD (= osteoporosis)
↓ thickness, elasticity, tensile strength
Effects of Aging on Body System Functioning: Body
composition
↓ lean mass
↑ % body fat
( fat replacing muscle= sarcopenia)
Effects of Aging on Body System Functioning: Cardiovascular
↑ arteriosclerosis (plaque build up)
= ↑ hypertension
↓ HRmax (age predicted)
↓ a-vO2 diff
↓ peak aerobic capacity
↓ a-vO2 lead to ↓ peak bc body can’t use energy efficiently
Effects of Aging on Body System Functioning: Respiratory
↑ chest wall stiffening (breathing=hard)
↑ residual volume and dead space
due to weaker muscles
Effects of Aging on Body System Functioning: Metabolic
↓ resting metabolic rate
less cal burned from breathing
↓ insulin sensitivity
insulin loses ability to function= ↑ blood sugar=↑ diabetes
↓ liver size and liver blood flow
↑ risk of diabetes
Effects of Aging on Body System Functioning: Thermoregulation
↓ thirst sense (and core temp and regulation)
↑ core temp & ↓ regulation= ↑ heat stroke
↓ sweat production per gland
Effects of Aging on Body System Functioning: Renal
↓ kidney size
↓ renal blood flow
↓ glomerular filtration rate
GFR: measures kidney function
Effects of Aging on Body System Functioning: Central Nervous
System
↓ β-adrenergic sensitivity (SNS- epi/norepi)
↓ receptors for epi/norepi= ↓ effective
↓ brain volume
↓ balance, coordination, hearing, vision
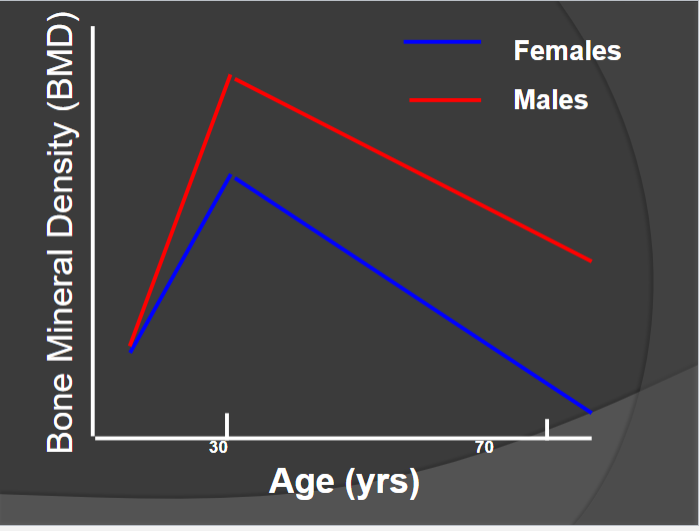
Male vs Female BMD
Females have ↓ BMD and lose at faster rate bc of menopause
↓ estrogen
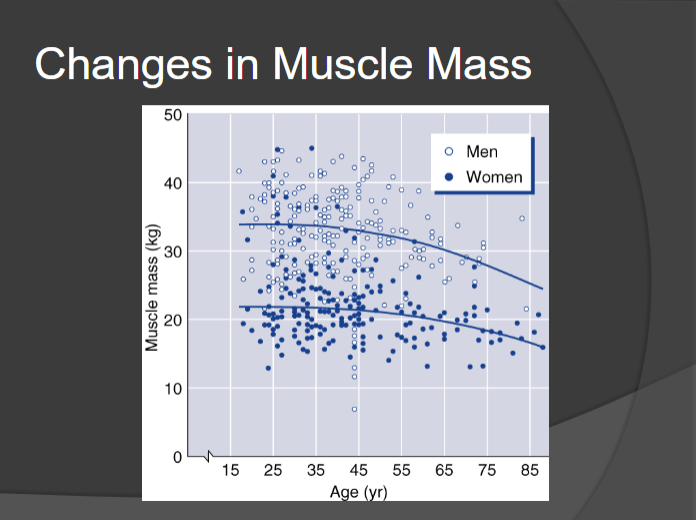
Male vs Female Muscle Mass
Men generally have more muscle mass to lose
by ~75 we have ½ the muscle mass compared to youth
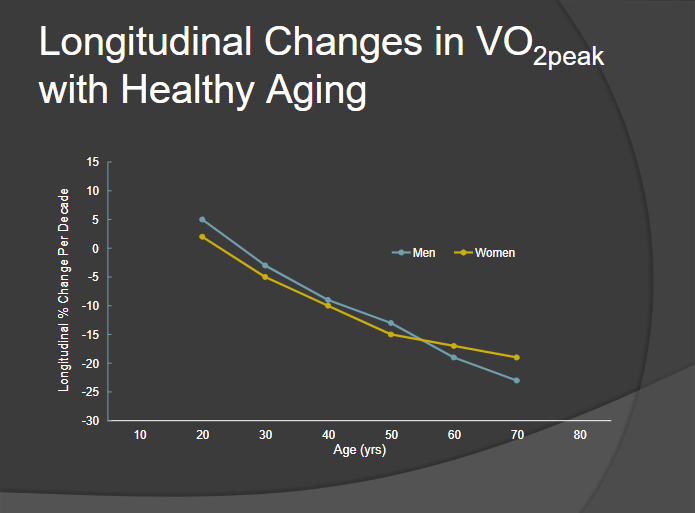
Male vs Female VO2
Both lose VO2peak at same rate until ~55 y/o
After 55 y/o women lose VO2peak at slower rate
World population
Population of 65+ is expected to double by 2050
Population of 80+ is expected to triple by 2050
Older Adults and Exercise
People 65+
20-25% exercise regularly
People 85+
5-10% exercise regularly
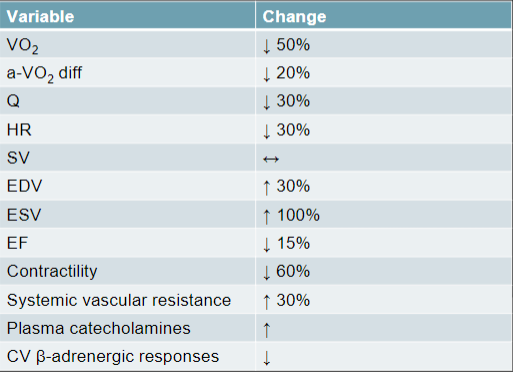
Exercise Response: Maximal Responses
*know arrows*
Benefits of Exercise Training
slows physiologic changes of aging
optimizes changes in body composition
promotes psychological/cognitive well-being
manages chronic disease
reduces risks of developing physical disabilities
increases longevity
Exercise Testing: Aerobic
Initial workload should be low
< 3 METs (low-moderate)
Small workload increments
.5-1.0 METs
Naughton Protocol (not Bruce, too intense)
Cycle ergometer vs. treadmill
Cycle ergometer is more practical and better for safety
Treadmill is better for testing- more large muscle groups are activated
Treadmill handrail support (makes easier)
Naughton Protocol
Speed is maintained, only grade increases
Grade increases by ½ MET every stage
By the end it should be vigorous (6-6.5
METs)
Exercise Testing: Aerobic (pre-test)
A resting 12-lead ECG should be performed on all older adults prior to exercise testing (for those 50+)
Look for:
Significant changes in ST segment
Any incidence of dysrhythmias
Exercise Testing
Resistance
Machines (better for safety)
Can estimate 1 RM (use 8-10 RM to estimate)
Focus on muscles used for ADLs (arms, legs)
Flexibility
Goniometers
Sit and Reach
Medications
Prevalence of those who take 5+ meds:
44% of older men
57% of older women
Common scenario for man in his 80s:
3-4 antihypertensive drugs (BP)
3-4 heart failure meds
aspirin or warfarin (circulation)
statin (cholesterol)
1-2 diabetic drugs
Exercise Prescription
Percent improvement in components of exercise is comparable to younger adults
↑ VO2max= 20-25%
Loss of independence (what does it look like?)
Low functional capacity
Muscle weakness
Deconditioning
Should include exercises to improve:
Balance
Agility (ability to change directions quickly)
Proprioception (body awareness— WHERE IS MY DICK AT?!)
Balance Exercises
Frequency: 2-3 days/week
Exercises:
Progressively difficult postures that ↓ BoS
2-legged stand, 1-legged stand
Dynamic movements that perturb COG
Circle turns (should take <4 steps to complete circle)
Various walking activities
Backwards, sideways, heel-to-toe
Reducing sensory input
Standing with eyes closed
Other Methods of Improving Balance
Get creative!
Tai chi
Should be supplemented with aerobic, resistance exercise
Using a bosu ball
Can improve balance and reduce falls
Virtual reality
6 wks of VR simulating obstacles during TM walking more effective with reducing fall risk vs. TM walking alone in 60-90 yr olds
Example exercise program
looks similar to program for YA
uses modified PRE for older adults (↓ HRmax)
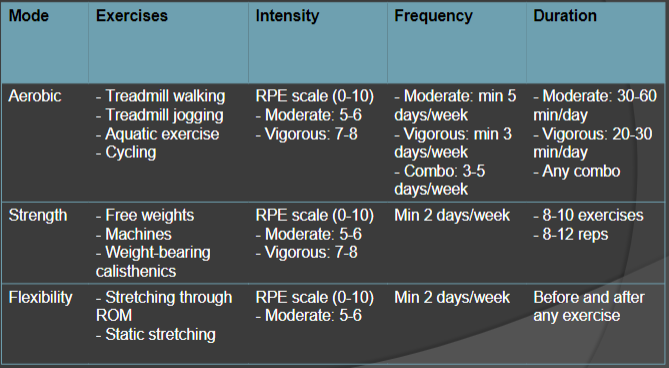
Special Considerations
Intensity/duration of exercise should be low at beginning
Especially for those who are:
highly deconditioned
Functionally limited
Afflicted with a chronic condition
Progression of exercises should be individualized
Gradually exceed recommended minimum amounts of exercise
Special Considerations (pt. 2)
Initial training sessions for those using weight-lifting machines should be supervised
Avoid the Valsalva maneuver (puts a lot of pressure internally)
Very frail individuals:
Resistance training should precede aerobic training
Incorporation of behavioral strategies